2️⃣ LE Orthotics
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
What are the goals of lower limb orthoses? Ideal properties?
Functional ambulation:
Stabilize weak or paralyzed segments
Support damaged or diseased joints
Unload distal segments
Control abnormal or spastic movement
Limit motion across joints

What are the functions of a foot orthosis (FO)?
Evenly distribute the weight-bearing stresses over the entire plantar surface of the foot.
Reduce the stress and strain on the ankle, knee, hip and spine.
Alleviate pain from sensitive and painful areas of the sole.
Support the various foot arches.
Correct congenital foot deformities.
Equalize foot length discrepancy.
Indications for foot orthosis?
Plantar fasciitis
Heel spurs
Degenerative joint disease
Pes planus (flat feet)
Posterior tibial tendonitis
Metatarsalgia (inflammation of the ball of the foot)

Name this orthosis. Uses?
Rocker sole
Assists in the heel-off and toe-off phases of the walking cycle.
Effective in relieving various causes of metatarsalgia:
Hallux rigidus
Hammer toes
Claw toes
Arthritis
Metatarsal fractures
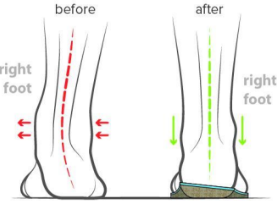
Name this orthosis. Uses?
Medial heel out-flare sole
It increases the size of the base of support of the shoe and helps to support the longitudinal arch.
Used to treat a severe flat foot caused by diabetic Charcot's foot, rheumatoid foot and chronic rupture of the posterior tibial tendon.
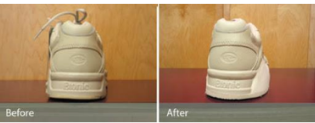

Name this orthosis. Uses?
Lateral heel out-flare sole
A wedge is inserted into the lateral aspect of the sole and heel to pronate the foot or to accommodate the Varus foot deformity.
Used to treat a clubfoot or a varus foot.
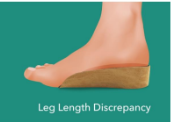
What orthosis can be used to target leg length discrepancies?
If the discrepancy is 1 inch or less, a lift is placed under the heel of the shorter leg to equalize the leg length.
If the discrepancy is much greater, lifts should be added to both the sole and the heel.

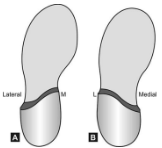
Name this orthosis. What is the difference between A and B?
Thomas Heel (A) & Reverse Thomas Heel (B)
Thomas Heel:
Extension of the standard heel on the inside to add rearfoot or midfoot support medially.
Provides support for excessive pronated foot.
The function of ankle-foot orthoses? Considerations for use?
Function:
Helps to lock the ankle when there is weak musculature, spasticity or absent proprioception.
Controls the ankle complex and influences the knee joint directly.
Considerations:
AFO should not be tight.
Spastic muscles should be stretched before placement.
Indications for ankle-foot orthoses?
Foot drop
CVA/stroke
Arthritis
Posterior tibial tendon dysfunction
Ankle instability
Paralysis
Ankle fusion
Multiple sclerosis
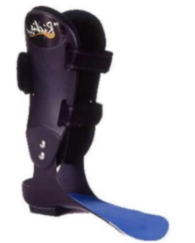
Name this ankle-foot orthosis.
Foot plate and split stirrups

Name this ankle-foot orthosis.
Solid stirrups

Name this orthosis. Uses?
Low profile - prefabricated?
Used for the rehabilitation of ankle sprains and minor fractures.
Offers less support and stability.
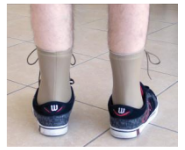

Name this orthosis?
Ground reaction AFO
Offers great control of the foot and ankle.
Helpful for knee extension.
Made up of polyethylene or polypropylene plastic.
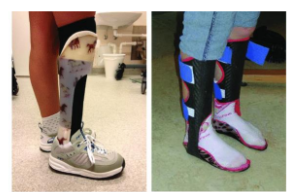
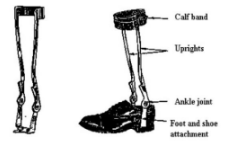
Name this orthosis. Indications? Disadvantages?
Conventional AFO
Indications:
Conditions with fluctuating edema or fluid retention.
Patient preference.
Heat sensitivity (e.g. some MS patients cannot have their leg casted or scanned).
Disadvantages:
Higher pressures on the skin due to the forces being applied to a relatively small surface area.
Less control is available due to reduced surface area.
Joints and uprights tend to be heavy.
Cosmetically unappealing.

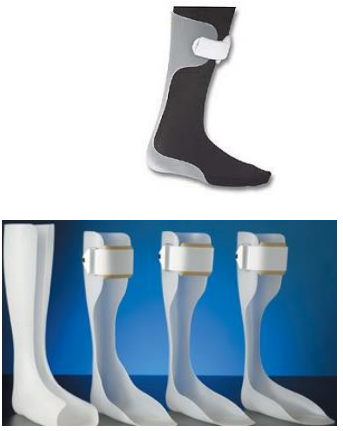
Name this orthosis. Indications? Contraindications?
Total surface bearing orthosis
Indications:
Foot drop
Contraindications:
When significant changes in volume are anticipated (fluctuating edema).
Advantages and disadvantages of total surface-bearing orthosis?
Advantages | Disadvantages |
Increases stability | Does not accommodate changes in volume (as well as conventional) |
Reduces pressure on the skin | |
Comfort | |
Lighter | |
Higher durability | |
Easy to clean/hygiencic | |
Can easily be changed to different shoes |
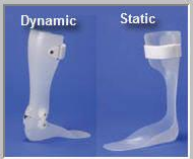
What are the advantages and disadvantages of a dynamic type AFO?
Advantages:
Controls medial/lateral stability at the ankle.
Controls the endpoints of the dorsiflexion/plantarflexion range.
Excellent orthosis during the post-trauma rehab period due to being multi-adjustable.
Disadvantage:
Difficult to apply with severe spastic varus or valgus deformity at the subtalar joint.
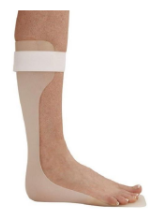
Name this orthosis. Indication, advantages and disadvantages?
Solid AFO/posterior spring leaf
Indication:
Individuals lacking medial/lateral control or active dorsiflexion and plantarflexion or low stability or have very limited or no range of motion.
Advantages:
Decreases tone by maintaining a stretch on calf muscles.
Assists push-off by not collapsing into dorsiflexion.
Disadvantages:
Blocks range of motion.
Knee flexion/foot flat moment produced at heel strike.
Fair quadriceps strength is required if set in dorsiflexion.
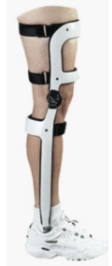
What is the purpose of using a knee-ankle-foot orthosis (KAFO)?
A knee-ankle-foot orthosis consists of a shoe, a pair of upright metals or a plastic calf shell that connects the foot/ankle components to the mechanical knee joint.
It provides knee control in one or more planes.
Helps to lock the knee if there are weak hip and knee extensors, impaired proprioception or the resulting extension thrust during a single-limb stance.
Indications for a KAFO?
Instability of the knee and ankle
CVA or stroke
Paralysis knee replacement
Weak quadriceps
Genu recurvatum (hyperextended knee)
Post-polio
Cerebral palsy
Suggested wearing schedule for a KAFO?
Days | Time |
1-3 | 1/2-1 hour |
3-5 | 1-2 hours |
5-7 | 2-4 hours |
7+ | As required |


Name this orthosis. Advantages and disadvantages?
Total surface bearing/thermoplastic orthosis
Advantages:
Increases control
Reduces pressure on the skin
More comfort
Considerably lighter
High durability
Easy to clean/hygienic
Can be used easily with different shoes
Disadvantages:
Does not accommodate changes in volume
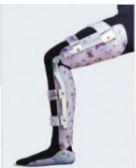
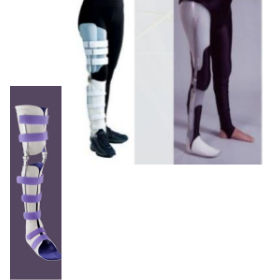
Indications for a total surface bearing/thermoplastic orthosis?
Poliomyelitis
Spinal cord injury
Peripheral nerve injury
Severe knee osteoarthritis
Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
Trauma

What is the free walk stance control knee/ankle system?
The automatic lock is initiated by knee extension (provides stability and prevents unwanted knee flexion in the weight-bearing stance).
It is only released to swing freely when a knee extension moment and dorsiflexion occur simultaneously in the terminal stance (allows for a seamless transition from the stance to the swing phase of walking).
The result is a more secure, efficient gait that also reduces the incidence of typical gait compensations.

Indications of free walk stance control knee/ankle system?
Isolated quad weakness
Polio/post-polio
Multiple Sclerosis
Trauma

Indication for the Craig-Scott KAFO? Advantages?
Most commonly prescribed bilaterally for patients with complete paraplegia.
Advantages:
Functional and comfortable gait by maximizing stability in stance.
It is lightweight and easy to put on and take off.
Use of hip-knee-ankle-foot orthosis (HKAFO)?
The addition of the hip joint and pelvic section provides control to selected hip motions (front to back, side to side, and rotation).
One reason the hip section is added to a KAFO is to reduce or minimize the risk of the hip moving out of proper position or dislocating.
To stabilize the hip and lower spine in cases where the patient is weak or paralyzed.
Give an example of a HKAFO? Advantages?
Reciprocating gait orthosis (RGO)
Provides support and mobility to the hip, knee, ankle and foot.
Improves body alignment and posture.
Increases bone and muscle strength.
Enhances independence and self-esteem.
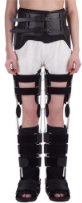
Indications for an RGO?
Used when there is a lack of stability and control of the pelvis and lower limbs:
Cerebral palsy
Myelomeningocele
Poliomyelitis