Health Science study guide
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/108
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
109 Terms
1
New cards
what is a neuron?
the basic structural unit of the nervous system
2
New cards
what is a dendrite?
appendages that are designed to receive communications from other cells.
3
New cards
what is an axon?
where electrical impulses from the neuron travel away to be received by other neurons.
4
New cards
what is the myelin sheath?
an insulating layer, or sheath, that forms around nerves, including those in brain & spinal cord.
5
New cards
what is the cell body?
the compact section of a nerve that contains the nucleus and the cytoplasm.
6
New cards
what is the difference between afferent and efferent nerves?
afferent nerves carry information to the brain. efferent nerves carry motor information to the muscles and glands.
7
New cards
what is the function of the pons?
conducts messages to other parts of the brain. reflex actions including chewing, tasting, and saliva production. assisting in respiration.
8
New cards
what is the function of the medulla?
regulating heartbeat, respiration, swallowing, coughing, and blood pressure.
9
New cards
what is the function of the cerebellum?
muscle coordination, balance, posture, and muscle tone.
10
New cards
what is the function of the pituitary gland?
growth and development. controls all other endocrine glands.
11
New cards
what is the function of the frontal lobe?
emotions, personality, morality, intellect, and speech.
12
New cards
what is the function of the parietal lobe?
sensory, motor, pain, heat, and touch.
13
New cards
what is the function of the occipital lobe?
vision.
14
New cards
what is the function of the temporal lobe?
hearing and smelling.
15
New cards
what is a synapse? where does it happen?
the site of transmission of electric nerve impulses. it occurs between 2 nerve cells or between a neuron and a gland or muscle cell.
16
New cards
what makes up the PNS?
12 cranial nerve pairs and 31 spinal nerve pairs.
17
New cards
what is amyotrophic lateral sclerosis? is it treatable?
a chronic, degenerative neuromuscular disease. there is no cure but drugs may slow progress.
18
New cards
what is a cerebrovascular accident? is it treatable?
aka a stroke. when the blood flow to the brain is impaired, resulting in a lack of oxygen and a destruction of brain tissue. "clot busting" drugs can restore blood flow.
19
New cards
what is multiple sclerosis? is it treatable?
a chronic, progressive, disabling condition resulting from a degeneration of the myelin sheath in the CNS. no cure but physical therapy and muscle relaxants are used to maintain functional ability for as long as possible.
20
New cards
what is shingles? is it treatable?
an acute inflammation of nerve cells. treatments is directed towards relieving pain and itching.
21
New cards
what is cerebral palsy? is it treatable?
a disturbance in voluntary muscle action caused by brain damage. no cure. physical, occupational, and speech therapy are important. drugs, muscle relaxants, casts, braces, and/or orthopedic surgery.
22
New cards
what is parkinson's? is it treatable?
a chronic progressive involving degeneration of brain cells. no cure. drugs are used to relieve symptoms, physical therapy can also be used.
23
New cards
what is meningitis? is it treatable?
inflammation of the meninges of the brain and/or spinal cord. antibiotics, antipyretics, anticonvulsants, and/or medications for pain and cerebral edema.
24
New cards
what is epilepsy? is it treatable?
a seizure syndrome associated with abnormal electrical impulses in the neurons of the brain. no cure. anticonvulsant drugs.
25
New cards
functions of epithelial tissue?
cover the surface of body & line internal organs & form gland. protection and secretion.
26
New cards
functions of connective tissue?
support, protect, and give structure.
27
New cards
functions of muscle tissue?
power & movement
28
New cards
functions of nervous tissue?
control & coordinate.
29
New cards
what are the frontal and coronal planes?
separates the body into front and back parts.
30
New cards
what is the transverse plane?
separates the body into top and bottom parts but will never be equal.
31
New cards
superior
above
32
New cards
inferior
below
33
New cards
medial
towards middle
34
New cards
lateral
away from middle
35
New cards
anterior
moving towards front (forward)
36
New cards
posterior
moving towards back (backwards)
37
New cards
superficial
towards outside
38
New cards
deep
inside
39
New cards
proximal
on a diagonal. towards midline
40
New cards
distal
on a diagonal. away midline
41
New cards
what is the ventral cavity?
made up of thoracic, abdominal, and pelvic cavities.
42
New cards
what is the dorsal cavity?
made up of cranial and spinal cavities.
43
New cards
what organs are in the hypogastric region?
small intestine, bladder, and uterus.
44
New cards
what happens in the epidermis?
cells grow from underneath and move to the top where they die. keratinization (the hardening of cells) occurs. Melanocytes produce melanin.
45
New cards
what happens in the dermis?
fingerprints are formed. blood vessels supply nutrients to the skin.
46
New cards
what happens in the hypodermis?
temperature regulation and storage. insulation. the connection between skin and underlying muscle.
47
New cards
what are active cells?
act as a repair system for the body
48
New cards
what happens to the body when temperature rises?
blood vessels dilate and you start to sweat
49
New cards
what happens to the body when tmperature falls?
blood vessels constrict and you start to shiver
50
New cards
what are melanocytes?
cells that produce melanin which gives your skin color.
51
New cards
what bones are in the axial skeleton?
the bones in your skull, neck, and vertebrae.
52
New cards
what bones are in the appendicular skeleton?
arms, pelvis, and legs.
53
New cards
how many bones are in the body?
you are born with 300 but adults have 206.
54
New cards
what are the types of vertebrae and how many are there?
cervical (1-7) thoracic (1-12) lumbar (1-5) sacral (1-5) coccyx(1-4)
55
New cards
describe skeletal muscle.
attached to bone and causes body movement that is voluntary.
56
New cards
what is a strain?
an injury to muscle or a band of tissue that connects muscle to bone.
57
New cards
what is a sprain?
an injury to the tissue that connects two bones.
58
New cards
what is origin?
where a muscle attaches to a bone, the end that does not move.
59
New cards
what is insertion?
the end that moves when a muscle contracts.
60
New cards
a simple fracture
a crack in the bone
61
New cards
a colles fracture
a crack in the distal radius
62
New cards
a communuted fracture
a break into 3+ pieces
63
New cards
a compound fracture
when bone breaks through the skin
64
New cards
a depressed fracture
occurs in hollow bone. a concave fracture
65
New cards
a dislocation
bone is removed from the joint
66
New cards
a greenstick fracture
bone is bent until splintering occurs
67
New cards
an impacted fracture
bone crushes into itself
68
New cards
a spiral fracture
bone twists while breaking
69
New cards
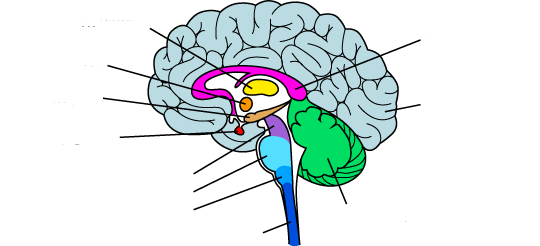
what is the yellow?
thalamus
70
New cards
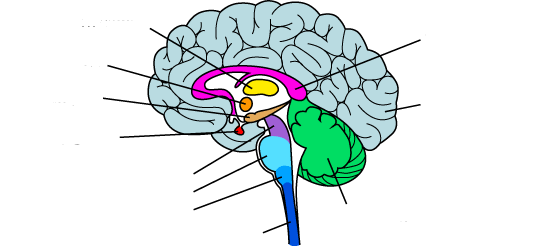
what is the orange?
hypothalamus
71
New cards
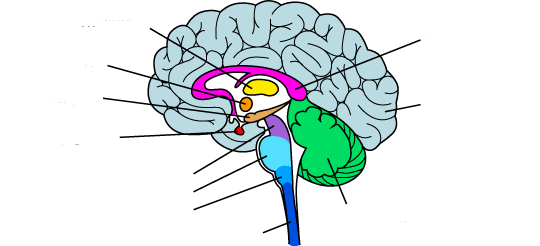
what is the red?
pituitary gland
72
New cards
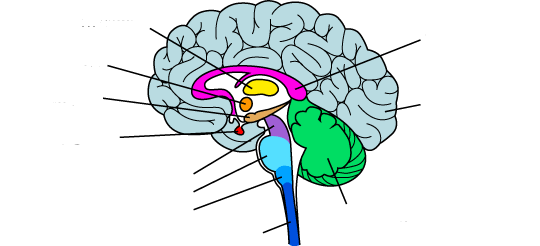
the midbrain
what is the purple?
73
New cards
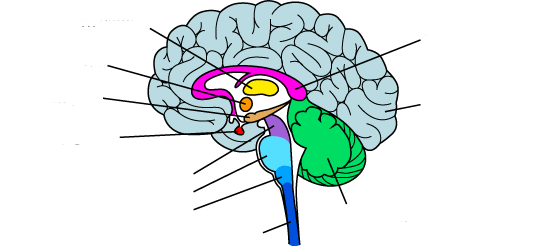
what is the light blue?
pons
74
New cards
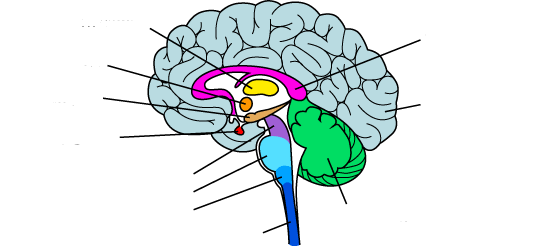
what is the medium blue?
medulla
75
New cards
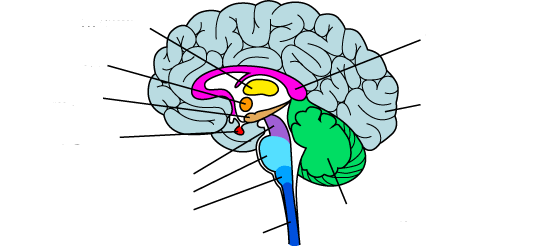
what is the dark blue?
spinal cord
76
New cards
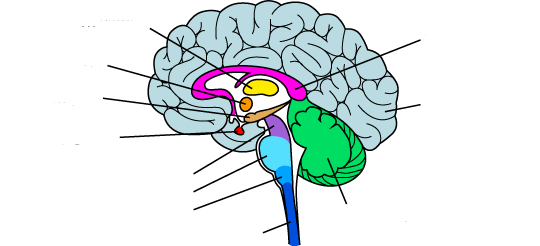
what is the light purple?
corpus callosum
77
New cards
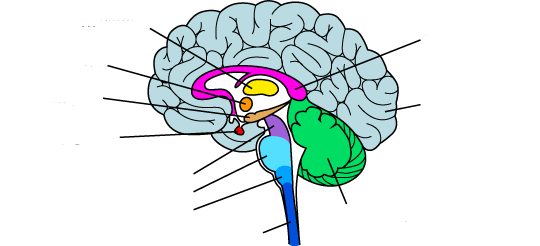
what is the light green?
the cerebellum
78
New cards
open wound descriptions
an injury involving an external break in body tissue involving the skin.
79
New cards
inflammation
tissues are injured by bacteria or toxins and cells release chemicals that cause blood vessels to leak fluid into tissue causing swelling
80
New cards
diarthrosis (synovial) joints
freely moveable. ex: ball and socket or hinge
81
New cards
amphiarthrosis joints
slightly moveable. ex: attachment of ribs to thoracic vertebrae and symphysis pubis
82
New cards
synathrosis joints
immovable. ex: suture joints in cranium
83
New cards
process of smelling
1. breath in
2. air stimulates the olfactory cells
3. impulse travels to temporal lobe through the olfactory nerve
4. temporal nerve determines smell
2. air stimulates the olfactory cells
3. impulse travels to temporal lobe through the olfactory nerve
4. temporal nerve determines smell
84
New cards
process of hearing
1. sound enters external canal
2. sound hits eardrum which vibrates & send sound into middle ear
3. sound travels from middle ear to inner ear.
4. vestibulocochlear nerve is stimulated. impulse travels to the temporal lobe.
2. sound hits eardrum which vibrates & send sound into middle ear
3. sound travels from middle ear to inner ear.
4. vestibulocochlear nerve is stimulated. impulse travels to the temporal lobe.
85
New cards
process of seeing
1. impulse occurs
2. light rays enter eye
3. optic nerve receives impulse
4. message travels to the occipital lobe
2. light rays enter eye
3. optic nerve receives impulse
4. message travels to the occipital lobe
86
New cards
process of tasting
1. eat or drink something
2. flavors are broken down & stimulate taste buds
3. brain (pons) interprets which taste buds were activated
2. flavors are broken down & stimulate taste buds
3. brain (pons) interprets which taste buds were activated
87
New cards
what are lymph vessels?
they're found throughout the body in almost all tissues that have blood vessels- pick up lymph and connect to lymph nodes
88
New cards
What are T cells?
develop stem cells in the red bone marrow
89
New cards
what are the innate defenses?
1. Species resistance
2. mechanical barriers
3. chemical barriers
4. natural killer cells
5. inflammation
6. phagocytosis
7. fever
2. mechanical barriers
3. chemical barriers
4. natural killer cells
5. inflammation
6. phagocytosis
7. fever
90
New cards
describe species resistance
certain animals are non-susceptible to certain pathogens
91
New cards
describe mechanical barriers
physically block pathogens from entering body
92
New cards
describe chemical barriers
destroy pathogens on the outer surface, body openings, & inner linings.
93
New cards
describe natural killer cells
lymphocytes that respond quickly to pathogens like viruses & cancer cells
94
New cards
describe phagocytosis
phagocytes ingest or engulf other cells of particles
95
New cards
describe fever
higher temperature releases lymphocytes
96
New cards
what is primary immune response?
1. activation of B cells or T cells
2. plasma cells release antibodies into the lymph
3. antibodies are transported to the blood and then throughout the entire body
2. plasma cells release antibodies into the lymph
3. antibodies are transported to the blood and then throughout the entire body
97
New cards
what is secondary immune response?
some B cells remain dormant as memory cells. if the same antigen is encountered again, these memory cells enlarge and respond rapidly
98
New cards
how many days does primary immune response take?
lasts 5-10 days.
99
New cards
how many days does secondary immune response take?
lasts 1-2 days
100
New cards
what is cellular immune response?
- T cells originating in red bone marrow
- primarily located in lymphatic tissue and make up 70-80% of the circulating lymphocytes in the blood
- interact directly with antigens or antigen-bearing agents to destroy them
- primarily located in lymphatic tissue and make up 70-80% of the circulating lymphocytes in the blood
- interact directly with antigens or antigen-bearing agents to destroy them