Clinical Correlations Exam 1
1/112
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
113 Terms
disc herniation
compression of spinal roots by herniated disc (nucleus pulposus surrounded by annulus fibrosus) as they exit intervertebral foramen
lumbar puncture (spinal tap) & epidural anesthesia
Sample CSF in the area that does not damage spinal cord – done in the region of the cauda equina (~around L4-L5 vertebrae)
lumbar puncture = subarachnoid space
epidural = epidural space
shingles - herpes zoster
Results from reactivation of latent varicella zoster infection within the dorsal root ganglia (or trigeminal ganglion)
when activated causes blistering in those areas that receive input from that spinal level
External Jugular Vein Distention
a markedly distended right external jugular vein (EJV); usually above clavicle
caused by elevated central venous pressure (from blockage of SVC)
Scalene Compression Syndrome (SCS
TYPE OF THORACIC OUTLET SYNDROME
Brachial plexus & subclavian a. become compressed since they pass between anterior & middle scalene m.
low BP in upper limb
Acromioclavicular (AC) joint separation (shoulder separation)
injury to the acromioclavicular ligament and/or coracoclavicular ligament; aka “piano key sign”
Glenohumeral Joint Dislocation (indirect vs direct)
humerus dislocates out of the joint capsule (GHJ reinforced by ligaments/muscles anteriorly, superiorly, and superiorly but NOT inferiorly)
indirect: excessive extenion
direct: hit by a force
Surgical neck of humerus fractures
commonly occur here because it is narrowest (may damage axillary nerve —> deltoid, teres minor)
related to brachial plexus case
elbow dislocation
force moving to proximal ulna causes olcecranon process of ulna out of olecranon fossa of humerus (injury to ulnar nerve)
ulnar collateral ligament tear
(“Tommy John surgery”) tear in ulnar collateral ligament common in baseball players
subluxation/dislocation of radial head
proximal head of radius subluxes (pulled downward from annular ligament)
Boxer’s fracture
fracture at head of 4th and/or 5th metacarpals
Scaphoid fracture
most common carpal bone fracture (results in nonunion and avascular necrosis)
MOI: falling on outstretched hand (force hits the wrist)
most common site of metastasis from breast cancer
axillary nodes (pectoral, apical, and central nodes)
risk of spreading through parasternal nodes
winged scapula
injury to long thoracic nerve resulting in scapula pulling away from posterior thoracic wall
“avoid knife fights”
subacromial impingement of rotator cuff
MOI: repeated ABduction and flexion of arm (throwing, swimming) causes humeral head and rotator cuff tendons, commonly supraspinatous, to impinge on coracoacromial arch
deltoid overrides rotator cuff muscle actions
superior displacement of humeral head
injury to supraspinatous muscle
inability to initiate ABduction
brachial plexus case
inability to ABduct arm + loss of sensation over lateral side of shoulder and proximal arm
surgical neck fracture = injury to axillary nerve and posterior circumflex humeral artery (quadrangular space)
compression of second part of axillary artery
branch of subclavian artery is involved in scapular anastomosis, allowing blood to bypass compression (suprascapular and dorsal scapular arteries involved)
popeye deformity
long head of biceps brachii shortens into middle of brachium (short head remains attached/functional)
lump in middle of upper arm
MOI: forced flexion against resistance or prolonged tendonitis
venipuncture
puncture of vein as part of medical procedure (withdraw blood sample) or for intravenous injection
mainly uses median cubital vein in cubital fossa
lateral epicondylitis (“tennis elbow”)
inflammation of common extensor tendon (sometimes extensor carpi radialis brevis)
MOI: overuse of extending wrist; repeatedly gripping object
anatomical snuffbox
between extensor pollicis longus tendon and extensor pollicis brevis tendon
radial artery, superficial branch of radial nerve, cephalic vein
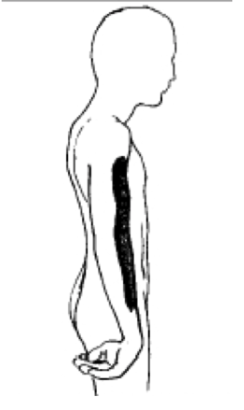
erb duchenne palsy
superior brachial plexus injury (injury to C5,C6)
musculocutaneous, axillary, suprascapular, radial nerves affected
waiter’s tip position (medially rotated, adducted arm, extended forearm)
wrist drop
inability to extend forearm and hand at wrist
MOI: spiral groove fracture of humerus
injury to radial nerve and deep brachial artery
palmaris longus signficance
absent in 14% of population
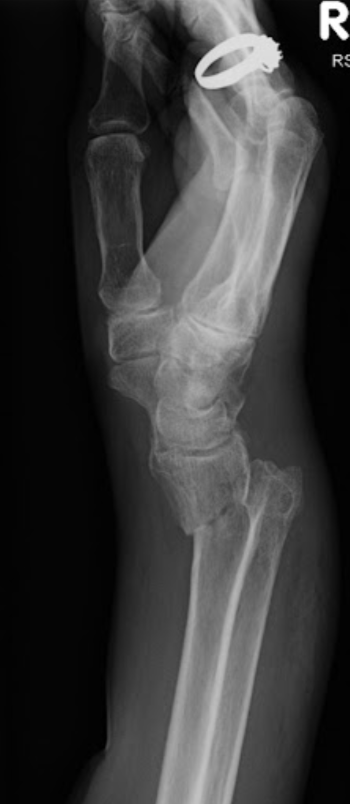
smith’s fracture
flexion fracture of radius (displaced anteriorly)
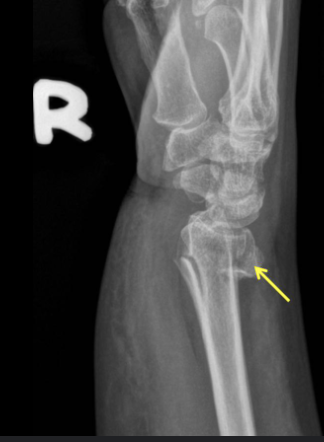
colle’s fracture
extension fracture of radius (displaced posteriorly)
mallet finger
injury to lateral bands on extensor tendon at the distal phalanx
inability to extend distal phalanx
hand of benediction
injury to median nerve at elbow or above
unable to make a fist or flex the thumb/2nd/3rd digitsc
carpal tunnel syndrome
entrapment of median nerve between flexor retinaculum (transverse carpal ligament) and carpal bones
inability to oppose thumb (but sensation remains on palm since it goes superficially)
claw hand
injury to ulnar nerve at elbow
Guyon’s canal syndrome
numbness and tingling on medial hand (can still flex 4th and 5th digits unlike claw hand)
injury to nerve passing through medial anterior wrist
clinical testing interosseous muscles
DAB (dorsal interossei, ABduction)
PAD (palmar interossei, ADduction)
both innervated by ulnar nerve
avocado hand
knife injures median nerve in hand
allen’s test
testing blood flow to hand before surgery (radial and ulnar arteries)
birth defects
leading cause of infant deaths (20% of all infant deaths)
congenital heart defects (most common)
cleft lip and palate (1 in 1600)
sacrococcygeal teratoma
part of primitive streak remains (type of germ cell tumor that contains tissues derived from all 3 germ layers in incomplete stages of differentiation)
rib dislocation
costal cartilage detaches from sternum at sternocostal joint
rib separation
rib detaches from costal cartilage at costo-chondral joint
costochondritis
inflammation of costal cartilage
common cause of chest pain in children/adolescents
flail chest (multiple rib fractures)
2+ contiguous rib fractures with 2+ breaks per rib
during inspiration = lung collapses on affected side and shifts mediastinum toward UNAFFECTED side
during expiration = mediastinum shifts to AFFECTED side
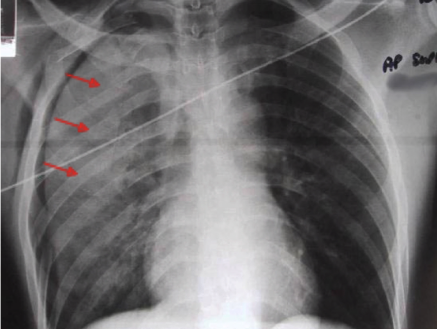
diagnosis
flail chest
cervical rib
extra rib arising from 7th cervical vertebrae (only 1 in 500)
causes a form of thoracic outlet syndrome (compression of lower trunk of brachial plexus or subclavian artery between cervical rib and scalene muscles
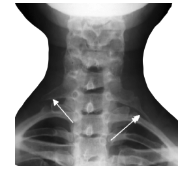
pectus excavatum
funnel chest
sternum pushed inward
pectus carinatum
pigeon chest
sternum pushed outward
kyphoscoliosis
combination of kyphosis (abnormal bending of thoracic spine) and scoliosis (lateral bending)
contracted scalene muscles
patients may use these muscles to help breathe when having difficulty breathing normally (advanced lung disease)
tripod position optimizes respiratory mechanics
herpes zoster (shingles)
viral disease characterized by painful skin rash with blisters often in dermatomal pattern
starts as chikcenpox (varicella zoster virus)
affects dorsal root ganglion and travels down nerve axons
thoracocentesis
requires catheter insertion
done middle of rib space or just above lower rib to avoid main neurovascular bundle (VAN)
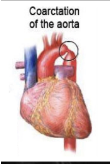
coractation of aorta
constriction of arch of aorta (congential defect)
may cause rib notching due to collateral circulation involving internal thoracic and intercostal arteries
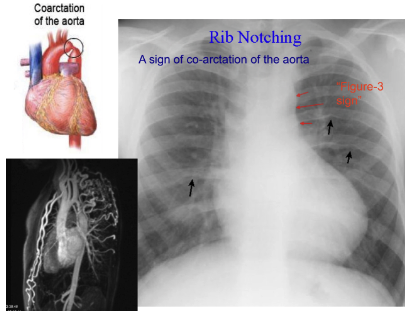
rib notching
sign of coractation of aorta
collateral circulation involving internal thoracic and intercostal arteries (may result in enlargement of intercostals)
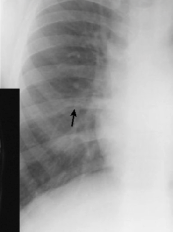
diagnosis
rib notching (coractation of aorta)
pleurisy
inflammation of pleura (inflamed visceral and parietal pleura rub against each other causing sharp pain during breathing, coughing, sneezing)
possible causes: (viral/bacterial) infection, pneumothorax, pulmonary embolism, lung cancer
may cause pleural effusion
pleural effusion
build-up of pleural space particularly in costodiaphragmatic recess (blunting in xray)
caused by pleurisy
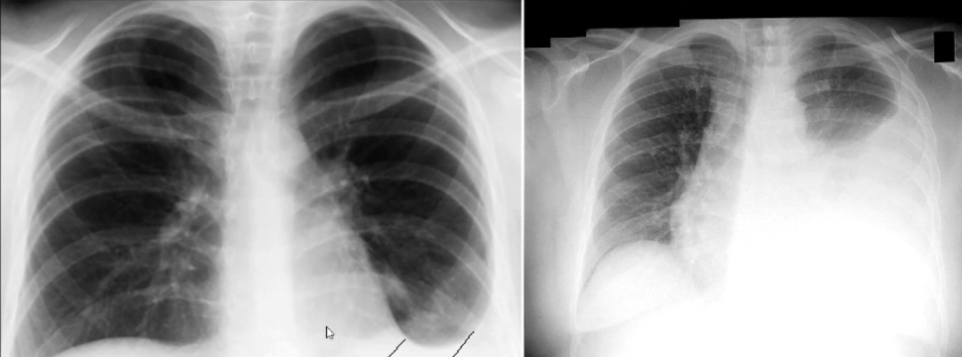
diagnosis
pleural effusion
sampling pleural fluid
in costodiaphragmatic recess
4 types of fluids that can accumulate in pleural space
serous (hydrothorax, pleural effusion)
blood (hemothorax)
pus (pylothorax)
lymph (chylothorax)
air (pneumothorax)
pneumothorax
when air gets into pleural space (can occur spontaneously)
caused by pulmonary blebs
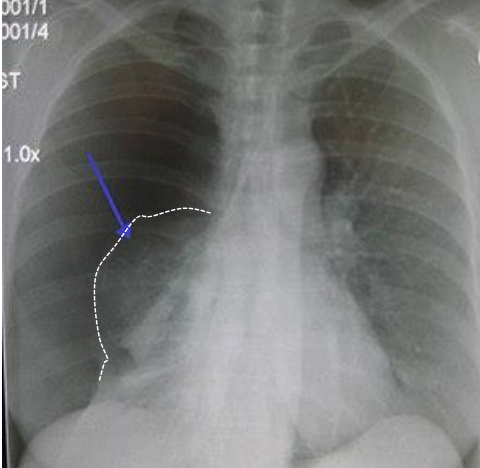
diagnosis
pneumothorax
tension pneumothorax
dangerous type of pneumothorax where air enters pleural cavity during inspiration but is NOT expelled during exhalation (buildup of pressure in pleural space)
symptoms: chest pain, tachycardia, tachypnea
left-side tension pneumothorax
collapse of left lung causes deviation of lung and mediastinum to opposite side of chest (mediastinal shift)
MEDICAL EMERGENCY
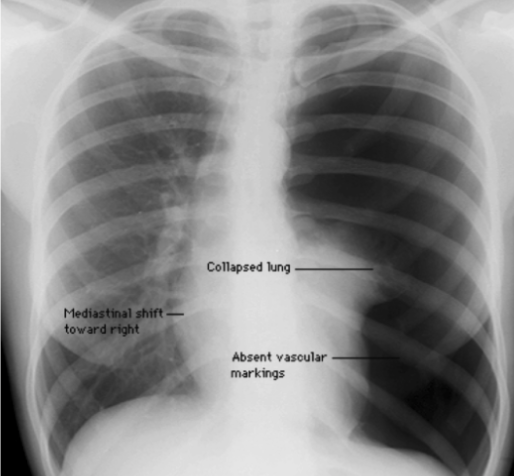
diagnosis
left side tension pneumothorax (right side if right lung is collapsed)
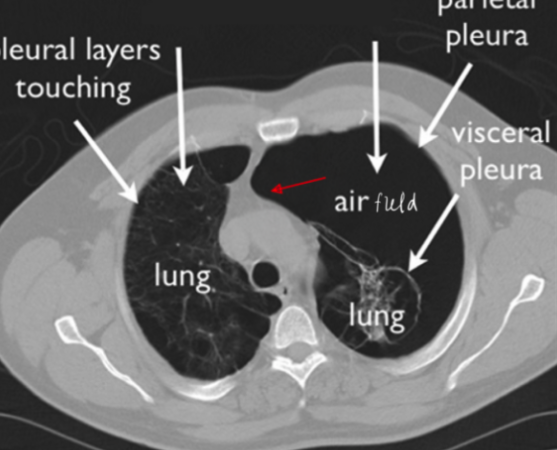
diagnosis
left side tension pneumothorax
pulmonary embolism
blockage of pulmonary artery or one of its branches by a substance (blood clot) that has traveled from else in body through bloodstream
sx: difficulty breathing, chest pain upon inspiration, low blood oxygen levels, cyanosis, rapid breathing, rapid heart rate
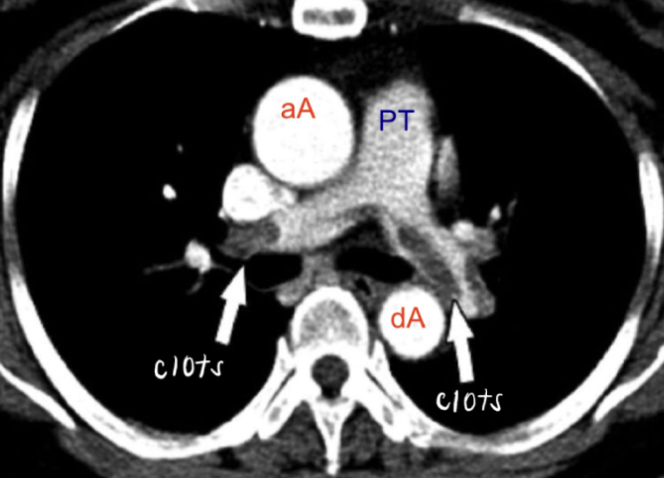
diagnosis
pulmonary embolism
inhalation of sympathomimetic substance
relax smooth muscle in bronchi and dilate airways (albuterol)
pericardial effusion
fluid in pericardial cavity
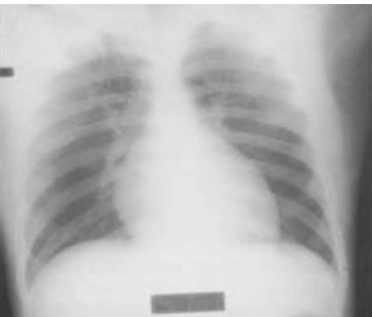
diagnosis
pericardial effusion
“water-bottle” silohuette
cardiac tamponade
acute version of pericardial effusion
space around heart fills with blood/fluid (puts pressure on heart)
becks triad
muffled heart sounds, jugular distension, low arterial pressure
coronary artery disease
build up of cholesterol “plaque” in coronary arteries makes it difficult to supply heart with blood, oxygen, nutrients
heart uses 3 perfusion strategies
3 perfusion strategies (CAD)
coronary artery collateralization (new capillary growth)
reverse blood flow in thebesian veins
endogenous bypass via vasa vasorum
(what happens if these don’t work?)
coronary artery bypass graft (CABG)
solution for when 3 perfusion strategies for CAD don’t work (take vein/artery from elsewhere and attach to ascending aorta to bypass problematic area)
graft options: great saphenous vein, radial artery, internal thoracic artery
most common vessels to be occluded in coronary artery disease
left anterior interventricular artery
right coronary artery
circumflex artery
transplanted heart
no external nervous input, no sensory input
tumor growing in mediastinal area has affected patient’s speaking
recurrent laryngeal branch of vagus nerve
hiatal hernia
part of stomach protrudes up into chest through diaphragm
portal hypertension
venous return from GI tract cannot get through to portal system of liver. therefore, it will try to fin ways of gettting around using superficial veins (which become enlarged)
seen in patients with liver disease, ascites
caput medusae
cluster of swollen veins in abdomen (usually with paraumbilical veins)
patients with liver cirrhosis, parasitic infections (ascites)
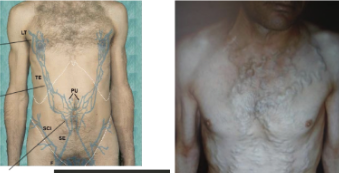
diagnosis
caput medusae
cremasteric reflex
stroke inner surface of thigh near testis → testis should pull up closer to body
used to test genitofemoral nerve (L1/L2) and testicular torsion
testicular torsion
testicle rotates, twisting the spermatic cord that brings blood to scrotum (reduced blood flow causes severe pain/swelling)
inguinal hernia (direct vs indirect)
direct (acquired): does NOT go through inguinal canal, medial to lateral umbilical fold
indirect (congential): does go through inguinal canal, lateral to lateral umbilical fold
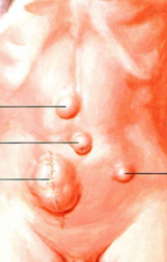
identify the types of hernias
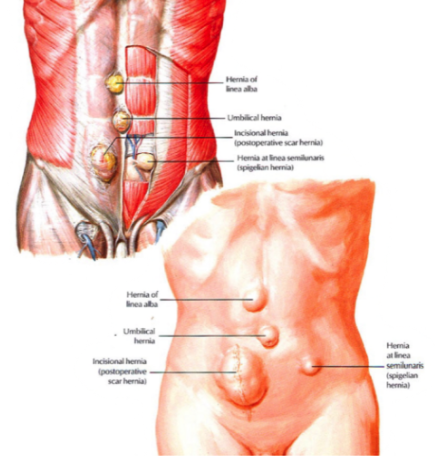
ascites
accumulation of protein-containing fluid within abdomen (enlarged abdomen)
caused by liver cirrhosis, cancer, kidney failure, pancreatitis, tuberculosis
gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)
stomach acid frequently flows back into esophagus which can irritate lining of esophagus (acid reflux)
caused by weakened sphincter
can cause esophageal ulcer, esophageal stricture, Barrett’s esophagus (precancerous changes to esophagus)
peptic ulcer disease
open sores on inside lining of stomach and upper portion of small intestine (duodenum)
includes gastric and dudodenal ulcers
commonly caused by bacterium H. Pylori
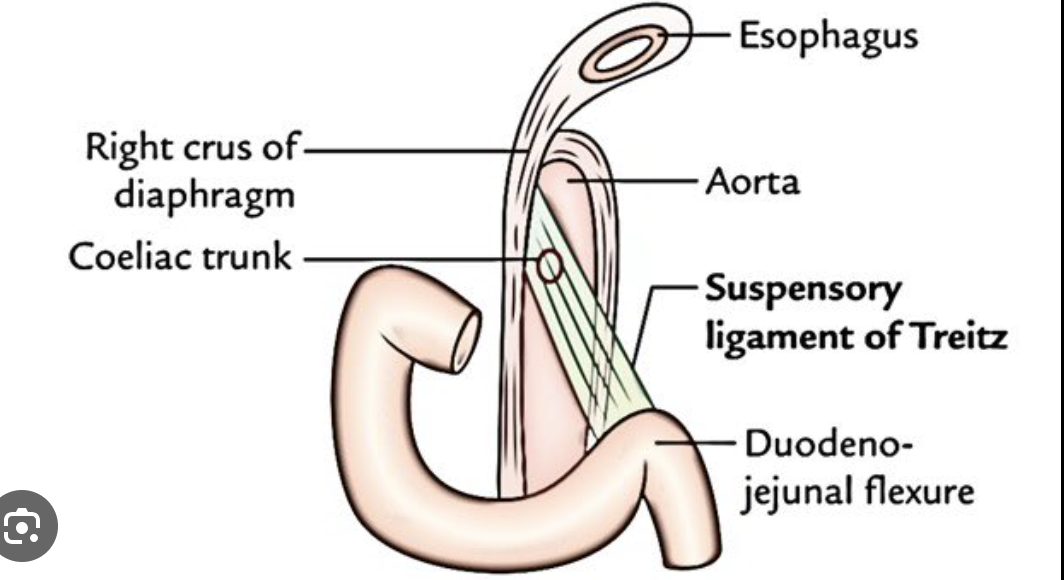
ligament of treitz
suspensory ligament of duodenum
can use as landmark for diagnosing intestinal malrotation and partial rotation AND discriminating upper/lower GI bleeding
ileocecal junction
can diagnose irritable bowel syndrome and Crohn’s disease by looking here
pancreatic endocrine malfunction
diabetes mellitus: high blood sugar due to not being able to produce insulin to regulate blood sugard
pancreatic exocrine malfunction
diarrhea and malnutrition (pancrease can’t produce digestive enzymes)
head of pancreas clinical significance
near numerous ducts/blood vessels (close relationship to duodenum)
jaundice
pressure on bile duct
irreversible cirrhosis
scarring of liver caused by alcohol abuse, hepatitis infection, autoimmune disease
presents as hobnail appearance, ascites, splenomegaly
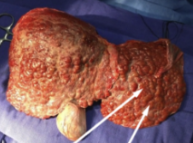
diagnosis
liver cirrhosis
Crohn’s disease
inflammation of ileocecal junction
presents as labial/gingival/mucosal swelling, cobblestoning of buccal mucosa, mucosal tags
diarrhea, stomach pain, bloody stool, reduced appetite, weight loss
diverticulosis
false diverticula (external vaginations of mucosa colon) develop along intestine
commonly found in sigmoid colon
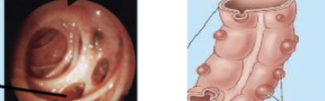
diagnosis
diverticulosis
volvulus of sigmoid colon
rotations/twisting of loop of sigmoid colon (obstruction of lumen of descending colon)