Principles of Cell and Molecular Bio Unit 1 (Ch 1 -6 )
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/161
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
162 Terms
1
New cards
Ch 1 : What is biology
Study of life
%%__Cell Bio__%% : study of cells
^^__Molecular Bio__^^ : study of biology at a molecular level
%%__Cell Bio__%% : study of cells
^^__Molecular Bio__^^ : study of biology at a molecular level
2
New cards
ch 6 : centrosomes and centrioles
**ONLY FOUND IN ANIMAL CELLS**
**ONLY FOUND IN ANIMAL CELLS**
centrosome is a cellular structure involved in the process of cell division.
a centrosome is made up of 2 centrioles
**ONLY FOUND IN ANIMAL CELLS**
a centrosome is made up of 2 centrioles
**ONLY FOUND IN ANIMAL CELLS**

3
New cards
Ch1 : what is science
Knowledge of natural world through observations and experiments
4
New cards
Ch 1 : 7 Characteristics of life
\
1. Order (cells)
2. Adaptation
3. Regulation
4. Response to Environment
5. Growth and development
6. Energy processing
7. Reproduction
1. Order (cells)
2. Adaptation
3. Regulation
4. Response to Environment
5. Growth and development
6. Energy processing
7. Reproduction
5
New cards
Ch 1 : Inductive reasoning vs deductive
Inductive : specific to general
%%deductive%% : general to specific
%%deductive%% : general to specific

6
New cards
Ch 1 : hypothesis
**DIFFERENT FROM A THEORY**
* Educated guess / proposed explanation
* If .. then logic
* Testable : through observations and experiments
* Falsifiable : can’t be fully proved
* Educated guess / proposed explanation
* If .. then logic
* Testable : through observations and experiments
* Falsifiable : can’t be fully proved

7
New cards
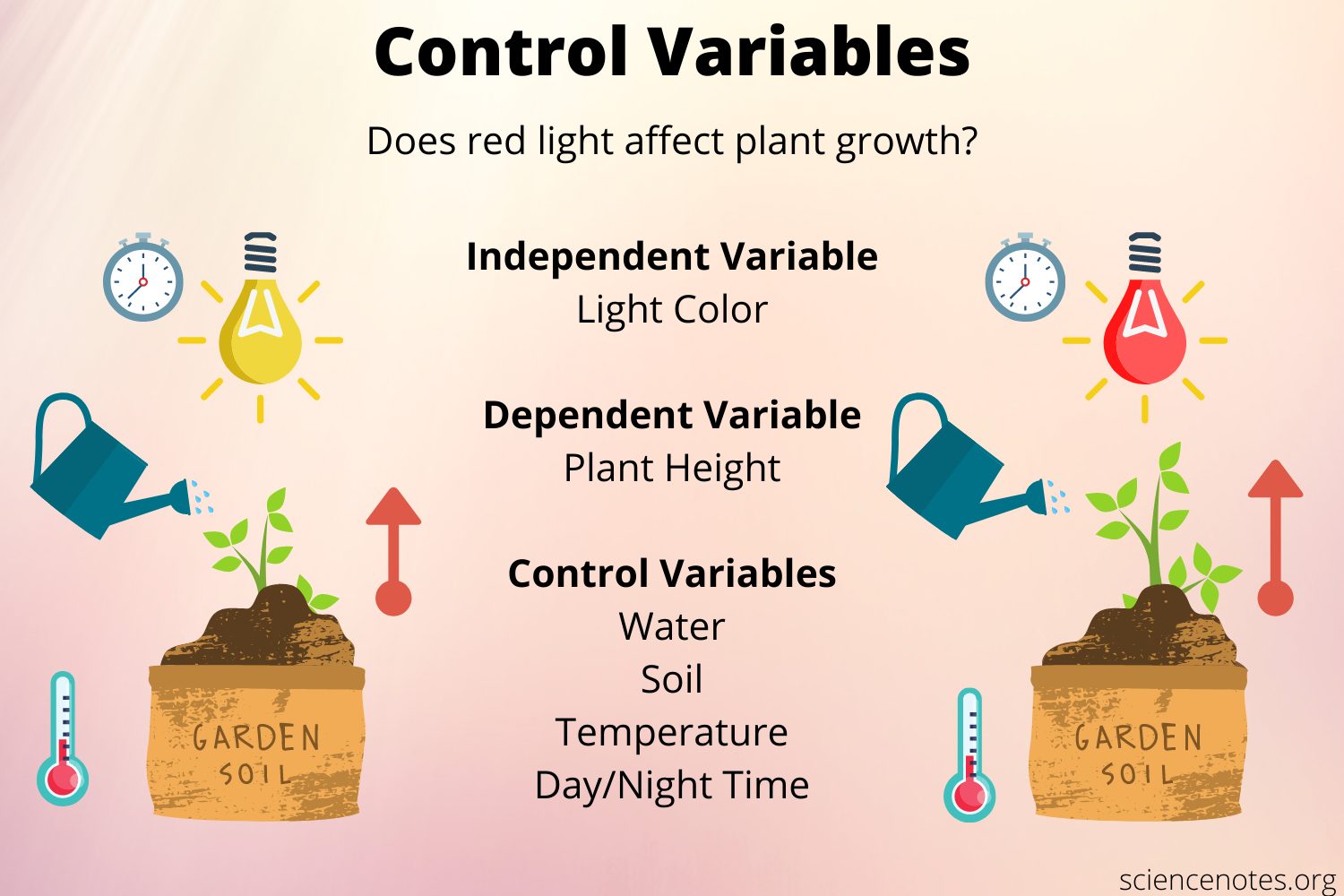
Ch 1: controlling for variables
Minimize affect on on dependent ( what you’re measuring ) to not draw incorrect conclusions on independent
8
New cards
Ch 1 : independent vs dependent
Independent: manipulated by researcher
Dependent: being measured , based on independent’s effect
Dependent: being measured , based on independent’s effect

9
New cards
Ch 1 : theory
==theory :== Explanation that is less specific than a hypothesis
* generates new hypothesis and is supported by way more evidence than a hypothesis
* generates new hypothesis and is supported by way more evidence than a hypothesis
10
New cards
Ch 1 : theory differences from hypothesis
==A theory is :==
* broader in scope ( umbrella ; hypothesis grouped under )
* evidence based
* current ( changes as new info is presented )
* doesn’t have to be testable
**Like a hypothesis it can be proven and rejected**
\
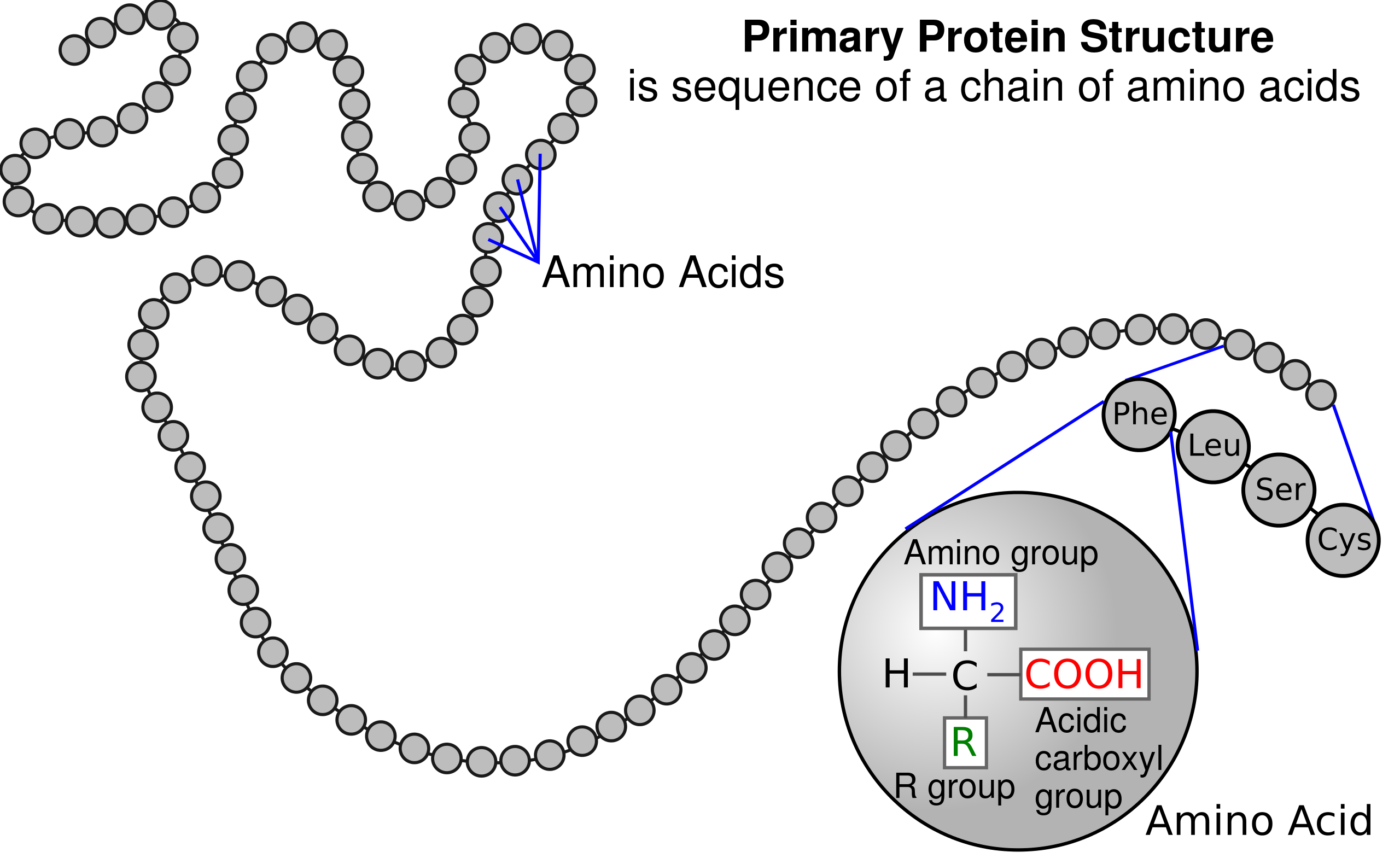
* broader in scope ( umbrella ; hypothesis grouped under )
* evidence based
* current ( changes as new info is presented )
* doesn’t have to be testable
**Like a hypothesis it can be proven and rejected**
\
11
New cards
Ch 2 : what is an element
%%element%% : substance that can’t be broken down to other substances by chemical reactions
* cannot be broken down w/o losing its identity
* example :sodium
* cannot be broken down w/o losing its identity
* example :sodium

12
New cards
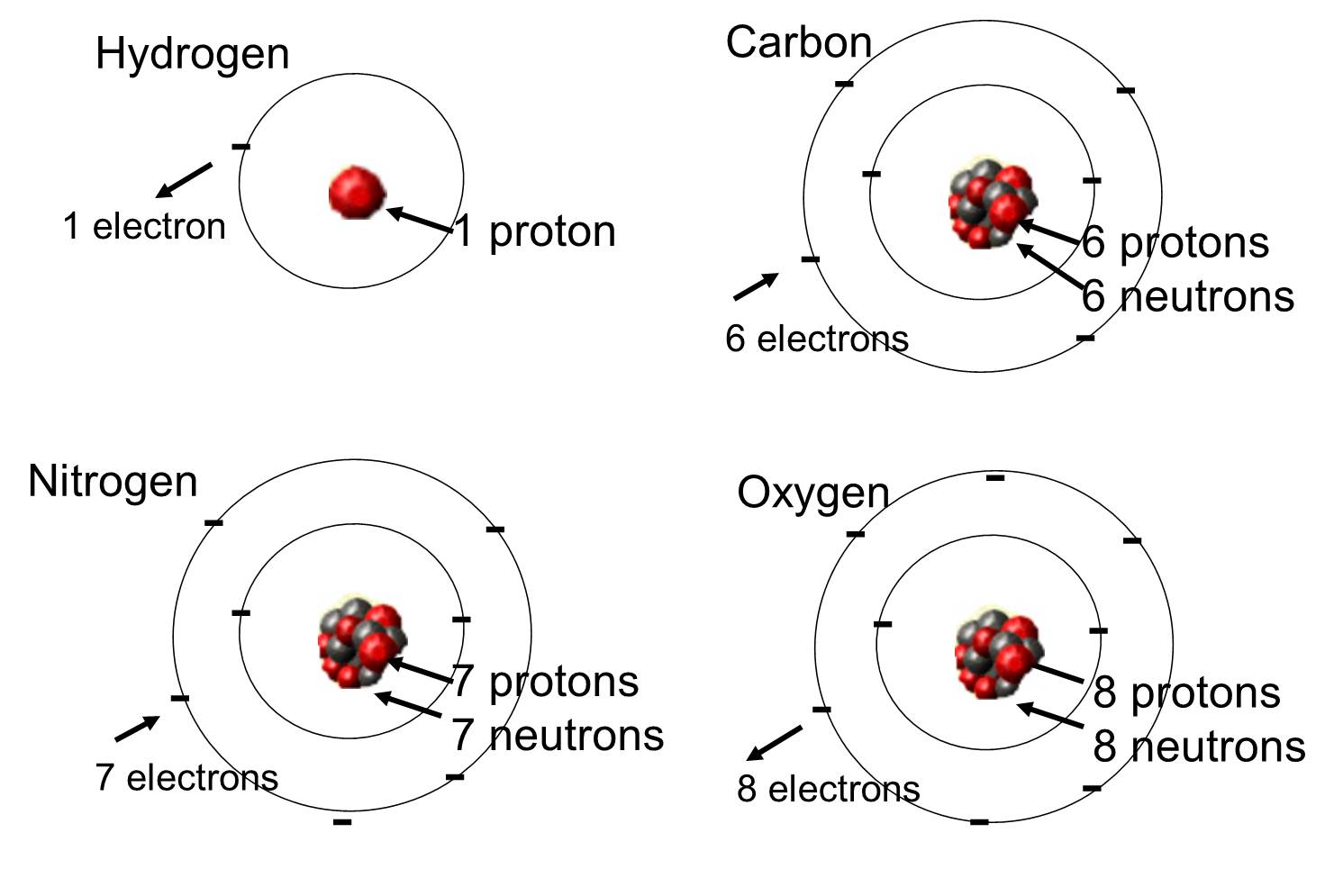
Ch 2 : Key elements
==key elements== : carbon , hydrogen , oxygen and nitrogen
13
New cards
Ch 2 : Compounds
==compound== : 2 or more elements combined in a fixed ratio
* compounds have different properties than when they are in their element form
* example : table salt
* compounds have different properties than when they are in their element form
* example : table salt
14
New cards
ch 2 : what determines properties of an element
the structure of its atoms ( protons , neutrons , electrons : electrical charges and locations )
example : oxygen has 8 protons , neutrons , electrons
\
example : oxygen has 8 protons , neutrons , electrons
\

15
New cards
ch 2 : what is an atom
==atom :== smallest unit of matter that still retains properties of an element
* atoms in a column of periodic table In same column behave the same
* atoms in a column of periodic table In same column behave the same

16
New cards
ch 2 : subatomic particles that make up atomic structure
Neutrons : no charge neutral ( found in nucleus )
@@Protons@@ : + charge ( found in nucleus )
^^Electrons^^ : - charge ( found moving around protons and neutrons )
**electrons are smaller than protons and neutrons**
@@Protons@@ : + charge ( found in nucleus )
^^Electrons^^ : - charge ( found moving around protons and neutrons )
**electrons are smaller than protons and neutrons**

17
New cards
Ch 2 : atomic number vs atomic mass
==Atomic number==
* protons ( changing the # of p changes identity )
%%Atomic mass%%
* protons + neutrons
* unit : amu ( atomic mass unit )
* protons ( changing the # of p changes identity )
%%Atomic mass%%
* protons + neutrons
* unit : amu ( atomic mass unit )

18
New cards
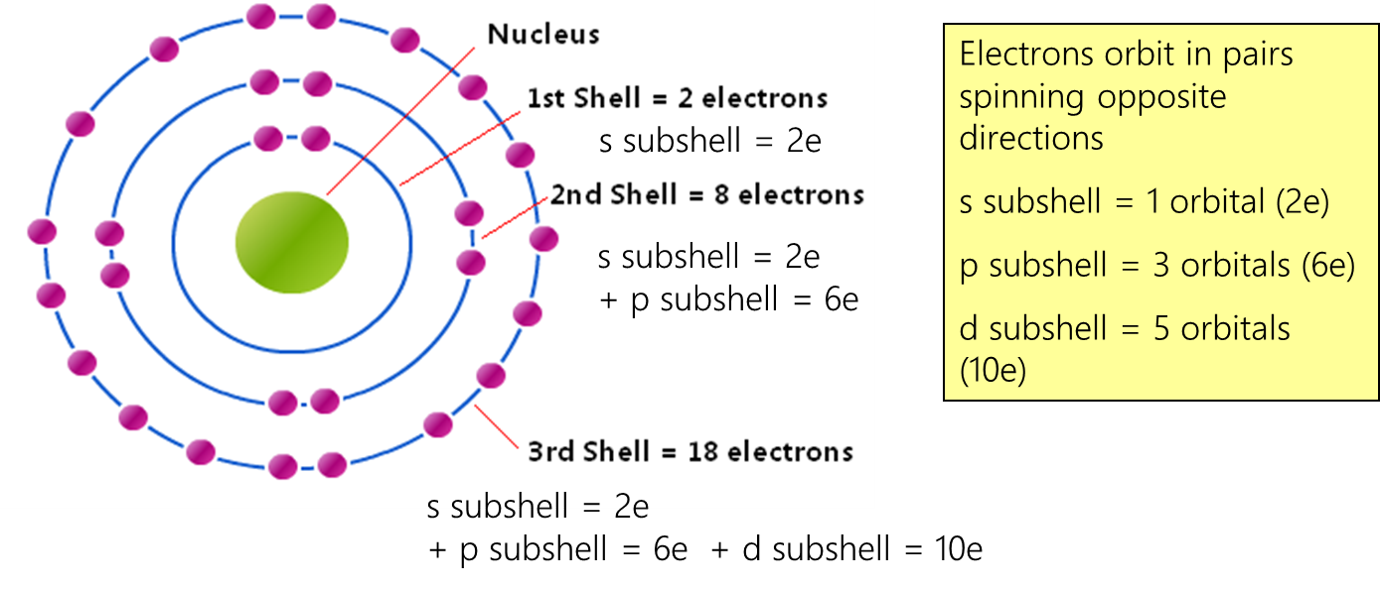
Ch 2 : electron orbitals
* orbitals have 2 electrons
* each electron shell has a different number of orbitals
* different shells have different energy
* orbitals are 3d shapes where electrons hang out
\
\
* each electron shell has a different number of orbitals
* different shells have different energy
* orbitals are 3d shapes where electrons hang out
\
\
19
New cards
Ch 2 : energy
energy : potential to cause change
20
New cards
ch 2 : potential energy and electrons
==Potential energy :== energy due to location
* The closer the electrons are to the nucleus, the lower the energy level. The farther the electrons are to the nucleus, the higher the energy level.
* The closer the electrons are to the nucleus, the lower the energy level. The farther the electrons are to the nucleus, the higher the energy level.

21
New cards
ch 2 : valence and valence electrons
@@valence@@ : # that shows how well atom can combine w/other atoms through covalent bonds
* is determined by %%valence electrons%% : which are the outermost electrons
* is determined by %%valence electrons%% : which are the outermost electrons
22
New cards
ch 2 : full valence shells
a full valence shell causes an atom to become unreactive
* the goal of every atom is to have a full valence shell which they can gain through ==covalent bonding (sharing electrons)== or %%ionic bonding ( transferring electrons )%%
* when an atom is reactive it either gives or takes electrons
* the goal of every atom is to have a full valence shell which they can gain through ==covalent bonding (sharing electrons)== or %%ionic bonding ( transferring electrons )%%
* when an atom is reactive it either gives or takes electrons
23
New cards
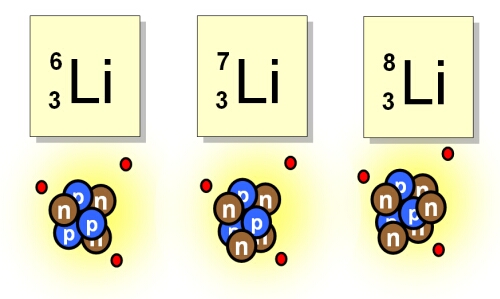
ch 2 : Isotopes
Isotopes : atom with the same %%# of protons%% and ^^electrons^^ as other of same elements but **has** **a different amount of neutrons** **( causes a different atomic mass )**
* even with diff atomic masses they behave the same in chemical reactions
* even with diff atomic masses they behave the same in chemical reactions
24
New cards
ch 2 : chemical bonds and how they form
chemical bonds are attraction between two atoms from covalent ( sharing electrons ) or ionic (transfer electrons ) bonds
* only valence electrons can participate in chemical reactions ( interactions with other atoms )
* only valence electrons can participate in chemical reactions ( interactions with other atoms )
25
New cards
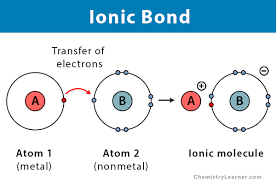
Ch 2 : Ionic bonds
**transfer of valence electrons**
* one atom is more electronegative
* transfer creates ions ( charged particles ) of different charges
* ==anions ( - charged )== ( have more electrons than protons b/c they gained electrons )
* %%cations ( + charged%% ) ( have more protons than electrons b/c they lost electrons )
* Opposites attract : Cations and anions are attracted to each other
* the strength is affect by environment : ionic bonds become weak in cells
* **between atoms**
* one atom is more electronegative
* transfer creates ions ( charged particles ) of different charges
* ==anions ( - charged )== ( have more electrons than protons b/c they gained electrons )
* %%cations ( + charged%% ) ( have more protons than electrons b/c they lost electrons )
* Opposites attract : Cations and anions are attracted to each other
* the strength is affect by environment : ionic bonds become weak in cells
* **between atoms**
26
New cards
Ch 2 : covalent bond
**sharing of valence electrons (custody agreement )**
* can be polar ( one parent hogs kids )
* can be non polar ( parents share kids equally )
* ==Polar :== one atom is more electronegative than other = atom with higher electronegativity hogs electrons
* %%Non polar :%% both atoms have a similar electronegativity and share electrons equally
* **is between atoms**
* can be polar ( one parent hogs kids )
* can be non polar ( parents share kids equally )
* ==Polar :== one atom is more electronegative than other = atom with higher electronegativity hogs electrons
* %%Non polar :%% both atoms have a similar electronegativity and share electrons equally
* **is between atoms**

27
New cards
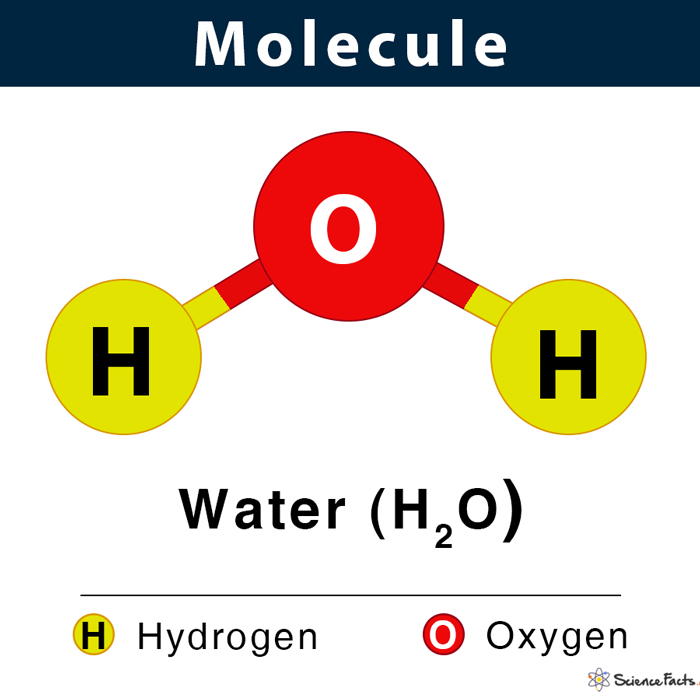
ch 2 : molecule
2 or more atoms held by a covalent bond ( sharing electrons)
28
New cards
ch 2 : what does it mean to be electronegative
have more strength to pull electrons
29
New cards
ch 2 : hydrogen bonds
weak chemical bond . formed when slightly %%positive hydrogen atom of a polar covalent%% ( unequal sharing ) in one molecule is attracted to a ==negative atom of a polar covalent bond== .OPPOSITEs attract ( + and - )
* **this bond is between whole molecules**
* **this bond is between whole molecules**
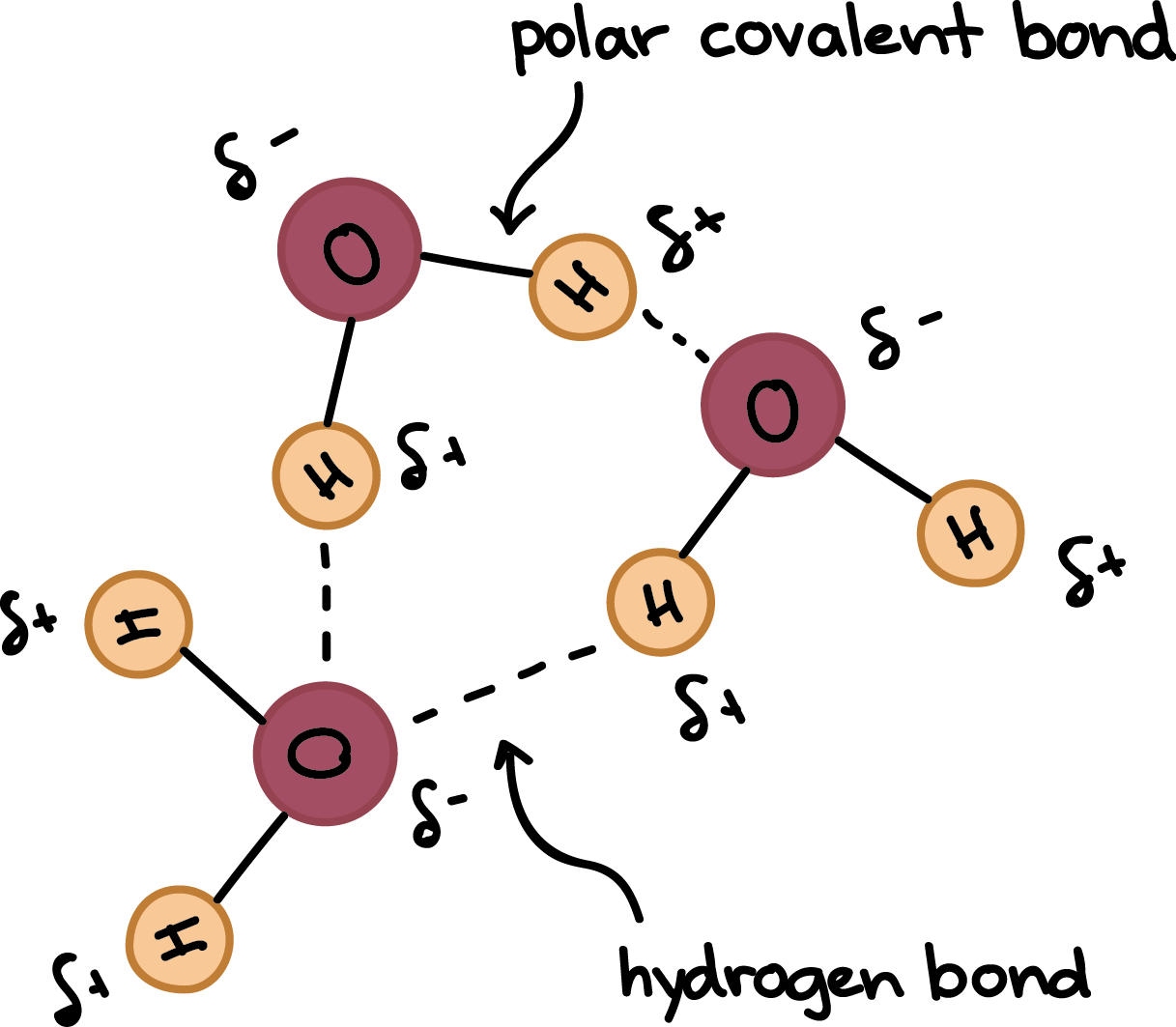
30
New cards
ch 2 : strong bonds vs weak bonds
%%strong bonds :%% needs a lot of force to break and to make
* covalent and ionic
==weak bonds :== easily breakable and easy to make
* hydrogen and van der waals
* covalent and ionic
==weak bonds :== easily breakable and easy to make
* hydrogen and van der waals
31
New cards
ch 2 : what determines the shape of a molecule
the bonds between the atoms in a molecule determine the molecules shape . the bonds are determined by valence electron arrangement
* changing shape alters function ( think of a key )
* changing shape alters function ( think of a key )
32
New cards
ch 2 : what happens to matter as chemical reaction occurs
Matter is rearranged as chemical bonds are made and broken
* Matter ( energy ) is not destroyed
* all atoms have to be on both sides in chemical equations
* most reactions are reversible
* Matter ( energy ) is not destroyed
* all atoms have to be on both sides in chemical equations
* most reactions are reversible

33
New cards
ch 2 : chemical equilibrium
Point where forward and reverse reactions occur at same rate causing c@@oncentrations to stop changing@@
* @@equal rates of reactions@@
* @@equal rates of reactions@@

34
New cards
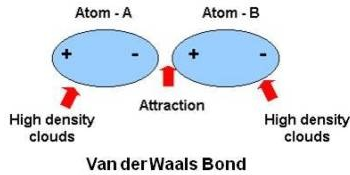
ch 2 : van der Waals
regions of + and - charge ( even in non polar covalent bonds)
* allows atoms and molecules to stick together
* allows atoms and molecules to stick together

35
New cards
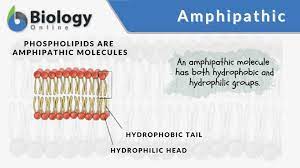
Ch 2 : Amphipathic molecules
part polar (hydrophilic ) and part non polar (hydrophobic) ; polar parts attract to water and non polar rejects
* phospholipid bilayer
* phospholipid bilayer
36
New cards
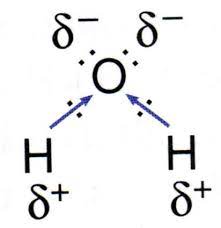
Ch 3 : Chemical structure of water
H20
* oxygen is more electronegative ( hogs electrons , partial neg charge ) than hydrogen ( partial pos charge )
* oxygen is more electronegative ( hogs electrons , partial neg charge ) than hydrogen ( partial pos charge )
37
New cards
Ch 2 : non polar molecules
non polar covalent bonds ( sharing electrons equally b/c of similar electronegativity ) are hydrophobic
* don’t like water
* don’t like water

38
New cards
ch 2 : polar molecule
polar covalent bonds ( one atom has more elctronegativity and hogs electrons ; not sharing equally ) are hydrophilic
* they do like water
* they do like water

39
New cards
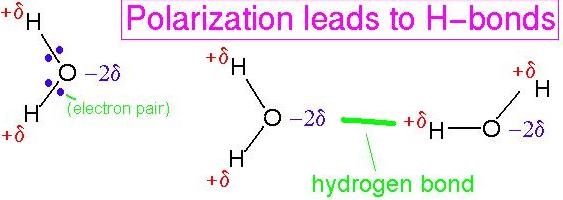
ch 3 : water’s internal and external bonds
**internal polar** (hydrophilic ) **covalent** ( no equal sharing b/c oxygen is more electroneg. ) causes **external hydrogen bonds** ( - and + molecules attract )
40
New cards
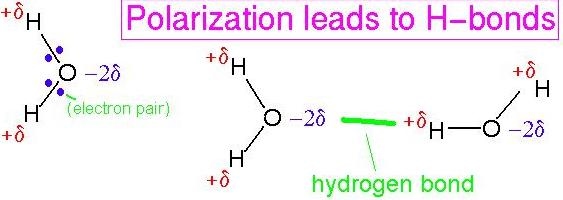
ch 3 : water bonding with water (cohesion )
When water bonds with water it causes hydrogen bonds ( - and + polar covalent in a molecule attracted to each other )
* this is called cohesion
* this is called cohesion
41
New cards
ch 3 : how does water’s ability to form hydrogen binds affect it’s properties
* allows for cohesion (hydrogen bonds holding together )
* high surface tension (difficultly breaking surface of a liquid )
* adhesion (water bonding to something else )
* floating of ice on water ( water is more dense as a solid than liquid )
* high surface tension (difficultly breaking surface of a liquid )
* adhesion (water bonding to something else )
* floating of ice on water ( water is more dense as a solid than liquid )
42
New cards
ch 3 : properties that result b/c of water’s polarity (hydrophilic - attracted to water )
* cohesion
* ice floating on water ( spread out b/c hydrogen bonds )
* water being a solvent ( dissolving agent )
* ice floating on water ( spread out b/c hydrogen bonds )
* water being a solvent ( dissolving agent )

43
New cards
ch 3 : how does a high specific heat and high heat of vaporization impact cells ? Organisism
* Water resists temp changes b/c of hydrogen bonds . Heat absorbed by water is used to break hydrogen bonds and release heat
* bodies of water moderate temp , organisms resist temp change , evaporative cooling allows temp stability for organism regions and planet
* bodies of water moderate temp , organisms resist temp change , evaporative cooling allows temp stability for organism regions and planet
44
New cards
ch 3 : specific heat
amount of heat absorbed or lost to change temp
45
New cards
ch 3 : heat of vaporization
quantity of heat required to change from liquid to gas
46
New cards
ch 3 : soultion
liquid that is a homogeneous ( evenly distributed ) mixture of two or more substances
47
New cards
H +
hydrogen ion
48
New cards
OH -
hydroxide ion
49
New cards
ch 3 : why does ice float on water
water is less dense as a solid than liquid
* water expands as it solidifies
* hydrogen bonds lock into place as water freezes
* water expands as it solidifies
* hydrogen bonds lock into place as water freezes

50
New cards
ch 3 : what kinds of molecules can water dissolve
* **Ions** ( - and + )
* **Polar** ( unequally sharing , hydrophilic )
* Ionic compounds ( transferring of valence electrons ) (salt)
* **covalent** polar ( sugar )
* large molecules w/polar/ionic regions
* **Polar** ( unequally sharing , hydrophilic )
* Ionic compounds ( transferring of valence electrons ) (salt)
* **covalent** polar ( sugar )
* large molecules w/polar/ionic regions
51
New cards
ch3 : adhesion
water sticks to something else ( charges or partial charges )
* allows plants to transport h2o
* allows plants to transport h2o
52
New cards
ch 3 : cohesion
water sticks to water , linking of like molecules by hydrogen bonds
* allows plants to transport h20
* causes high surface tension
* allows plants to transport h20
* causes high surface tension
53
New cards
ch 3 : solvent
dissolving agent of solution
* example : water
* example : water
54
New cards
ch 3 : solute
substance dissolved in solution
55
New cards
ch 3 : hydrophilic
water loving ; polar ( don’t share e equally ) won’t always dissolve , attracted to water molecules
56
New cards
ch 3 : hydrophobic
water fearing ; non polar ( share electrons equally ) hydrogen carbon bonds

57
New cards
Ch 3 : dissociation of water
hydrogen ion (h+ ) moves to another water molecule leaving its electron behind

58
New cards
ch 3 : 3 characteristics of dissociation of water
* reversible
* rare
* reactive hydrogen ion
* rare
* reactive hydrogen ion
59
New cards
ch 3 : acids
substance that %%**increases hydrogen ion concentration**%%
* donates a H + (hydrogen ion )
* more hydrogen (H+ ) than hydroxide (OH-)
* ex: Hydrochloric acid
* donates a H + (hydrogen ion )
* more hydrogen (H+ ) than hydroxide (OH-)
* ex: Hydrochloric acid

60
New cards
ch3 : bases
substance that ==**decreases hydrogen ion concentration**==
* accepts H + (hydrogen ion )
* less H + than OH - ( hydroxide )
* accepts H + (hydrogen ion )
* less H + than OH - ( hydroxide )
61
New cards
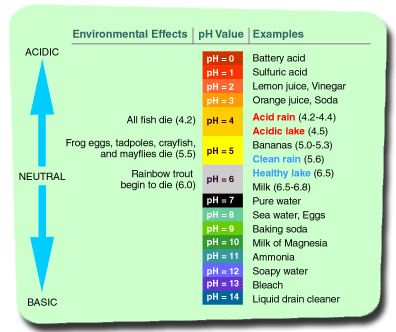
Ch 3 : PH SCALE
Numerical method for expression range of hydrogen ion in concentrations
* 0 to 14
* 7 is neutral ( equal amount of hydrogen ion to hydroxide )
* small # more acidic
* ph changes molecular structure
* 0 to 14
* 7 is neutral ( equal amount of hydrogen ion to hydroxide )
* small # more acidic
* ph changes molecular structure
62
New cards
ch 3 : strong and weak acids and bases
==**strong**==
* acids and bases completely ionized ( break apart) when dissolved in water
* **dissociate completely ( break apart )**
* shown with single arrow
**weak**
* **partially dissociates ( partially break apart )**
* shown with double arrow
%%**dissociation**%% is a chemical reaction where a compound breaks into two or more parts.
* acids and bases completely ionized ( break apart) when dissolved in water
* **dissociate completely ( break apart )**
* shown with single arrow
**weak**
* **partially dissociates ( partially break apart )**
* shown with double arrow
%%**dissociation**%% is a chemical reaction where a compound breaks into two or more parts.

63
New cards
Ch 3 : Buffers and how they work
buffers are substances that minimize changes of hydrogen and hydroxide ions
* accepts hydrogen (h + ) when there’s too much and donate hydrogen when there not enough
* accepts hydrogen (h + ) when there’s too much and donate hydrogen when there not enough
64
New cards
ch 4 : how does carbon bond
carbon has 4 valence electrons
* forms single or double covalent bonds ( sharing custody )
* carbon based molecules have structural diversity
* forms single or double covalent bonds ( sharing custody )
* carbon based molecules have structural diversity
65
New cards
Ch 4 : Isomers
Compounds w/ the same # of atoms of same elements , have different structures which cause different properties
* equal parts different properties
same molecular formula - diff structure - diff properties
\
\
* equal parts different properties
same molecular formula - diff structure - diff properties
\
\

66
New cards
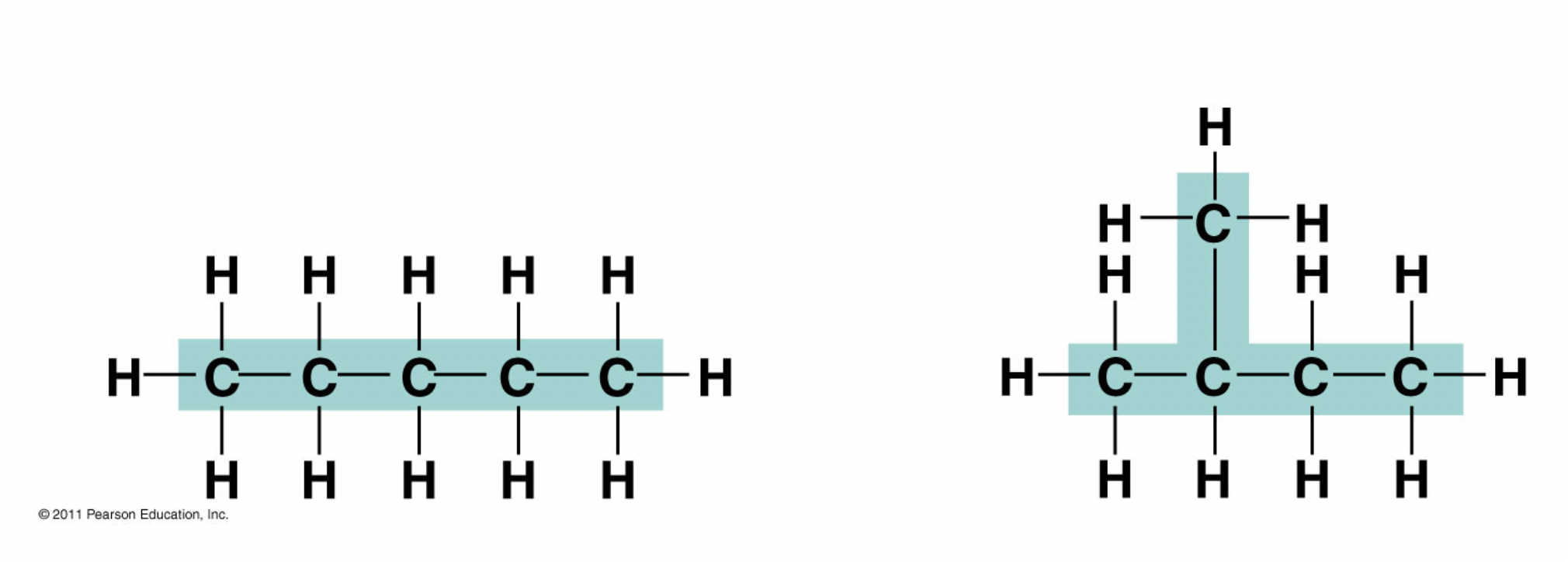
Ch 4 : Structural isomers
same formula , different arrangement
* covalent bonds b/w atoms
* more possible structural isomers as molecule gets bigger
* covalent bonds b/w atoms
* more possible structural isomers as molecule gets bigger
67
New cards
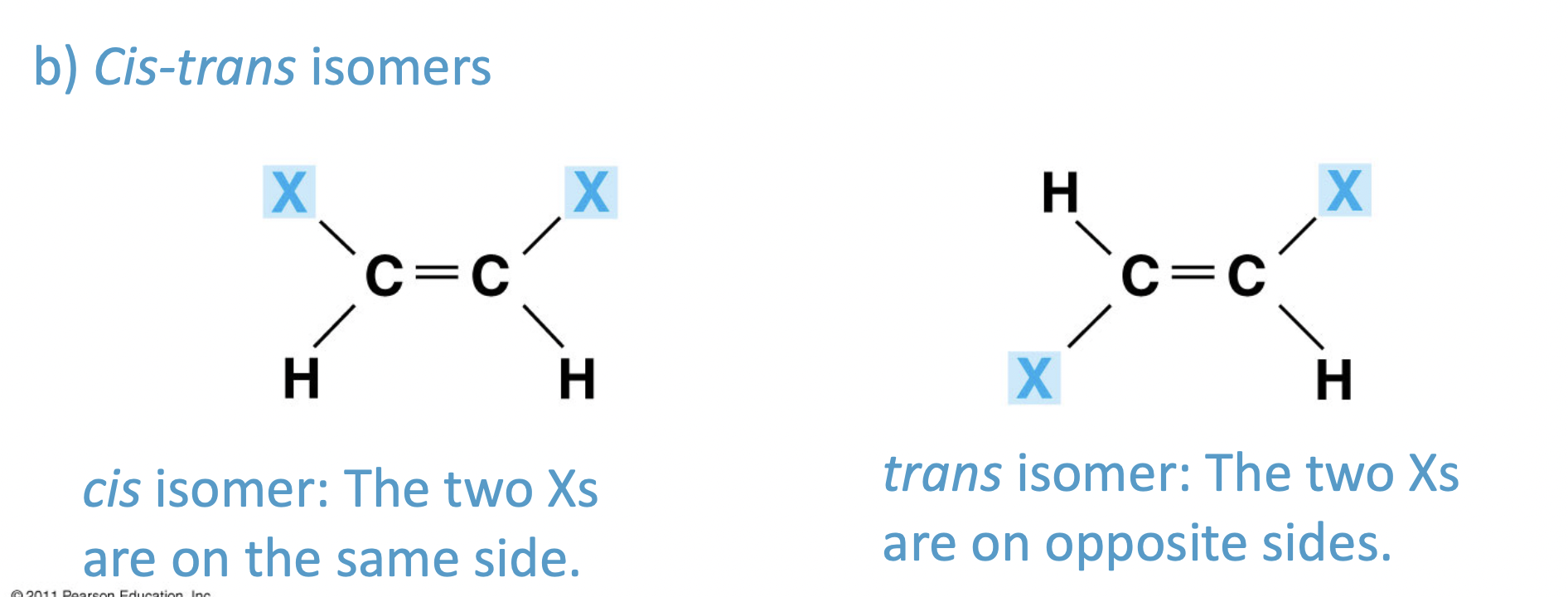
ch 4 : cis - trans isomers
arrangement of functional groups in relation to double bonds (or sometimes rings)
%%Cis :%% the two are on the same side
* Think of sisters
==Trans== : the two are on opposite sides
**different shapes = different functions**
\
%%Cis :%% the two are on the same side
* Think of sisters
==Trans== : the two are on opposite sides
**different shapes = different functions**
\
68
New cards
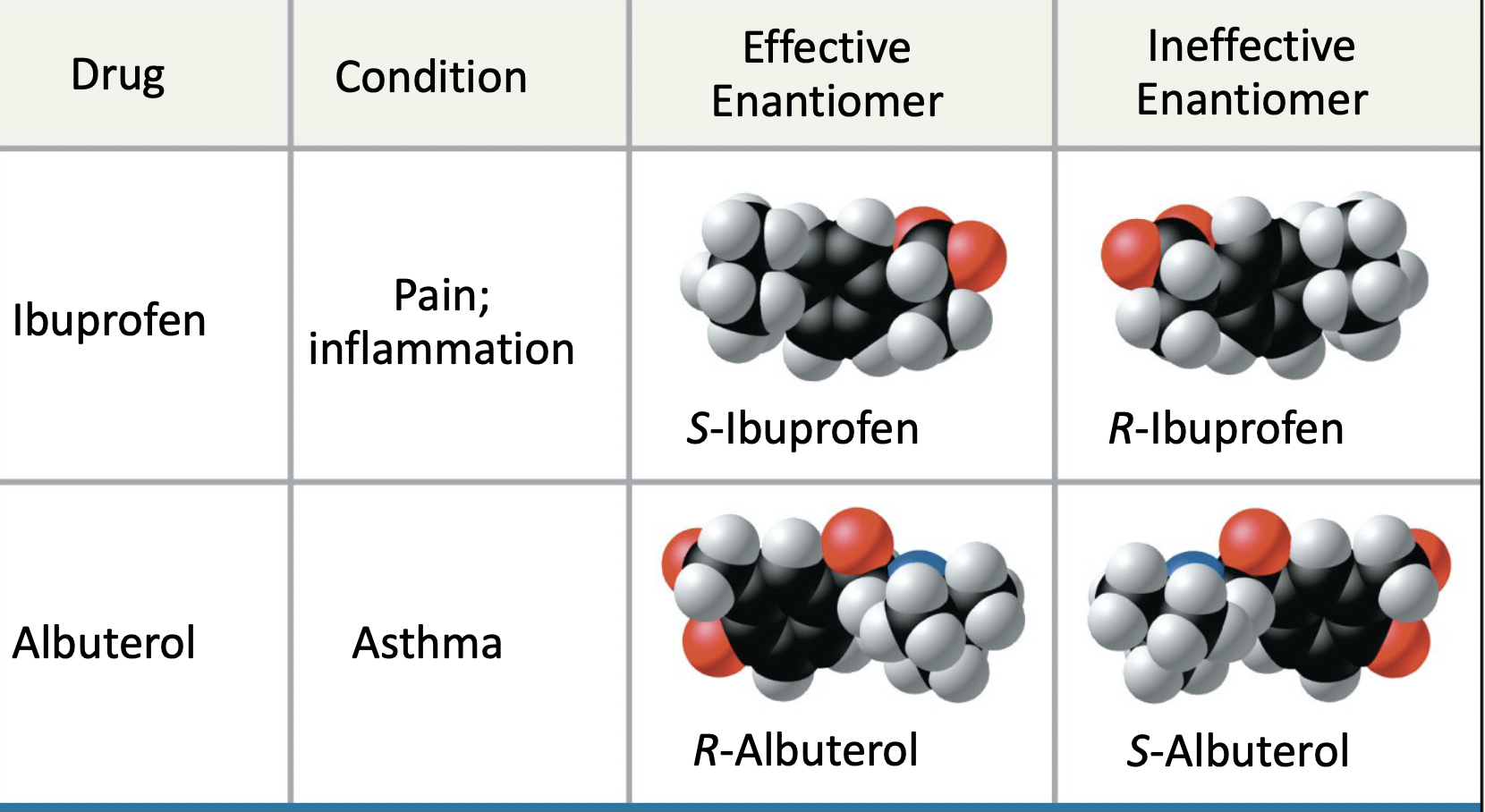
ch 4 : enantiomers
mirror images ( left and right hand )
* different shapes = different functions
* right handed molecule won’t fit into left handed molecule spot
* different shapes = different functions
* right handed molecule won’t fit into left handed molecule spot
69
New cards
functional groups
specific groups of atoms that affect molecular function by being directly involved in chemical reactions.
70
New cards
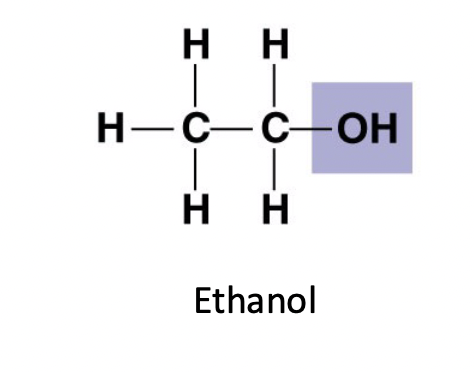
Hydroxyl (-OH )
==Alcohols==
* Names end in -ol
* Polar ( hydrophilic )
* Forms hydrogen bonds with water molecules ( dissolve in water )
* Names end in -ol
* Polar ( hydrophilic )
* Forms hydrogen bonds with water molecules ( dissolve in water )
71
New cards
Carbonyl ( C=O)
%%•Sugars%%
* names end in -oses
* polar
Two types
* Ketone- carbonyl in the middle
* Aldehyde- carbonyl at the end
* names end in -oses
* polar
Two types
* Ketone- carbonyl in the middle
* Aldehyde- carbonyl at the end

72
New cards
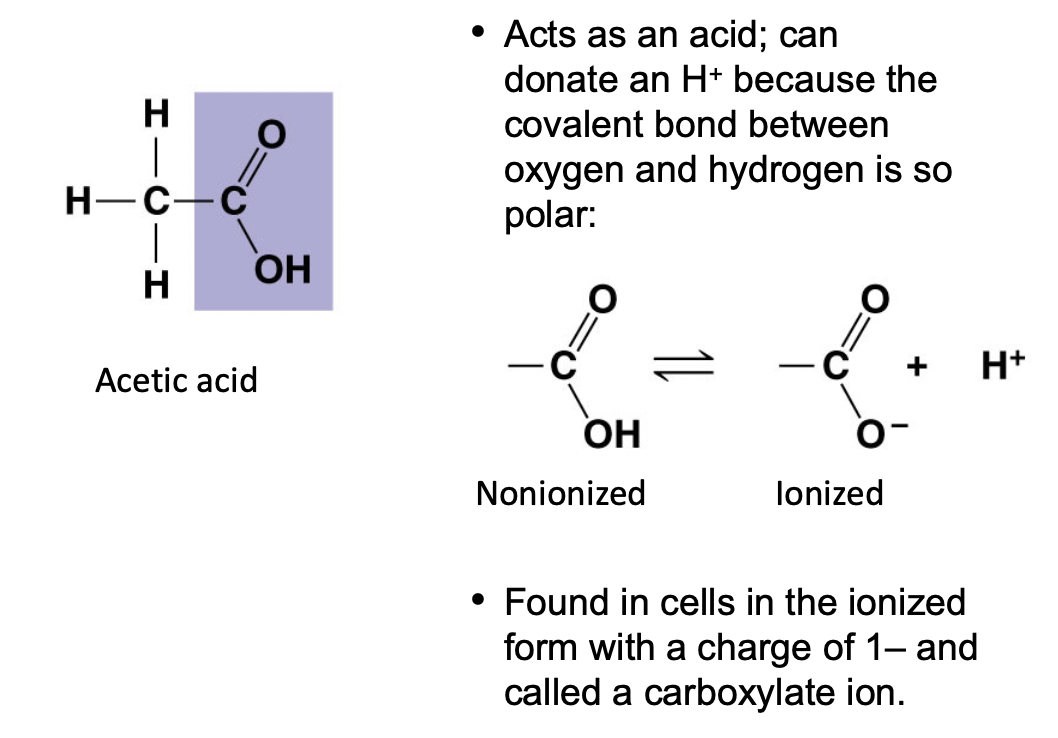
Carboxyl ( - COOH)
* ==Acts as an acid== because of the polar covalent bond between O and H
* (-) charged
* Found in cells as the carboxylate ion
* (-) charged
* Found in cells as the carboxylate ion
73
New cards
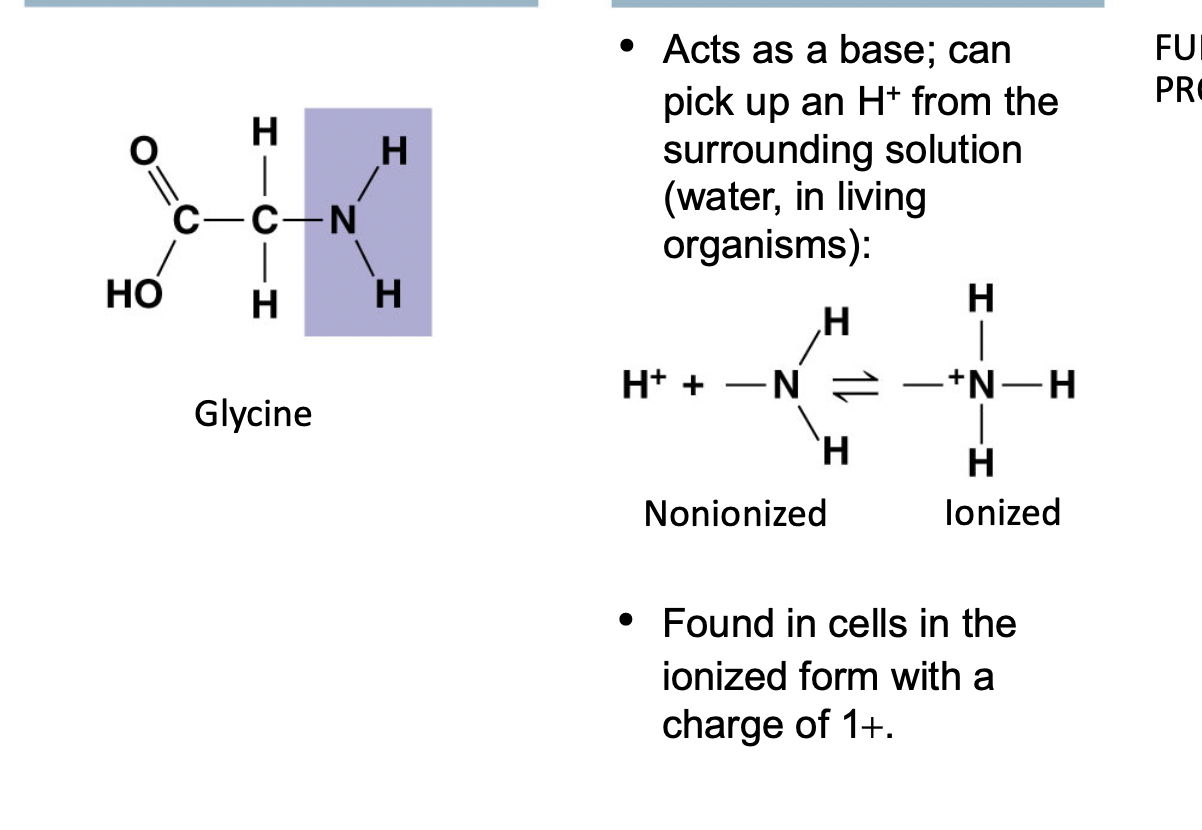
Amino ( - NH2 )
^^Acts as a base (+) charged^^
* Found in cells in ionized form
* Amino acids have a ==carboxyl group== and an %%amino group%%
* Found in cells in ionized form
* Amino acids have a ==carboxyl group== and an %%amino group%%
74
New cards
Sulfhydryl ( -SH)
Cross links: two sulfhydryl groups can bond covalently which stabilizes protein structure
polar
polar
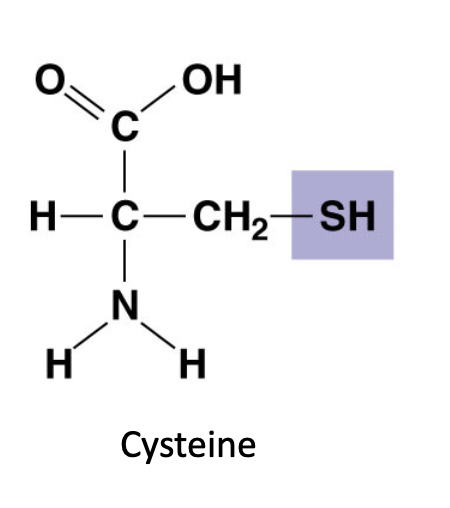
75
New cards
Phosphate ( -OP3)
* Acts as an acidic
* (-) charge
* hydrophilic
* (-) charge
* hydrophilic
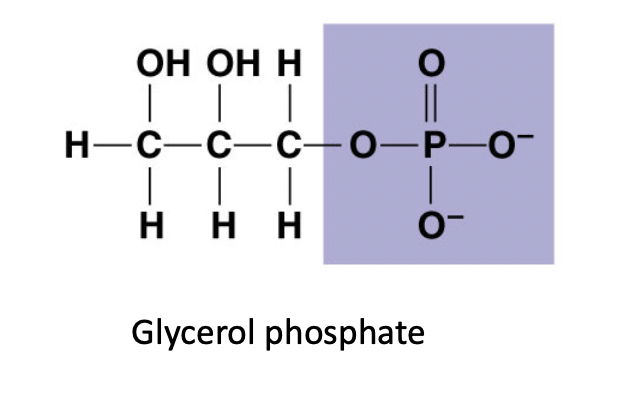
76
New cards
Methyl (-CH3)
* Isn’t a functional group b/c its not reactive
* Acts as a tag
* Affects gene expression when bound to DNA
* Affects shape and function of molecules, like sex hormones
* NON POLAR
* Acts as a tag
* Affects gene expression when bound to DNA
* Affects shape and function of molecules, like sex hormones
* NON POLAR

77
New cards
Ch 4 : ATP and its purpose
Adenosine triphosphate
* “molecular currency”
* Transports chemical energy within cells
* transfer of energy b/w molecules
* “molecular currency”
* Transports chemical energy within cells
* transfer of energy b/w molecules
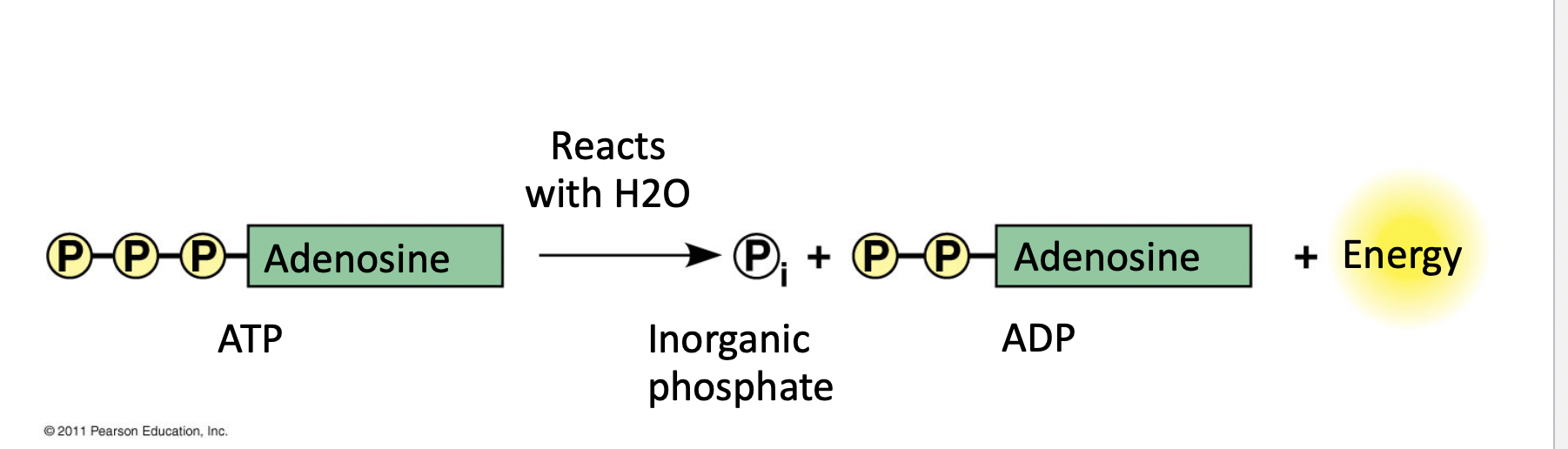
78
New cards
Ch 5 : Macromolecules
macromolecules are giant polymers formed by joining of small monomers ( train cars )
* monomers linked by covalent bonds
* monomers linked by covalent bonds
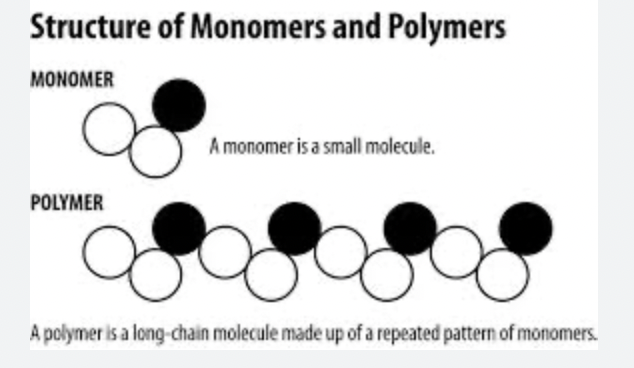
79
New cards
Ch 5 : dehydration synthesis
water is lost to form a bond b/w 2 molecules
* Water is taken away to make something new
* Water is taken away to make something new
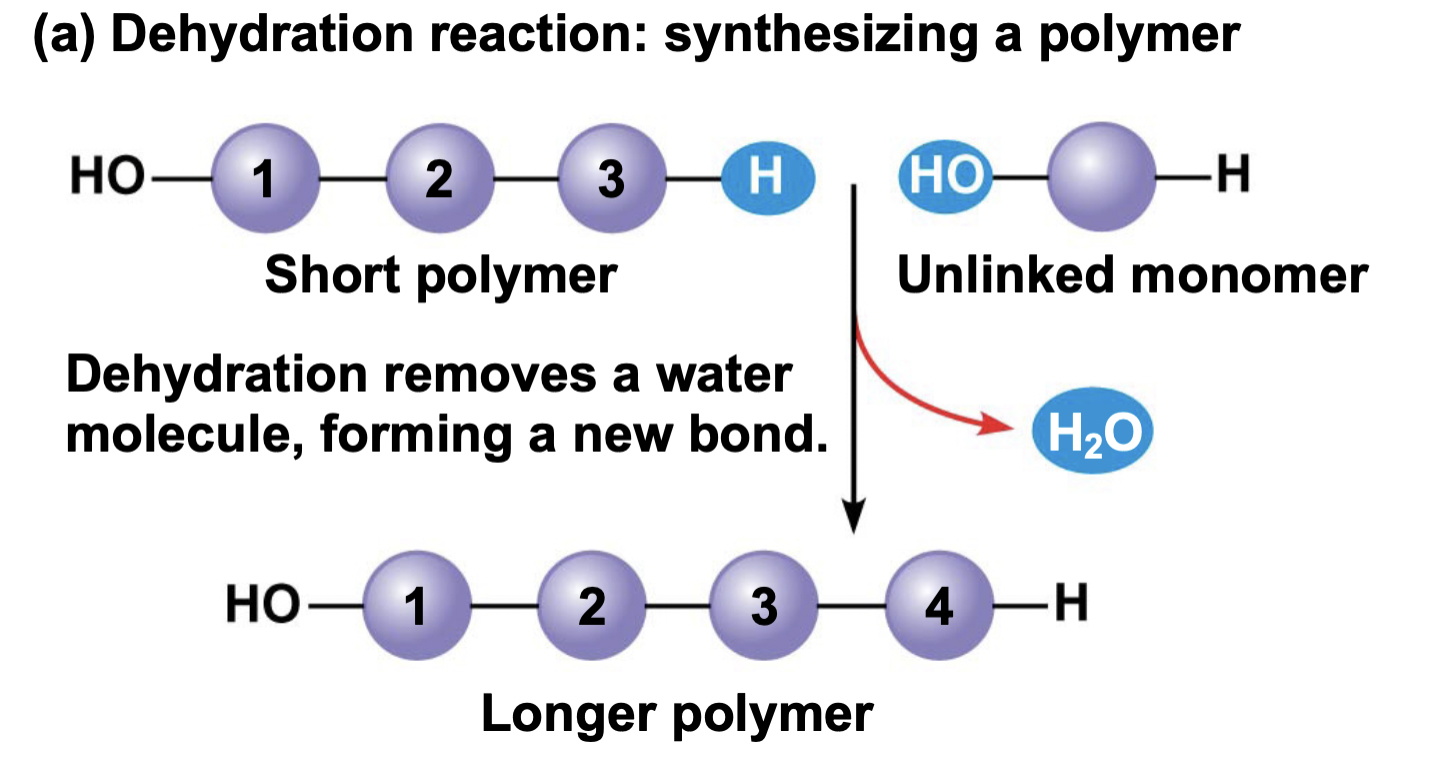
80
New cards
ch 5 : hydrolysis
water is gained to break a bond and form two molecules
* breaking down into small parts
* breaking down into small parts
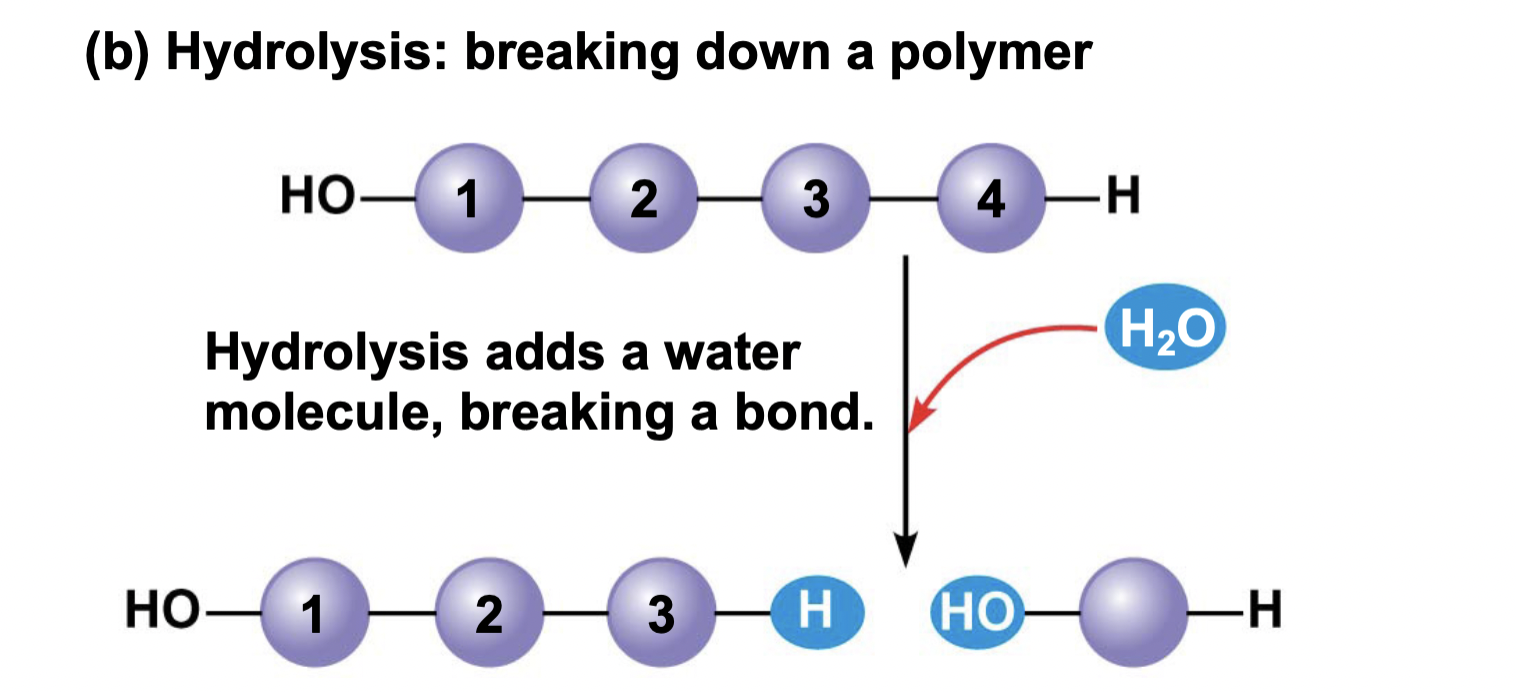
81
New cards
Ch 5 : how are polymers covalent bonds formed and broken ?
* Monomers connected by ^^dehydration reaction^^ (water is lost to form a bond b/w 2 molecules )
* Polymers broken by ==hydrolysis== (water is gained to break a bond and form two molecules)
* Polymers broken by ==hydrolysis== (water is gained to break a bond and form two molecules)
82
New cards
Ch 5 : enzymes
enzymes are
* macromolecule
* end in -ase
* catalyst (increase rate of reaction)
* proteins
* macromolecule
* end in -ase
* catalyst (increase rate of reaction)
* proteins
83
New cards
Ch 5 : cataylst
Facilitates reaction but is not consumed by reaction
84
New cards
Ch 5 : carbohydrates
sugars that end in -ose
* Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen
* Carbonyl group
* monomers : monosaccharides
* Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen
* Carbonyl group
* monomers : monosaccharides
85
New cards
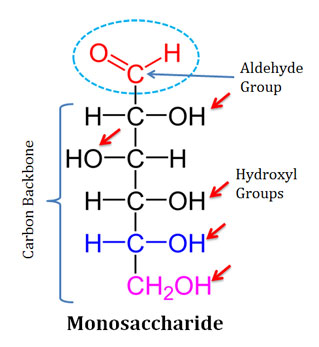
Ch 5 : Monosaccharides
one sugar
* building block of carbohydrates
* CxH2xOx
* Example: Glucose
* Source of energy and raw materials for cell
* building block of carbohydrates
* CxH2xOx
* Example: Glucose
* Source of energy and raw materials for cell
86
New cards
Ch 5 : Disaccharides
two sugars
* two monosaccharides joined through dehydration synthesis
* example : glucose + fructose = sucrose ( disaccharide)
* two monosaccharides joined through dehydration synthesis
* example : glucose + fructose = sucrose ( disaccharide)
87
New cards
Ch 5 : Polysaccharides
* Many sugar
* Storage molecule for energy
* Structural molecule
* Storage molecule for energy
* Structural molecule
88
New cards
Ch 5 : Cellulose
Plant structural polysaccharide
* In plant cell walls
* Unbranched polymer of glucose which allows for microfibrils
* Linked differently than starch resulting in different shape
* Different enzymes needed to break the different linkages
* Called β linkages
* In plant cell walls
* Unbranched polymer of glucose which allows for microfibrils
* Linked differently than starch resulting in different shape
* Different enzymes needed to break the different linkages
* Called β linkages
89
New cards
Ch 5 : Glycogen
In animals
* Polysaccharide storage molecule
* Branched polymer of glucose
* Polysaccharide storage molecule
* Branched polymer of glucose
90
New cards
ch 5 : starch
In plants
* Polysaccharide for storage
* May be amylose and/or amylopectin
* Amylo- “starch”
* Amylose- unbranched polymer of glucose
* Amylopectin- branched polymer of glucose
* Polysaccharide for storage
* May be amylose and/or amylopectin
* Amylo- “starch”
* Amylose- unbranched polymer of glucose
* Amylopectin- branched polymer of glucose
91
New cards
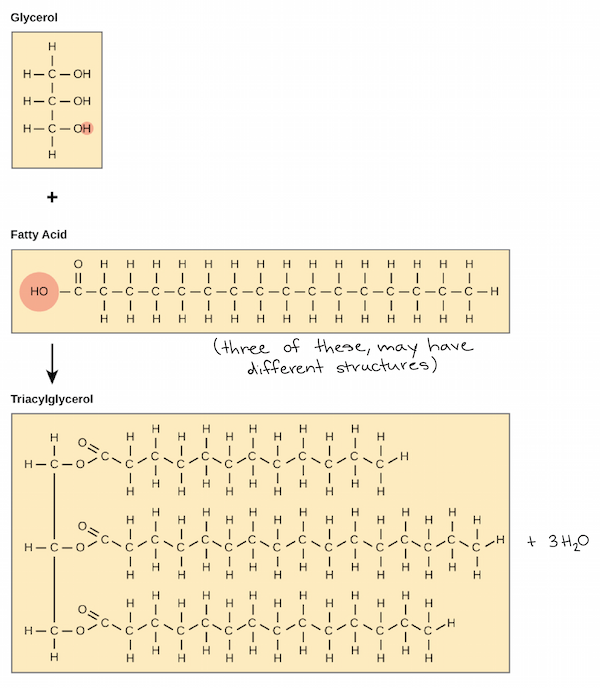
Ch 5 : Lipids
Hydrophobic molecules
* fats , phospholipid , steroids
* hydrophobic b/c of main hydro-carbon regions that are non polar
* building blocks : glycerol and fatty acids
* fats , phospholipid , steroids
* hydrophobic b/c of main hydro-carbon regions that are non polar
* building blocks : glycerol and fatty acids
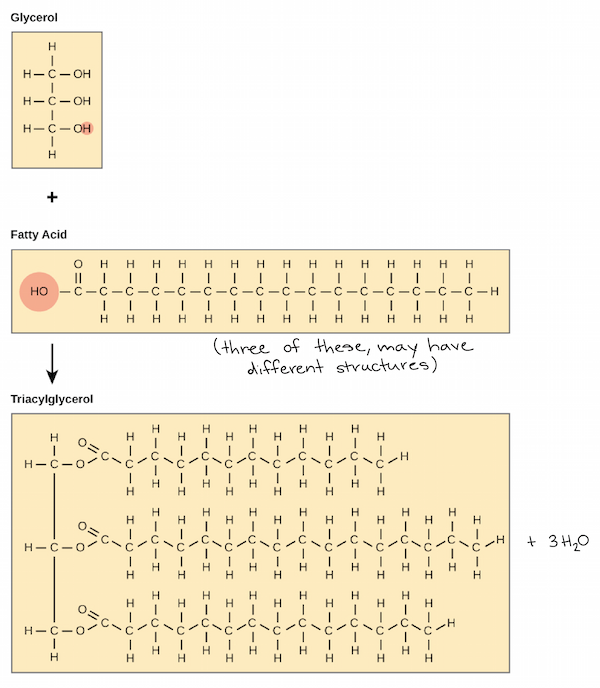
92
New cards
Ch 5 : Fats
Large molecules assembled from smaller molecules by a dehydration reaction
* function : energy storage
* function : energy storage
93
New cards
Ch 5 : Phospholipids
Hydrophobic tails and hydrophilic head
* Bilayer structure in aqueous environment
* Cell membranes have phospholipid bilayers
* Bilayer structure in aqueous environment
* Cell membranes have phospholipid bilayers
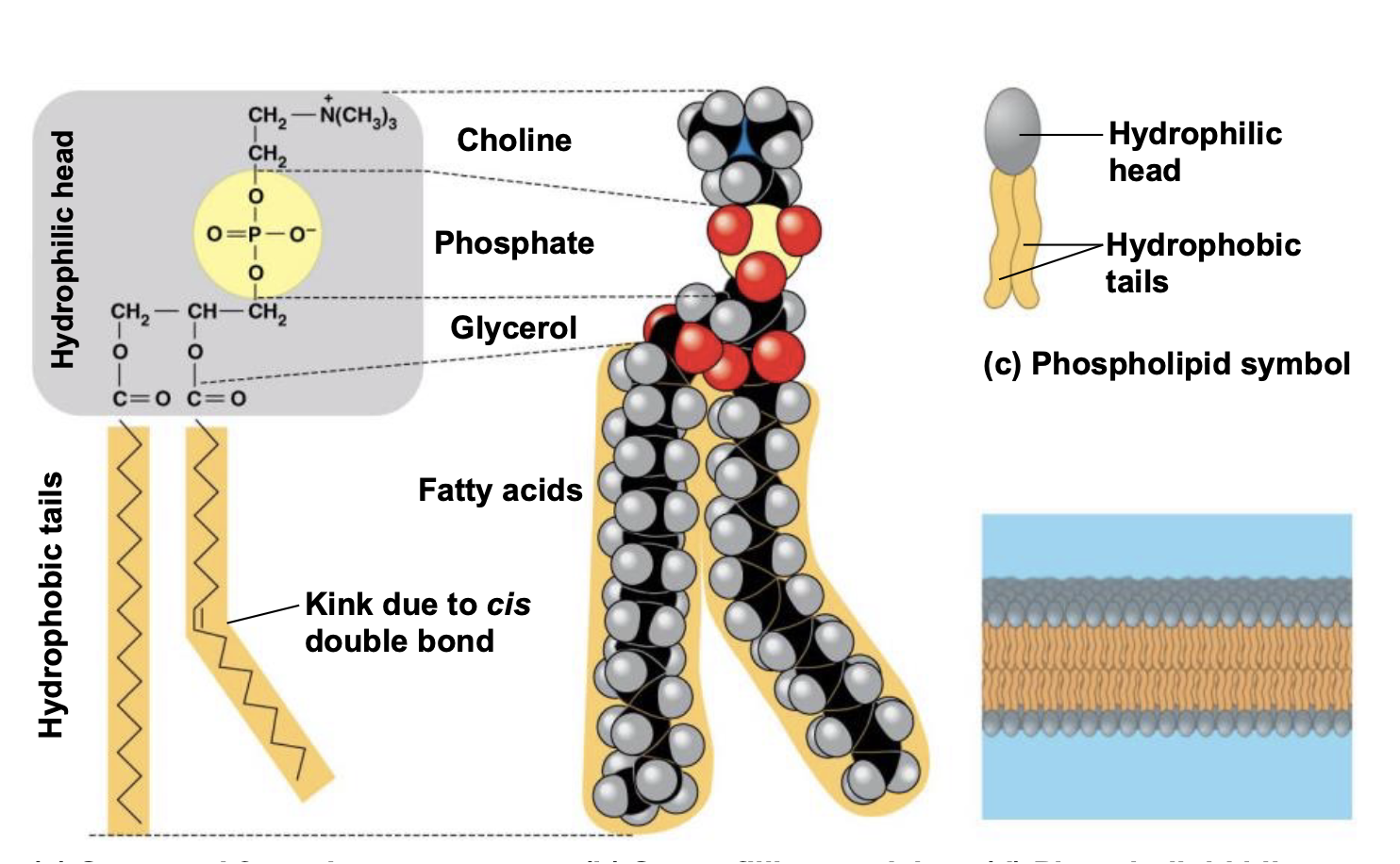
94
New cards
Ch 5 : Steroids
Lipids with 4 carbon rings
must have a hydroxyl group ( polar )
must have a hydroxyl group ( polar )
95
New cards
Ch 5 : Unsaturated and Saturated fats
%%Unsat%%
* Cis double bonds
* Fewer hydrogens
* Liquid at room temperature because the double bonds cause kinks in the chain and cannot pack tightly together
* Plants and fish, called oils
Sat
* No double bonds
* Hydrogen in every available spot
* Solid at room temp because the molecules can pack close together
* Cis double bonds
* Fewer hydrogens
* Liquid at room temperature because the double bonds cause kinks in the chain and cannot pack tightly together
* Plants and fish, called oils
Sat
* No double bonds
* Hydrogen in every available spot
* Solid at room temp because the molecules can pack close together
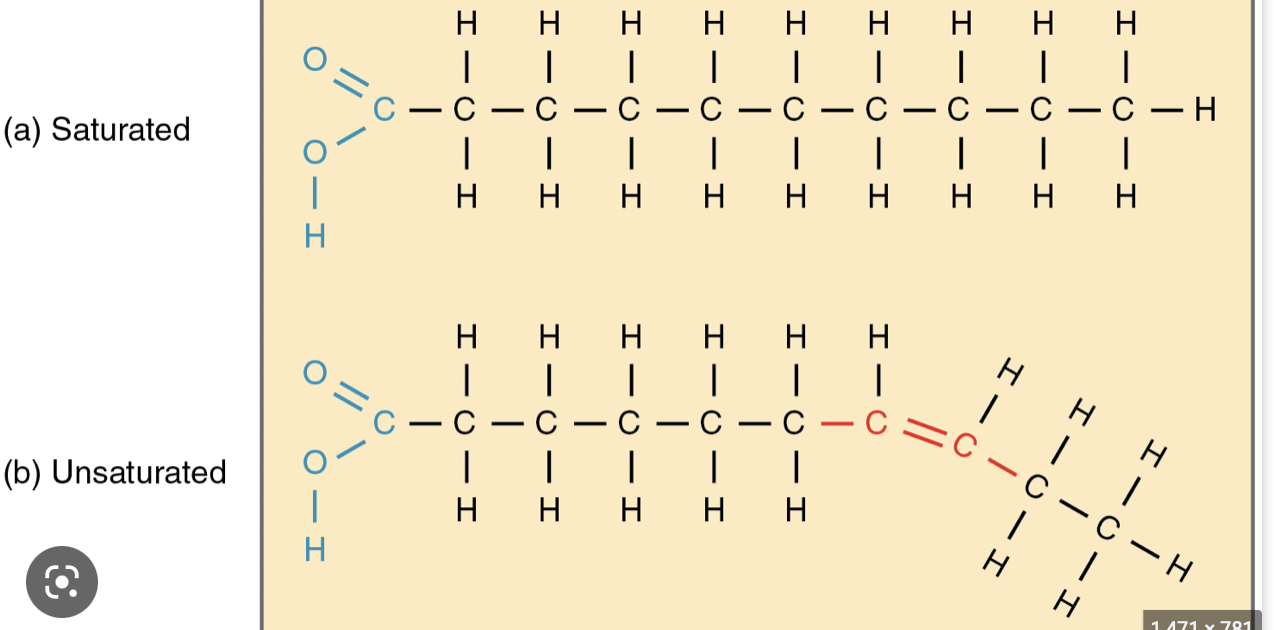
96
New cards
Ch 5 : proteins
* Un-branched polymers of amino acids
* Monomers : amino acids
* An amino acid has both a carboxyl group and an amino group
* Monomers : amino acids
* An amino acid has both a carboxyl group and an amino group
97
New cards
Ch 5 : amino acid monomer
* Amino group
* Alpha carbon
* Carboxyl group
* R group (side chain)
* r group determines properties of amino acid
* Alpha carbon
* Carboxyl group
* R group (side chain)
* r group determines properties of amino acid
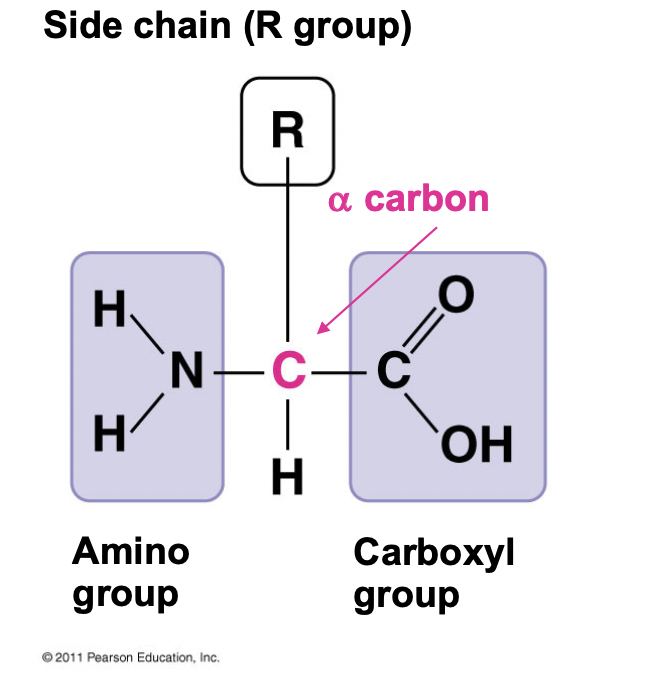
98
New cards
Ch5 : what determines Properties of a protein
Structure determines funciton
* %%**R groups**%% (side chains) outnumber the ends so the properties of the side chains determine the properties of the polypeptide
* %%**R groups**%% (side chains) outnumber the ends so the properties of the side chains determine the properties of the polypeptide
99
New cards
Ch 5 : Polypeptide
When amino acids are covalently bonded together (peptide bonds) by a dehydration reaction they make a long chain of linked amino acids
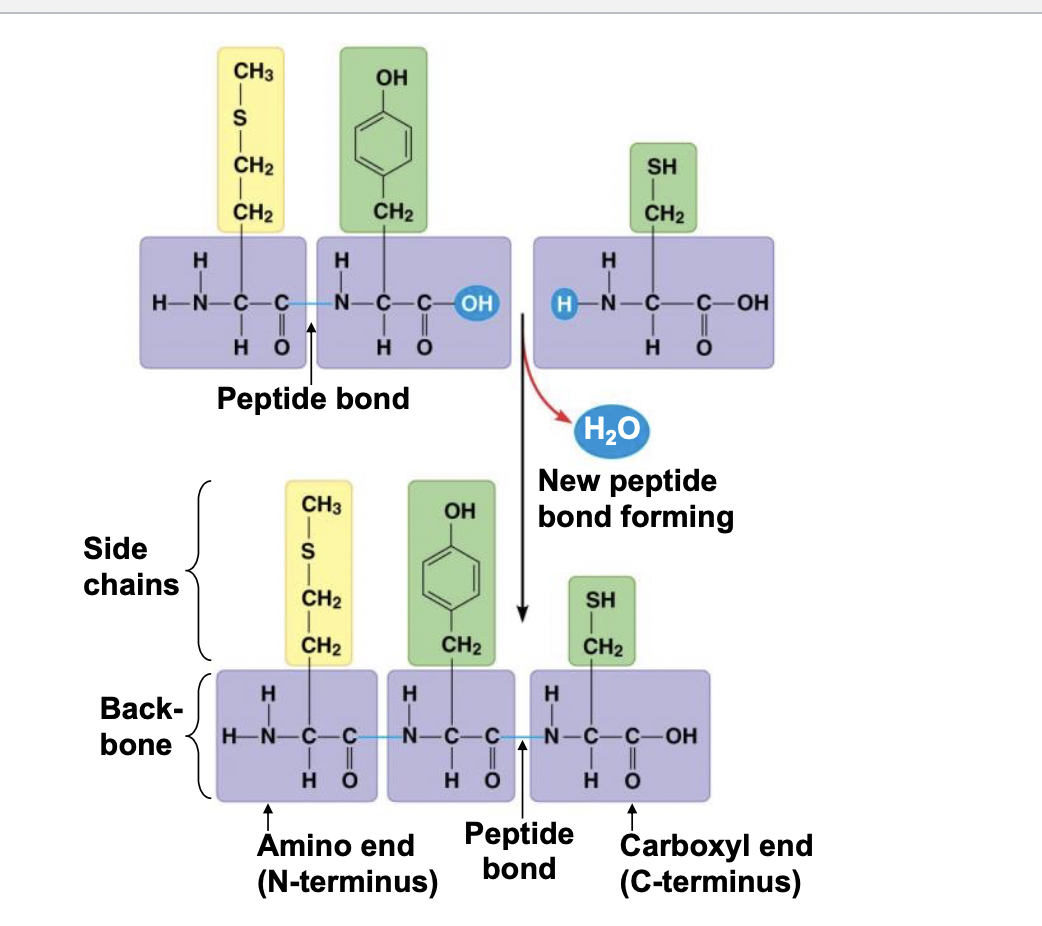
100
New cards
Ch 5 :what determines protein structure
SEQUENCE OF AMINO ACIDS