chemistry u3 aos 2 (electrolysis and faraday's laws)
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
electrolysis
= a process of passing through electric current into an electrolytic solution (conducting liquid) to make non-spontaneous redox reactions
electrical energy → chemical energy
applications of electrolysis
electroplating
electrorefining
rechargeable batteries
hydrogen production from water
compare electrolytic cell and galvanic cell
similarities
they are both electrochemical cell
both have an anode for oxidation and a cathode for reduction
galvanic cell
chemical energy → electrical energy
produce electricity
anode (-); cathode (+)
spontaneous redox reactions
two half cells are needed
electrolytic cell
electrical energy → chemical energy
consume electricity
a battery/ energy source is needed
anode (+); cathode (-)
non-spontaneous redox reaction
only one cell
why is cathode in electrolysis negative?
the power source forces electrons towards cathode, resulting in a negative charge
what would be/ how do we determine the required voltage applied for the electrolytic cell to operate?
greater than the cell emf/ potential difference, as it is a non-spontaneous reaction;
HOWEVER the voltage cannot be too high, or else side reactions may occur
** the calculated emf in electrolytic cell is always negative (coz non-spontaneous)
what is needed for electrolysis to occur?
free moving ions/ charged particles
aqueous solution (water may undergo electrolysis)
molten salt (no water); but more expensive
what to be considered when choosing species to react in your mini ECS?
any repulsion? (same charge?)
the strongest RA/ OA
the concentrations of the RA/ OA (e.g. Cl- VS H2O)
species running out, the next strongest RA/ OA will react
any direct reactions between species
disadvantage and advantage of using molten salt for electrolysis
(disadvantage)
high cost
(advantage)
no water is present to be preferentially reduced
any metals below Zn can only be produced via electrolysis of molten salt
ECS is determined under standard conditions (298K, 1M, 100kPa), how would different concentration of NaCl(aq) affect its electrolysis?

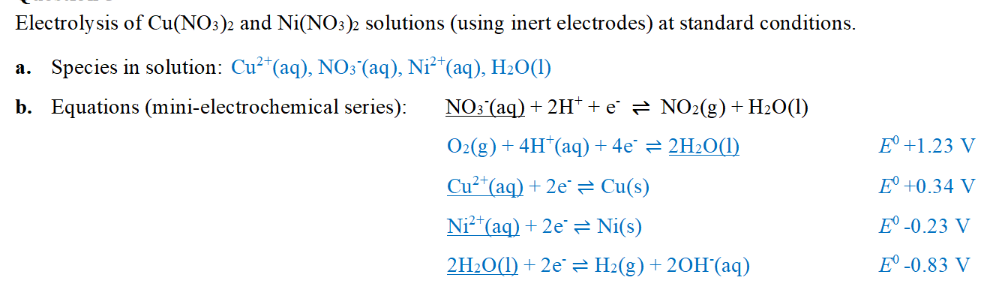
why nitrate ion is not reduced?
reduction occurs at cathode (+) which will therefore repel the positive nitrate ion
H+ ions are required for reduction of nitrate ions which is not present initially
choose using an aqueous solution/ molten salt to produce Mg and Cl2 from MgCl2

why does electrolysis sometimes yield different products to those predicted using ECS?
ECS is under standard conditions, sometimes conditions are not standard
use of sodium and chlorine
sodium
raw material for bleach
to produce number of organic chemicals
used in nuclear sectors
chlorine
disinfectant
manufacture of plastics and pharmaceuticals
what is the purpose of adding chemical additives into the electrolytic cell with molten electrolyte? any criteria?
to lower the melting point, to reduce the energy used to melt the substance
these additives do not compete with the OA/RA or react within the cell to ensure the desired product is still obtained (e.g. CaCl in down cell, mixed with NaCl)
what’s the point of ‘electrolyte provides resistance to the electric current’?
this produces sufficient heat to keep the electrolyte molten
why is a low melting point of electrolyte desirable?
lower energy required to melt
lower the cost
what is the purpose of having a membrane/ screen/ mesh in an electrolytic cell?
to separate the (reactive) products, prevent them from reacting
how to abide with green chemistry principles when designing an electrolytic cell?
renewable energy sources can be used (e.g. solar power, wind power)
how does those chemical additives (e.g. cryolite for alumina) lower the m.p.?
different sizes of particles
alumina is less dense in cryolite than molten aluminium
less energy to break the bonds
lower the melting point
except from an energy source to keep the electrolyte molten, where else could we get the heat?
the electrical resistance of the electrolyte to the electric current keeps the electrolyte molten
any other subsequent reaction that is exothermic will contribute energy to maintain molten electrolyte
advantage of having unreactive electrodes
avoid production of CO2 for carbon electrode
reduce the cost to replace the reactive electrodes
compare primary cell and secondary cell
(primary cell)
chemical energy → electrical energy
oxidation at anode (-); reduction at cathode (+)
goes flat when the reaction reaches equilibrium must be discarded
products migrate away from the electrodes
(secondary cell)
both discharge and recharge
discharge follows the rule for galvanic cell
can be recharged to convert the products back to reactants
recharge: electrical energy → chemical energy
BECAUSE products from discharge remain in contact with electrodes
compare discharge (galvanic cell) and recharge (electrolysis)
(discharge)
chemical energy → electrical energy
oxidation at anode (-); reduction at cathode (+)
(recharge)
electrical energy → chemical energy
oxidation at anode (+); reduction at cathode (-)
this is can happen coz the products from discharge remains in contact with the electrodes
a source of electricity is supplied to convert electrical → chemical energy
the electrical energy must be greater than the emf of the cell (overpotential)
when considering the secondary cell undergoing both discharge and recharge reactions, which remains no change? charge OR ‘anode’ ‘cathode’
the charge of each electrode remains unchanged
i.e. reaction at anode (during discharge) is then reversed and become a reaction at cathode (during recharge), while both electrodes in this case is still negative
combustion reaction for H2
only water is produced (no CO2) since there was no carbon provided initially
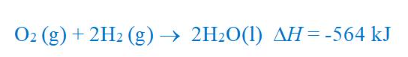
advantage and disadvantage of hydrogen as a fuel
(advantage)
high energy density
abundant on earth
water is a sole product of its combustion
(disadvantage)
it is not found as an element, energy is needed for production, which could be using non-renewable energy sources
energy is needed to liquify it due to its very low boiling point
high pressure is also needed to store hydrogen as gas
the hydrogen is highly flammable and explosive, careful storage is needed
also difficult to be transported safely as a gas/ liquid
green hydrogen VS brown hydrogen
(brown hydrogen)
derived from fossil fuel
produced using steam reforming of methane (also produces CO)
production generates CO2
however this is the predominant type of hydrogen
(green hydrogen)
produced by chemical processes that use renewable energy sources
production is largely carbon neutral
(grey hydrogen)
hydrogen derived from industrial processes
(blue hydrogen)
derived from fossil fuels with carbon capture
ways to produce green hydrogen
electrolysis of water using Hofmann voltameter
PEM (polymer electrolyte membrane) electrolysis cell
artificial photosynthesis
electrolysis of water using Hofmann voltameter
a low concentration of H2SO4 (electrolyte) is added to water to allows conduction of electricity
COZ (pure water CANNOT be electrolysed; free-moving charged particles are needed to conduct electricity)
why wouldn’t H2SO4 react in the Hofmann voltameter
the concentration of H2SO4 is too low for the ions to react
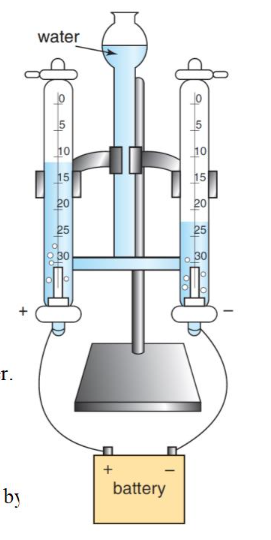
where is hydrogen produced
RHS, because the amount of gas produced is twice as much as that on the LHS
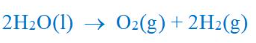
except from H2SO4 being added to conduct electricity in the electrolysis, what else can be added to increase the rate if gas production
salt
increase salt concentration
increase conductivity
increase the rate of reaction
increase rate of gas production
how can you make electrolysis of water produce green hydrogen?
using renewable energy source (e.g. wind energy/ solar energy) to generate electricity for electrolysis of water
electrodes in PEM electrolytic cell
expensive inert metals (e.g. Pt)
porous, to allow passage of gases whilst preventing the flow of liquid
electrolyte in PEM electrolytic cell
solid polymer membrane electrolyte
allows movement of hydrogen ions from anode to cathode
electrically insulating the electrodes
separating the hydrogen gas and oxygen gas produced
any solution in PEM electrolytic cell?
no solutions, all solid, acidic cell, starts when water is pumped into the anode
advantage and disadvantages of PEM electrolytic cell
(advantage)
pure hydrogen produced
high rate of hydrogen production
(disadvantage)
expensive (due to electrodes and electrolyte)
reactions in PEM electrolytic cell (cathode and anode)

reactions in Hofmann voltameter (cathode and anode)

artificial photosynthesis
solar energy to produce hydrogen
the photochemical cell resembles a solar panel operating in a solution
the anode is coated with catalyst to absorb energy from sun
the solar energy causes excitation of metal in electrode
results in oxidation of water at anode to form oxygen gas and hydrogen ions
hydrogen gas migrate to cathode where they are reduced
equations in artificial photosynthesis reaction (very similar/ same as that of PEM electrolytic cell)
** MAJOR DIFFERENCE:
PEM electrolytic cell uses a battery/ external energy source e.g. solar/ wind
artificial photosynthesis is initiated by sunlight directly (as it activates the anode with catalyst)

advantage of artificial photosynthesis
higher efficiencies due to fewer energy conversions
decrease in the need for large-scale storage tanks for electricity
according to the Faraday’s law, what is the amount of product formed dependent on?
the size of electric current
operating time
** Q = It
applications of electroplating
appearance
corrosion prevention (with a less reactive metal)
if nitrate ions in the electrolyte don’t react, what function do they perform?
to move towards anode to allow the current to flow
how does the concentration of metal ions change as the electroplating is operating
no change:
metal ions are generated at anode as the same rate as the metal ions are consumed at cathode, this maintains a constant concentration of metal ions
faraday’s first law
the mass of any substances deposited/ consumed at the electrode is directly proportional to the amount of electricity passed through the cell
faraday’s second law
for one mole of substance to be deposited/ consumed requires whole number of electrons (one, two, three or other moles)
how should the objected to be electroplated to be placed in the electrolyte?
fully immersed in the solution to ensure it is completely electroplated
why must electrolysis be used to extract lithium metal from its ore?1
lithium ion is a very weak OA that no stronger RA could reduce it through spontaneous reactions
what is the purpose of constantly blowing inert gas to the cathode during an electrolysis of molten MgCl
since Mg has a property of reacting vigorously with oxygen
the inert gas would prevent air from entering the cell to react with molten Mg