last minute studying
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
Natural versus artificial
Natural = one reactant, spontaneous, any decay
Artificial = non spontaneous, two reactants,
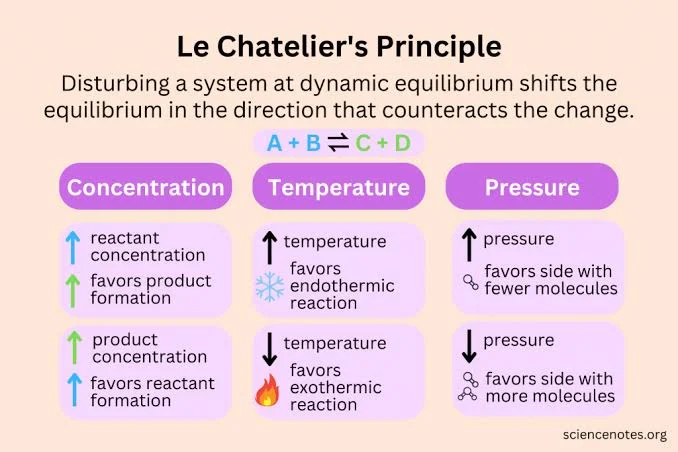
Le chatliers principle
Electrolytic
Anode positive
Fission versus fusion
Fission: split large into daughter with energy
Artificial needs neutron
Fusion: combining smaller into bigger with help, more nuclear waste, greater energy released then fission
Require high temp
Sublimation v deposition
Solid —> gas : sublimation.
pH = -log [H]
H+ = 10^-pH
pH + oH = 14
Arrhenius acid and base
Spesific, h and oh
Balanced in
Energy
Mass
Charge
PPP
Phase change on the plateaus where potential energy increases and kinetic energy stays the same
Hydrogen with metal v nonmetal
W/ metal = -1
W/o metal = +1
What is a mole
1 mol = liters gas
Mole = 6.022 × 10²3
1 mil = 22.4 L
Redox
Synthesis, decomposition, single, electron change
Order of strength for particles (strong to weak)
Gamma, beta, alpha
Stable nucleus v radioisotope
Stable nucleus: closest to 1:1, more then more than 82 are radioactive
Radioisotope: atoms with unstable nucleus
Transmutation
Reaction where element is transformed into another by gaining or losing protons
Half life
Cannot be changed, unique to all elements
Chain reaction
What a fission reaction triggers another by hitting it with a neutron
Fission in the world versus fusion in the world
Fission = nuclear bombs, nuclear energy
Fusion = sun
Mass defect
Difference between actual mass and calculated mass
Mass _> energy
OIL RIG AN OX