Macro Final Rutgers
1/104
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
105 Terms
The functions of money are
M1, M2 or currency.
interest rates, prices and output.
currency, deposits, and traveler's checks.
medium of exchange, unit of account, and store of value.
medium of exchange, unit of account, and store of value.
Barter is
the exchange of goods and services for any type of money.
printing too much money.
the exchange of goods and services directly for other goods and services.
another type of money.
the exchange of goods and services directly for other goods and services.
If an economy has no money, then all transactions must be conducted through the use of
barter.
tobacco or wampum.
credit cards.
debit cards.
barter
In the United States today, money consists of
currency and deposits at banks and other depository institutions
deposits at banks only.
currency only.
coins only.
currency and deposits at banks and other depository institutions
Checks ________ money and checking deposits ________ money.
are not; are not
are not; are
are; are not
are; are
are not; are
Bank reserves include
I. | the cash in the bank's vault. |
II. | the bank's deposits at the Federal Reserve. |
only II
neither I nor II
only I
both I and II
both I and II
An open market sale of securities by the Fed
increases banks' reserves and decreases banks' securities.
involves a bank selling government securities to the Fed.
increases banks' total assets.
decreases banks' reserves and increases banks' securities.
decreases banks' reserves and increases banks' securities.
Which of the following is the central bank of the United States?
Office of the Budget
Treasury Department
Comptroller of the Currency
Federal Reserve System
Federal Reserve System
The Federal Reserve System
Neither answer regulates the nation's financial institutions nor conducts the nation's monetary policy is correct.
regulates the nation's financial institutions.
conducts the nation's monetary policy.
Both answers regulates the nation's financial institutions and conducts the nation's monetary policy are correct.
Both answers regulates the nation's financial institutions and conducts the nation's monetary policy are correct.
The monetary base is
depository institutions' reserves minus Federal Reserve notes.
currency minus depository institutions' reserves.
currency and reserves of depository institutions.
the money borrowed by banks from other banks.
currency and reserves of depository institutions.
Changing which of the following is a Federal Reserve monetary policy tool?
desired reserve ratios
excess reserve ratios.
required reserve ratios
gold and foreign reserve ratios
required reserve ratios
An open market operation involves
the Federal Reserve's issuance of new stock.
changing federal income tax rates.
the Federal Reserve's purchase or sale of securities.
raising the debt limit of the United States.
the Federal Reserve's purchase or sale of securities.
An open market sale of securities by the Fed
increases banks' reserves and decreases banks' securities.
involves a bank selling government securities to the Fed.
increases banks' total assets.
decreases banks' reserves and increases banks' securities.
decreases banks' reserves and increases banks' securities.
In response to the financial crisis of 2007 and the ensuing recession, the Fed announced three rounds of "quantitative easing," where the Fed purchased billions of dollars of securities. What impact would quantitative easing have on the monetary base?
The monetary base would decrease.
The monetary base would not change.
The monetary base would increase.
While the monetary base would change, it is impossible to predict in which direction.
The monetary base would increase.
Commercial banks are able to create money by
exchanging their reserves at the Fed for currency.
making customers pay back their loans.
making loans.
printing Federal Reserve Notes.
making loans.
Which of the following best describes the chain of events in the money creation process?
Low interest rates discourage people from holding currency. When they deposit the currency, interest rates rise, increasing the quantity of money.
Currency is drained from the quantity of money into the banking system, where it is lent out. The loans are spent, increasing the currency drain and also the quantity of money.
The monetary base increases. Banks acquire unplanned reserves which they loan out, increasing deposits and also the quantity of money. The new deposits then create additional unplanned reserves.
Desired reserves increase, encouraging banks to seek new deposits. When the new depositors come in, desired reserves decrease and the quantity of money increases.
The monetary base increases. Banks acquire unplanned reserves which they loan out, increasing deposits and also the quantity of money. The new deposits then create additional unplanned reserves.
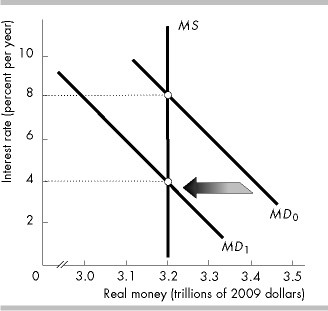
The figure above illustrates the effect of
a decrease in the monetary base.
a decrease in real GDP.
an increase in real GDP.
an increase in the monetary base.
a decrease in real GDP.
In the short run, which of the following actions lower the interest rate?
an increase in the demand for money
a decrease in bond prices
a decrease in the quantity of money
a decrease in the demand for money
a decrease in the demand for money
In the short run, when the Fed increases the quantity of money
the demand for money increases.
the supply of money curve shifts leftward.
bond prices fall and the interest rate rises.
bond prices rise and the interest rate falls.
bond prices rise and the interest rate falls.
In the short run, when the Fed decreases the quantity of money
the supply of money curve shifts rightward.
bond prices fall and the interest rate rises.
the demand for money increases.
bond prices rise and the interest rate falls.
bond prices fall and the interest rate rises.
In the long run, when the Fed increases the quantity of money,
the price level falls.
the real interest rate rises.
the nominal interest rate falls.
no real variable changes.
no real variable changes.
If real GDP decreases, the demand for money curve will shift
rightward and the interest rate will rise.
leftward and the interest rate will rise.
leftward and the interest rate will fall.
rightward and the interest rate will fall.
leftward and the interest rate will fall.
The equation of exchange states that the price level is equal to
the velocity of circulation.
real GDP multiplied by the velocity of circulation divided by nominal GDP.
the quantity of money.
the velocity of circulation multiplied by the quantity of money divided by real GDP.
the velocity of circulation multiplied by the quantity of money divided by real GDP.
The quantity theory of money predicts how changes in
the quantity of money affect the price level.
the price level affect nominal GDP.
real GDP affect the nominal GDP.
the price level affect real GDP.
the quantity of money affect the price level.
The quantity theory of money asserts that inflation is the result of growth in
potential GDP.
the quantity of money.
the natural rate of unemployment.
money wage rates.
the quantity of money.
In long-run macroeconomic equilibrium
the price level is fixed and aggregate demand determines real GDP.
real GDP and the price level are determined by short-run aggregate supply and aggregate demand and long-run aggregate supply is irrelevant.
real GDP is less than potential GDP.
real GDP equals potential GDP.
real GDP equals potential GDP.
A change in the full-employment quantity of labor ________ the short-run aggregate supply curve and ________ the long-run aggregate supply curve.
shifts; shifts
shifts; does not shift
does not shift; does not shift
does not shift; shifts
shifts; shifts
An individual holds $10,000 in a checking account and the price level rises significantly. Hence
the individual's real wealth decreases but real national wealth increases.
there is no change in the individual's real wealth.
the individual's real wealth and consumption expenditure decrease.
the individual's real wealth increases.
the individual's real wealth and consumption expenditure decrease.
A change in ________ creates a movement along the aggregate demand curve but does not shift the aggregate demand curve.
the price level
None of these because they all shift the aggregate demand curve.
fiscal policy
tax rates
the price level
A change in the capital stock ________ the short-run aggregate supply curve and ________ the long-run aggregate supply curve.
shifts; shifts
does not shift; does not shift
does not shift; shifts
shifts; does not shift
shifts; shifts
A decrease in government expenditure on goods and services
decreases the aggregate quantity demanded.
increases aggregate demand.
increases the aggregate quantity demanded.
decreases aggregate demand.
decreases aggregate demand.
A recessionary gap means that the level of real GDP at the short-run macroeconomic equilibrium
equals full-employment GDP.
is less than full-employment GDP.
is more than full-employment GDP.
may be less than, more than, or the same as full-employment GDP depending on the level of potential GDP.
is less than full-employment GDP.
A change in the money wage rate shifts
the LAS curve but not the SAS curve.
the SAS curve but not the LAS curve.
neither the SAS nor the LAS curve.
both the SAS and LAS curves.
the SAS curve but not the LAS curve.
A technological advance ________ the long-run aggregate supply curve and ________ the short-run aggregate supply curve.
does not shift; shifts
does not shift; does not shift
shifts; does not shift
shifts; shifts
shifts; shifts
A decrease in short-run aggregate supply ________ the equilibrium price level and ________ the equilibrium quantity of real GDP.
decreases; decreases
increases; decreases
decreases; increases
increases; increases
increases; decreases
An inflationary gap means that the level of real GDP at the short-run macroeconomic equilibrium
may be less than, more than, or the same as full-employment GDP depending on the level of potential GDP.
is less than full-employment GDP.
is more than full-employment GDP.
equals full-employment GDP.
is more than full-employment GDP.
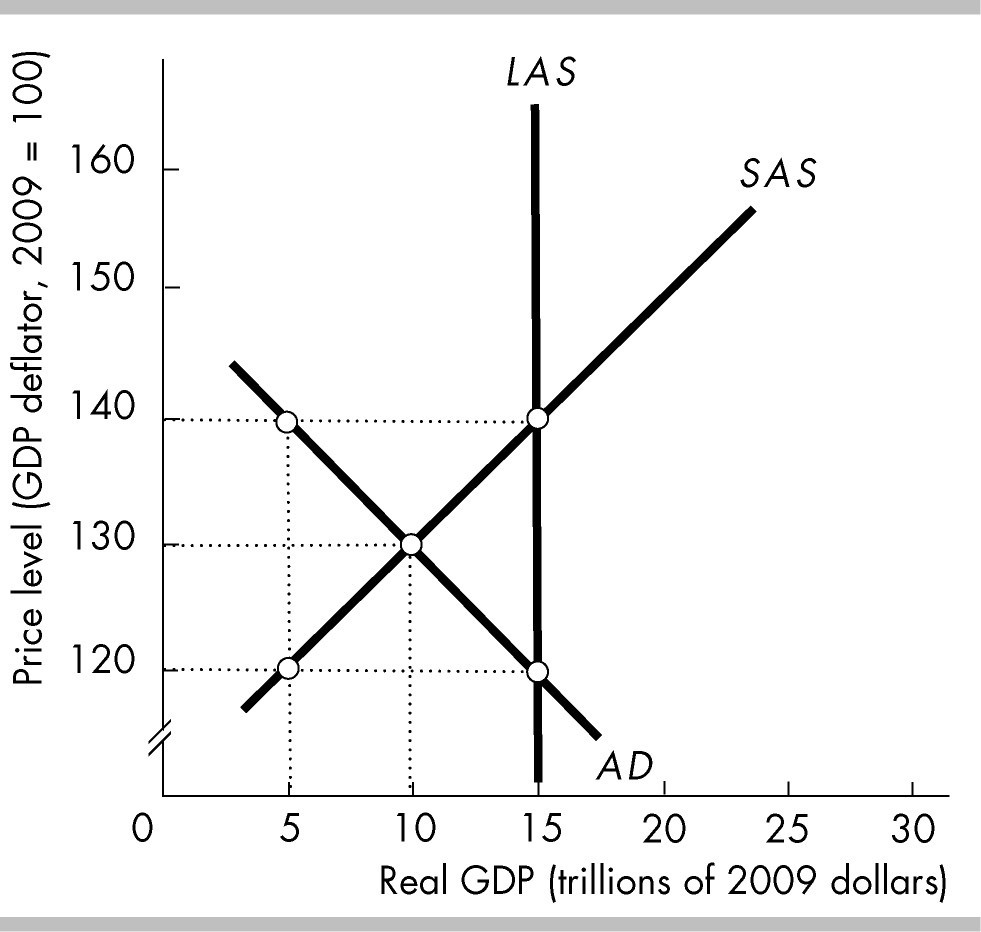
In the above figure, at the price level of 140 and real GDP of
$5 trillion, firms will not be able to sell all their output.
$5 trillion, consumers will not be able to buy all the goods and services they demand.
$15 trillion, firms will not be able to sell all their output.
$15 trillion, consumers will not be able to buy all the goods and services they demand.
$15 trillion, firms will not be able to sell all their output.
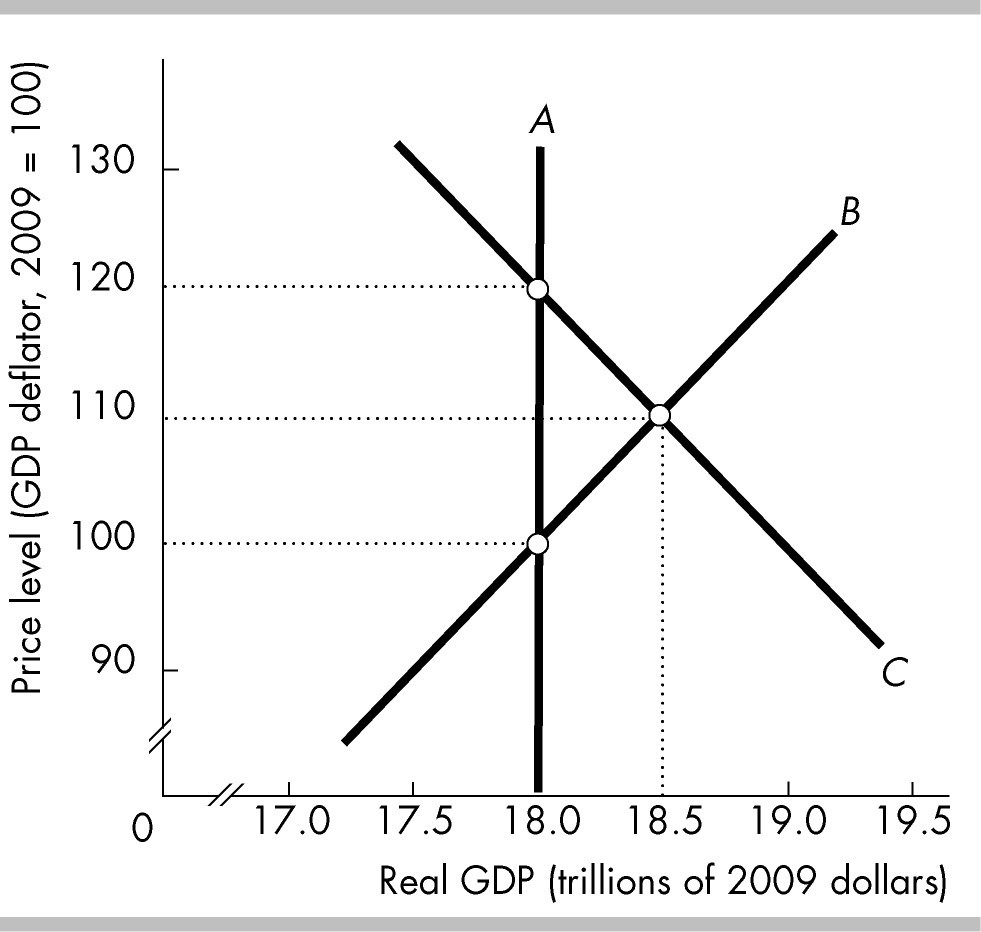
In the above figure, curve A is the ________ curve, curve B is the ________ curve, and curve C is the ________ curve.
long-run aggregate supply; short-run aggregate supply; aggregate demand
short-run aggregate supply; long-run aggregate supply; aggregate demand
long-run aggregate supply; aggregate demand; short-run aggregate supply
aggregate demand; short-run aggregate supply; long-run aggregate supply
long-run aggregate supply; short-run aggregate supply; aggregate demand
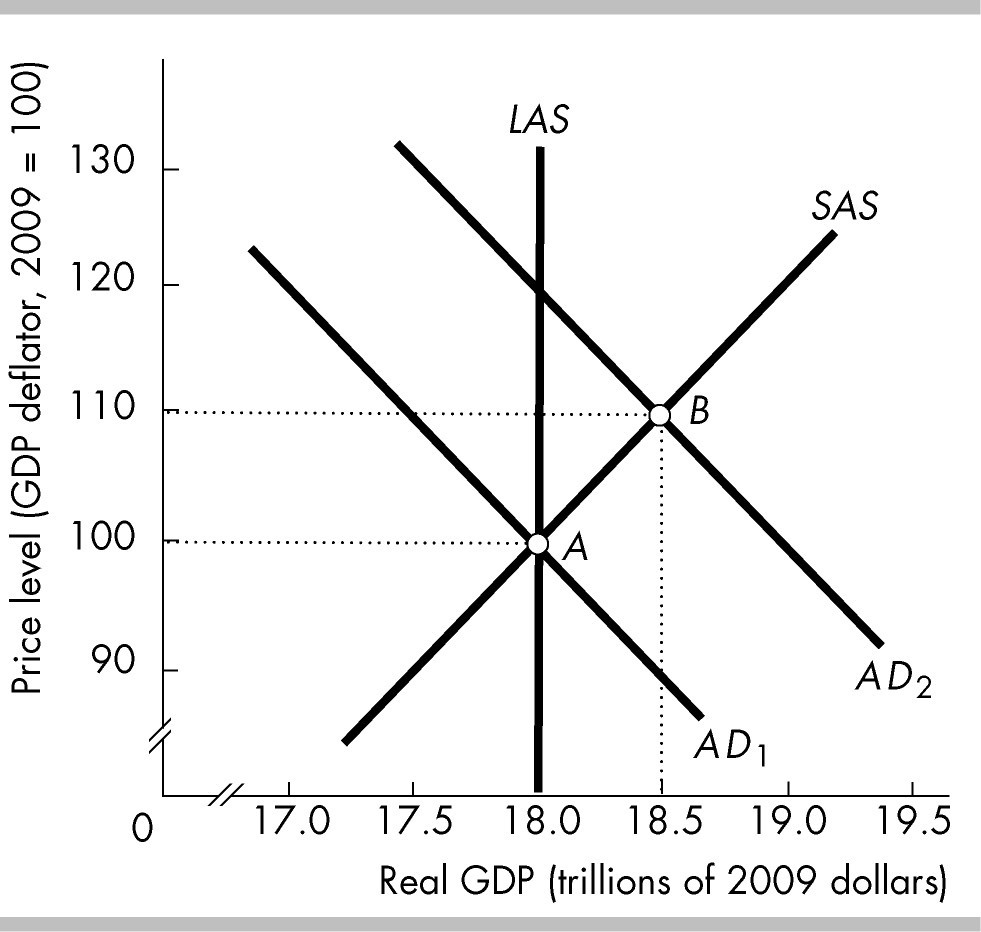
In the above figure, the aggregate demand curve is AD2, so the short-run equilibrium level of real GDP is
$18.5 trillion.
$18 trillion.
None of these answers is correct.
more than $18 and less than $18.5 trillion.
$18.5 trillion.
Which of the following changes would NOT shift the aggregate demand curve?
a change in monetary policy
a change in fiscal policy
an increase in technology
a change in expectations about future income
an increase in technology
The factor that leads to business cycle events within real business cycle theory is represented by
changes in the growth rate in productivity.
changes in the growth rate in the quantity of money.
adverse shocks to international trade.
changes in expected future sales and profits of firms
changes in the growth rate in productivity.
Which of the following can start an inflation?
an increase in aggregate demand
an increase in aggregate supply
a decrease in aggregate supply
Both answers an increase in aggregate demand and a decrease in aggregate supply are correct.
Both answers an increase in aggregate demand and a decrease in aggregate supply are correct.
Demand-pull inflation starts with
an increase in aggregate demand.
a decrease in aggregate demand.
an increase in short-run aggregate supply.
a decrease in short-run aggregate supply.
an increase in aggregate demand.
Increases in the quantity of money can start a ________ inflation and an increase in government expenditure can start a ________ inflation.
demand-pull; demand-pull
demand-pull; cost-push
cost-push; cost-push
cost-push; demand-pull
demand-pull; demand-pull
Which of the following is NOT a potential start of a demand-pull inflation?
an increase in the quantity of money
an increase in government expenditure
an increase in taxes
an increase in exports
an increase in taxes
An initial increase in aggregate demand that is NOT followed by an increase in the quantity of money results in a long-run equilibrium with
a higher price level but the same real GDP.
a higher price level and a higher level of real GDP.
the same price level and a lower level of real GDP.
None of these answers are correct.
a higher price level but the same real GDP.
Demand-pull inflation persists because of
continuing increases in government expenditures.
continuing increases in the quantity of money.
continuing increases in real wage rates.
continuing increases in aggregate supply.
continuing increases in the quantity of money.
When the AD and SAS curves intersect at a level of real GDP which exceeds potential GDP and there is no government policy undertaken, which of the following will occur?
The AD curve shifts rightward because the Fed decreases the money supply.
The SAS curve shifts leftward because the money wage rate rises.
The SAS curve shifts leftward because the money wage rate falls.
The AD curve shifts leftward because the money wage rate rises.
The SAS curve shifts leftward because the money wage rate rises.
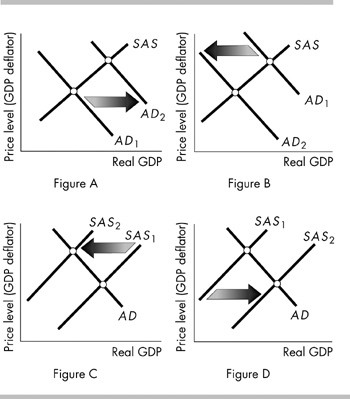
In the above, which figure shows the start of a cost-push inflation?
Figure A
Figure B
Figure C
Figure D
Figure C
The main sources of cost-push inflation are increases in
money wage rates and the cost of raw materials.
real wage rates and the cost of raw materials.
money wage rates and aggregate demand.
aggregate demand and real wage rates.
money wage rates and the cost of raw materials.
Assuming that GDP currently equals potential GDP, a cost-push inflation could result from which of the following?
a decrease in tax rates
an increase in the labor force
a large crop failure that boosts the prices of raw food materials
an increase in the nation's capital stock
a large crop failure that boosts the prices of raw food materials
An increase in the money wage rate shifts the SAS curve ________ and an increase in the money prices of raw materials shifts the SAS curve ________.
rightward; rightward
leftward; leftward
rightward; leftward
leftward; rightward
leftward; leftward
Stagflation is the combination of a ________ and ________.
falling inflation rate; an increasing real GDP
falling price level; an increasing real GDP
rising price level; a decreasing real GDP
rising inflation rate; a decreasing real GDP
rising price level; a decreasing real GDP
If the Fed responds to repeated decreases in the short-run aggregate supply with repeated increases in the quantity of money, the economy will be faced with
a one-time increase in prices.
continuous inflation.
alternating periods of inflation and deflation.
steady decreases in real GDP.
continuous inflation.
Suppose the velocity of circulation increases by 2 percent and potential GDP grows by 2 percent. The trend inflation rate will equal zero if the quantity of money grows by
0 percent.
2 percent.
4 percent.
-2 percent.
0 percent.
To end a deflation, the government must
decrease government expenditures.
increase the quantity of money.
increase taxes.
increase the growth rate of the money stock.
decrease government expenditures.
Phillips curves show the relationship between the
nominal interest rate and the real interest rate.
expected rate of inflation and the nominal interest rate.
real interest rate and the unemployment rate.
unemployment rate and the inflation rate.
unemployment rate and the inflation rate.
The short-run Phillips curve
slopes downward.
slopes upward.
is horizontal.
is vertical.
slopes downward.
Moving along the short-run Phillips curve indicates
that higher inflation leads to a higher unemployment rate.
that higher unemployment leads to a higher inflation rate.
a tradeoff between inflation and unemployment so that higher inflation is related to lower unemployment.
that the natural unemployment rate falls when the inflation rate rises.
a tradeoff between inflation and unemployment so that higher inflation is related to lower unemployment.
The short-run Phillips curve and the long-run Phillips curve intersect at the ________ and ________.
expected inflation rate; the expected unemployment rate
expected inflation rate; the natural unemployment rate
natural inflation rate; the expected employment rate
expected inflation rate; the expected employment rate
expected inflation rate; the natural unemployment rate
Prior to the Great Depression, the purpose of the federal budget was to
stabilize the economy.
finance the activities of the government.
maintain low interest rates.
decrease unemployment.
finance the activities of the government.
Fiscal policy includes
only decisions related to government expenditure on goods and services.
only decisions related to government expenditure on goods and services and the value of transfer payments.
only decisions related to the value of transfer payments and tax revenue.
decisions related to government expenditure on goods and services, the value of transfer payments, and tax revenue.
decisions related to government expenditure on goods and services, the value of transfer payments, and tax revenue.
Changes in which of the following is included as part of fiscal policy?
the quantity of money
the level of interest rates
monetary policy
tax rates
tax rates
All of the following are part of fiscal policy EXCEPT
setting tax rates.
setting government spending.
choosing the size of the government deficit.
controlling the money supply.
controlling the money supply.
Which of the following government bodies does NOT participate directly in formulating U.S. fiscal policy?
the President and his cabinet
the Federal Reserve Board
the House of Representatives
the Senate
the Federal Reserve Board
The largest source of government revenues is
personal income taxes.
indirect taxes.
corporate income taxes.
Social Security taxes.
personal income taxes.
The largest item of government outlays is
debt interest
transfer payments
expenditures on goods and services
debt reduction
transfer payments
Social Security benefits and expenditures on Medicare and Medicaid are classified as
debt interest.
purchases of goods and services.
production of goods and services.
transfer payments.
transfer payments.
The U.S. government's budget
must be balanced each year.
has mostly been in surplus during the past 30 years.
has mostly been in deficit during the past 30 years.
has always been in deficit during the past 30 years.
has mostly been in deficit during the past 30 years.
When tax revenues exceed outlays, the government has a ________, and when outlays exceed tax revenues, the government has a ________.
budget surplus; budget debt
budget deficit; budget surplus
budget debt; budget surplus
budget surplus; budget deficit
budget surplus; budget deficit
If the government has a balanced budget, the total amount of government debt is
increasing.
decreasing.
constant.
zero.
constant.
If the government runs a surplus, the total amount of government debt is
increasing.
decreasing.
constant.
zero.
decreasing.
Suppose a country has been running a persistent government budget deficit. If the deficit is reduced, but remains positive
government debt will increase.
government debt will decrease.
the country will experience a budget surplus.
interest payments on the debt immediately will decrease.
government debt will increase.
One characteristic of automatic fiscal policy is that it
requires no legislative action by Congress to be made effective.
automatically produces surpluses during recessions and deficits during inflation.
has no effect on unemployment.
reduces the size of the federal government debt during times of recession.
requires no legislative action by Congress to be made effective.
A discretionary fiscal policy is a fiscal policy that
involves a change in government defense spending.
is triggered by the state of the economy.
requires action by the Congress.
involves a change in corporate tax rates.
requires action by the Congress.
The stimulus package passed by Congress in 2009 to combat the recession is an example of
automatic fiscal policy.
discretionary fiscal policy.
monetary policy.
increased taxation.
discretionary fiscal policy.
When the economy is hit by spending fluctuations, the government can try to minimize the effects by
changing government expenditures on goods.
changing taxes.
changing government expenditures on services.
All of these
All of these
The government budget deficit tends to decrease during the expansion phase of a business cycle because tax revenues ________ and government transfer payments ________.
increase; increase
increase; decrease
decrease; increase
decrease; decrease
increase; decrease
An increase in government expenditure shifts the AD curve ________ and an increase in taxes shifts the AD curve ________.
rightward; rightward
rightward; leftward
leftward; rightward
leftward; leftward
rightward; leftward
If real GDP is less than potential GDP, which of the following fiscal policies would increase real GDP?
only a decrease in government expenditure
only an increase in taxes
an increase in government expenditure and/or a decrease taxes
a decrease in government expenditure and/or an increase taxes
an increase in government expenditure and/or a decrease taxes
Suppose the economy is at a short-run equilibrium with real GDP greater than potential GDP. Which of the following fiscal policies would decrease real GDP and the price level?
an increase in government expenditure
a decrease in taxes
an increase in taxes
None of these answers is correct.
an increase in taxes
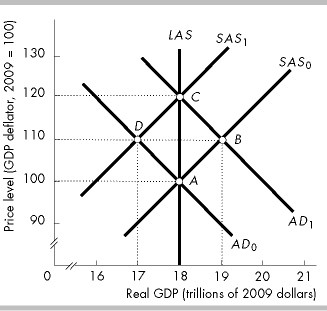
In the above figure, if the economy is initially at point B and taxes are raised while potential GDP does not change, then the economy will
move to point C.
move to point A.
move to point D.
stay at point B.
move to point A.
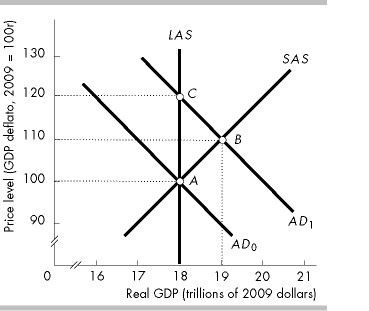
In the above figure, if the economy initially is at point A and government expenditure increases, in the short run the economy will move to point
B.
C.
A, that is, the equilibrium will not change.
None of these answers is correct.
B.
The use of fiscal policy is limited because
there is never a long enough time lag.
the economy is almost always at full employment.
the President may have different goals than Congress.
time lags associated with fiscal policy may cause the policy to take effect too late to solve the problem it was supposed to address.
time lags associated with fiscal policy may cause the policy to take effect too late to solve the problem it was supposed to address.
Which of the following are limitations of fiscal policy?
I. | There is a lag between recognizing that fiscal policy might be needed and when it actually takes |
effect.
II. | Economic forecasts might be incorrect. |
III. | Monetary policy might counter fiscal policy. |
I only
I and II
I and III
I, II and III
I and II
The Federal Reserve's monetary policy goals include
zero percent unemployment in the domestic economy.
discount rate stability.
price level stability.
ensuring banks can meet their profit maximization objectives.
price level stability.
In the short run, the Federal Reserve faces a tradeoff between
economic growth and employment.
inflation and unemployment.
real GDP growth and potential GDP growth.
inflation and price stability.
inflation and unemployment.
When the output gap is positive, it represents ________ gap, and when it is negative, it represents ________ gap.
an inflationary; an employment
an employment; an unemployment
a recessionary; an inflationary
an inflationary; a recessionary
an inflationary; a recessionary
Monetary policy is controlled by
the Federal Reserve.
Congress.
the president.
the Treasury Department.
the Federal Reserve.
The federal funds rate is the interest rate
on the 30-year treasury bond.
that the Fed charges commercial banks on loans.
banks charge each other on overnight loans.
on the 3-month Treasury bill.
banks charge each other on overnight loans.
Federal Reserve open market operations directly influence
firms.
Congress.
banks.
consumers.
banks.
The Fed buys U.S. government securities from banks in order to
lower the federal funds rate.
None of these answers are correct.
reduce the government's budget deficit.
decrease banks' reserves.
lower the federal funds rate.
Long-term interest rates are ________ than short-term interest rates because long-term loans are ________ than short-term loans.
higher; riskier
lower; riskier
lower; safer
higher; safer
higher; riskier
Long-term interest rates fluctuate ________ short-term interest rates.
more than
less than
depending on their level sometimes less than, sometimes more than
the same as
less than
If the Fed wants to decrease the quantity of money, it can
purchase U.S. government securities.
decrease the government budget deficit.
sell U.S. government securities.
raise income tax rates.
sell U.S. government securities.
In the short run, an increase in the federal funds rate ________ the real interest rate and ________ investment.
raises; increases
raises; decreases
lowers; decreases
lowers; increases
raises; decreases
In the aggregate supply-aggregate demand model, raising the federal funds rate initially
decreases long-run aggregate supply.
decreases aggregate demand.
increases aggregate demand.
increases long-run aggregate supply.
decreases aggregate demand.
Suppose the economy is in a recession and the Fed lowers the federal funds rate. Then
real GDP and the price level will both increase.
real GDP will decrease and the price level will increase.
real GDP will increase and the price level will decrease.
real GDP and the price level will both decrease.
real GDP and the price level will both increase.
Which of the following describes the chain of events the Fed uses to fight recession?
Raise the federal funds rate target, buy government securities, increase reserves and loans, decrease aggregate demand.
Lower the federal funds rate target, buy government securities, increase reserves and loans, increase aggregate demand.
Raise the federal funds rate target, sell government securities, decrease reserves and loans, increase aggregate demand.
Lower the federal funds rate target, buy government securities, decrease reserves and loans, decrease aggregate demand.
Lower the federal funds rate target, buy government securities, increase reserves and loans, increase aggregate demand.
If the Fed is concerned with inflation it will ________ the federal funds rate in order to ________ aggregate demand.
lower; decrease
raise; decrease
raise; increase
lower; increase
raise; decrease