4.2 Energy, Power, Resistance
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
What is potential difference? State the units.
The work done per unit of charge. (V) It is used when charged particles lose energy to a component, it is the energy transferred from the electrical energy to other forms (heat, light, etc) per unit charge.
What is E?
electromotive force (e.m.f)- the energy transferred from one form of electrical energy per unit charge.
What is the difference between e.m.f and p.d in terms of energy transfer?
Voltage is the energy transferred per coulomb across a load resistance. Emf is the total amount of work done by the battery per coulomb.
Give the equation relating energy transferred to voltage.
W = VQ = EQ, where W = work done (energy transferred), V = potential difference, Q = charge.
How do you find the energy transferred to electrons?
eV = 1/2mv²
Define resistance.
How difficult it is for current to flow through an appliance. The potential difference required for each unit of current to flow through a resistor.
R = V/I
What is the definition of 1 Ohm?
When a resistor is subject to a voltage of 1V and allows a current of 1A through, it has a resistance of 1 Ohm.
What is Ohm’s Law?
The current through an ohmic conductor is directly proportional to the potential difference across it. (ie. the resistance doesn’t vary with voltage or current)
(This is only true if temperature is constant.)
What does the gradient of an IV graph represent?
1/R
How is an Ohmic conductor represented graphically?
Straight line through the origin of the IV graph. (Voltage is directly proportional to current).
How is a filament bulb represented on an IV graph?
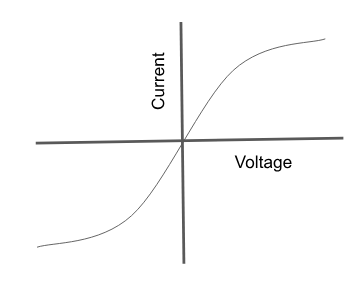
Why does the current increasing on a filament lamp increase the resistance?
The flow of current causes collisions between the electrons and the metal lattice.
These collisions increase the temperature (vibrations of particles) of the lattice.
As the temperature increases, more collisions occur, causing resistance to increase.
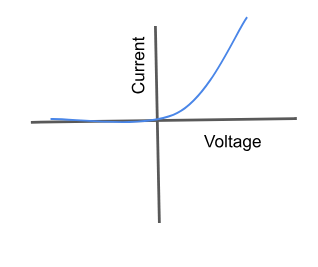
What is a diode?
An appliance that only allows current to flow in one direction.
Non-Ohmic
behaviour depends on polarity
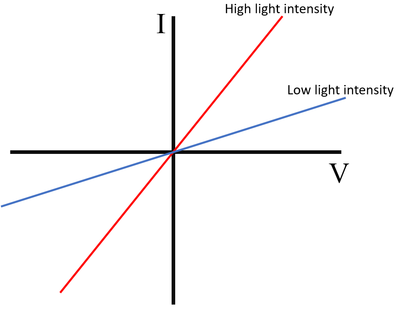
What is a Light Dependant Resistor?
A semiconductor that is sensitive to light: as the light intensity increases, the resistance decreases.
What is a thermistor?
A semiconductor that is sensitve to temperature: as the temperature increases, the resistance decreases. (Thermistors that work this was are called negative coefficient (NTC) thermistors)
What is resistivity?
A property of a metal which shows how easy or difficult it is for current to flow in the material (at a specific temperature)
p = RA/L
p = resistivity, R = resistance, A = cross sectional area, L = length
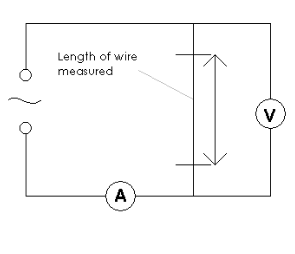
Describe an experiment to determine the resistivity of a metal.
Measure the diameter of wire using a micrometre
Use this to calculate the area
Set up the circuit as shown
Vary the length and record the voltage and current for each length
Use R = V/I to work out the resistance
Plot a graph of resistance against the length
The gradient = resistivity / area
Rearrange to work out resistivity
How does the resistance of metals vary with temperature?
Resistivity increases with temperature because the metal ions heat up and they vibrate more. This means there are more collisions with the delocalised electrons, slowing them down overall.
How does the resistance of semiconductors vary with temperature?
Some semiconductors get less resistive as temperature increases, because supplying energy actually causes more charge carriers to be released, so current can flow more easily.
Define Power.
The rate of energy transfer. Measured in J/s or Watts.
Give an equation for power in terms of current and voltage?
P = VI
What is a kilowatt-hour a unit of?
Energy: it’s a unit of power multiplied by time.
Why do electricity companies use ‘units’ (kWh) rather than joules or watts?
Joules and Watts are both so small that everyone would use vast quantitates of them, so its impractical to use just large numbers.
What are the circuit symbols?
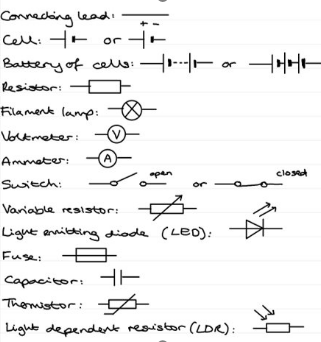
What property does an ideal Ammeter have?
0 resistance, so that it doesn’t affect the current.
What are the properties of a Voltmeter?
measure potential difference
placed in parallel
highest possible resistance in order to prevent current passing through them
and ideal voltmeter has infinite resistance
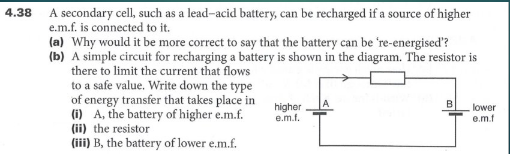
charge is not lost or gained, instead the charges gain more energy, hence ‘re-energised’
energy transferred electrically from the chemical store of the higher emf battery to the electrons in the circuit
energy transferred electrically from the electrons to the resistors, which increases the thermal store of the resistor and surroundings.
energy transferred electrically from the current to the chemical store of the lower emf battery.
extra- a red-hot conductor would quickly lose a negative charge but would retain a positive one. why?
Less energy needed to free an electron from an outer shell or a free electron. No easy mechanism to gain electrons to counteract a positive charge.
Thermionic emission: a much more effective method of freeing electrons from a metal in order to create cathode rays.