basic organic concepts and alkenes
1/41
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
Homologous series definition
-a series of compounds with the same functional group and therefore similar chemical properties
-each successive member differs by CH2
-as you move along, there’s a gradual change in physical properties due to increasing molecular size and mass
What’s a functional group?
-a group of atoms in an organic molecule that’s responsible for the characteristic reactions of that molecule
-e.g. double bond in alkenes
What is a pi bond?
-a bond formed by the sideways overlap of adjacent p-orbitals
-pi bond forms above and below plane of molecule
-in a C=C double bond, it locks both C atoms in position and prevents them rotating around the double bond (restricted rotation)
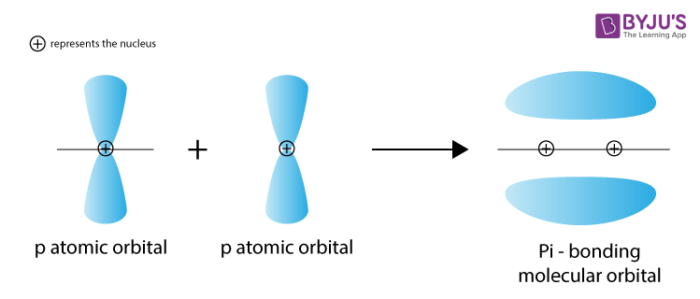
What’s a pi orbital?
-pi bond
-they lie above and below rest of molecule
-p-orbitals don’t overlap as effectively as s-orbitals so pi bonds are weaker, and alkenes are more reactive than alkanes
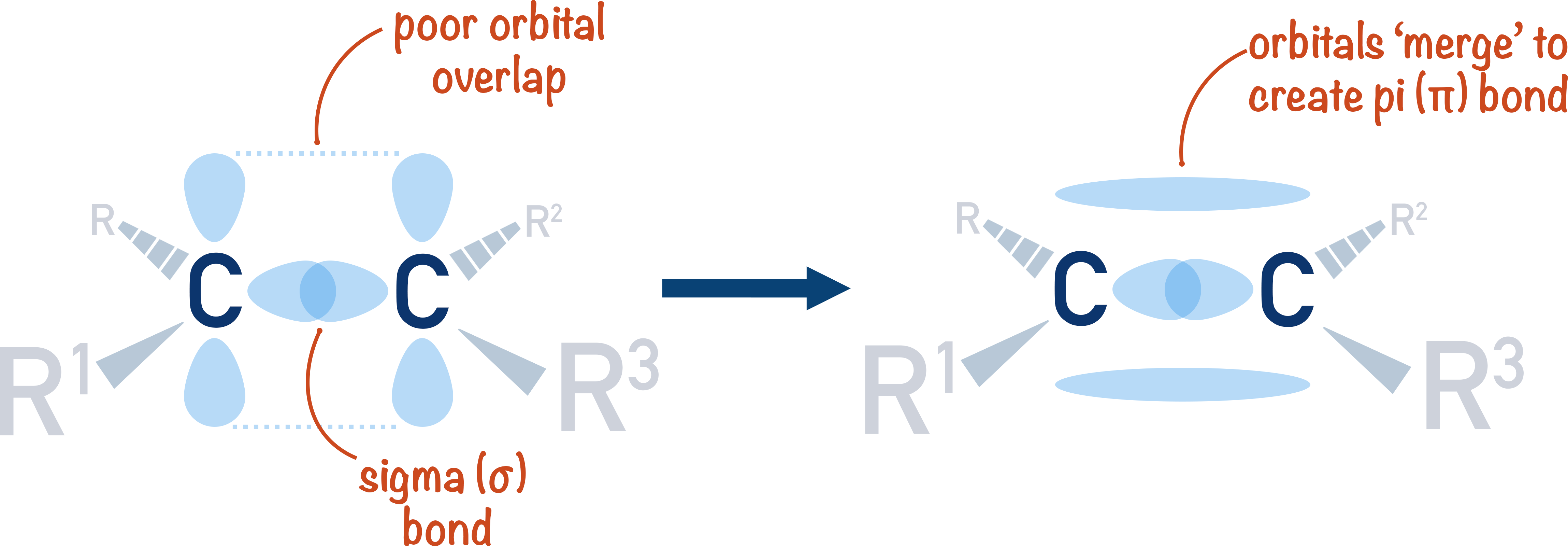
What’s in a double alkene bond?
-one of the shared pairs lies in a molecular orbital on the line between 2 nuclei (sigma bond), formed by overlap of 2 s-orbitals
-the other pair is found above and below plane of molecule, it’s a pi-bond, formed by the sideways overlap of 2 p-orbitals
Why are alkanes unreactive?
-C-H bonds is non-polar and short, so nuclei are close to shared pair of electrons and the bond is strong
-for a sigma bond, the overlap is along the line directly between 2 nuclei, higher e- density, stronger than pi bond
-alkane molecule is a tetrahedral shape, bond angle 109.5
What happens to physical properties of alkanes as number of carbons increases?
-boiling point increases, molecule gets bigger, more electrons per molecule, induced dipole forces get stronger
-viscosity increases
-flammability decreases
-volatility decreases (ability to evaporate)
What are structural isomers?
-molecules with the same molecular formula but different structural formula
What is an aliphatic molecule
-an organic molecule containing H and C joined in straight/branched chains or non aromatic rings, that doesn’t contain a benzene ring
e.g. alkanes, cycloalkanes
What’s an aromatic compound
-any organic compound that contains benzene ring
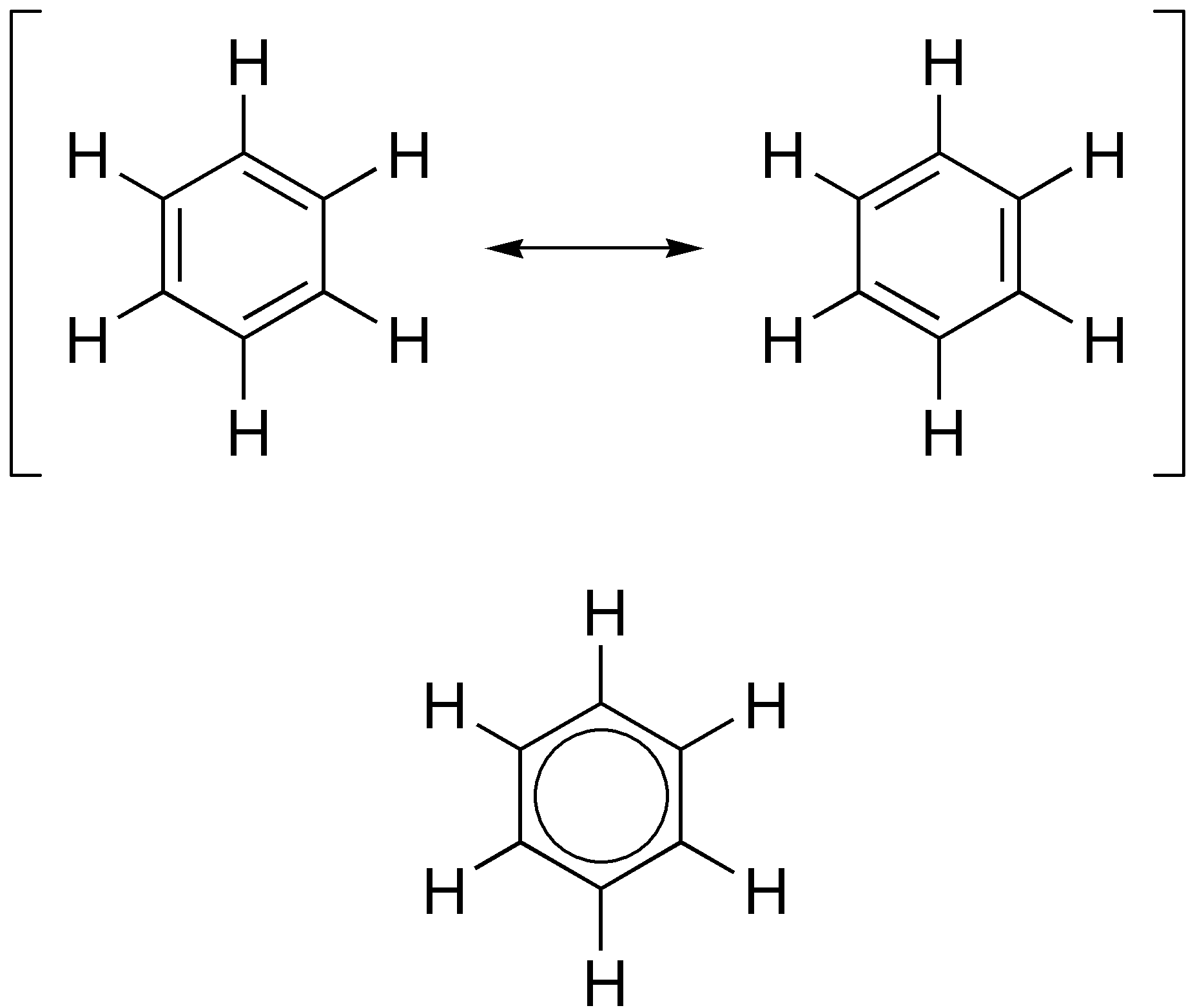
What does alicyclic mean?
-any carbon ring that isn’t the benzene ring
-cyclic is any ring
general formula: CnH2n (same as alkenes)
alcohol general formula
CnH2n+1 OH
empirical formula definition
simplest whole number ratio of atoms of each element in a compound
structural formula definition
the arrangement of atoms in a molecule without showing all the bonds
-e.g.CH3CH2CH3
Skeletal formula
-show the bonds of the carbon skeleton only
-carbon and hydrogen atoms aren’t shown but functional groups are
Displayed formula definition
show the arrangement of atoms showing all the bonds and atoms in a molecule
ketones
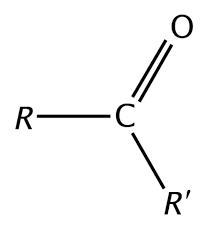
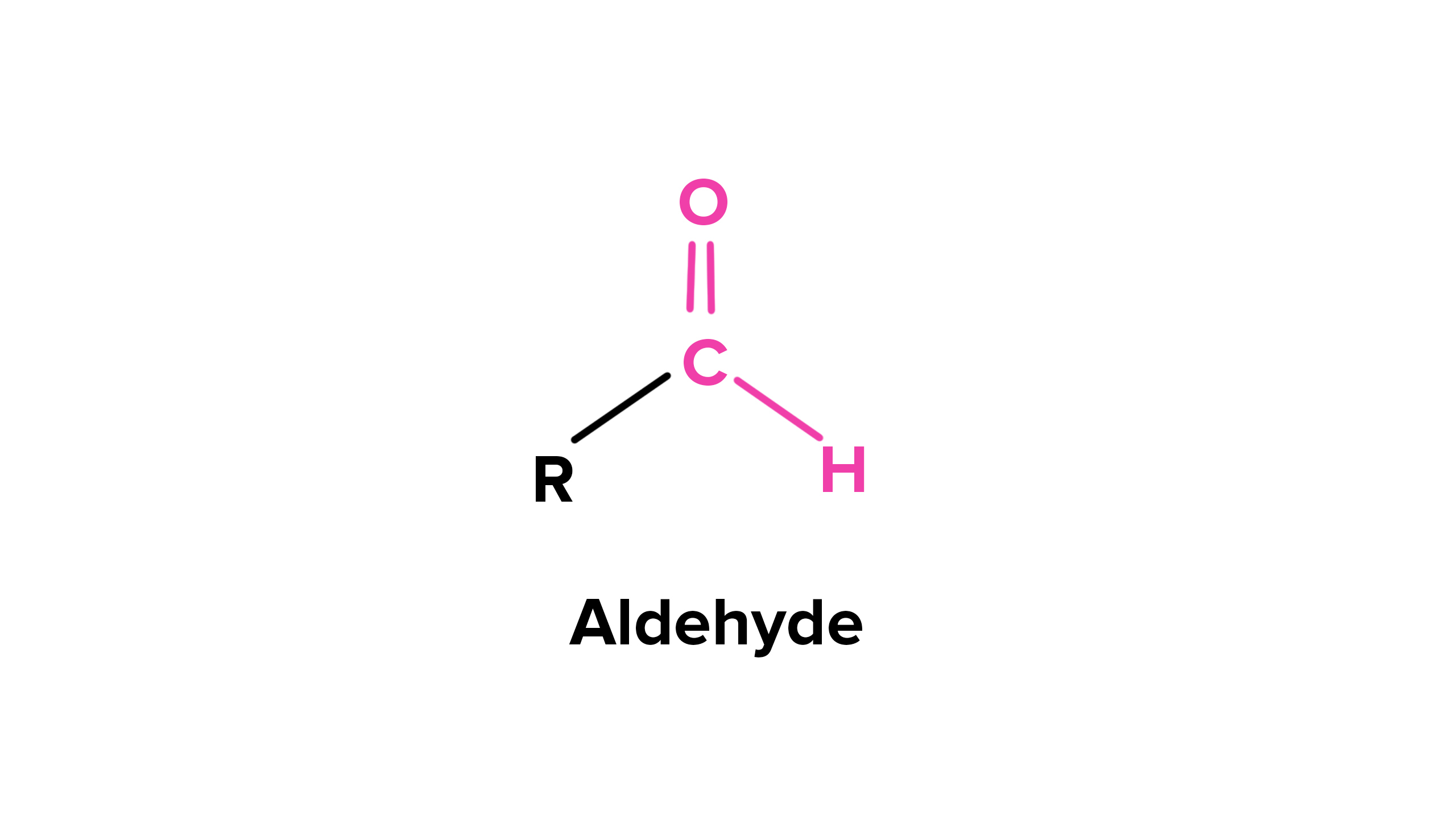
aldehydes
cycloalkanes
esters
-alkyl…anoate
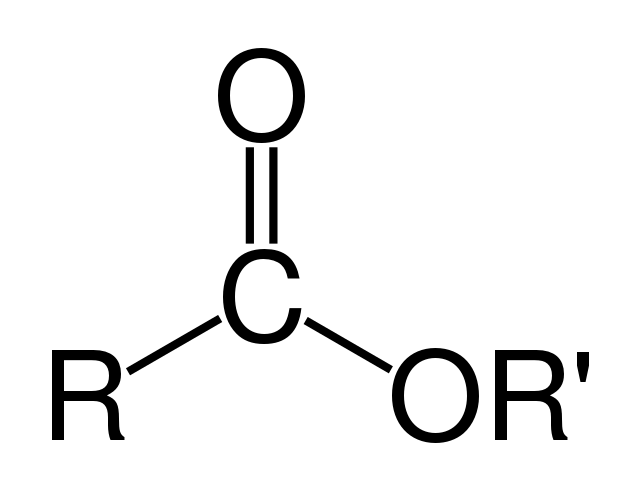
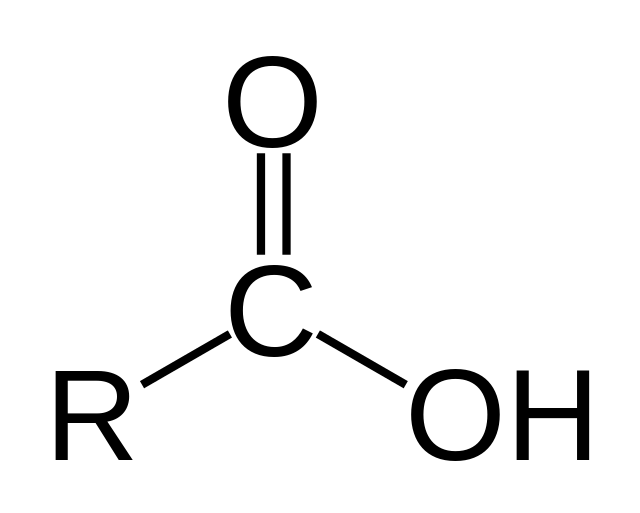
carboxylic acid
CnH2nO2
Heterolytic fission
-a way which a covalent bond can break
-pair of electrons moves to one of the atoms and you end up with 2 ions
e.g. C=O > C-O:-
electrophile
-a species that accepts a pair of electrons
rules for naming alkanes
-find longest continuous carbon chain
-identify and name groups attached to chain
-number the chain consecutively, starting at the end nearest a substituent group
-designate the location of each substituent group by a number and name
-assemble name, listing groups alphabetically
-prefixes (di, tri) aren’t considered when alphabetising
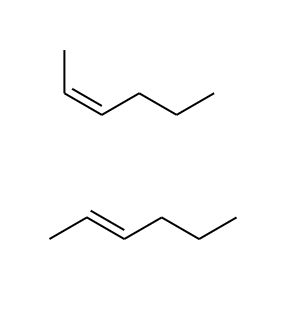
E/Z isomerism checklist
-an alkene which needs to have 2 different groups attached to each C of the C=C
-and if one of the groups on both carbons is a H, we call the stereoisomers cis/trans rather than E
-(special case of E/Z isomerism)
stereoisomers
-molecules with the same molecular and structural formula but have different spatial arrangements of atoms
-e.g. E/Z stereoisomers
How to draw a reaction mechanism
1- show bond polarities using partial charges
2-show transfer of pair of electrons using curly arrows
3-show reaction intermediates including charges as necessary
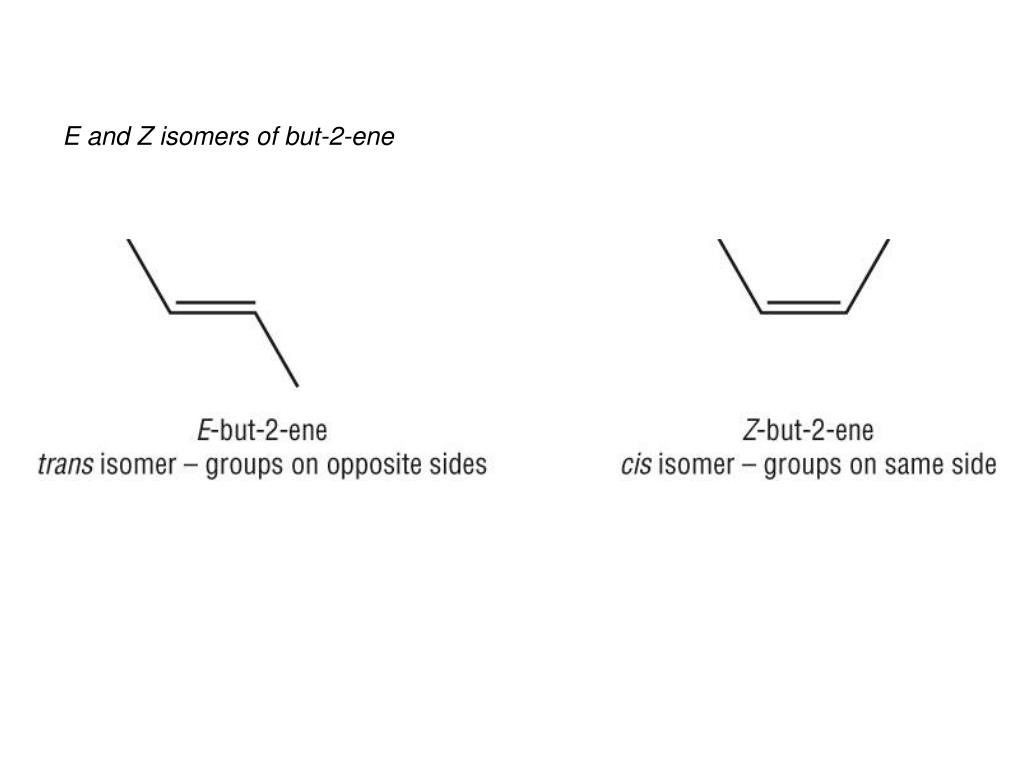
E/Z isomerism (Cahn, Ingold, prelog)
-due to double bond, rotation round double bond is restricted
-they’re compounds with different spatial arrangements of groups attached to carbons
-there must be 2 different groups on each carbon of the C=C
-CIP rules are that whichever element directly attached to carbon has a higher atomic number is priority group
electrophilic addition mechanism for ethene and water to make an alcohol
-necessary conditions are that water has to be vapour, over 100 degrees C(steam), and a phosphoric/sulphuric acid catalyst
-ethanol
electrophilic addition reaction for ethene and H2 to make alkane
-necessary conditions: nickel catalyst and H2
-curly arrow from double bond to delta + H
-curly arrow from H-H bond to delta - H
-intermediate is carbocation
-curly arrow from H- (hydride) ion to carbocation
-product is ethane (alkane)
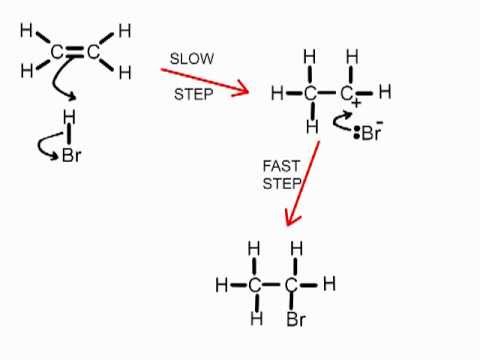
tertiary carbocations (markownikoff’s rule)
-ion with positive carbon atom with 3 alkyl groups
-more likely to form than secondary, which are more likely to be formed than primary
-as positive charge is stabilised by alkyl groups
-so tertiary carbocation intermediates are the most stable
-so will be formed in greater proportion
-(H add onto alkene carbon with the most H already attached)
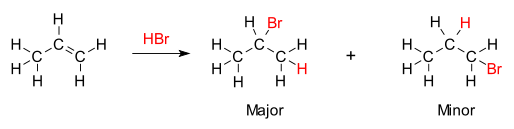
When can there be 2 possible products in electrophilic addition?
-if both electrophile and alkene are asymmetric
-alkene doesn’t have mirror plane through C=C
dehydration of cyclohexanol
-heated with concentrated phosphoric /sulphuric acid
-the liquid cyclohexene distills off and collected and purified
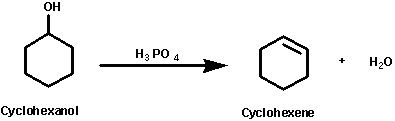
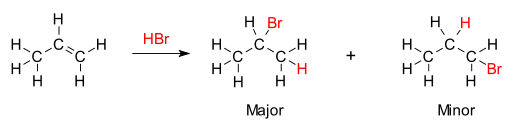
markownikoff’s rule
-major product from addition of a hydrogen halide to an unsymmetrical alkene is the one where hydrogen adds to carbon with the most hydrogens already attached
What’s the shape and bond angle around a C=C
-trigonal planar
-120 degrees
How can waste polymers be processes to reduce their environmental impact?
-cracked to give monomers then used as organic feedstock to make more plastics
-sorted, melted and remoulded (recycled)
-combustion to produce energy, burnt as fuel, but makes HCl, toxic, must be removed
why do straight chain molecules have higher boiling points than branched molecules
-can pack more tightly
-more contact surface area
-stronger induced dipole forces
Use of methanol
-manufacture esters
-solvent
alternatives for polymers
-biodegradable polymers
-photodegradable (chemically broken down by sunlight)
-used as organic feedstock
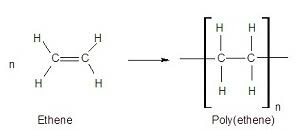
bromine test for alkenes
orange to colourless
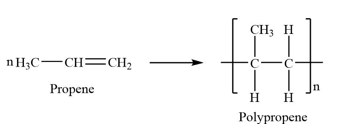
polypropene
double bond is broken
molecular formula
shows all atoms of each element in a molecule
e.g. C6H12O