Bioenergetics and Metabolism: ATP, Glycolysis, and Oxidative Phosphorylation
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
What is metabolism?
The total of all cellular reactions, including anabolic (synthesis) and catabolic (breakdown) reactions.
Define bioenergetics.
The process of converting energy stored in chemical bonds (like glucose or fatty acids) into high energy bonds in ATP.
What is ATP?
Adenosine Triphosphate, a high-energy molecule that provides energy for various cellular processes.
What are the components of ATP?
Adenine, ribose, and three phosphate groups.
How is energy from food substrates converted in ATP?
Energy from food substrate molecules is converted into phosphate bond energy in ATP.
What happens to ATP during muscle contractions?
The rate of ATP hydrolysis can increase up to 100 times compared to rest during intense contractions.
What is the role of ATP in muscle cells?
ATP provides energy for processes such as synthesis, transport, work, and heat.
What are the three general pathways of ATP supply?
Anaerobic, aerobic, and oxidative phosphorylation.
What is anaerobic metabolism?
A metabolic process that does not require oxygen.
What is oxidative phosphorylation?
A group of metabolic pathways that produce ATP by harnessing energy from carbohydrates, fats, and amino acids, requiring oxygen.
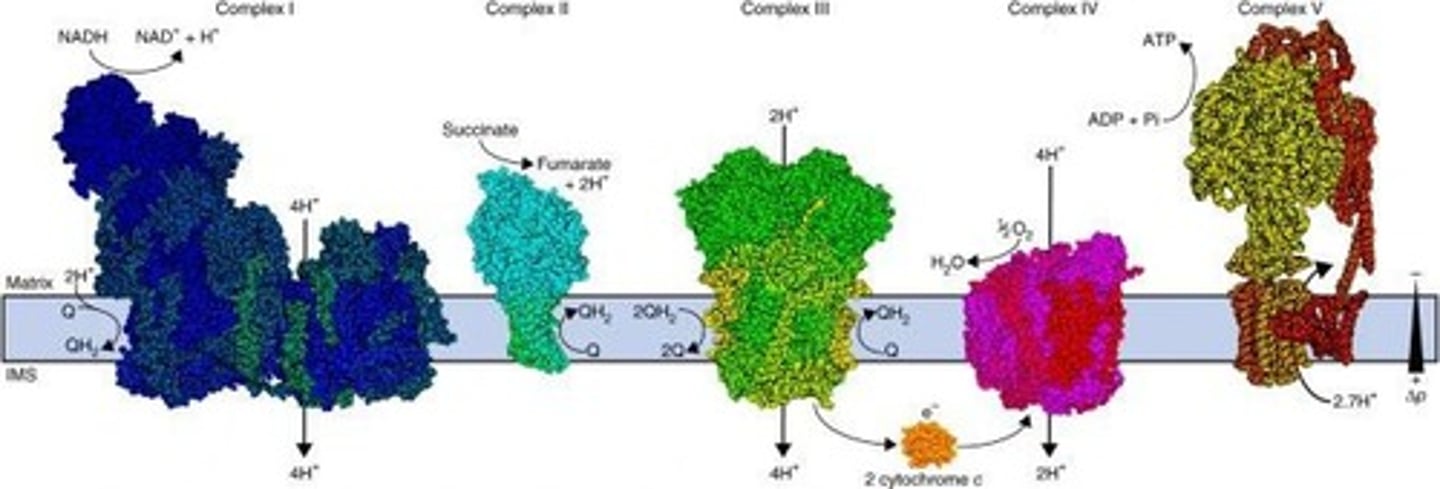
What is glycolysis?
An anaerobic process occurring in the cytosol that breaks down glucose to produce ATP.
What is the net yield of glycolysis?
2 lactate + 2 H+ + 2 ATP from blood glucose or 3 ATP from glycogen.
What is the function of glycogen synthase?
It adds glucosyl units to glycogen, helping to store glucose.
What are the two phases of glycolysis?
Energy investment phase and energy extraction phase.
What is the role of lactate in muscle metabolism?
Lactate can be converted back to pyruvate in the mitochondria or transported to neighboring muscle cells.
What are the three stages of oxidative metabolism?
Formation of Acetyl-CoA, harnessing energy via NADH and FADH2, and donating electrons to the electron transport chain.
What is the chemiosmotic hypothesis?
It explains how ATP is formed from ADP and Pi using the energy from the H+ electrochemical gradient in the electron transport chain.
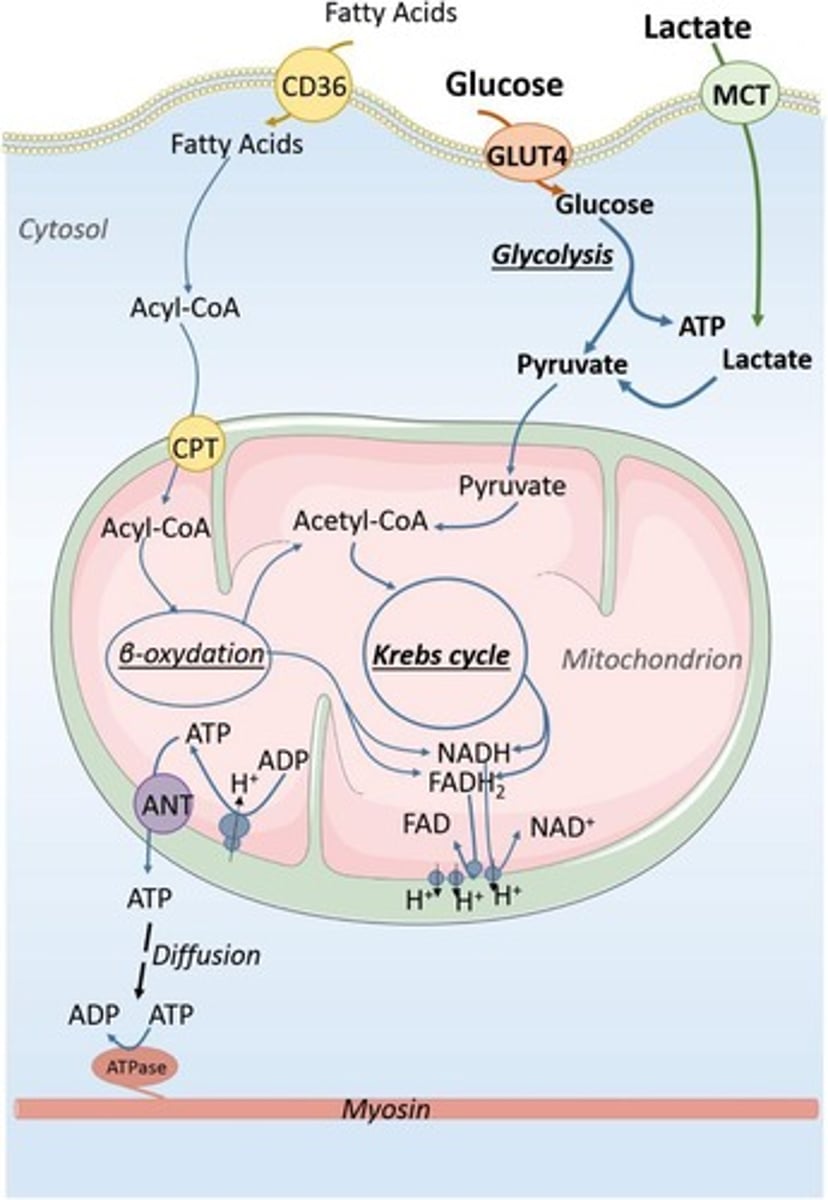
What is the importance of ATP supply matching ATP demand?
If ATP supply does not meet demand, homeostasis is compromised, leading to impaired contractile function and fatigue.
What is the role of pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH)?
It converts pyruvate from glycolysis into Acetyl-CoA for entry into the Krebs cycle.
What is the significance of the HEPT system?
It is important at the onset of exercise and during transitions to higher intensities.
How much ATP can be produced from glucose during aerobic metabolism?
32 ATP from one molecule of glucose.
What is the capacity of the aerobic system for ATP production?
It has a large capacity due to significant triglyceride stores and glycogen stores.
What is the role of ATPase?
It catalyzes the hydrolysis of ATP to ADP and Pi, releasing energy.
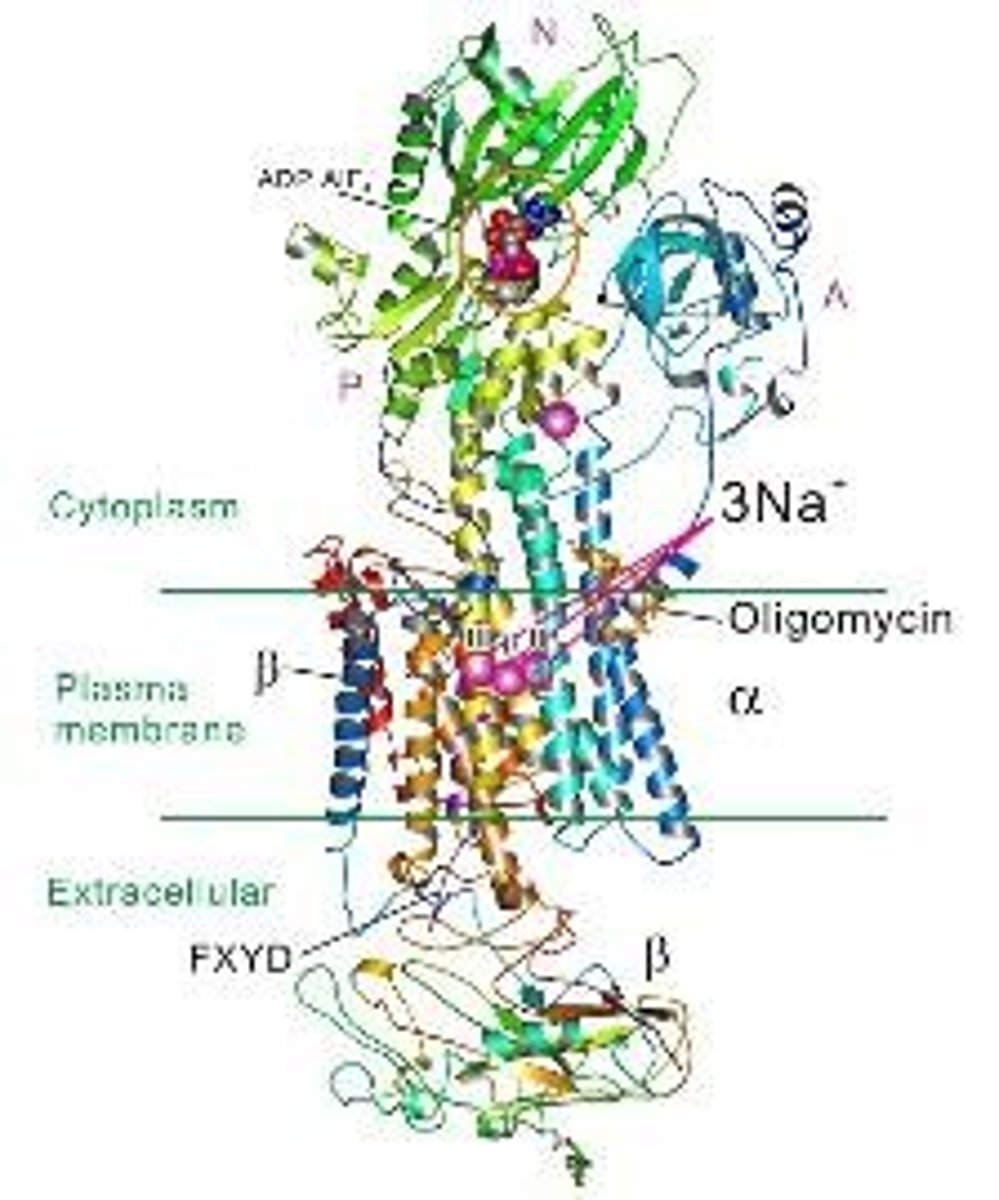
What happens to ATP during heavy exercise?
Stored ATP is used quickly, sustaining only about 2-3 seconds of heavy exercise.
What is the function of the Na+-K+ ATPase?
It helps maintain cellular ion balance by pumping sodium out and potassium into the cell.
What is the primary purpose of ATP in the body?
To sustain all body functions through energy expenditure.
What is the relationship between ATP production and foodstuffs?
ATP production requires the consumption of foodstuffs (carbohydrates, fats, and amino acids) and oxygen.
How does heat production relate to metabolic rate?
The rate of heat production is directly proportional to energy expenditure and metabolic rate.
What does direct calorimetry measure?
It accurately quantifies energy expenditure by measuring heat released by an individual.
What is the function of indirect calorimetry?
It estimates energy expenditure by measuring chemical by-products of metabolism, specifically oxygen consumption and carbon dioxide production.
How does oxygen consumption (VO2) relate to energy expenditure?
There is a direct relationship between oxygen consumption and the amount of heat produced by the body, making VO2 an indirect estimate of whole body energy expenditure.
What is the equation for the overall reaction of ATP production?
Foodstuffs + O2 → Heat + CO2 + H2O + ATP.
What does VO2 represent?
The volume of oxygen that the whole body utilizes to produce ATP in a given period of time.
How is whole body carbon dioxide production (VCO2) expressed?
It can be expressed in absolute terms (L/min or mL/min) or relative terms (mL/kg/min).
What does the respiratory quotient (RQ) indicate?
RQ reflects the composition of fuels oxidized at rest and during exercise in the body's cells.
What is the respiratory exchange ratio (RER)?
RER is measured at the mouth and estimates RQ, though its accuracy can be reduced during intense exercise.
What is the Fick equation used for?
It calculates VO2 based on cardiac output and the difference in oxygen content between arterial and venous blood.
What is the significance of VO2 kinetics?
VO2 kinetics is the exponential increase in VO2 from a prior value to a new steady-state during exercise.
What happens to ATP demand during exercise?
There is an instantaneous increase in ATP demand that is directly proportional to exercise intensity.
What is oxygen deficit?
Oxygen deficit is the difference between measured VO2 and the steady-state value after the onset of exercise.
What factors influence the slow component of excess post-exercise oxygen consumption (EPOC)?
Elevated body temperature, catecholamines, conversion of lactate to glucose, and elevated heart rate and ventilation.
What occurs during the transition from rest to submaximal exercise?
There is a rapid increase in heart rate, stroke volume, and cardiac output within the first seconds of exercise.
What is the expected change in RER at the onset of exercise?
RER is expected to increase, indicating a shift from fat oxidation to carbohydrate oxidation.
What is the significance of the Kreb's cycle in metabolism?
It is a key metabolic pathway for the production of carbon dioxide and energy during aerobic respiration.
How does exercise intensity affect substrate utilization?
Higher exercise intensity typically shifts substrate utilization from fats to carbohydrates.
What are typical VO2 values for a normal young healthy active individual at rest?
VO2 is approximately 0.25 L/min.
What is the role of mitochondria in ATP production?
Mitochondria utilize oxygen to produce ATP through oxidative phosphorylation.
What is the relationship between heart rate (HR) and stroke volume (SV) during exercise?
Both HR and SV increase to meet the elevated oxygen demand of the body during exercise.
What does the term 'steady state' refer to in exercise physiology?
Steady state refers to a condition where the body's physiological variables stabilize during prolonged exercise.
What is the effect of exercise on blood flow kinetics?
Blood flow to active muscles increases rapidly at the onset of exercise to meet metabolic demands.