Synthesis pathways: benzene & phenol
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
benzene → nitrobenzene
conc HNO3
conc H2SO4
reflux 50°C
mechanism for formation of electrophile in nitration of benzene
HNO3 + H2SO4 ⇌ H2NO3+ + HSO4-
H2NO3+ → H2O + +NO2
nitrobenzene → phenylamine
Sn(s)
conc HCl
heat under reflux
nitrobenzene → phenylamine equation

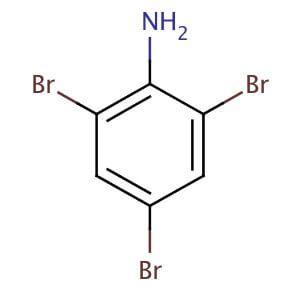
phenylamine → 2,4,6 tribromo aniline
Br2
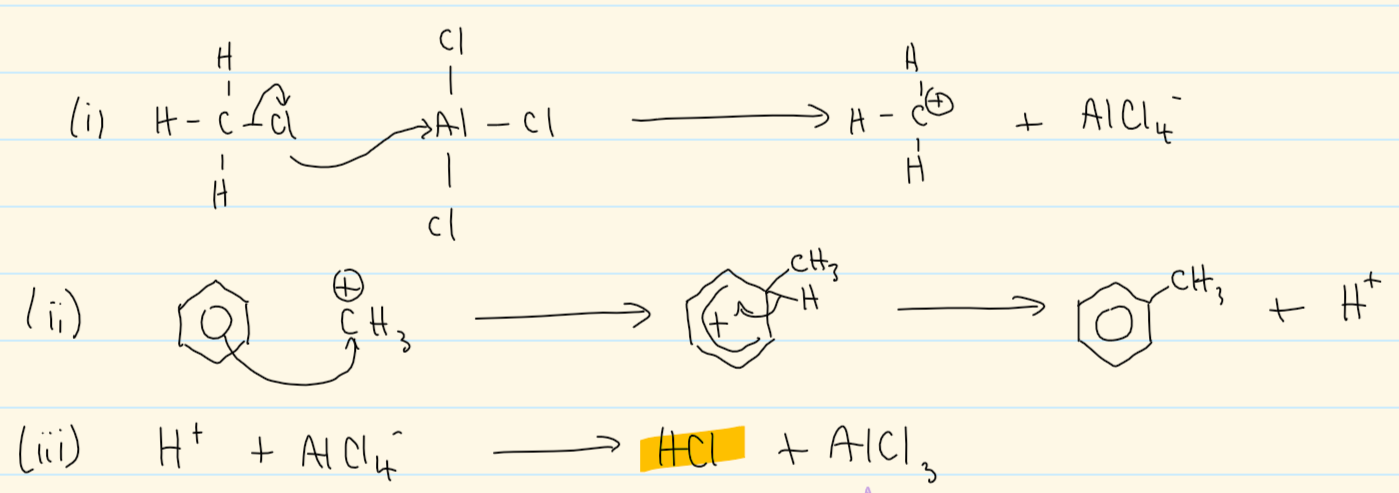
benzene → methylbenzene
CH3Cl
AlCl3
mechanism for benzene → methylbenzene
methylbenzene → 1-methyl-2-nitrobenzene/1-methyl-4-nitrobenzene
monosubstitution:
conc H2SO4
conc HNO3
room temp
methylbenzene → 1-methyl-2,4,6-nitrobenzene
conc H2SO4
conc HNO3
reflux
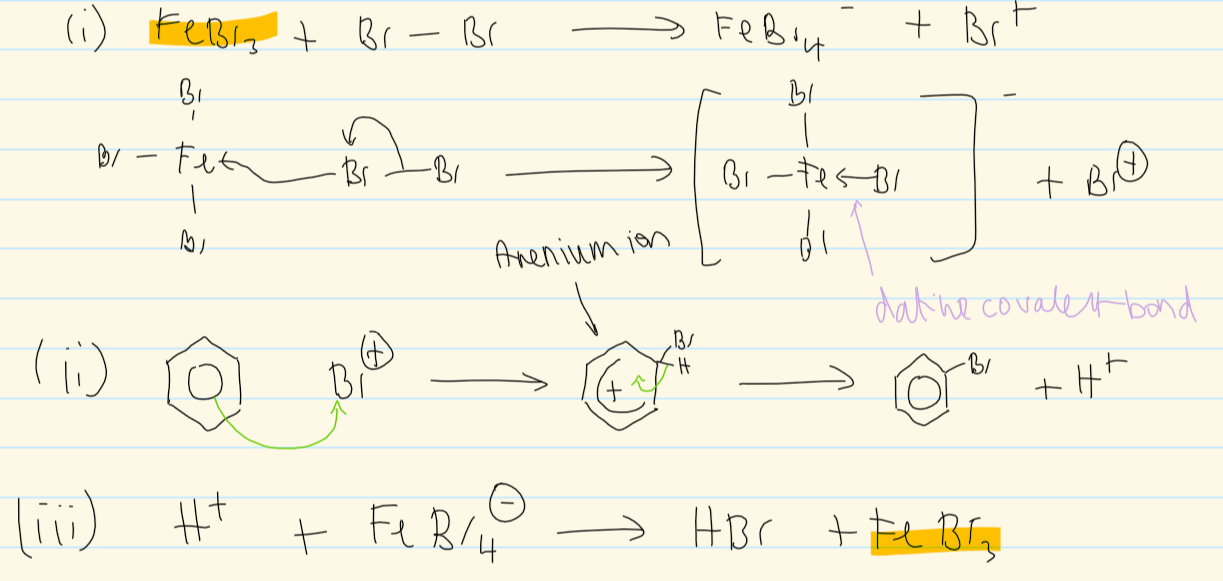
benzene → bromo-benzene
FeBr3 (halogen carrier e.g. Fe, AlCl3)
Br2
mechanism for benzene → bromobenzene
benzene → phenylethanone
AlCl3
ethanoyl chloride
phenylethanone → phenylethanol
NaBH4
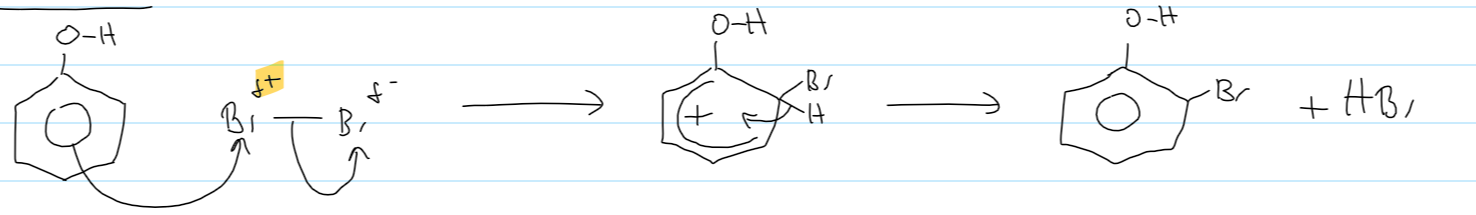
phenol → 2,4,6-tribromo phenol
Br2
(white ppt) + 3HBr
orange decolourises
mechanism for phenol + Br2 (1 substitution)
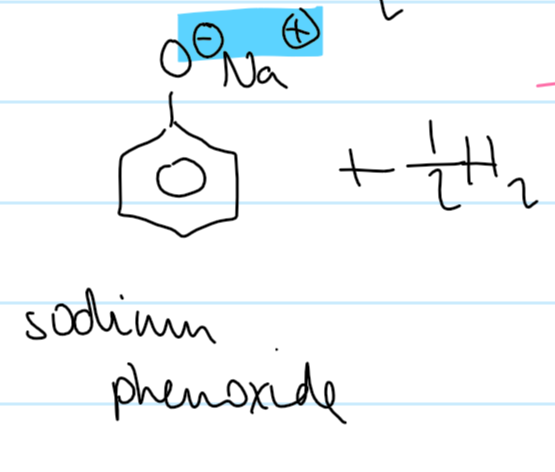
phenol → sodium phenoxide
+ Na/NaOH
phenol → 2-nitrophenol/4-nitrophenol
HNO3(aq)
room temp
(product is also + H2O)
phenol → 2,4,6-nitrophenol
3HNO3(aq)
conc H2SO4(aq)
room temp
(product is also + 3H2O)
acid strength vs reactivity w Na compounds table

what substituents are 3 directing
RCOR
-COOR
-SO3H
-CHO
-COOH
-CN
-NO2
-NR3+
(all are sightly e- withdrawing)
what substituents are 2,4 directing
-NH2 or -NHR
-OH
-OR
-R or -C6H5
-F, -Cl, -Br, -I
(all are slightly e- donating)