SciOly Materials Science Vocabulary
1/29
Earn XP
Description and Tags
BESSO Competiton
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
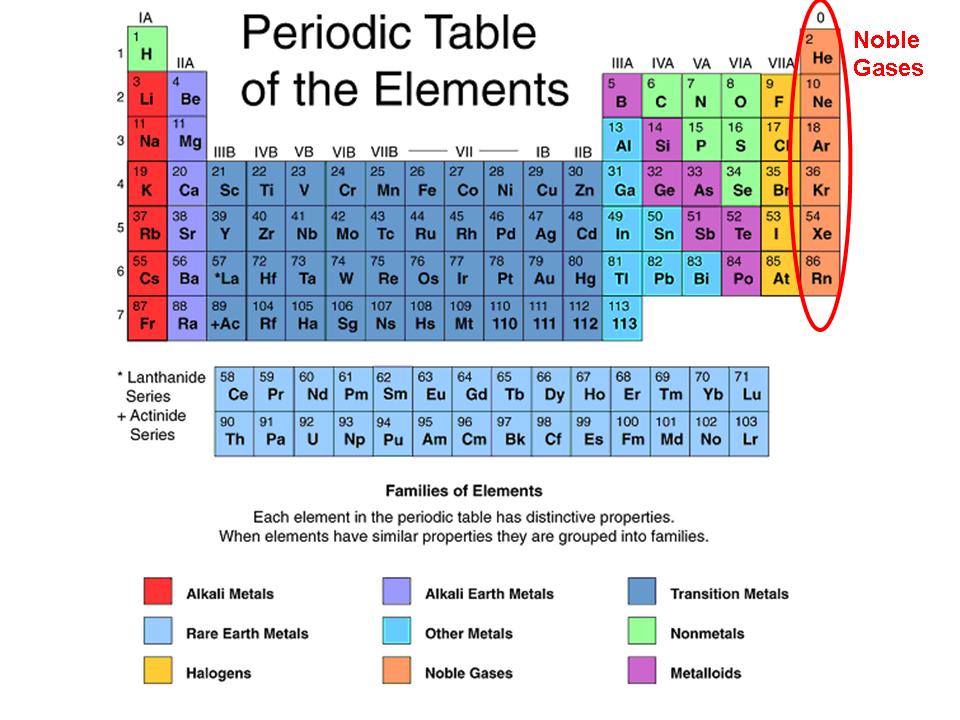
What is Stable Gas Configuration?
Arrangement of electrons in an atoms’s outermost energy level that is complete, making the atom very stable and unreactive.
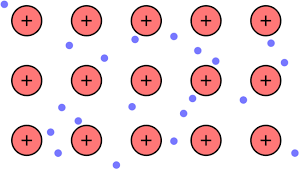
What is a Sea of Electrons?
Model of metallic bonding where valence electrons are delocalized and move freely throughout a crystal lattice of positively charged metal ions.
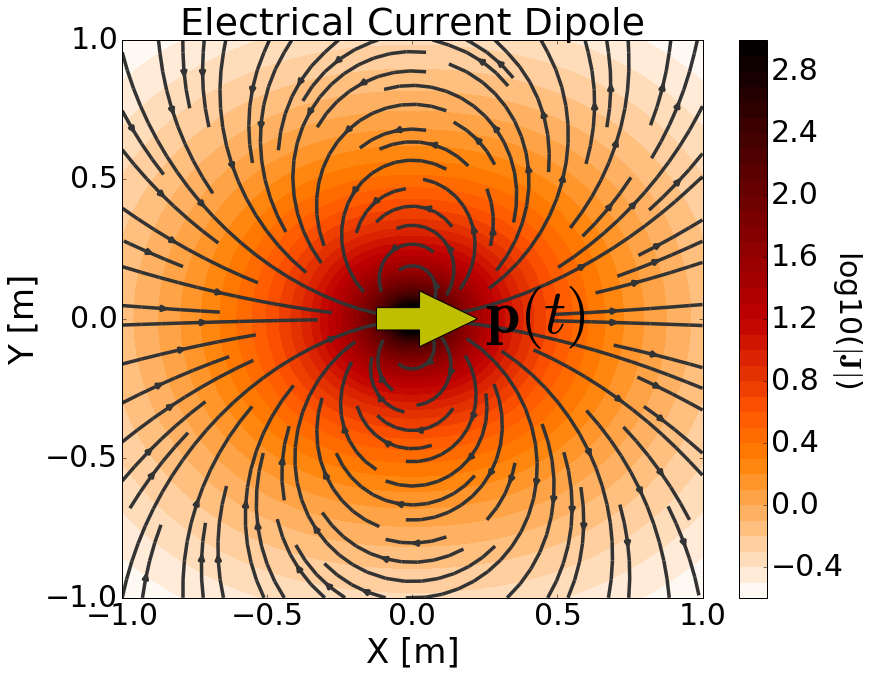
What is Transient Electric Dipole?
Temporary and fleeting electric dipole moment that arises in a neutral atom or molecule due to the random movement of its electrons.
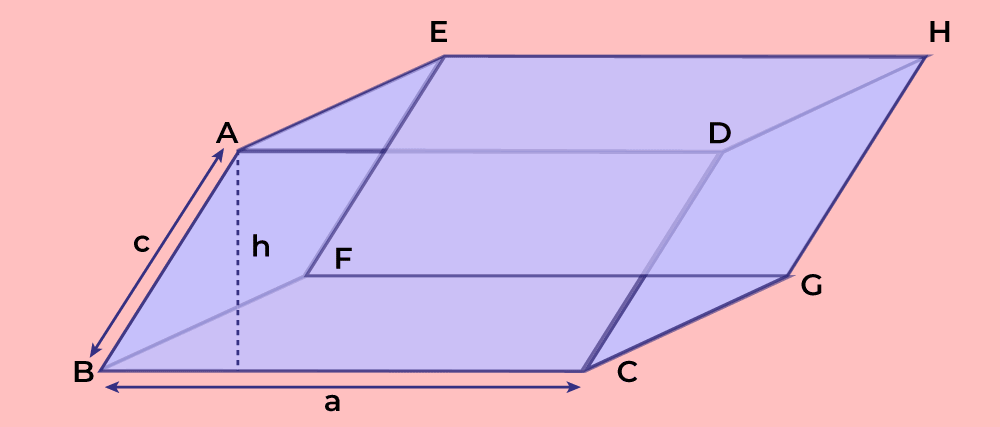
What is Paraallelelepiped?
Three dimensional figure with six faces, each of which is a parallelogram.
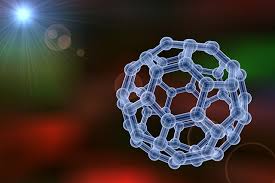
What is a Nanomaterial?
Material with at least one external dimension or internal structure in the size range of 1-100 nanometers which can exhibit unique properties compared to its larger-scale counterparts.

What are Alloys?
Substance composed of 2+ metals, or a metal and non-metal, which is mixed to create a material with different and often more desirable properties than individual materials.
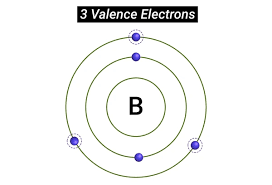
What is Valence?
Combining capacity of an atom, determined by number of chemical bonds it can form with other atoms.
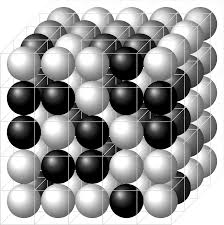
What is Lattice?
Periodic three-dimensional arrangement of points that represents the positions of atoms, molecules, or ions in a crystalline solid.
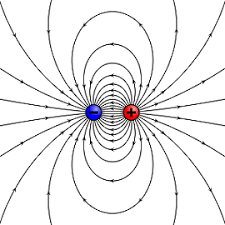
What is an Electric Dipole?
Pair of equal and opposite electric charges separated by small distance.

What is Catalysis?
The process by which the rate of a chemical reaction is increased by a catalyst which is a substance that is not consumed in the reaction.

What is a Semiconductor?
Material whose ability to conduct an electric current is between that of a conductor and an insulator and can be controlled by eternal conditions.

What is a Micrometer?
Either a precise instrument for measuring small distances or unit of length equal to 1 millionth of a meter.
What is Constituent?
Component or part that makes up a whole mixture, substance, or system.

What is Sonication?
Technique that uses high-frequency sound waves (ultrasound) to agitate particles in a liquid to clean, mix, or break apart materials.
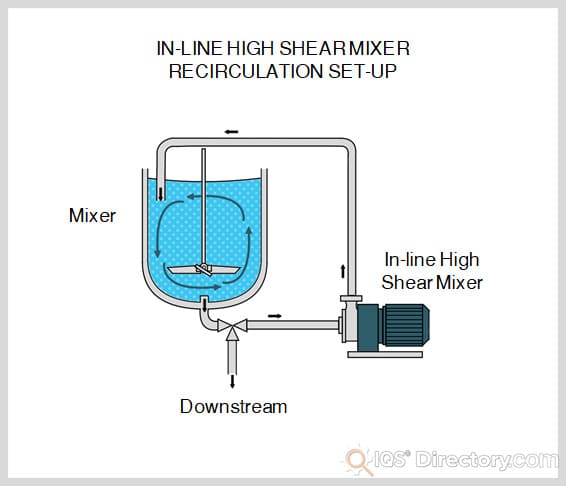
What is Shear Mixing?
Process that applies intense stress to materials by forcing part of the mixture to move in one direction while the other part moves in the opposite direction simultaneously, often using high speed rotors or blades.
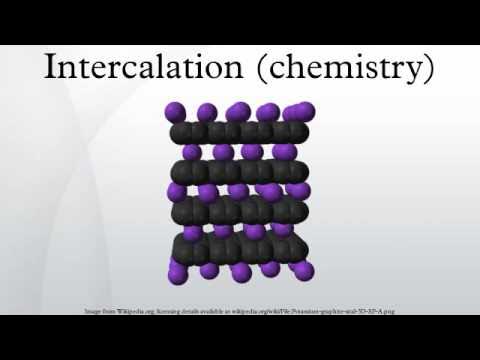
What is Intercalated?
Process of inserting something like a molecule or layer of material in between other layers or things.
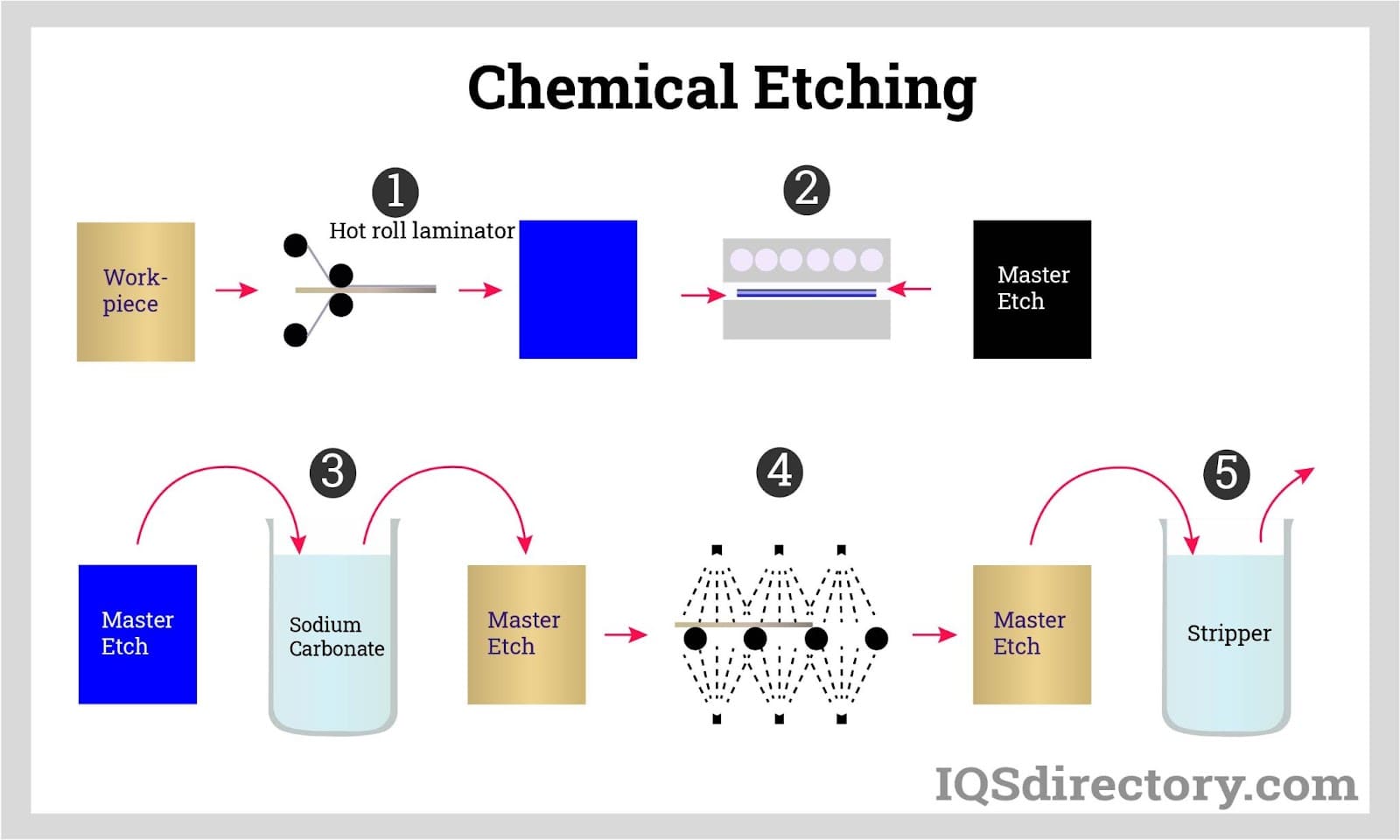
What is Etching?
Process that uses strong acid or other corrosive chemicals to cut or engrave a pattern into a metal plate, glass, or other material.
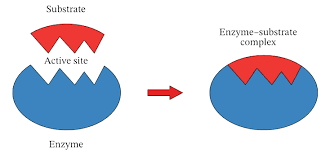
What is Substrate?
Underlying substance, layer, or surface on which another substance or material is applied or on which an organism grows.
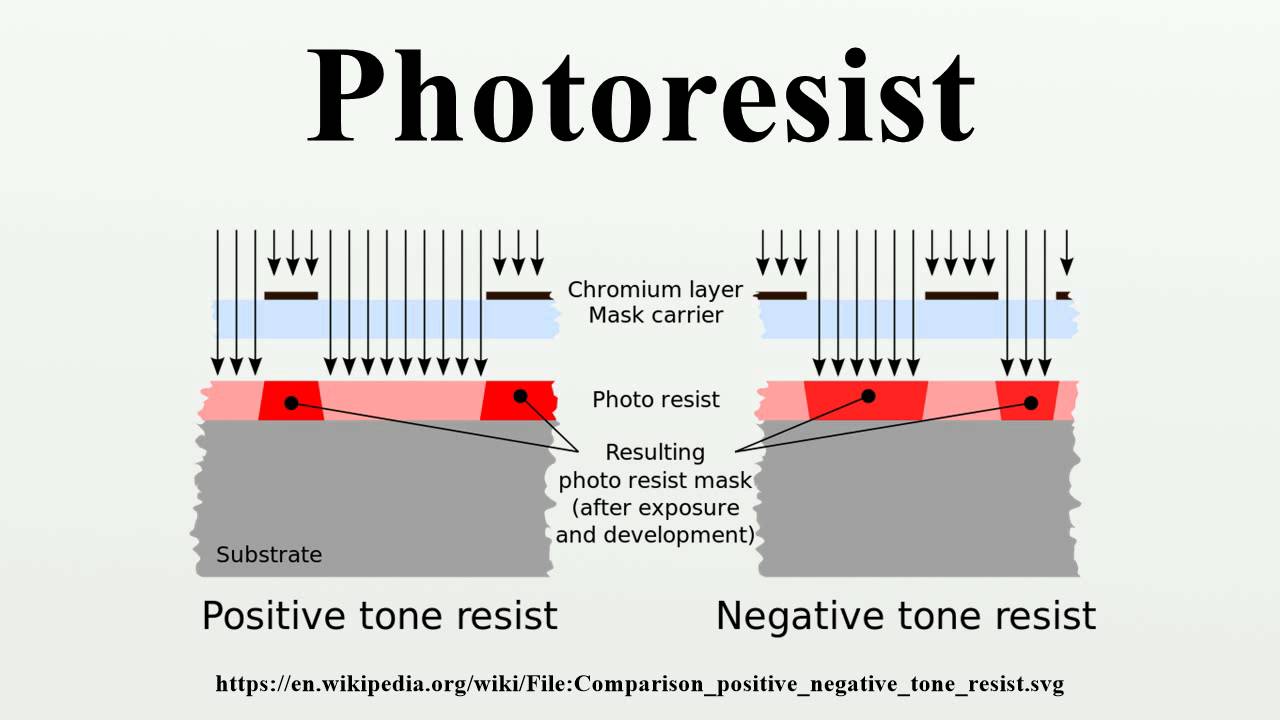
What is Photoresist?
Light sensitive polymer material used in photolithography to form a patterned coating on a surface which then protects the underlying material during a subsequent etching process.

What is Precursor?
Chemical substance that is transformed into another compound during a chemical reaction preceding it in the synthetic pathway.
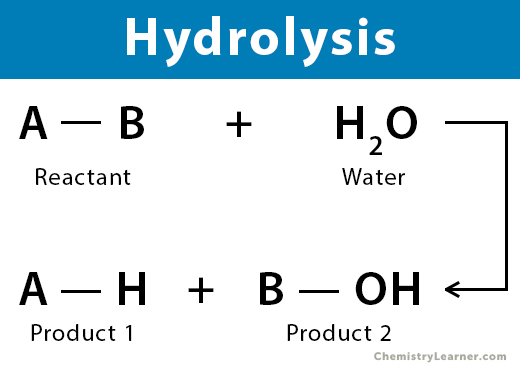
What is Hydrolysis?
Chemical reaction in which a molecule of water reacts with another substance, causing one or more chemical bonds to break and splitting the compound into two or more new products.
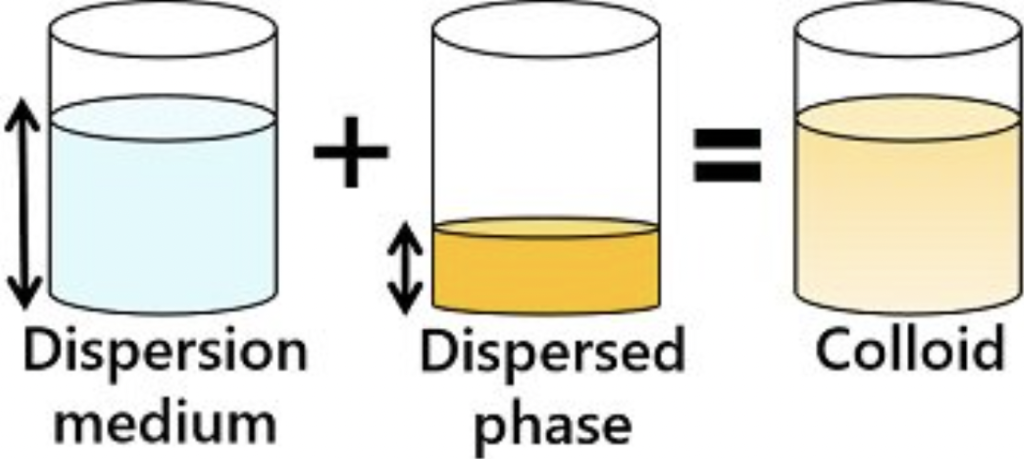
What is Colloidal?
State of a mixture that consists of microscopically dispersed insoluble particles that are suspended throughout another substance with particle dimensions typically between 1-1000 nm.
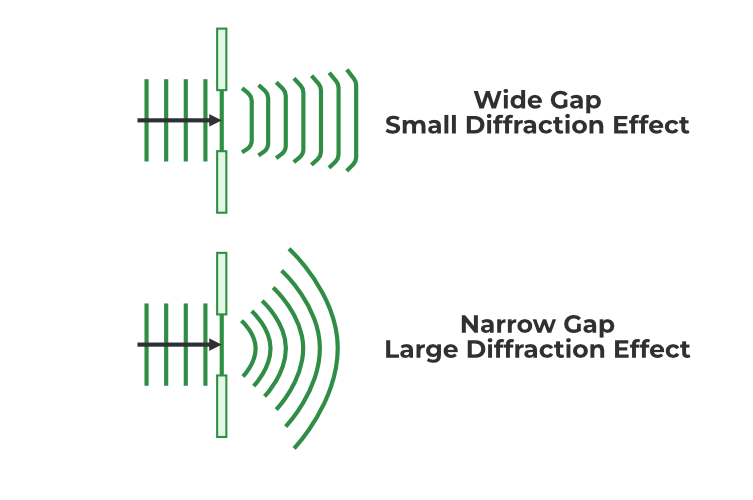
What is Diffraction?
Bending and spreading of waves such as light, sound, or matter waves as they pass through an aperture or around an obstacle.
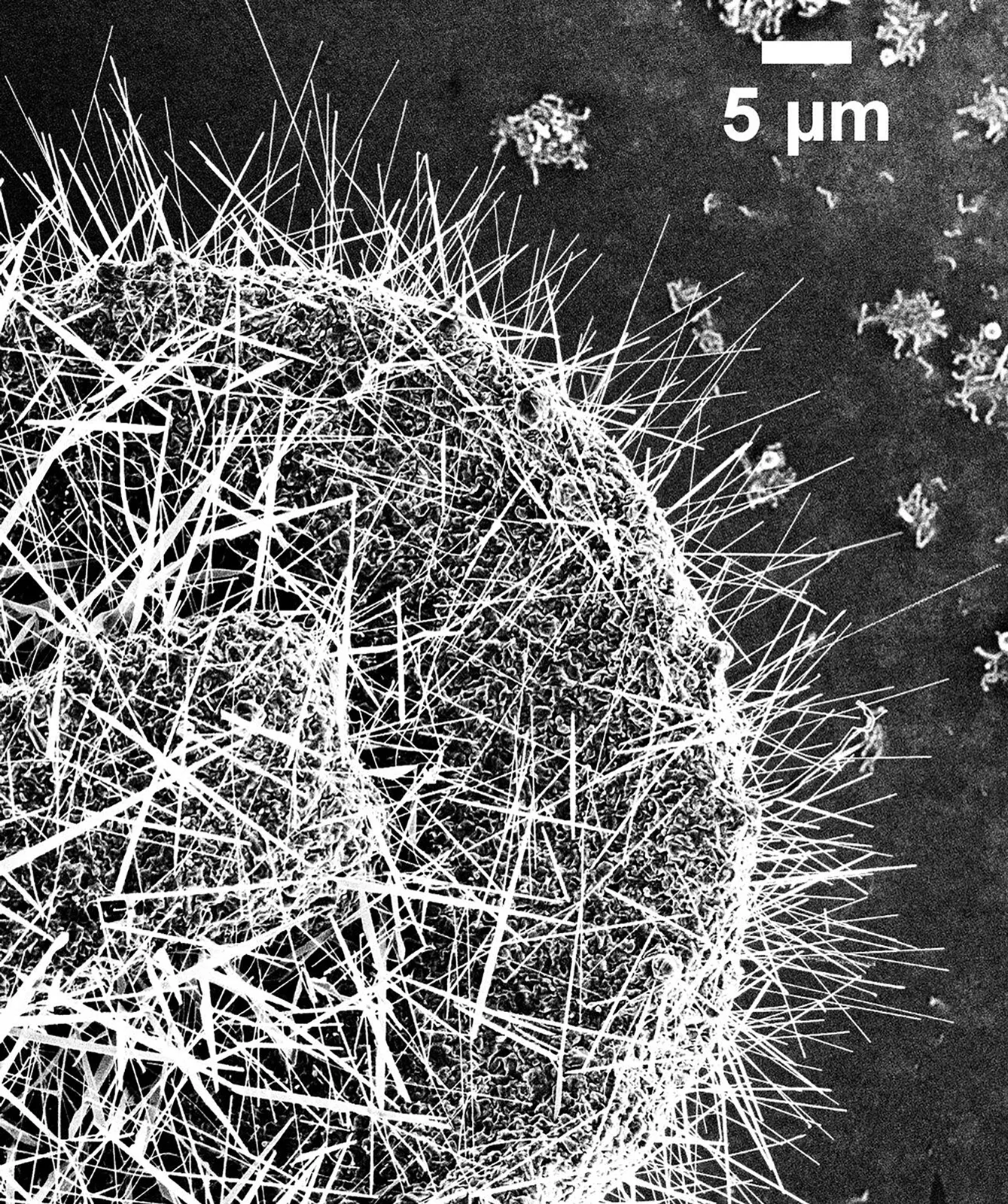
What is a Nanowire?
One-dimensional nanostructure, with a diameter in the nanometer range and a length that can be greater, exhibiting unique electrical and optical properties.
What are Flurophores?
Molecules that absorb light of specific wavelength and then re-emit it at a longer, lower-energy wavelength.

What is Excitation?
Process of adding energy to a molecule, atom, or particle, rising from its ground state to a higher, more energetic state.

What is a Probe?
A tool, instrument, or substance used to thoroughly investigate, explore, or detect something..

What are Piezoelectric Crystals?
Material that generates an electrical charge when subjected to mechanical stress, and conversely experiences mechanical deformation when exposed to electric field.
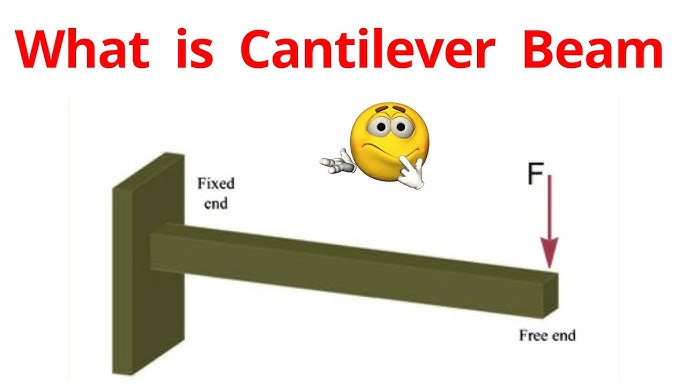
What is Cantilever?
Rigid structure element that is supported at only one end, with other end projecting into space.
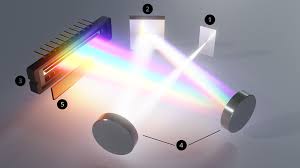
What is Spectrometer?
Scientific instruments are used to separate and measure the spectral components of a physical phenomenon.