Human Physiology Exam 1
1/103
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
104 Terms
2 types of electrical signals
graded and action potentials
graded potentials
short distance signals
>local flow between active area and inactive areas
>passive flow
>decremental
>occur in cell body and dendrites
>magnitude and duration varies
action potentials
long distance signals: how neurons communicate
> Occur along the axon
what leads to an Action potential
graded potentials, if magnitude is great enough
cell body
contains the nucleus and organelles
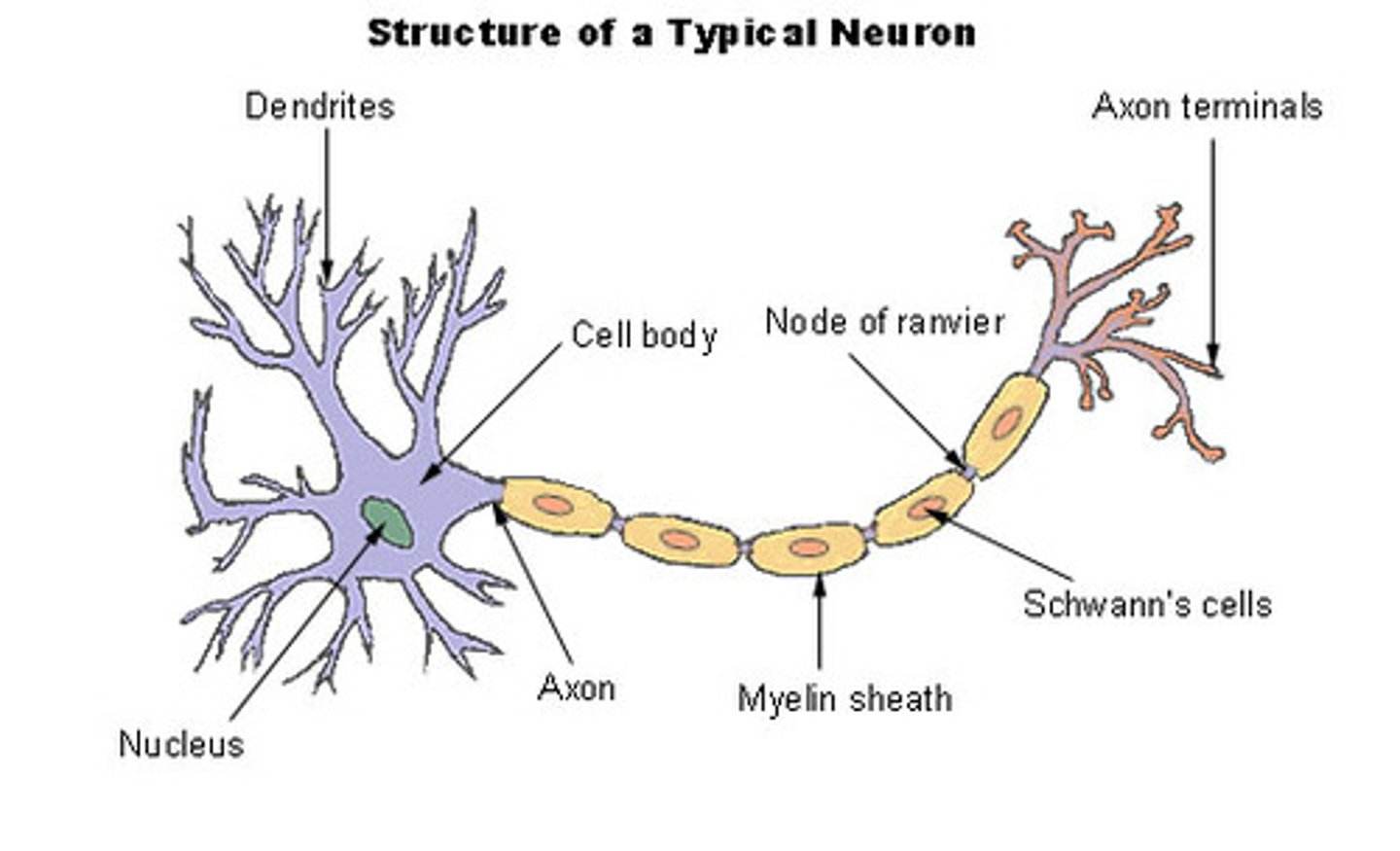
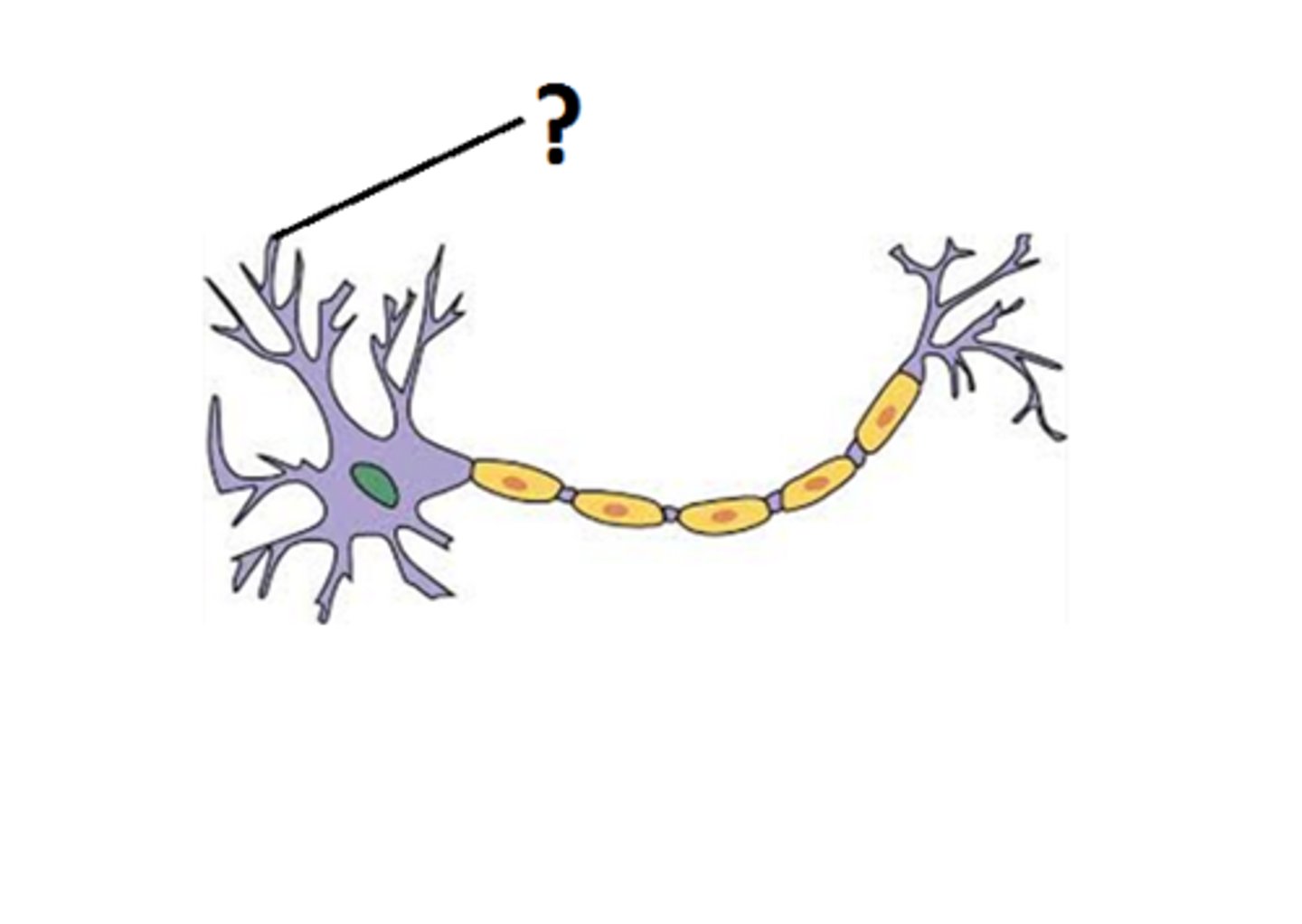
dendrites (input zone)
numerous extensions from cell body
axon hillock (trigger zone)
first portion of axon, initiates action potentials, lowest threshold potentials
Axon (conducting zone)
single elongated tubular extension
> conducts action potentials away from cell body
axon terminals (output zone)
releases neurotransmitters that influence other neurons
what are triggering events
1) a stimulus
2) interaction of a chemical messenger with surface receptor
3) change in membrane potential caused by an imbalanced leak-pump cycle
how does the potential change in graded potentials
-70 to -60
what is resting membrane potentials
-70
can graded potentials summate??
yes
Where is an axon potential generated?
axon hillock
How does the membrane potential change in a triggering event (threshold potential)
-70 to -50 (depolarization)
what is the mV for after hyperpolarization
-80
the membrane of axons contain what type of channels
voltage gated Na and K channels
at rest, some ____ are open, but much fewer ___ are open..
k+, Na+
K+ equilibrium potential
Ek+= -90
explain the positive feed back loop in the action potential mechanism
Na+ concentration and electrical gradients are INTO cell, so Na+ begins to move into cell. This causes further depolarization, which opens more voltage-gated Na+ channels and a positive feedback loop is established as more voltage-gated Na+ channels rapidly open
what is threshold mV
-50
what happens at threshold
membrane becomes more permeable to Na+ than K+ bc all VG Na channels are open
as Na+ flows into the cell, the potential of the cell becomes
30
Na+ equilibrium potential
-60
voltage gated Na+ channels become inactive by ball and chain at ___ mV
30
what repolarizes the membrane?
K+ leaving.
remember at this time there is a positive membrane potential, meaning the inside of the membrane is more positive compared to the outside
what would happen without ATPase pumps?
repeated action potentials would eventually erode separation of Na+ and K+
how does conduction of action potential occur
local current flow down axon along every patch of membrane
What happens when the first action potential is generated in a neuron?
It triggers another action potential in the adjacent area, creating a self-perpetuating (self-regenerating) cycle down the neuron.
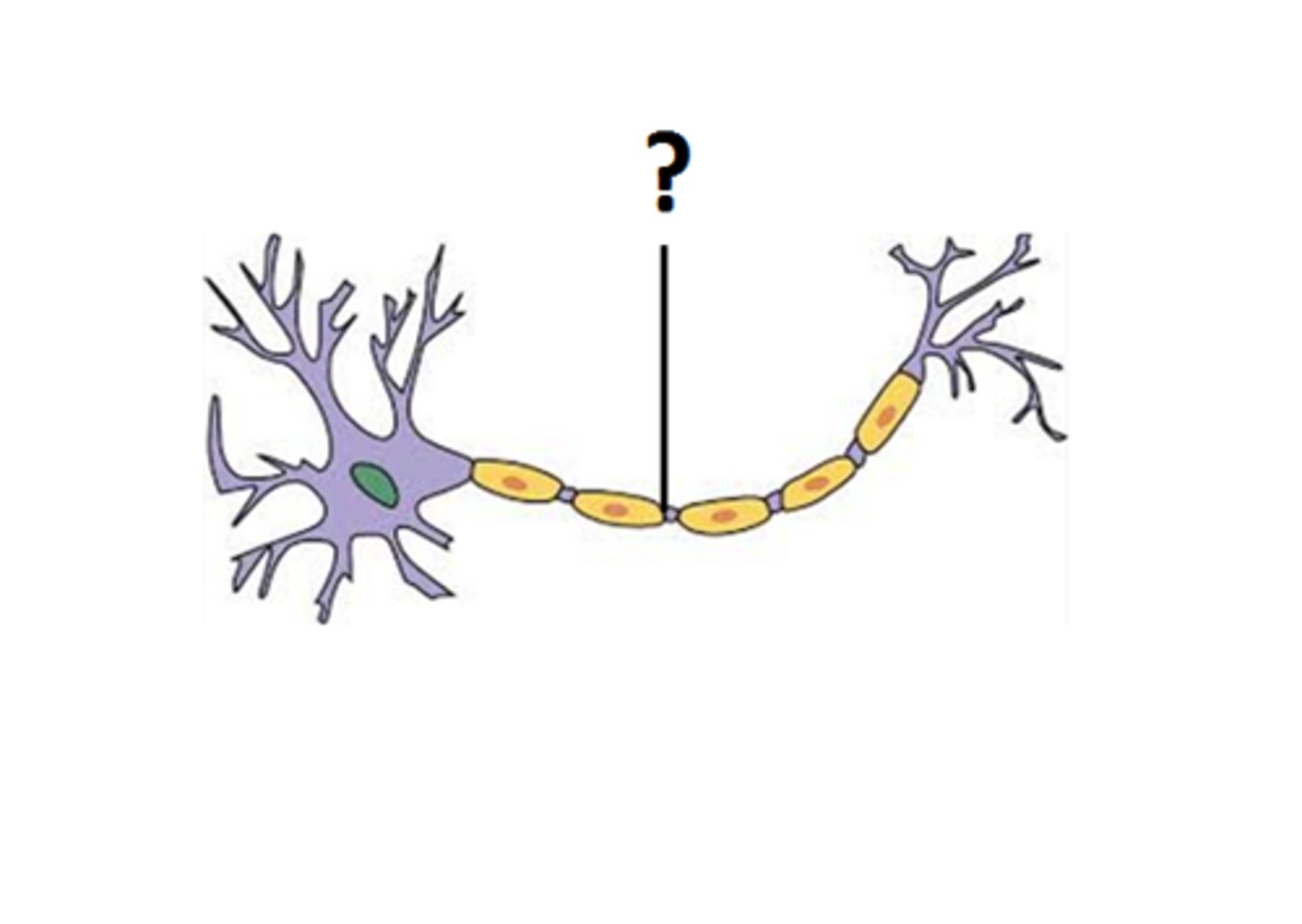
what is myelin
thick layer composed mostly of lipids that surround a portion of axon and acts like a rubber insulation
Myelin forming cells in CNS
oligodendrocytes
myelin forming cells in PNS
schwann cells
gaps between myelin
nodes of ranvier
saltatory conduction
impulse jumps from node to node along a myelinated axon
what does myelin do
increase the speed of the conduction of action potentials
do we want action potentials to move in both directions along an axon?
NO!
refractory period is required to keep an action potential from bouncing back and forth
absolute refractory period
Na+ gates are closed and inactivated; no action potential can occur.
relative refractory period
an action potential can occur, but the stimulus must be much larger than normal to get one started. Occurs after the action potential is complete. K+ gates are slow to close and are still open during this time. In addition, not all of the Na+ channels have been reset.
what do refractory periods ensure
unidirectional movement of action potentials and sets and upper limit to the frequency of occurrence of action potentials
physiology
study of how the body functions
chemical level
all matter, living or nonliving is composed of atoms. O,H,N,C make up 96% body chemistry
Cellular level
cells are the least complex organization capable of performing the tasks of life
Tissue level
made up of similar types of cells
muscle tissue
specialized cells for contracting
nervous tissue
specialized cells for initiating and transmitting electrical impulses
epithelial tissue
tissues with many cells arranged close together with little extracellular matrix and specialized barrier
connective tissue
few cells arranged in extensive extracellular matrix to support the body
Organ level
two or more primary tissues
body systems
MURDERS LINC
Muscle
urinary
respiratory
digestive
epithelial
reproductive
skeletal
lymphatic
immune
nervous
connective
homeostasis
dynamic steady state in the internal environment
> cells require homeostasis for survival
ECF made up of
interstitial fluid & plasma
plasma membrane composed of what 4 things
phospholipid bilayer, carbohydrates, cholesterol and proteins
what are the 3 subdivisions of the cells
plasma membrane, nucleus and cytoplasm
Rough ER vs Smooth ER
RER- ribosomes for protein synthesis and contain enzymes for protein synthesis
SER- packages proteins in transport vesicles to move new synthesized proteins to the golgi complex. Lipid metabolism
Golgi complex
packages secretory vesicles for release by exocytosis. Sorting and segregating products by function and final destination
> adds docking markers(address)
lysosomes
intracellular digestion- removes aged or damaged cells
peroxisomes
produces and decomposes H2O2 into water and oxygen by an enzyme called catalase
mitochondria
power plants
generates ATP needed by the cell.
vaults
cellular transport from nucleus out of the cell
Centrosomes and Centrioles
cells main microtubule organizing center.
> moving vesicles throughout the cytosol and function in formation of cilia, flagella and mitotic spindles
cytosol
intermediary metabolism, ribosomal protein synthesis and nutrient storage
Cytoskeleton
integral whole and links other parts of the cell together
microtubules
help maintain shape and complex cell movements
microfilaments
contractile systems and mechanical stiffeners
intermediate filaments
important in cell regions subject to mechanical stress
integral proteins
proteins embedded in in lipid bilayer
peripheral proteins
outer layer of lipid bilayer
membrane proteins
found on outer layer that function to recognize self cells. Types include- channels, receptors, carriers/transporters, docking marker acceptors, membrane bound enzymes, CAMs and glycoproteins
what are CAMs
specialized proteins protude from both of the adjacent membranes and form hooks and loops that hold adj cells together- cadherins and integrins
what is the extracellular matrix composed of
elastin, collagen and fibronectin
Desmosomes
act like velcro that anchors tow adjacent non touching cells.
> plaques and strong filaments containing cadheriams
Tight junction
bind touching adjacent cells firmly together to seal off passageway
> epithelial cells
Gap junctions
gap linked by small connecting tunnels formed by connexons
> connexon formed by 6 proteins called connexins
what can directly pass through the plasma membrane
lipid soluble and small water soluble substances
passive transport
the movement of substances across a cell membrane (H->L)without the use of energy by the cell
Simple diffusion
uniform spreading out of molecules die to random movements along the chemical gradients directly through the plasma membrane (lipophilic) or through channels (hydrophilic)
Ficks Law of diffusion
rate of diffusion
osmosis
net diffusion of water down its concentration gradient.
Movement of water across a permeable membrane is driven by
by net osmotic pressure (pulling pressure)
Osmotic pressure is the result of
unequal distribution of non penetrating and penetrating solutes across the membrane
What type of solution will promote the movement of water into the solution?
high osmotic pressure (hyperosmotic)
Active transport
Energy-requiring process that moves material across a cell membrane against a concentration difference
Facilitated diffusion
passive transport of ions from hight to low using a carrier
Primary active transport
directly uses ATPase to physically change shape of pumps
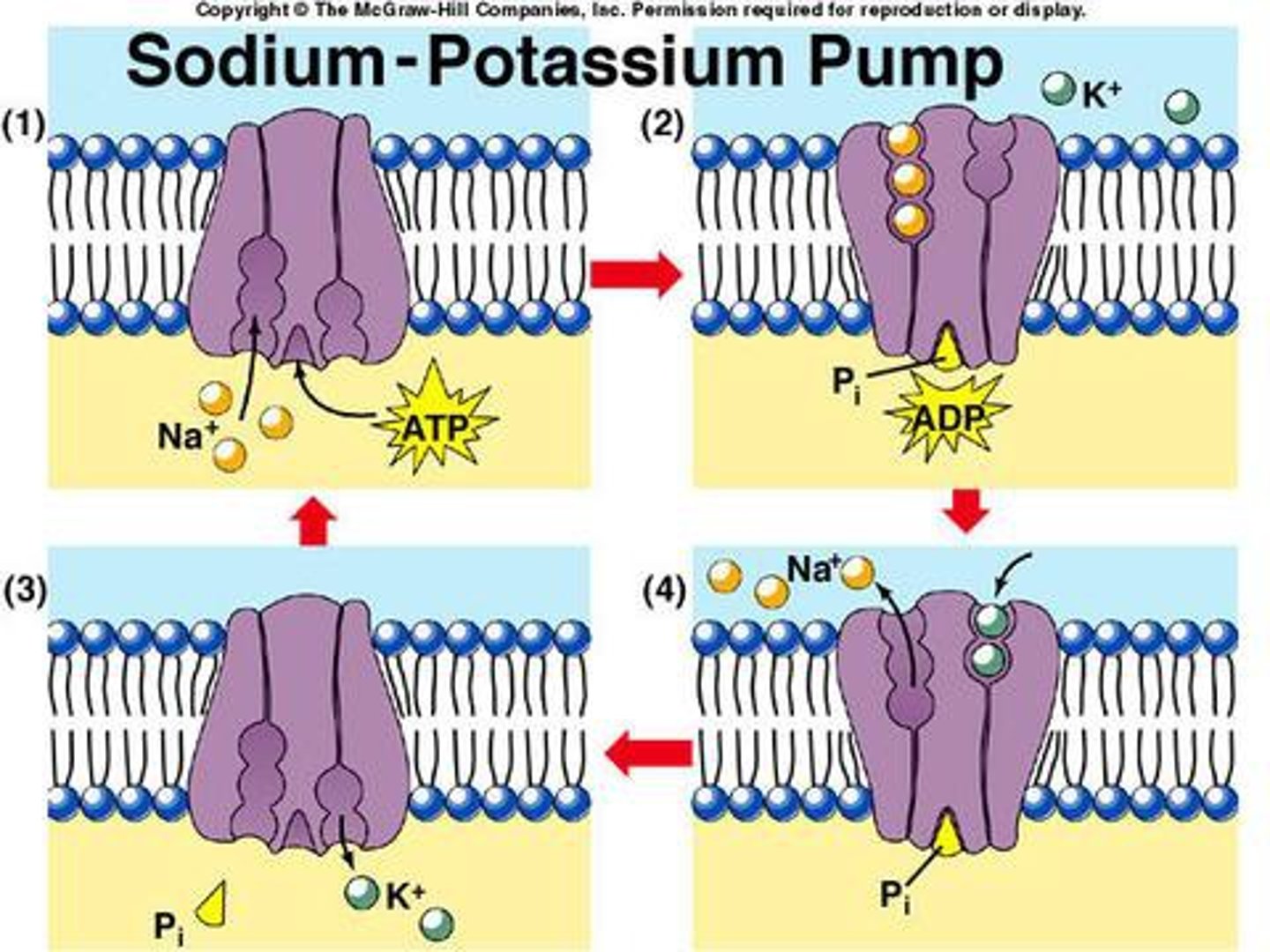
Secondary Active transport
driven by ion concentration gradient (Na+) and requires a carrier
>symport and antiport
endocytosis
transport of materials into the cell
exocytosis
transport of materials out of a cell
membrane potential
separation of opposite charges or the difference in relative number of cations and anions across the plasma membrane (mV)
what is membrane potential due to
differences in concentration and permeability of key ions
Nernst equation
equilibrium potential for specific ion.
> The equilibrium potential is the membrane potential that would need to exist for a single ion,such as Na+, to balance across the membrane so that no net movement of that ion would occur.
Goldman-Hodgkin-Katz equation
calculate resting membrane potential resulting from the relative distributions and membrane permeabilities of ALL permeable ions (Na, K and cl)
what are excitable tissues
nerve and muscle
at RMP is there a separation of charge?
yes, this results in polarization of the membrane
chemically gated channels
change shae in response to specific chemicals binding to surface receptors
voltage gated ion channels
open or close in response to changes in membrane potential
mechanically gated channels
respond to stretching or other deformations in the channel
thermally gated channels
respond to local changes in temperature
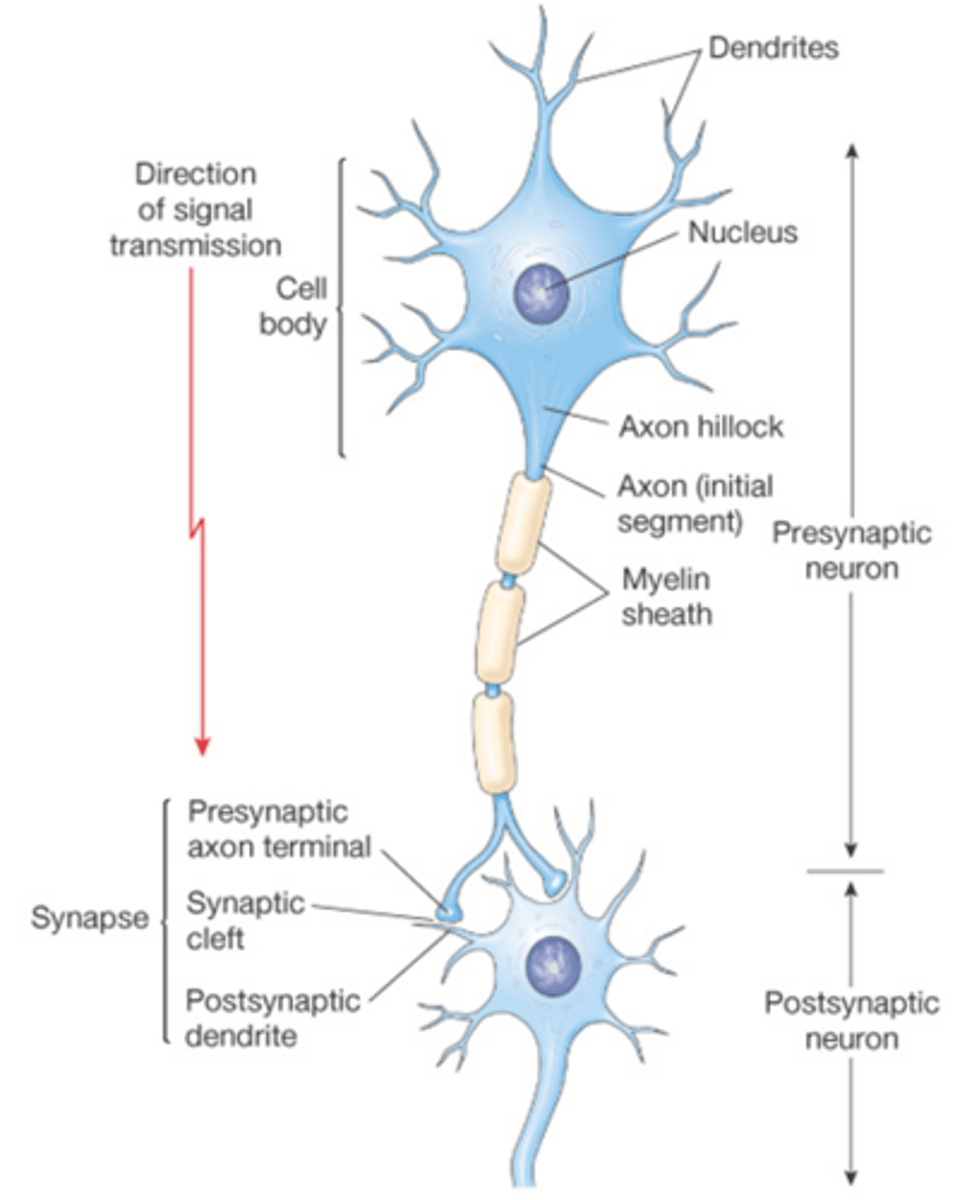
synapses
junctions between presynaptic and postsynaptic neurons.
> can be electrical where 2 neurons are connected by gap junctions which allow ions to flow directly between cells however most are chemical
chemical synapses
neurotransmitters are released from the presynaptic cell into synaptic cleft and diffuse across the synapse to the postsynaptic cell where NTs may bind to promote EPSP or IPSP
explain the process for events at a synapse
1) AP travels down axon terminals and opens VG Ca2+ channcels
2) Calcium enters presynaptic knob which induces binding of the synaptic vesicle to the presynaptic membrane
3) synaptic vessicles fuse with the membrane and nts are released unto cleft
4) nts diffuse across cleft and bind to chemically gated channels or receptors on post synaptic membrane
5) either EPSP or IPSP produced