Models of Covalent Bonding: Lewis, VSEPR, Hybridization, and Molecular Orbital Theory
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
What do Lewis structures represent in molecular shape?
They are planar (flat) depictions of molecules.
How do real molecules differ from Lewis structures?
Molecules have a 3D shape.
What does VSEPR stand for and what does it predict?
Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion; it predicts molecular shape based on electron pair repulsion.
What is the bond angle in a tetrahedral molecular geometry?
109.5°.
What is the magnetic property of O2 and how does VSEPR predict it?
O2 is paramagnetic; VSEPR incorrectly predicts no unpaired electrons.
What is the basis of Valence Bond Theory?
A covalent bond is formed by the overlap of atomic orbitals.
What is the significance of shared electrons in Valence Bond Theory?
Shared electrons are located primarily between the nuclei of bonded atoms and have opposite spins.
How does the degree of orbital overlap affect a bond?
It affects bond strength and stability.
What is the electronic configuration of carbon and how many valence electrons does it have?
Carbon has an electronic configuration of 1s² 2s² 2p² and has 4 valence electrons.
What is hybridization in the context of covalent bonding?
Hybridization is the mixing of atomic orbitals to form new hybrid orbitals for bonding.
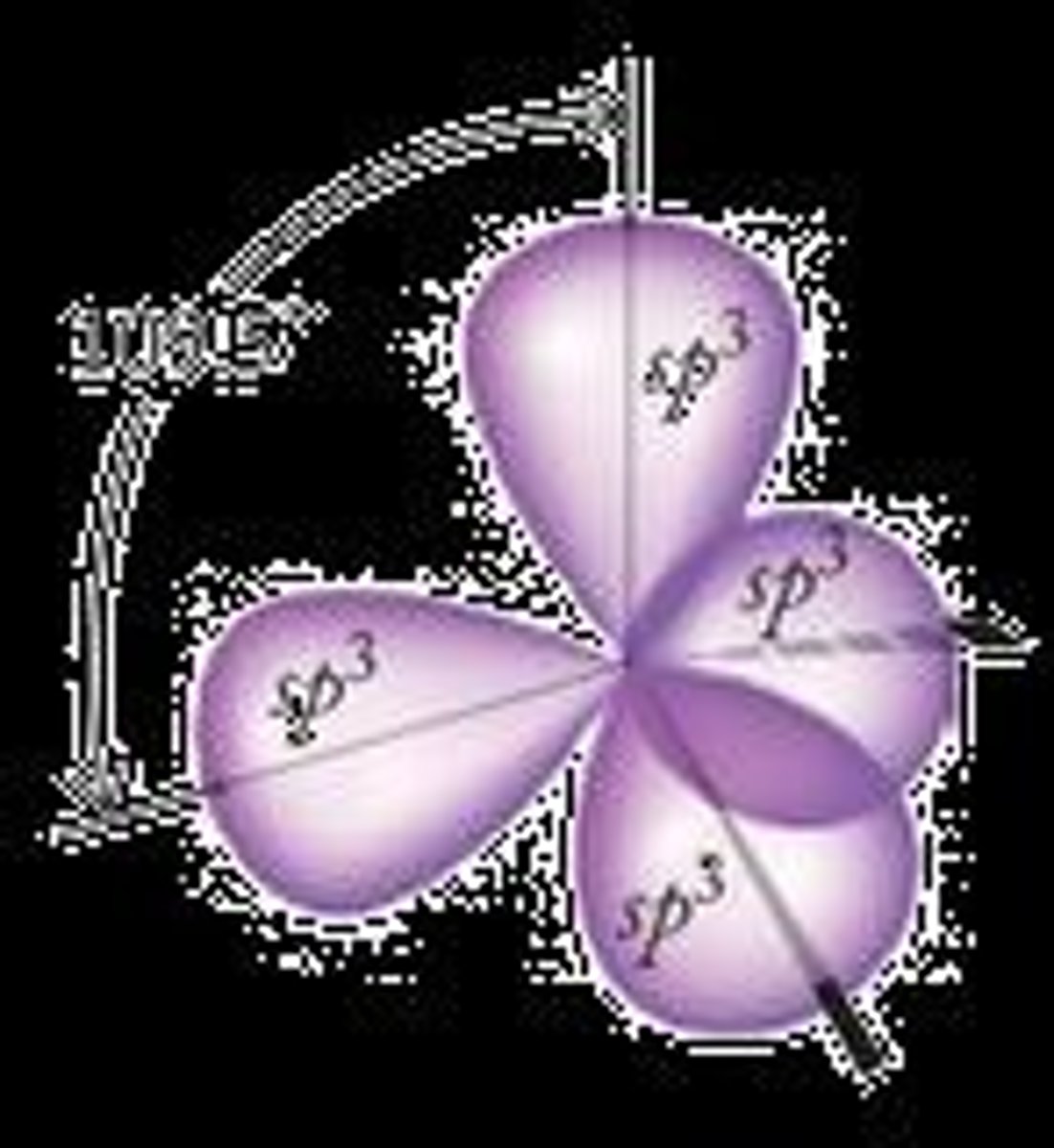
How many hybrid orbitals are formed from one s and three p orbitals?
Four sp³ hybrid orbitals are formed.
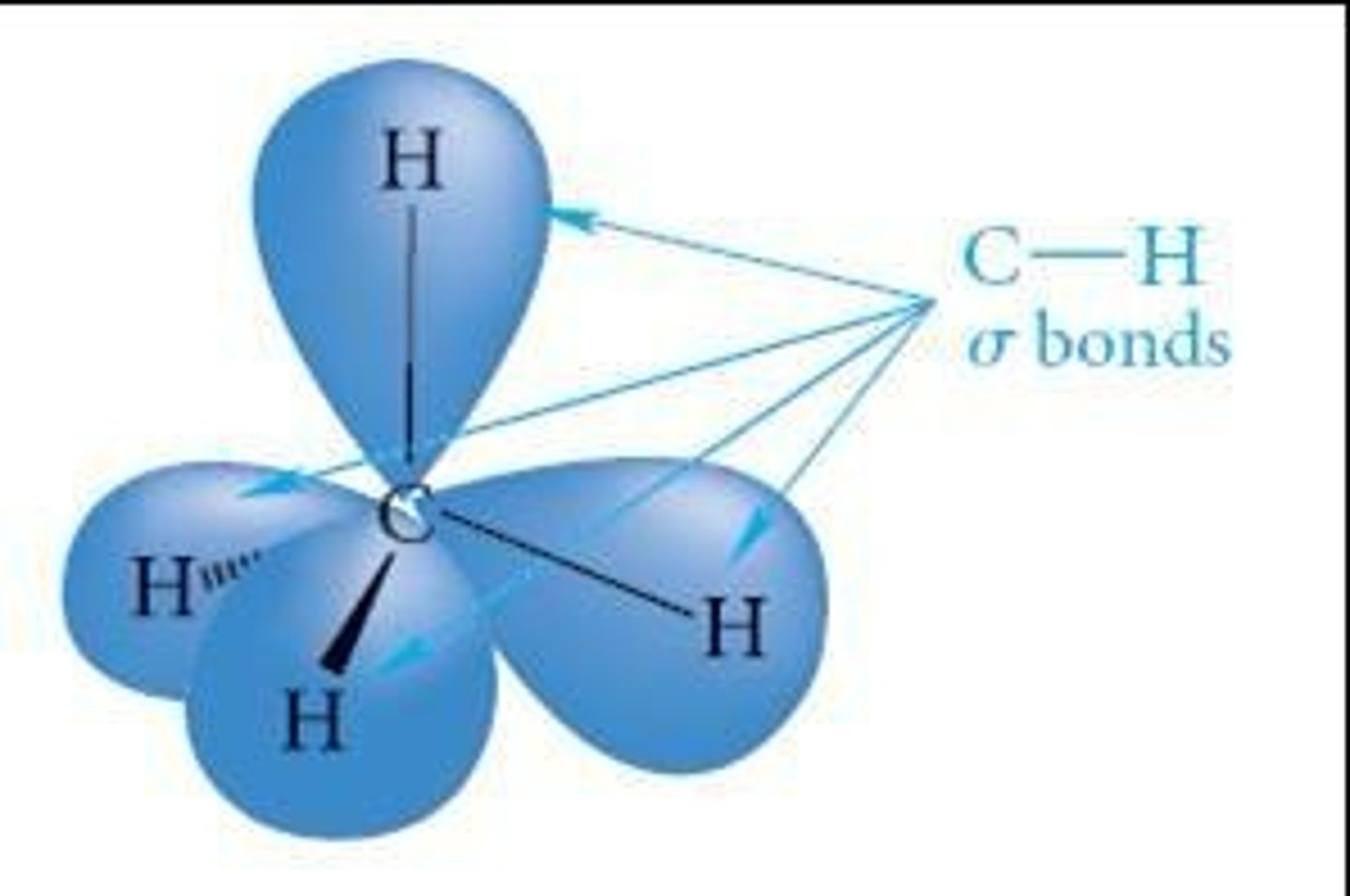
What is the geometry of CH4 and its bond characteristics?
CH4 has a symmetrical tetrahedral geometry with four equivalent bonds.
What happens to atomic orbitals during hybridization?
Atomic orbitals required for bonding mix to form hybrid orbitals that are equivalent in shape and energy.
What is the molecular orbital theory's approach to bonding?
It views orbitals as probabilities and bonding as a combination of wave functions.
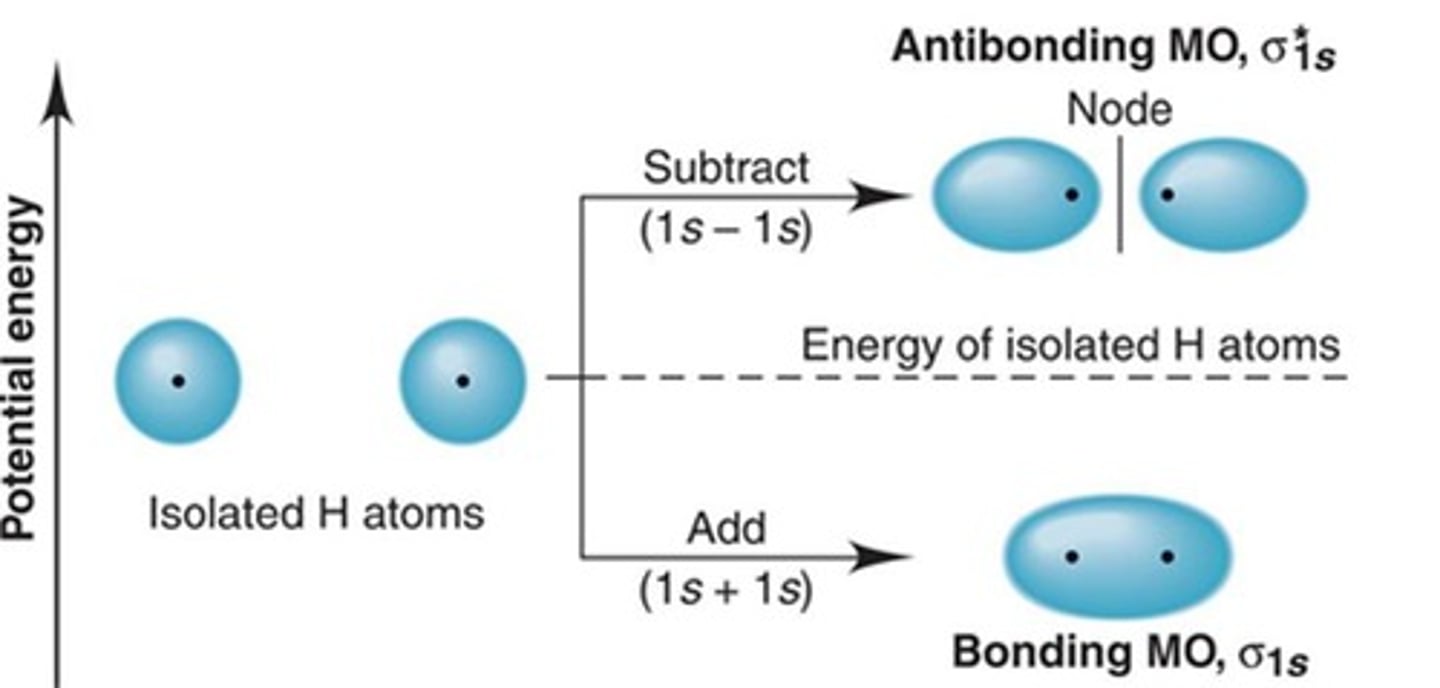
How do molecular orbitals form?
Atoms bond by moving together, leading to interference of wave functions from overlapping orbitals.
What is the bond order for CH4?
The bond order for each C−H bond in CH4 is 1.
How does molecular orbital theory differ from Valence Bond theory?
MO theory considers bonding and antibonding interactions and does not localize bonds between two atoms.
What does the VB model focus on in covalent bonding?
The VB model focuses on the behavior of individual bonds and explains geometries.
What does MO theory explain that VB theory does not?
MO theory explains spectral properties, molecular energies, and delocalization of electrons.
Why is the VB model generally more useful in organic chemistry?
It is conceptually simpler and focuses on making and breaking of individual bonds.
What is the relationship between C−H bonds and molecular orbitals in CH4?
Electrons are distributed over the entire molecule, and MO theory does not distinguish individual bonds.
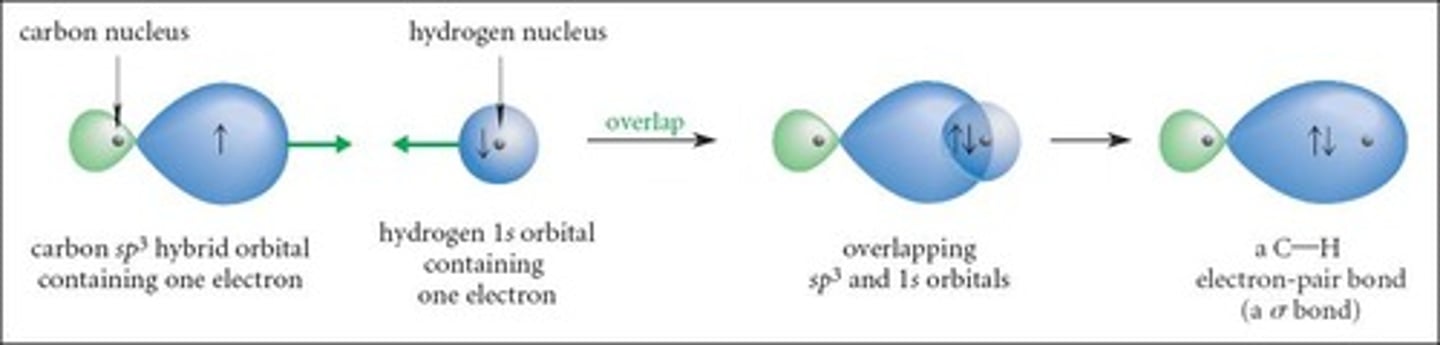
What is the significance of hybrid orbitals in the bonding of methane?
Each sp³ orbital can combine with a 1s orbital from a hydrogen atom to form equivalent bonds.
What is the role of the National Science Foundation in the context of these models?
The work on these models was supported by the National Science Foundation under specific grant numbers.