Organisms response - Receptors
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
What is a receptor?
An organ or cell able to respond to stimuli and create a generator potential
What is a pacinian corpuscle?
Deep pressure receptor located in the skin
What are pacinian corpuscle connected to?
Sensory neurones
What does a pacinian corpuscle consist of?
Single sensory neurone wrapped with layers of tissue called lamellae
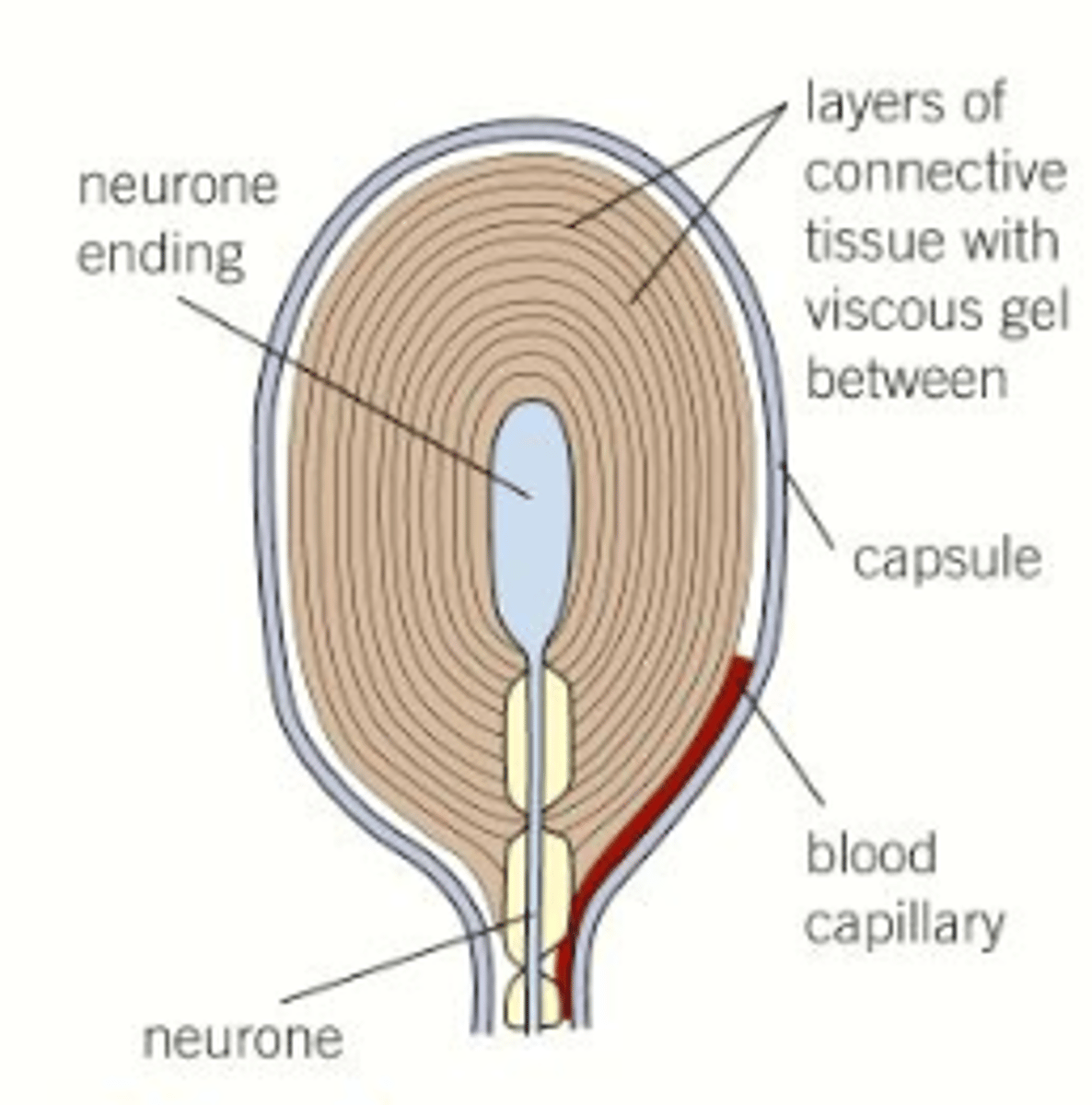
How is a generator potential produced?
1. Pressure on the skin changes the shape of the pacinian corpuscle
2. This changes the shape of the pressure sensitive sodium channels in the membrane, causing them to open
3. Sodium ions diffuse through the channels leading to depolarisation called a generator potential
Production of a generator potential diagram.
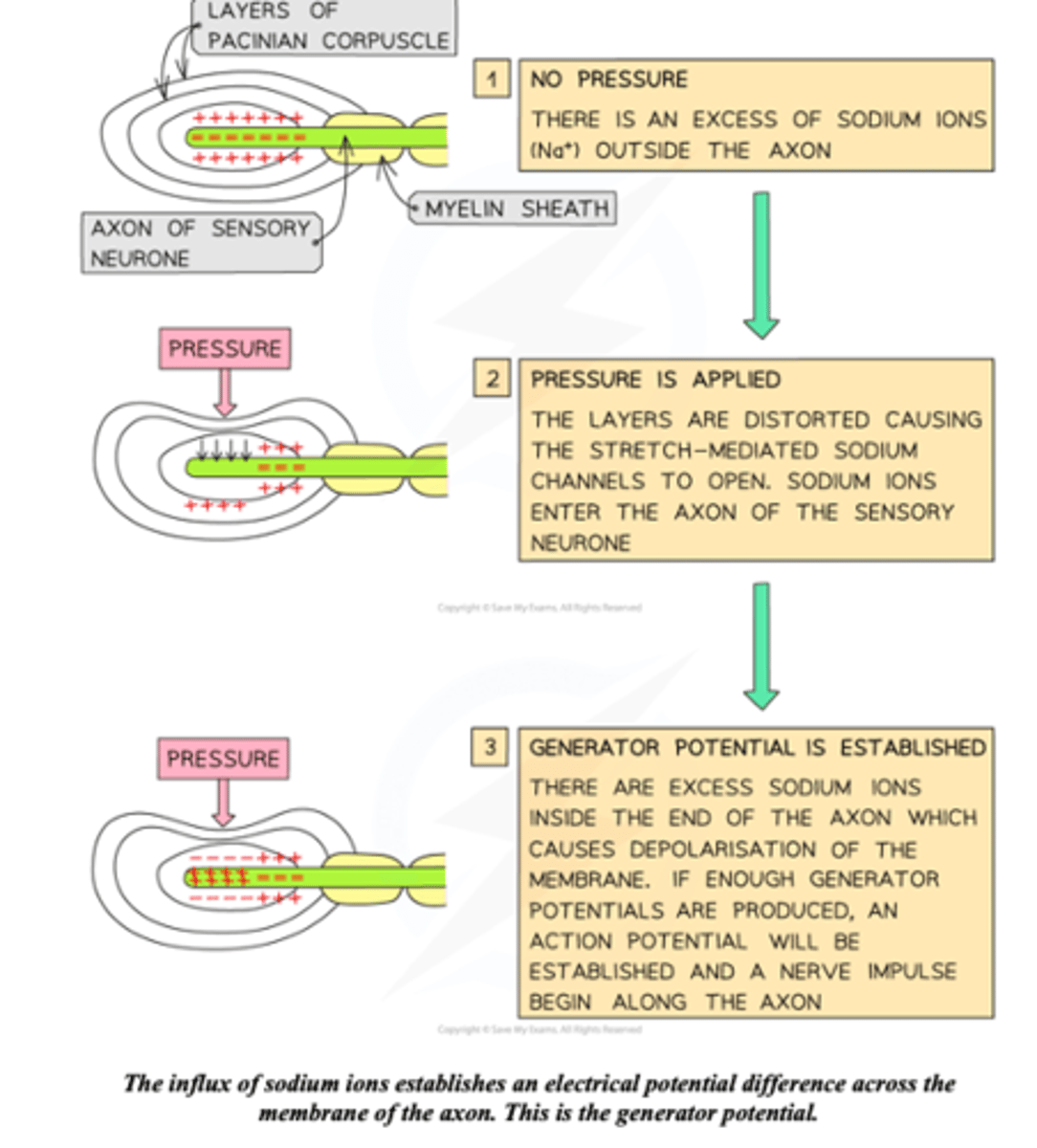
What is the difference between a generator potential produced by light and heavy pressure?
As action potentials never increase in size, they can only increase in frequency. A heavy pressure will cause a generator potential to be sent more frequently than a light pressure
How and why does higher pressure cause the membrane to depolarise?
Higher pressure causes more Na+ channels to open which flow inside the membrane. This positive charge causes the membrane to go from polarised (-) to depolarised (+)
How does the membrane repolarise?
The positive ions that moved in when the pressure caused the channels to open leave e.g. Na+ and K+ so the membrane goes from + to -
Describe the movement of a signal along a neurone.
1. Stimulus from sensory neurone causes the target cell to depolarise towards the action potential
2. If the threshold potential is reached the membrane depolarises causing an action potential
3. At the peak action potential the membrane repolarises
4. The membrane becomes hyper polarised during the refractory period and cannot fire
5. Resting potential is restored
Graph to show the movement of an electrical impulse along a membrane
ADD THIS
Where are the receptors in the eye located?
Retina
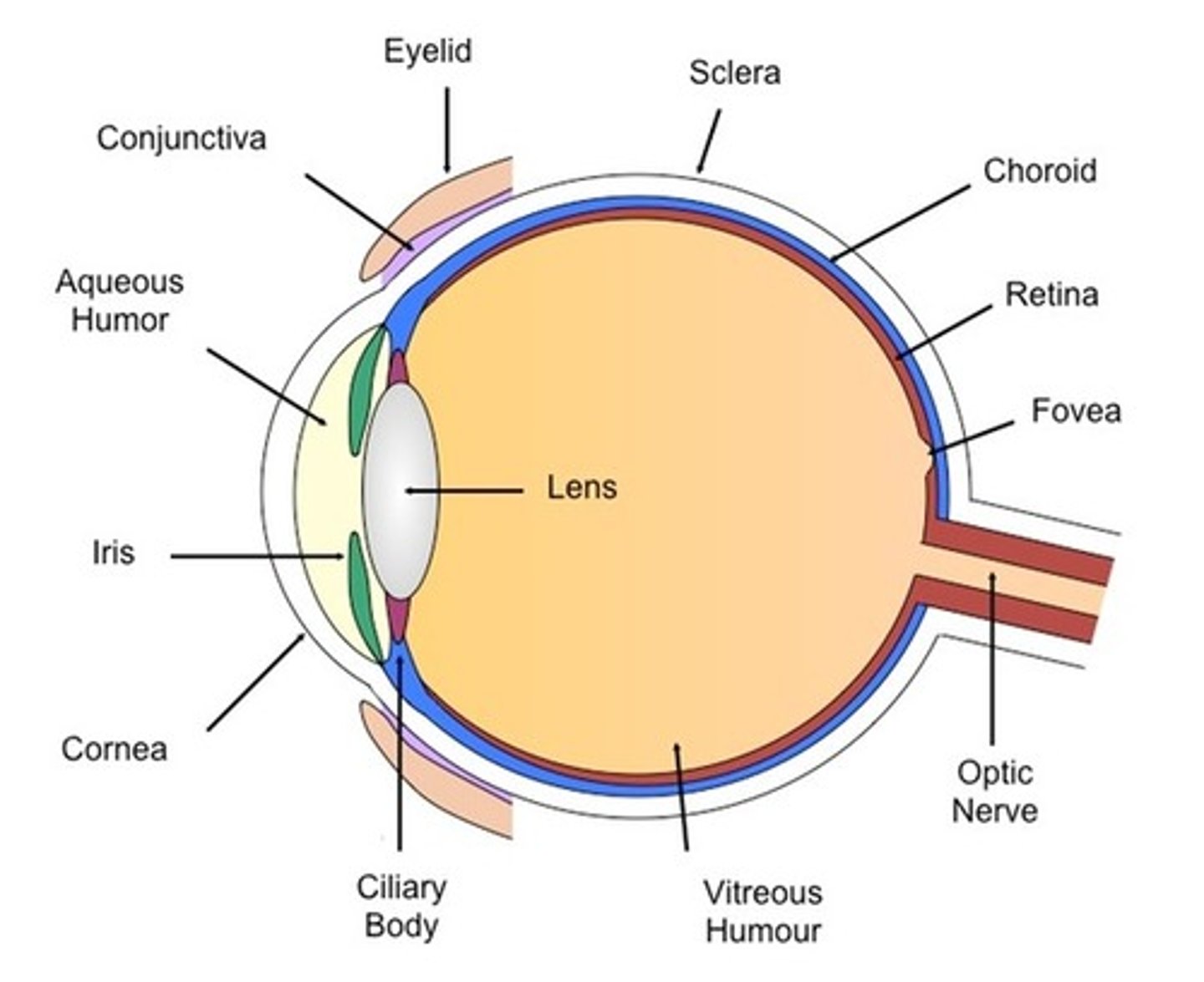
What are rod and cone cells?
Photoreceptors
What are photoreceptors?
Receptors that respond to light
Where are rod and cone cells found?
In the retina
How do photoreceptors produce a generator potential?
When they absorb light, their chemical structure is changed (due the excitation of the electron in the LDR of photosynthesis) and this produces a generator potential
Rod and cone cells do not connect directly to the CNS, what do they connect to instead?
They have synapses that connect them to bipolar neurones which are also in the retina
How do bipolar neurones connect to the brain?
They have synapses which connect to ganglion cells that have fibres which connect to the brain via the optic nerve
Rod and cone cell.
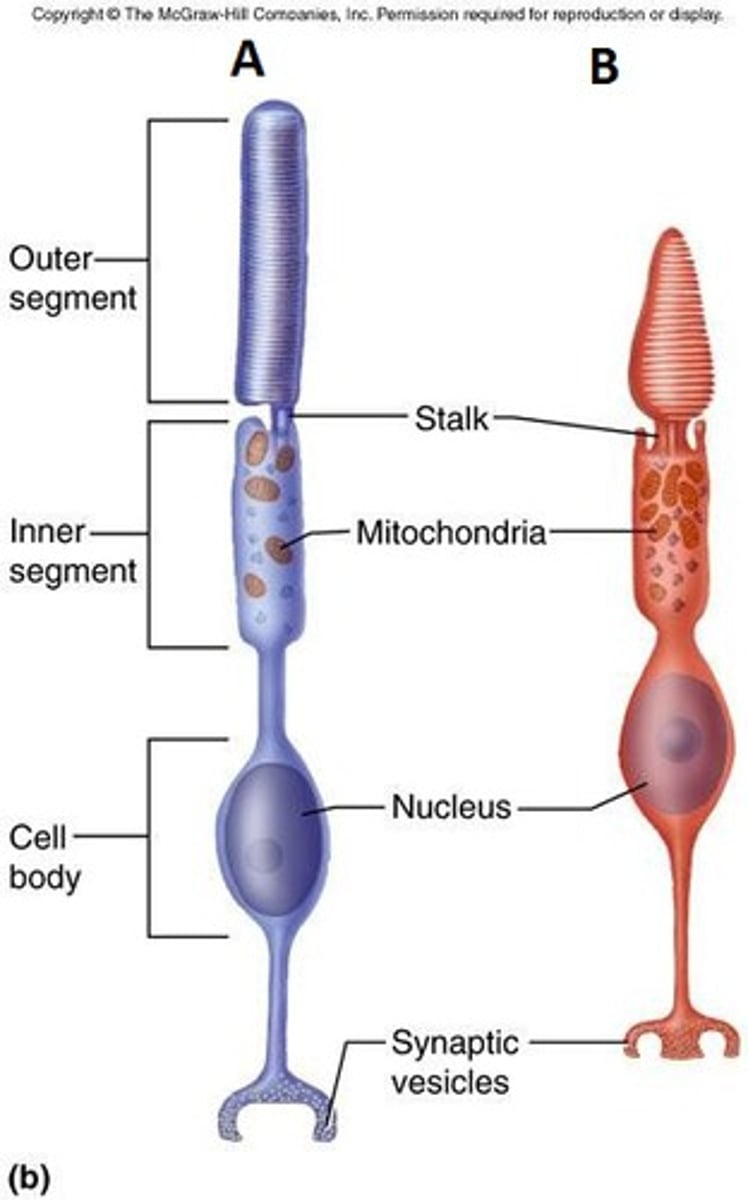
Where do rod and cone cells function best?
Rod - low light conditions (more sensitive to light)
Cone - bright light conditions (need more photons of light to be activated)
Why do rod cells not function well in bright light?
They are bleached
Describe the pigment that rod cells contain.
They all contain the same pigment which absorbs a wide range of wavelengths
Can rod cells differentiate between colours?
No they are monochromatic
Where are rod cells most abundant?
At the periphery of the retina
What vision are rod cells responsible for?
Peripheral vision
What type of images do rod cells produce and why?
Poorly resolved images. This is because many rod cells connect to only one bipolar neurone
Describe the pigment contained within cone cells.
There are three types of cone cell and these each have a different pigment that absorbs different wavelengths
Can cone cells differentiate between colours?
Yes (red, blue and green)
Where are cone cells most abundant?
In the centre of the retina
What vision are cone cells responsible for?
Visual focusing
What type of image do cone cells produce and why?
Well defined images because each cone cell synapses with a single bipolar neurone
How does resolution in an image we see from the eyes differ?
It s dependent on the way receptors are connected to the optic nerve fibres (number of bipolar neurones the rod or cone cells attach to)
Describe and explain the differences in resolution of images coming from rod and cone cells.
Rod cells - many rod cells synapse with a single bipolar cell resulting in a low resolution image
Cone cells - most cone cells only synapse with a single bipolar cell resulting in high resolution
Information from the rod cells is therefore combined at one point and therefore they are not as good at giving details