
Looks like no one added any tags here yet for you.
Electrochemistry
study of how electrons are transferred from one chemical species to another
Redox Reaction
a chemical reaction in which electrons are transferred between entities
oxidation and reduction must happen together, cant happen alone
always one is reduced, and the other is oxidized
Electron Transfer in Redox Reactions
transfer of valence electrons from the strongest reducing agent (SRA) to the strongest oxidizing agent (SOA)
SRA → SOA
Spontaneous Reaction
OA is higher than the RA on the redox table.
always have evidence of reaction:
change in energy (exo/endothermic?)
colour change
change in odour
formation of precipitate/gas
Non-Spontaneous Reaction
RA is higher than the OA on the redox table.
no evidences of a reaction
IMPORTANT RULE IN REDOX REACTIONS
total # of electron gain = total # of electron lost
must have both oxidation and reduction process occurring
Electrochemical reaction involves…
loss of electrons by one reactant
gain of electrons by another reactant
only one type of reaction.. not every reaction is a electrochemical reaction!
Electrochemical reactions may either be…
EXOTHERMIC:
reactants → products + electrons
ENDOTHERMIC:
reactants + electrons → products
Half-Reaction
a balanced chemical equation that represents either a loss or gain of electrons by a substance
created from net-ionic equations (separated into ions)
Reduction
gain of electrons
reactant electron = “gain”
ion → atom
Oxidation
loss of electrons
product electron = “loss”
atom → ion
OIL RIG
Oxidation Is Loss
Reduction Is Gain
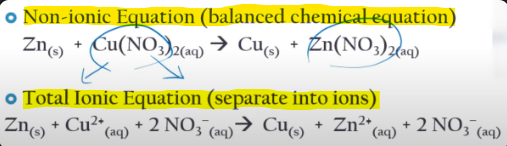
Non-Ionic Equations vs. Net-Ionic Equations (or Total Ionic Equations)
Atom
no charge
# of electrons = # of protons → charge is 0
Ion
atom that has a charge
cation = positive charge
anion = negative charge
Species
ion or an atom
Spectator Species
chemical species that are present in a reaction but do not participate by reacting
seen in the “net-ionic equations”
Half-Reaction Generalizations
OXIDATION:
atom → ion (needs to lose electrons to become charged)
losing electrons = electrons in product
REDUCTION:
ion → atom (needs to gain electrons to equal out)
gaining electrons = electrons in reactant
Reducing Agent
the species that is being oxidized
Oxidizing Agent
the species that is being reduced
Disproportionation
reaction in which a species is both oxidized and reduced
Oxidation State
an atom in an entity is defined as the apparent net electric change that it would have the more electronegative atom took all the shared electrons.
Oxidation Number
a positive or negative number corresponding to the oxidation state assigned to an atom, indicating its loss or gain of electrons
“ON”
abbreviation for Oxidation Number
IMPORTANT RULES FOR DETERMINING OXIDATION NUMBERS
do not count coefficients
does not matter if its balanced or not
no change in ON = no redox reaction
ON ↑ = ON ↓
since during redox reactions, both oxidation and reduction occurs…
Oxidation Number Rules
Elements ON = ZERO
Simple Ions ON = CHARGE
Oxygen ON = -2
peroxides = -1
Hydrogen ON = +1
metallic hydrides = -1
Compounds:
Group 1 = +1
Group 2 = +2
Group 3 / Aluminum = +3
Total of Neutral Compound ON = ZERO
Total of Ionic Compound ON = ZERO
Total of Complex/Polyatomic Ion = CHARGE
ON (Oxidation #) ↑
an increase in oxidation number is an oxidation
results in the reducing agent
ON (Oxidation #) ↓
a decrease in oxidation number is a reduction
results in the oxidation agent