Pancreas Pathology (Quiz 3)
1/55
Earn XP
Description and Tags
UT 402 - Abdomen 2
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
Endocrine
secreting into blood
Exocrine
secreting into duct
Acini cells
cells of pancreas that perform exocrine functions by secreting digestive enzymes such as amylase and lipase
Amylase
enzyme that aids in digestion of complex carbs
Lipase
enzyme that aids in digestion of fats
Islets of Langerhans
Cells of the pancreas that perform endocrine function
Made up of alpha/beta cells
Alpha calls
secrete glucagon
Glucagon
hormone that increases activity of phosphorylase and increases blood sugar
Beta cells
secrete insulin
Insulin
hormone that increases uptake of glucose and amino acids (decreases blood sugar)
Indications for pancreatic US
Assess for pancreatic malignancy, pancreatitis and its complications
Abnormal blood tests
Elevated liver function tests (AST, ALT, bilirubin)
Elevated pancreatic enzymes (amylase and lipase)
Painless jaundice
Suspected acute or chronic pancreatitis
Epigastric pain
Hx of Gallstones
High amylase
increase indicative of acute pancreatitis
Low amylase
indicative of permanent damage to pancreas, hepatitis, cirrhosis
High lipase
indicative of acute pancreatitis, obstruction of pancreatic duct, and pancreatic carcinoma
High fat excretion (levels of undigested fat in stool)
indicative of pancreatitis
Bilirubin and liver function tests (LFT)
May have abnormal values
Normal Pancreas
Non-encapsulated
Retroperitoneal
Located between duodenal loop and splenic hilum
Size:
Length: 12.5-15 cm
Head: 2-3.5 cm
Body: 2-3 cm
Tail: 1-2 cm
Pancreatic Duct/Duct of Wirsung: < 2 mm
US not used to evaluate pancreas for diabetic pts due to nonspecific findings, but there may be …
a slight decrease in pancreas size
Type 1 (AKA insulin-dependent diabetes)
Autoimmune disease in which insulin-producing cells are destroyed by body’s immune system
Genetic component, diagnosed early on
No cure
Complications: cardiovascular disease, skin issues, gum disease, pregnancy problems, etc.
Type 2 (AKA insulin-resistant diabetes)
Metabolic disorder in which body still produces insulin but unable to use effectively
Diagnosed later in life
Manageable by diet, exercise, medication
Cystic Fibrosis
Inherited disorder that damages lungs, digestive system, other organs
Affects cells that produce mucus, sweat, and digestive juices → decreased enzyme production
Mucus becomes thick and sticky
Can lead to acute/chronic pancreatitis
Major cause of pancreatic exocrine failure in children
Sonographic appearance of Cystic Fibrosis
Hyperechoic and small pancreas
Hypoechoic areas may be present and represent pancreatic fibrosis
Calcifications
Small cysts
Gallstones and liver disease common
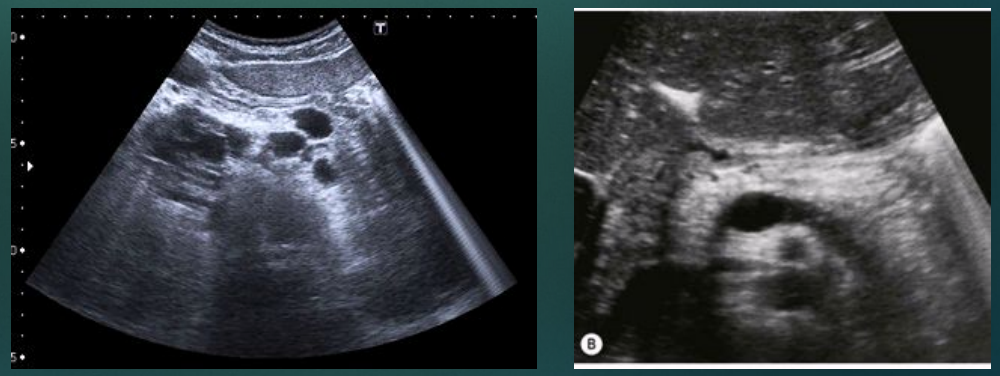
Inflammatory Disease
Pancreas becomes damaged and malfunctions → increased secretion and ducts blocked → pancreatic enzymes digest the pancreas’ own tissues
Acute pancreatitis
Causes: chronic alcoholism, toxicity from medications, blunt trauma, viral infections, mechanical obstruction of bile ducts (gallstones)
Lab results: elevated amylase and lipase
Symptoms: sudden onset of epigastric pain, fever, malaise, nausea, and vomiting
Acute pancreatitis treatments
Aimed at treating symptoms and providing rest for pancreas
Surgical removal of gallstones
Alcoholic pancreatitis responds well to quitting alcohol
Surgical removal of pancreas only for life-threatening complication
Acute pancreatitis sonographic appearance
Many cases, pancreas can appear normal
Diffuse/focal enlargement of pancreas
Mainly seen on pancreatic head
More reliable indicator of disease
Hypoechoic compared to chronic pancreatitis
Pancreatic edema or peripancreatic fluid
Dilation of pancreatic duct, mainly due to blockage (double barrel sign)
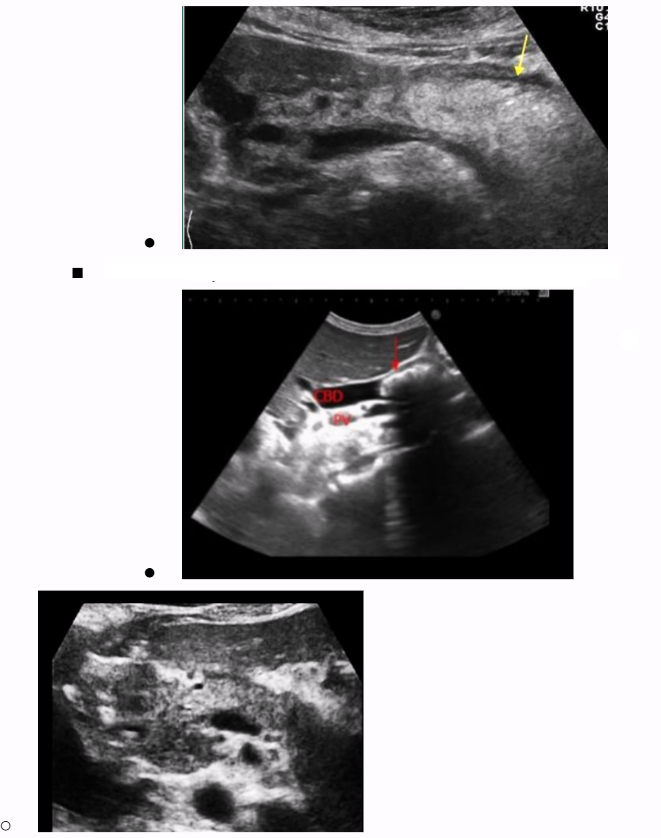
Chronic pancreatitis
Chronic pancreatitis is acute pancreatitis that lasts > 6 months
Due to recurring attacks of acute pancreatitis
Destruction of pancreatic tissue → atrophy, fibrosis, scarring, calcifications
Common causes: alcohol-related liver disease, hepatitis B and C, NASH, biliary disease, and autoimmune hepatitis
Symptoms: persistent epigastric pain, nausea, vomiting, jaundice,
Complications: dilated biliary system, pseudocyst formation, venous thrombosis
Sonographic appearance of chronic pancreatitis
Calcifications
Can appear normal, usually more hyperechoic
Pseudocysts (25-40% of patients)
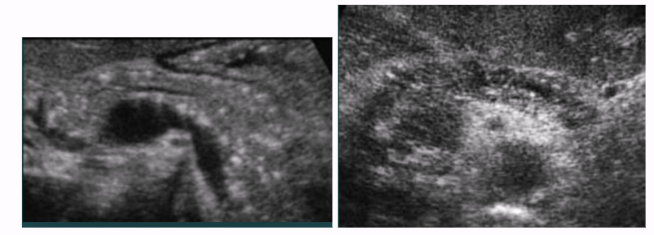
Pancreatic pseudocysts
Collection of pancreatic enzymes and bodily fluid in cyst, without epithelial lining
Formed from pancreas damage → pancreatic fluid leaks → cyst
Most common cystic lesions of the pancreas (75-85% of cases)
Appearance: well-circumscribed, outside pancreas
Most common symptom: abdominal pain and bloating
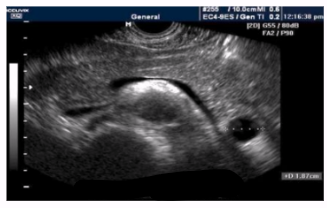
Pancreatic pseudocyst rupture
Requires immediate surgical intervention if causes signs of peritonitis
Mortality rate very high without surgical intervention
Fatal complications of chronic pancreatitis
Pancreatic pseudocyst rupture
Hemorrhagic pancreatitis
Phlegmonous pancreatitis
Hemorrhagic pancreatitis
Rapid progression of acute pancreatitis
Destruction of parenchyma by pancreatic enzymes
Causes: alcoholic binge or large meal
Characteristic: bleeding necrosis and paralysis of digestive tract
Focal fat necrosis or extravasated blood may be visualized
Grey-Turner sign
High mortality rate
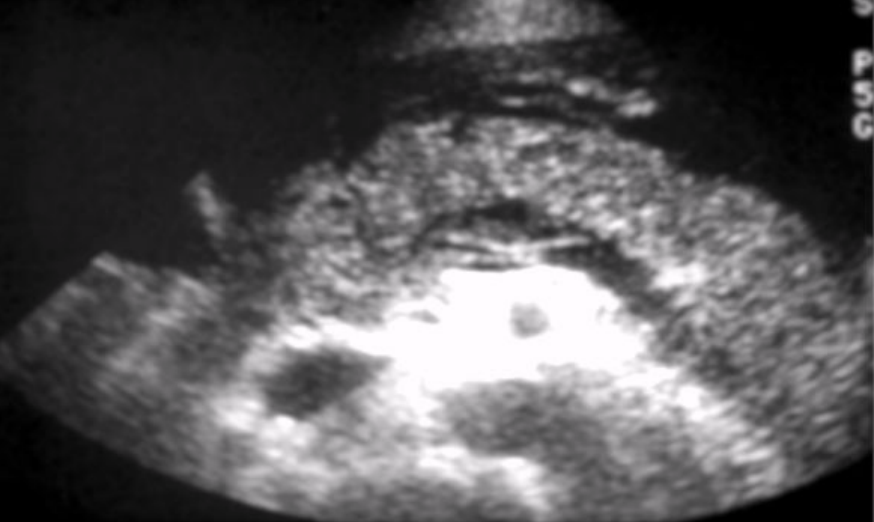
Grey-Turner sign
blood vessel necrosis causes discoloration of the flanks
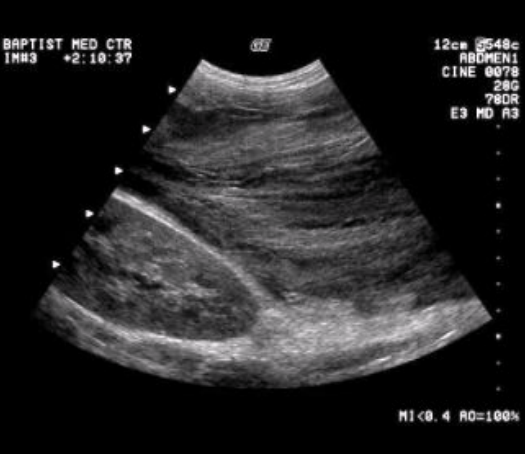
Phlegmonous pancreatitis
Inflammation spreads along fascial pathways → localized area of diffuse inflammatory edema of soft tissue → can lead to necrosis or suppuration
Involves lesser sac, LT anterior pararenal space, or transverse colon
Sonographic appearance: hypoechoic ill-defined mass
Neoplastic Disease
Can be solid or cystic
Malignant tumors of pancreas = 4th leading cause of cancer-related deaths in US
Early detection uncommon because symptoms start at later stages
More common in men older than 30
Risk factors: smoking, high-fat diet, chronic pancreatitis, diabetes, cirrhosis of the liver
Adenocarcinoma
type of cancer that originates in glandular cells, which are cells that produce mucus or other bodily fluids
Pancreatic adenocarcinoma
Exocrine origin
Largest group of pancreatic cancers
Accounts for 90% of all pancreatic malignancies
Most commonly found in head (60-70%)
One of most lethal of all malignancies
Most people are diagnosed when the cancer is already advanced
Can arise in ampulla of Vater → difficult to visualize
Sonographic appearance of pancreatic adenocarcinoma
Nonspecific
Usually ill-defined, poorly marginated, hypoechoic
Can be well-defined, solid, and ovoid
Increased vascularity
Diffused through parenchyma so appears as matted mass of tumor
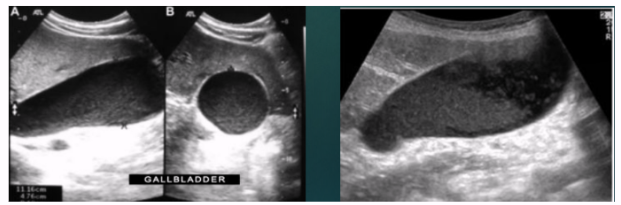
Obstruction of biliary tract → dilatation of ducts and GB
Courvoisier GB
Enlarged lymph nodes in porta hepatitis and near the aorta indicate nodal metastasis
Inflammation of pancreas is a common result of carcinomatosis
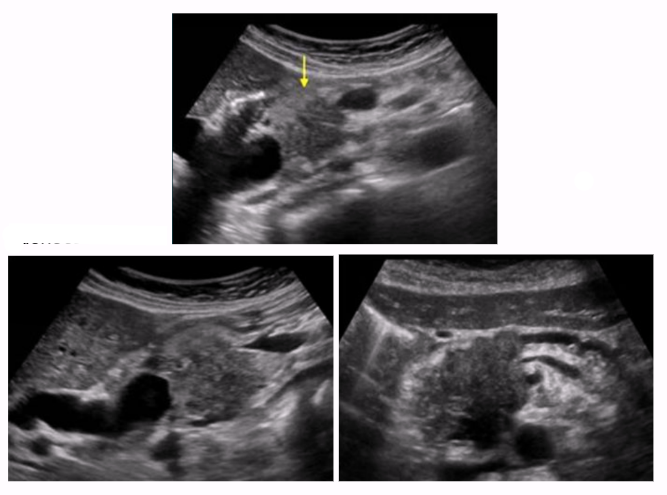
Carcinomatosis
condition where cancer cells spread widely throughout the body, often to the peritoneum
Courvoisier GB
markedly distended and palpable GB
Other Exocrine Lesions
Benign solid adenoma
More common in women
Cystadenoma
More common in women
Cystadenocarcinoma
Squamous cell carcinoma
Adenoacanthoma
Adenoacanthoma
Uncommon variant of exocrine pancreatic neoplasm
Endoscopic Sonography
Best imaging method for detecting pancreatic masses < 2 cm
Aids in biopsy
Most sensitive to detecting venous and gastric invasion
Islet Cell Tumors
Aka pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors (PNET)
~7% of pancreatic tumors
Slower growing than exocrine tumors
3 types
Insulinomas
Gastrinomas
Glucagonomas
Insulinomas
70% of cases
Most common functioning islet cell tumor
Benign, small, well-encapsulated, good vascularity
Seen in pts with hyperinsulinism or hypoglycemia
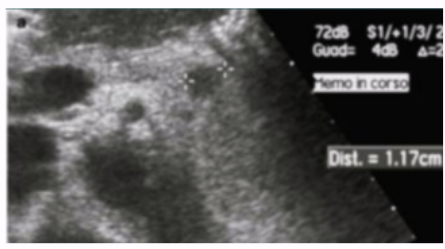
Gastrinomas
20% of cases
Most are malignant
Multiple
Extrahepatic
Difficult to locate
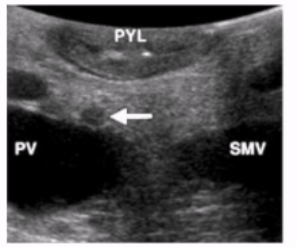
Glucagonomas
10% of cases
Solid and very small
Size makes difficult to detect on US
Can be single or multiple
More common in pancreatic body/tail
Cystic Neoplastic Lesions
~10% of all pancreatic neoplasms
Usually benign (1% of malignant)
Fluid-filled structure around or within pancreas → most likely pseudocyst
Differentiate with lab tests
2 groups
Benign serous cystadenomas
Malignant mucinous cystic adenomas
Benign serous cystadenomas
Tumor with multiple cysts < 2cm
Possible calcifications
Occurs mainly in head
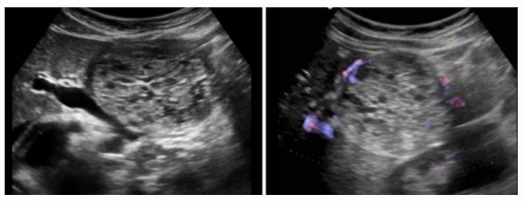
Malignant mucinous cystic adenomas
AKA cystadenocarcinoma
Larger cystic areas (> 2 cm)
Peripheral calcifications
Large, unilocular, encapsulated masses
Occurs mainly in tail
Has good prognosis for pancreatic malignancy
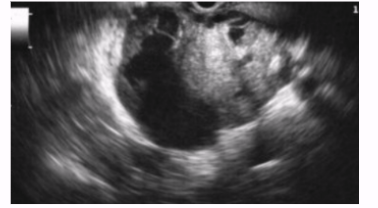
Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Tumor (IPMT)
Mucinous cystic neoplasm
Originates from main pancreatic duct or its branches
Slow-growing, affects men and women, tends to occur in 60s and 70s
Can be benign or malignant
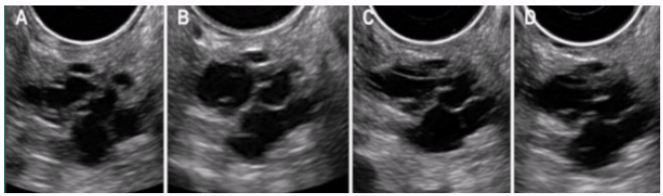
Nonneoplastic Cystic Lesions
Polycystic disease (ADPKD)
Von Hippel-Lindau Disease
Polycystic disease (ADPKD)
Characterized by cysts in kidney, liver, and (in 10% of pts) pancreas
Pts typically have FMHx of PCD or are being evaluated for HTN, renal insufficiency, or pyelonephritis
Slowly growing and multiplying cysts destroy normal pancreatic tissue
Pts will succumb to renal failure before pancreas is physiologically affected
Von Hippel-Lindau Disease
Genetic disorder that involves central nervous system
Includes adenomas and islet cell tumors
65-75% of pts have some form of pancreatic lesion
Peripheral calcifications possible
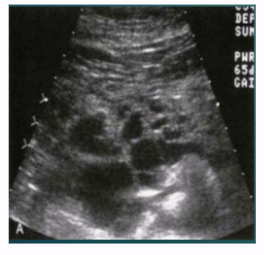
Pancreas Transplant
Surgical intervention to treat insulin-dependent diabetes
Gives pt healthy pancreas → pt can now produce their own insulin and don’t need to inject it
Transplanted pancreas seen in pelvis
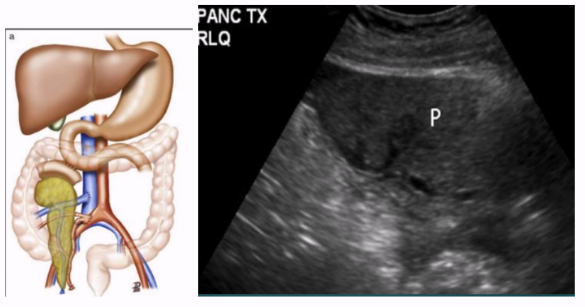
Annular Pancreas
Head of pancreas wraps around duodenum → constricts it and blocks/impairs flow of food to intestines
Usual treatment: surgical bypass of obstructing segment of duodenum