Test 4 ultrasound, mri, ct, nuc med
1/123
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
124 Terms
What is another name for ultrasound?
Sonography.
Positron emission tomography is a form of imaging in which the
____, _______, and ________
rather than the atomic structure, are displayed in the image.
Physiology, Metabolism and Biochemistry
What is the primary function of ultrasound?
To delineate surface contours and identify internal structures using sound waves.
What is the role of the transducer in ultrasound?
To generate a mechanical disturbance (pressure wave) that moves through tissue and reflects ultrasound energy to create an image.
What effect does the piezoelectric crystal have in ultrasound?
It creates ultrasound waves when a momentary electrical shock is applied.
What is B-Mode acquisition in ultrasound?
Brightness Modulation, the most common form of ultrasound imaging that displays a 2D map based on the brightness of echoes.
What is M-Mode acquisition used for?
To display a one-dimensional image for analyzing moving body parts, commonly in cardiac and fetal cardiac imaging.
What are some anatomical structures that can be identified using ultrasound?
Prostate, breast, kidney, liver, urinary bladder, thyroid.
Which anatomical structures are not typically identified using ultrasound?
The lung or chest wall.
What is the significance of distinguishing between solid and cystic lesions in ultrasound?
It is particularly useful in breast imaging.
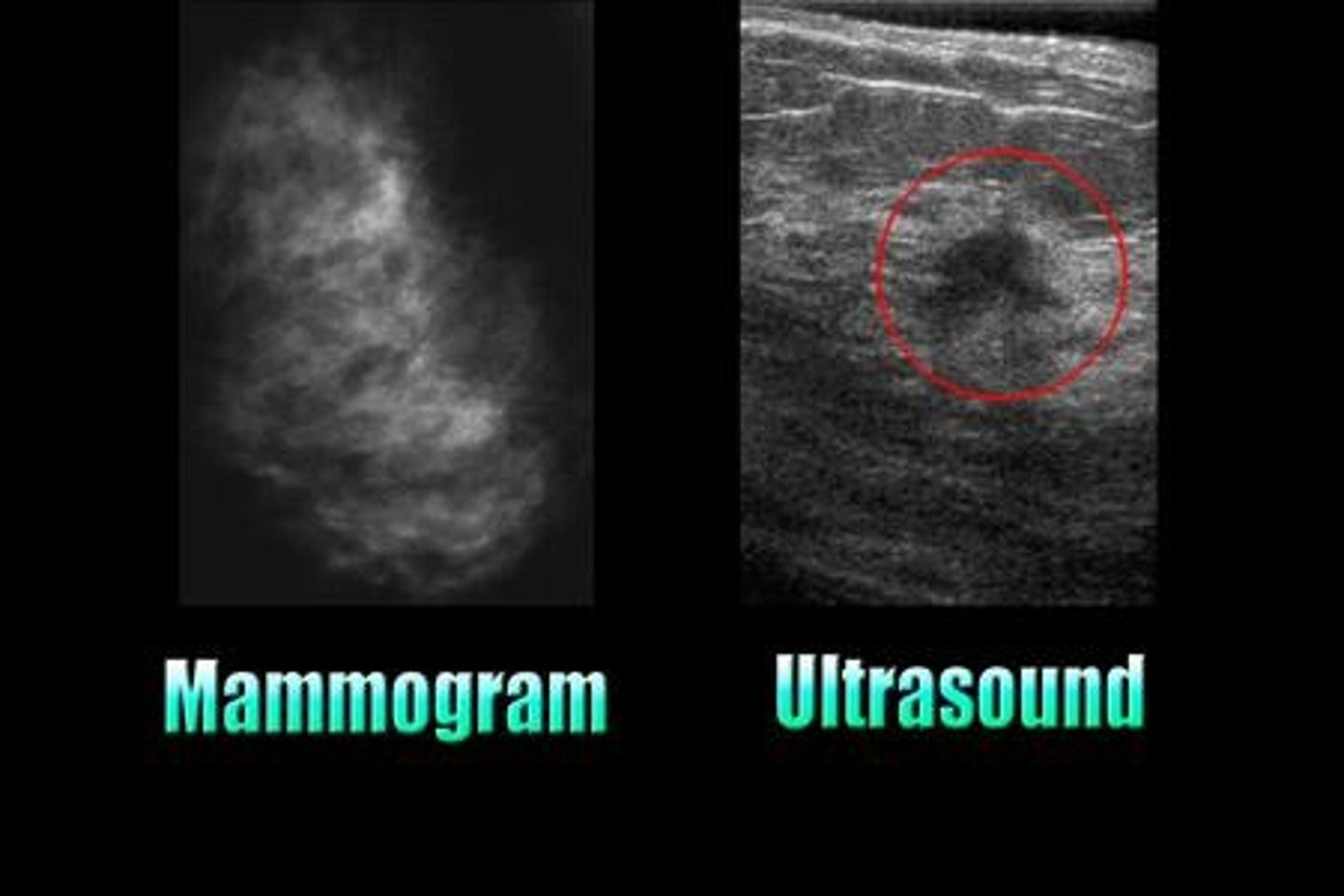
What happens to the ultrasound energy as it moves through the body?
It interfaces with various tissues that reflect and refract the ultrasound energy.
What is the purpose of applying an electrical shock to the piezoelectric crystal?
To initiate the creation of ultrasound waves.
What does the term 'echo' refer to in ultrasound imaging?
The reflected sound wave that returns to the transducer to create an image.
What is the difference between B-Mode and M-Mode in ultrasound?
B-Mode displays a 2D map of data based on brightness, while M-Mode displays a one-dimensional image for analyzing motion.
Why is ultrasound useful for delineating anatomy that differs slightly?
It can provide clear images of structures that have subtle differences.
What is the main feature of a sound wave used in ultrasound?
It is a mechanical disturbance that propagates through tissues.
What is the primary imaging technique for cardiac and fetal imaging in ultrasound?
M-Mode acquisition.
What is Nuclear Medicine?
A branch of medicine that uses radioisotopes in the diagnosis and treatment of disease, focusing on physiological function rather than just anatomical structure.
How does Nuclear Medicine work?
It involves the introduction of low-level radioactive chemicals (radionuclides, radiopharmaceuticals, or radiotracers) into the body, which are then detected by gamma cameras.
What is a gamma camera?
A device used in nuclear medicine that detects gamma ray signals emitted by radionuclides taken up by organs, converting them into images.
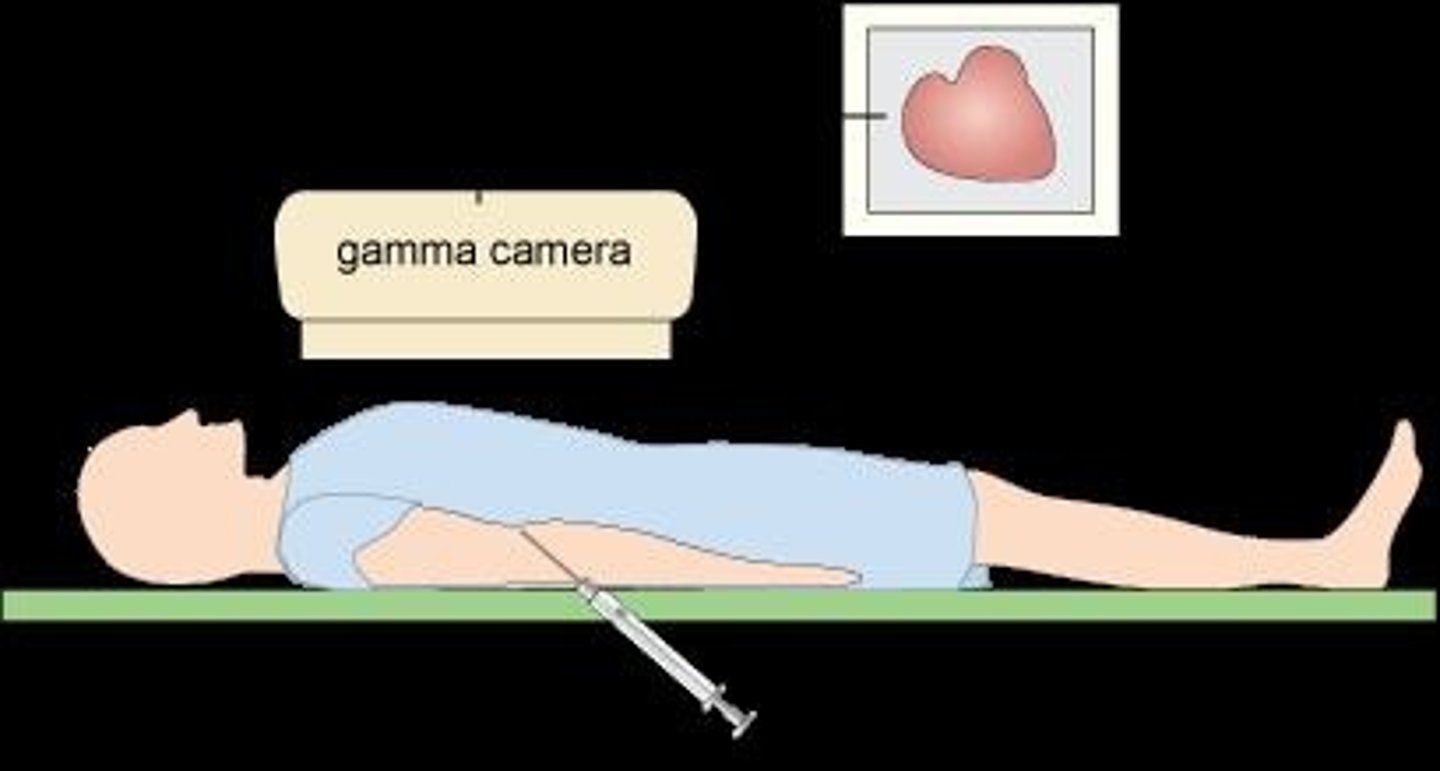
What is the function of the scintillation crystal in a gamma camera?
It detects emitted radiation signals and converts them into faint light, which is digitized to form an image.
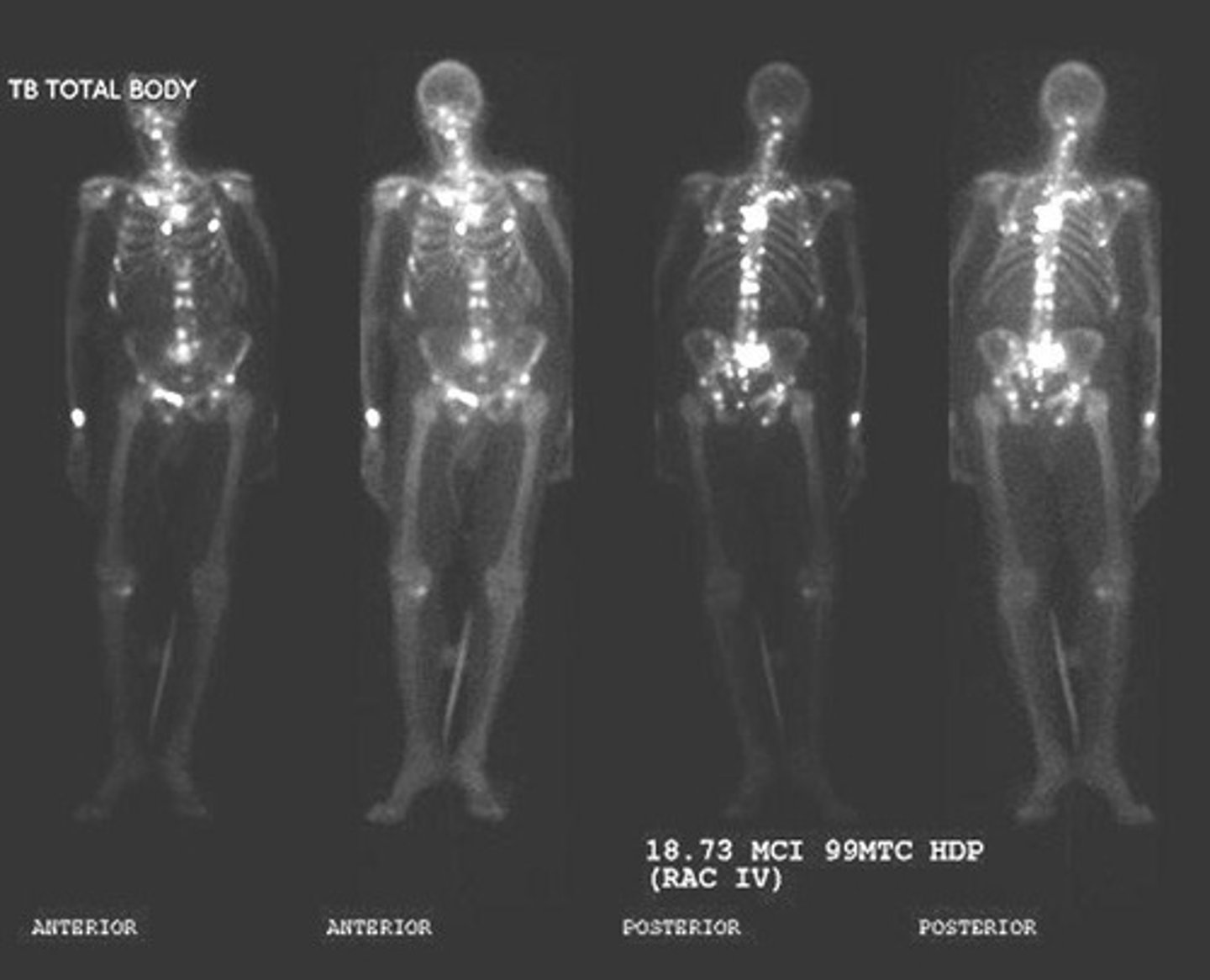
What is Technetium 99m used for in nuclear medicine?
It is injected into patients for bone scans to detect potential bone metastases.
What is Positron Emission Tomography (PET)?
An imaging technique that uses physiological, metabolic, and biochemical processes in the body for image formation, rather than just anatomical structure.
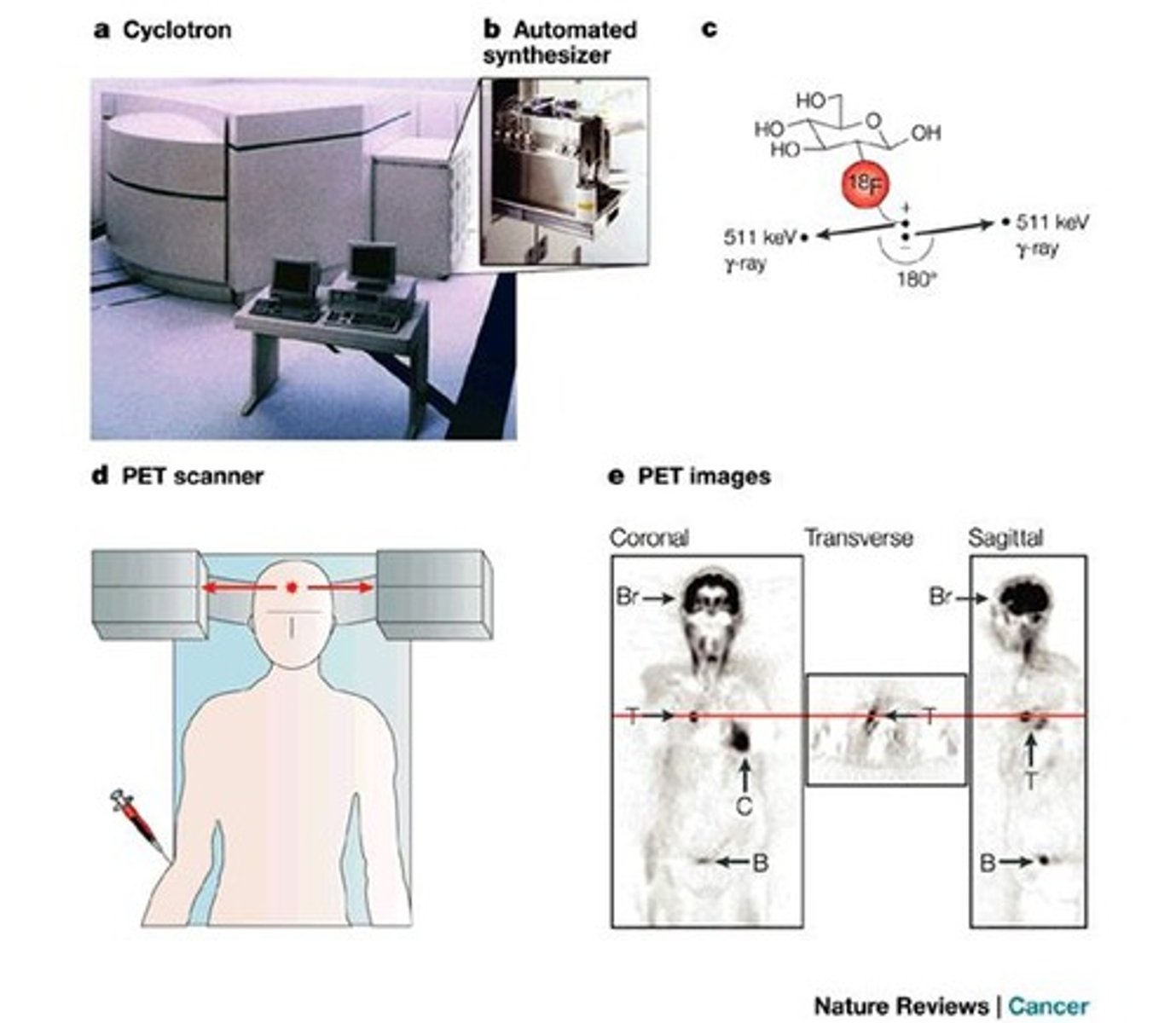
What is the most common agent used in PET scans?
Fluorine-18 fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG 18), a radioactive sugar.
What is the half-life of FDG 18?
110 minutes.
What is the purpose of a Geiger-Mueller Counter?
To detect radiation and measure low levels of radioactive emissions, such as beta particles or gamma rays.
What is assay in the context of nuclear medicine?
Examination and determination of characteristics (weight, measure, or quality) to ensure the correct dose and radioactivity is administered to patients.
What units are used to measure doses of radioactivity in nuclear medicine?
Millicurie (mCi) and Becquerel (Bq), where 1 mCi = 3.7 x 10^7 disintegration/sec.
What is the difference between Curie and Becquerel?
Curie (Ci) is an old unit equivalent to 3.73 x 10^10 Bq (disintegrations per second), while Becquerel (Bq) is the SI unit for radioactivity.
What is the purpose of assay and dose calibration?
To ensure patients receive the correct radiopharmaceutical dosage and the minimum absorbed dose for effective imaging or treatment.
What is a Hot Lab in nuclear medicine?
A specially designed room where radiopharmaceuticals are delivered, stored, and prepared, with radiation doses measured by a G-M counter.
What types of cancers are commonly diagnosed with bone scans using Technetium 99
Prostate, breast, lung, melanoma, urinary bladder, and cervix cancers.
What is the role of radiopharmaceuticals in nuclear medicine?
They are formulated to be temporarily collected in specific parts of the body for imaging studies.
What is the significance of the physiological function in nuclear imaging?
It allows for the assessment of how tissues or organs are functioning, unlike traditional imaging that focuses on structure.
What is the primary use of PET/CT scans?
They are widely used for staging lymphomas and lung cancers and for simulation purposes.
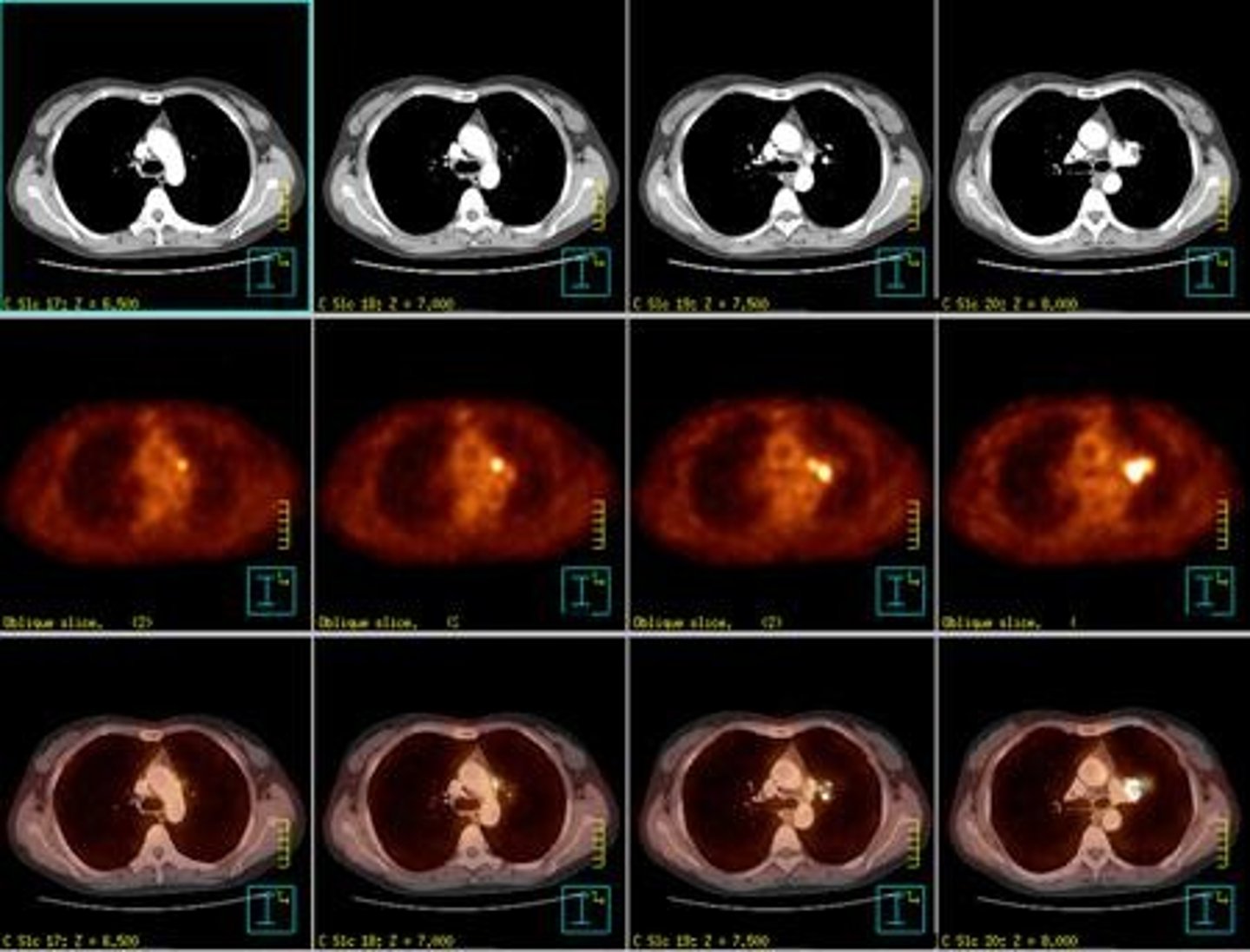
How do malignant cells utilize FDG 18 in PET scans?
Malignant cells have a higher need for glucose, allowing FDG 18 to accumulate in these cells for imaging.
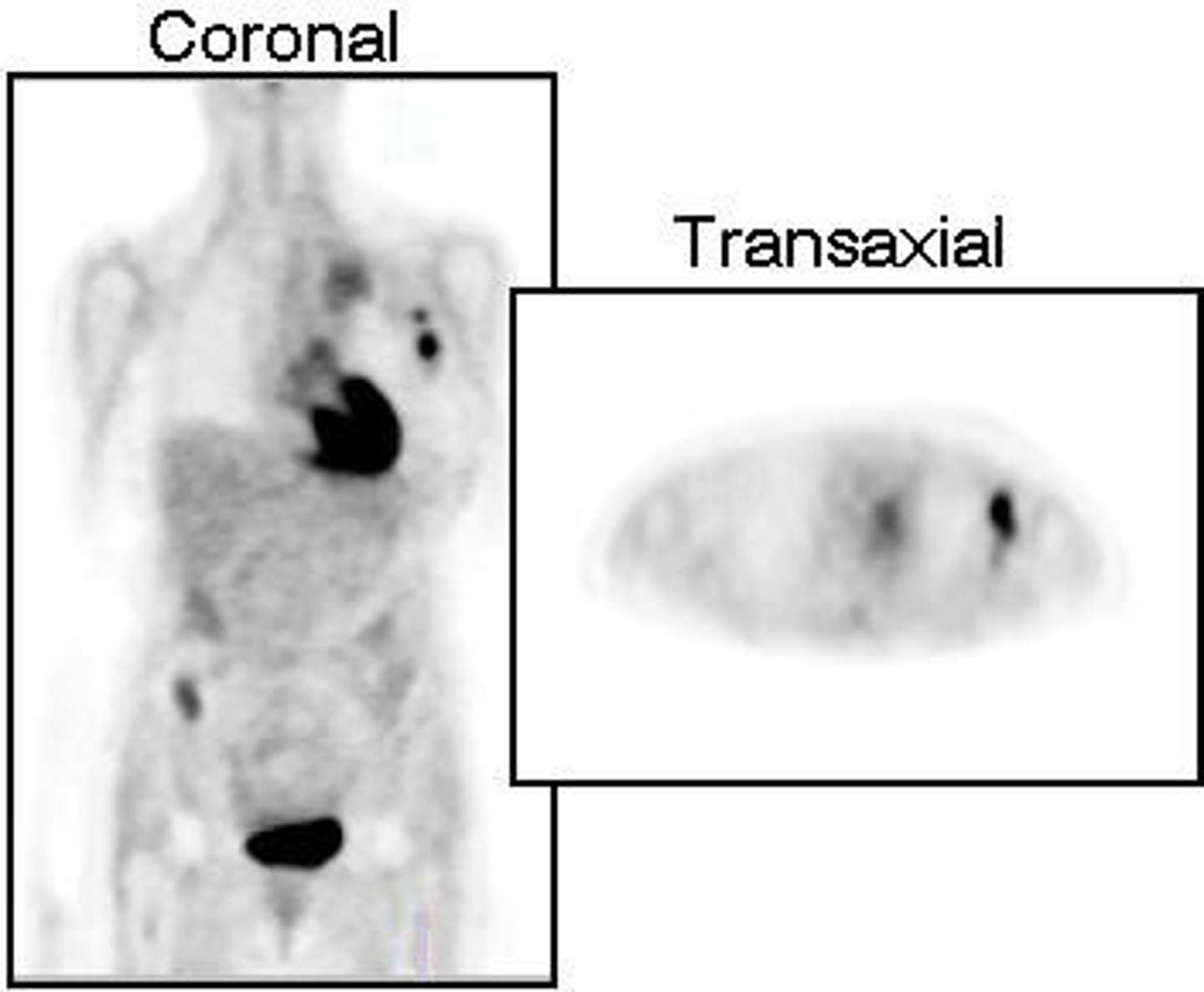
What is the importance of maintaining standards in a Hot Lab?
To optimize patient care and minimize radiation exposure to personnel, patients, the public, and the environment.
What type of radiation can a Geiger-Mueller Counter detect?
It can detect radioactive emissions such as beta particles and gamma rays.
What is the objective of the assay in nuclear medicine?
To ensure that the patient receives the minimum absorbed dose compatible with obtaining high-quality diagnostic images or achieving therapeutic outcomes.
What is the process of radioactive decay?
Radioactive atoms spontaneously transform or disintegrate into different atoms, measured as the number of disintegrations per second.
What is the primary purpose of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)?
To form images of body structures using radio frequency signals from hydrogen protons.
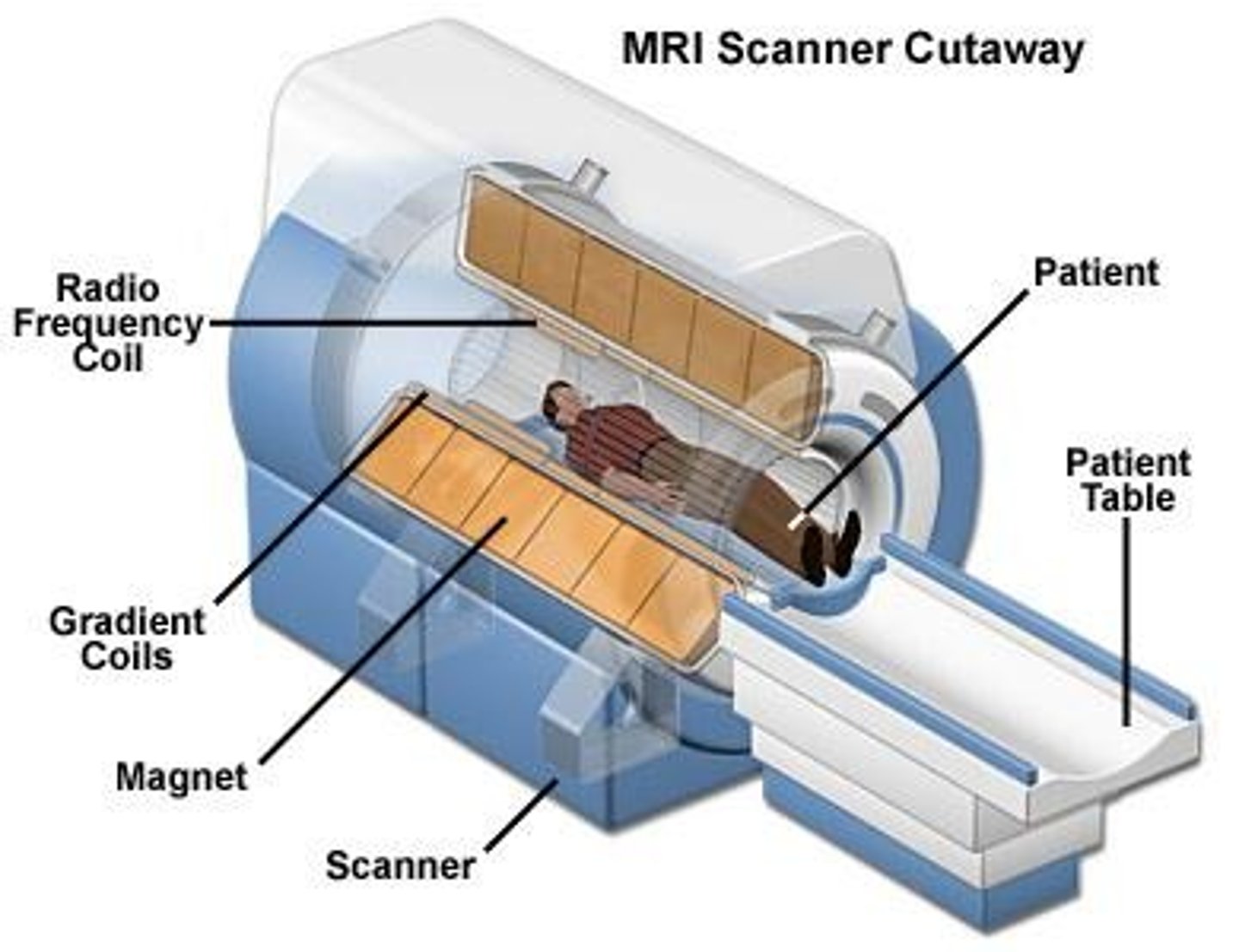
What is the significance of hydrogen in MRI?
The human body consists of 60% to 80% water, which contains hydrogen atoms that are used to create MRI images.
What are the SI units of magnetism used in MRI?
tesla (T)
What is the typical strength of an MRI magnet?
MRI magnets typically range from 0.1 to 3.0 tesla.
What is resonance in the context of MRI?
Resonance refers to the flipping of protons out of alignment with the external magnetic field due to radio frequency pulses.
What are T1-weighted scans used for in MRI?
T1-weighted scans are used to differentiate fat from water in imaging.
How do T2-weighted scans differ from T1-weighted scans?
In T2-weighted scans, fat appears darker and water appears lighter, often better demonstrating pathologies.
What is a paramagnetic contrast agent commonly used in MRI?
Gadolinium, which increases visibility of inflammation, tumors, and blood flow.
What are some common adverse reactions to gadolinium contrast agents?
Brief headache, nausea, and dizziness.
What is the most serious reaction associated with gadolinium contrast agents?
Anaphylactic shock.
What safety precautions are necessary before administering gadolinium?
A blood draw for kidney function (GFR, BUN, creatinine) is recommended.

What is the role of magnetic fields in MRI?
Magnetic fields align protons in the body tissues, which are then manipulated to create images.
What happens to protons when they are moved out of alignment in MRI?
They produce an RF signal when returning to alignment, which is used to construct the MR image.
What is the magnetic field strength of the Earth's magnetic field?
Approximately 0.5G or 5 x 10^-5 T.
What does the term 'spin magnetic movement' refer to?
The effect created by the spinning of orbital electrons around the nucleus of an atom.
What is the difference between T1 and T2 relaxation times?
T1 relaxation time is the time it takes for protons to align with the magnetic field, while T2 relaxation time is the time it takes for protons to lose phase coherence among the spins.
What is the significance of adjusting technical factors in MRI?
Adjusting technical factors optimizes the diagnostic value of the image.
What is the relationship between charged particles and magnetic fields?
A charged particle in motion creates a magnetic force, and the force field moves perpendicular to the particle.
What is the structure of a magnet?
Every magnet is bipolar, having a North and South pole.
What is the effect of placing magnetic material in a magnetic field?
The magnetic material experiences a force that aligns its domains along the magnetic field.
Why is understanding atomic structure important for magnetism?
It helps explain how magnetic forces and fields are generated and interact.
Computed Tomography (CT)
A medical imaging technique that uses computer-processed combinations of many X-ray measurements taken from different angles to produce cross-sectional images of specific areas of a scanned object.
Diagnostic CT Scanner
A type of CT scanner used primarily for diagnostic imaging purposes.
Radiotherapy CT Simulator
A specialized CT scanner used to simulate the treatment planning for radiation therapy.
Hounsfield Numbers
A scale used in CT imaging that ranges from +1000 to -1000, representing various tissue densities and linear attenuation coefficients.

Transverse Plane
The plane in which patients are scanned during a CT procedure.
Coronal Plane
The plane in which images are reconstructed from the transverse scans.
Sagittal Plane
Another plane in which images are reconstructed from the transverse scans.
3-Dimensional Imaging
An imaging technique that provides a three-dimensional view of the scanned area, beneficial for radiation therapy treatment planning.
Gantry
The donut-shaped structure of a CT scanner that contains the X-ray circuit, X-ray tube, collimators, radiation detectors, and high voltage generator.
Patient Support Table
The table on which the patient lies during a CT scan, which can be curved for diagnostic CT or flat for radiation therapy simulation.
CT Scanner Generations
There have been 7 generations of CT scanners, each leading to faster scan times and reduced patient exposure.
6th Generation CT Scanner
Also known as the helical/spiral scanner, it uses slip ring technology for continuous rotation of the X-ray tube and detectors.
7th Generation CT Scanner
Multi-section or multi-slice scanners that can expose multiple detectors simultaneously, reducing total scan time.
Spatial Resolution
How sharp and detailed the image looks
The minimum separation of two objects that can be distinguished in an image as two separate objects.
Ex:
If you can see a tiny lung nodule clearly, that’s because of good spatial resolution (fine detail, sharpness).
Contrast Resolution
How well you can tell different tissues apart based on shades of gray.
The ability to distinguish two objects with similar attenuation values, which is a major advantage of CT imaging.
Ex: If you can tell that the nodule is a little denser (whiter) than the surrounding lung tissue, that’s because of good contrast resolution (differences in gray shades).
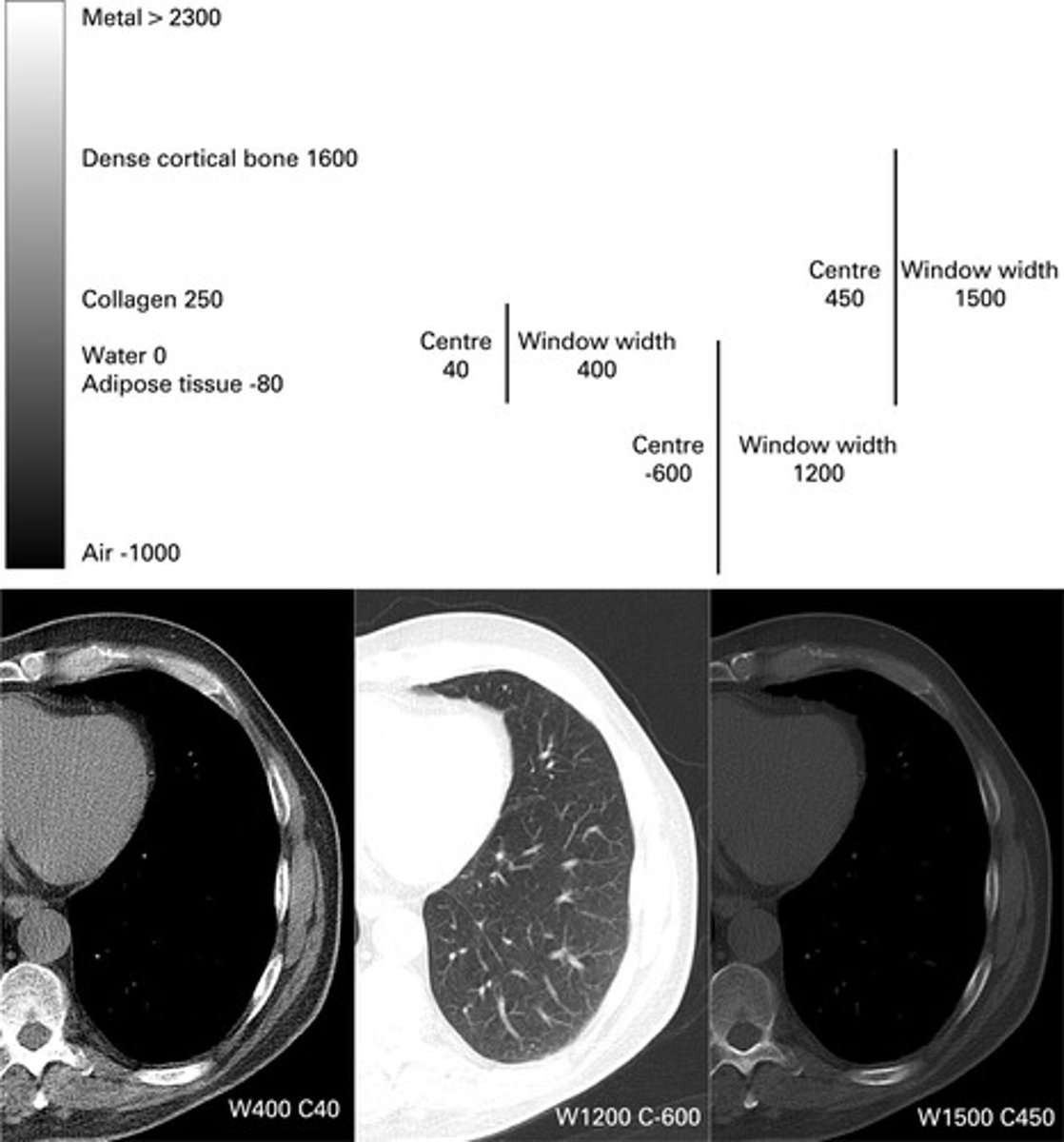
Noise
The graininess of an image that can affect the quality of CT scans.
Scanning Slices
Refers to the sectional anatomy depicted in CT images, with a single slice at the skin surface ranging from 1 to 6 cGy.
Dose
The amount of radiation exposure, which increases with mAs in CT imaging.
kVp
Kilovolt peak, the maximum voltage applied across the X-ray tube, typically ranging from 120-140 in CT imaging.
Slice Thickness
The thickness of the scanning slice, which depends on the technical settings used and can vary from several millimeters to centimeters.
Window Levels and Widths
Adjustments made to enhance the visualization of structures with similar densities in CT images.
what is the roi
Region of interest
What is the slip ring for in ct
Allows the ct xray to go all the way around the bore (360 degree capabilities)
What are the lap lasers
The rad therapy lasers that help u drive and Align the patient
If the pitch is less the one is that more or less rad for the patient
More radiation
differences in the shades of grey that can be distinguished in an image as two separate objects
Contrast resolution
what are the collimators set to when doing ct simulation
OPEN ALL THE WAY TO ALLOW FOR BODY CONTOUR FOR TX PLANNING
What helps u to see the difference between the spleen and the stomach and the liver and the gallbladder
Contrast resolution
Major advantage to CT imaging
Ability to distinguish two objects with similar attenuation values
Contrast resolution
What is the best way to adjust graininess on an image
Kvp and mas
What weight is for water and fat
T1
What weight mri scan looks at pathology
T2
What is a mri quench
Sudden loss of superconductivity when temperature is raised
What kind of metal or allowed around MRI?
non ferromagnetic metals
what is tomotherapy machine
Mv ct machine
Zone 1 mri
General public
zone 2 mri
More strictly supervised (usually where u r mri screened)
Zone 3 mri
MRI personal located outside treatment room where mri people sit and control the machine
Zone 4 mri
Actual room where mri is