AP environmental science unit 7
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
primary pollutant
A pollutant that is put directly into the atmosphere by human or natural activity
- combustion
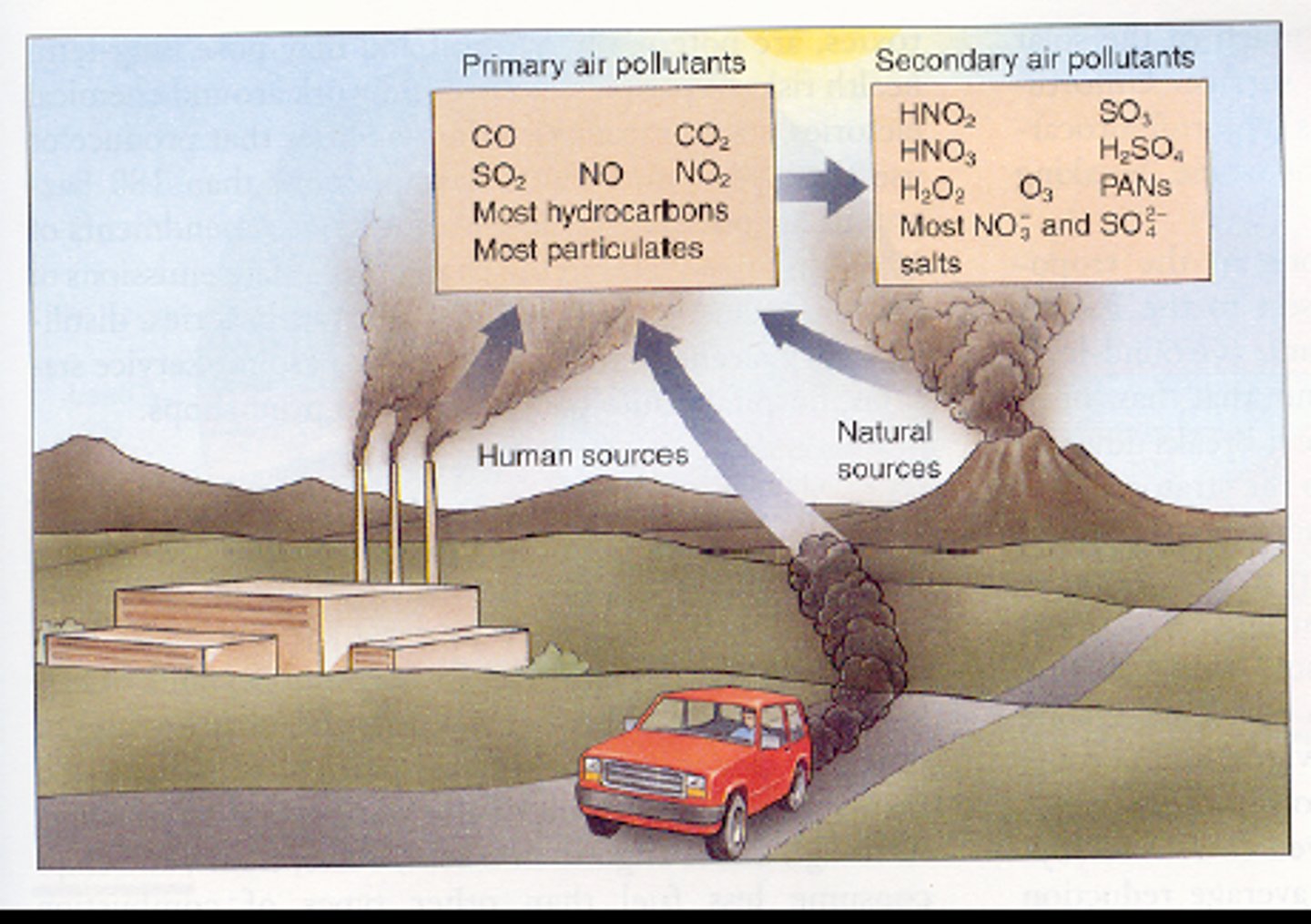
secondary pollutant
A primary pollutant that has undergone transformation in the presence of sunlight, water, oxygen, or other compounds
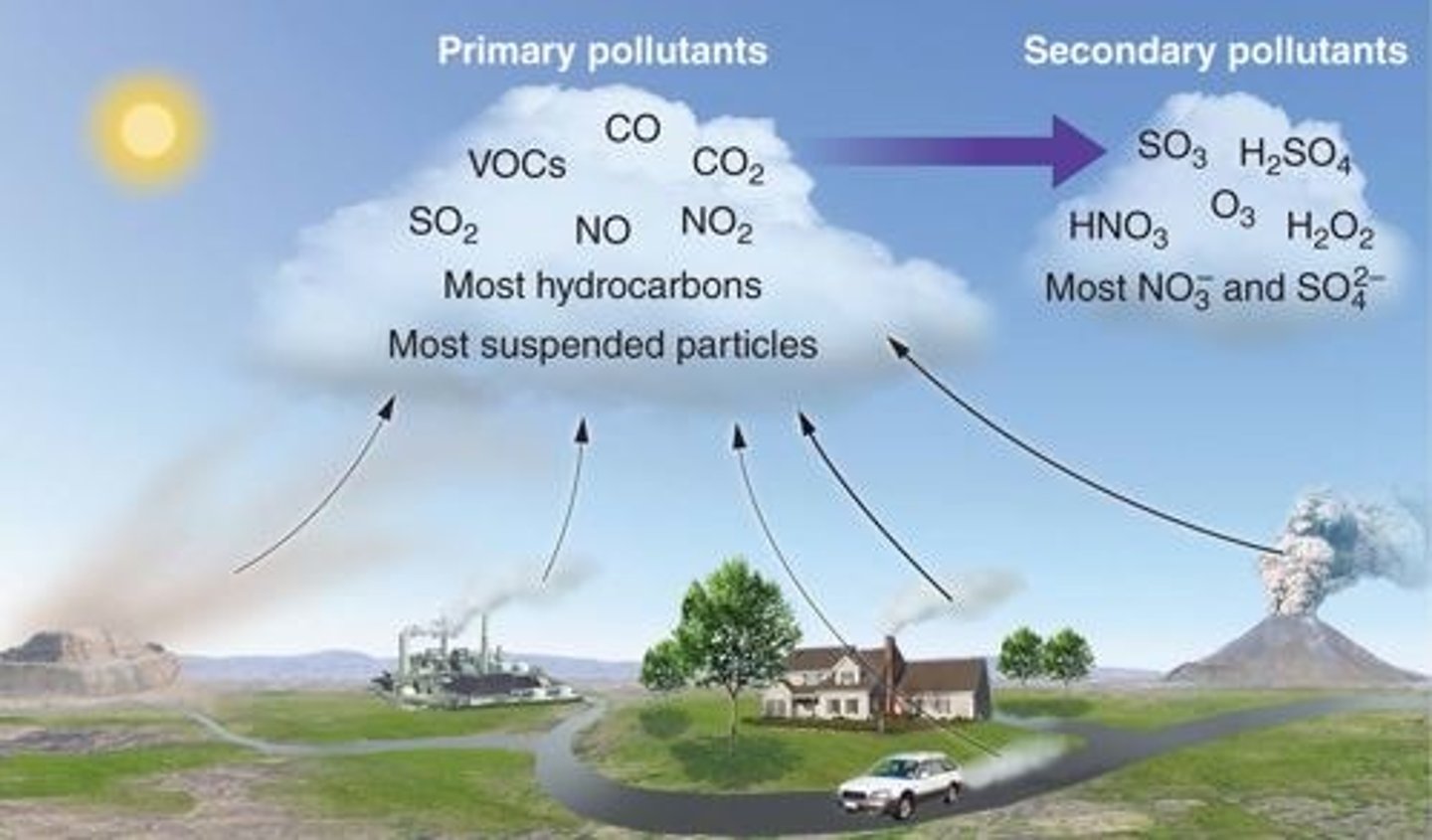
CO
carbon monoxide
- source: incomplete combustion of fossil fuels
- health impact: headaches, dizziness, unconsciousness, death
CO2
carbon dioxide
- source: volcanoes, decomposition, respiration, combustion of hydrocarbons
- health impact: increased death from rates due to heat waves, severe storms, loss of agricultural productivity
SOx
sulfur oxides
- source: combustion of fossil fuels (coal)
- health impacts: irritate nose, throat, respiratory pathway, coughing, wheezing, tightness in chest
NOx
nitrogen oxides
- source: combustion of fossil fuels (gasoline)
- health impact: irritate respiratory track, headaches, nausea, difficulty breathing
photochemical smog
air pollution that forms from the interaction between chemicals in the air and sunlight
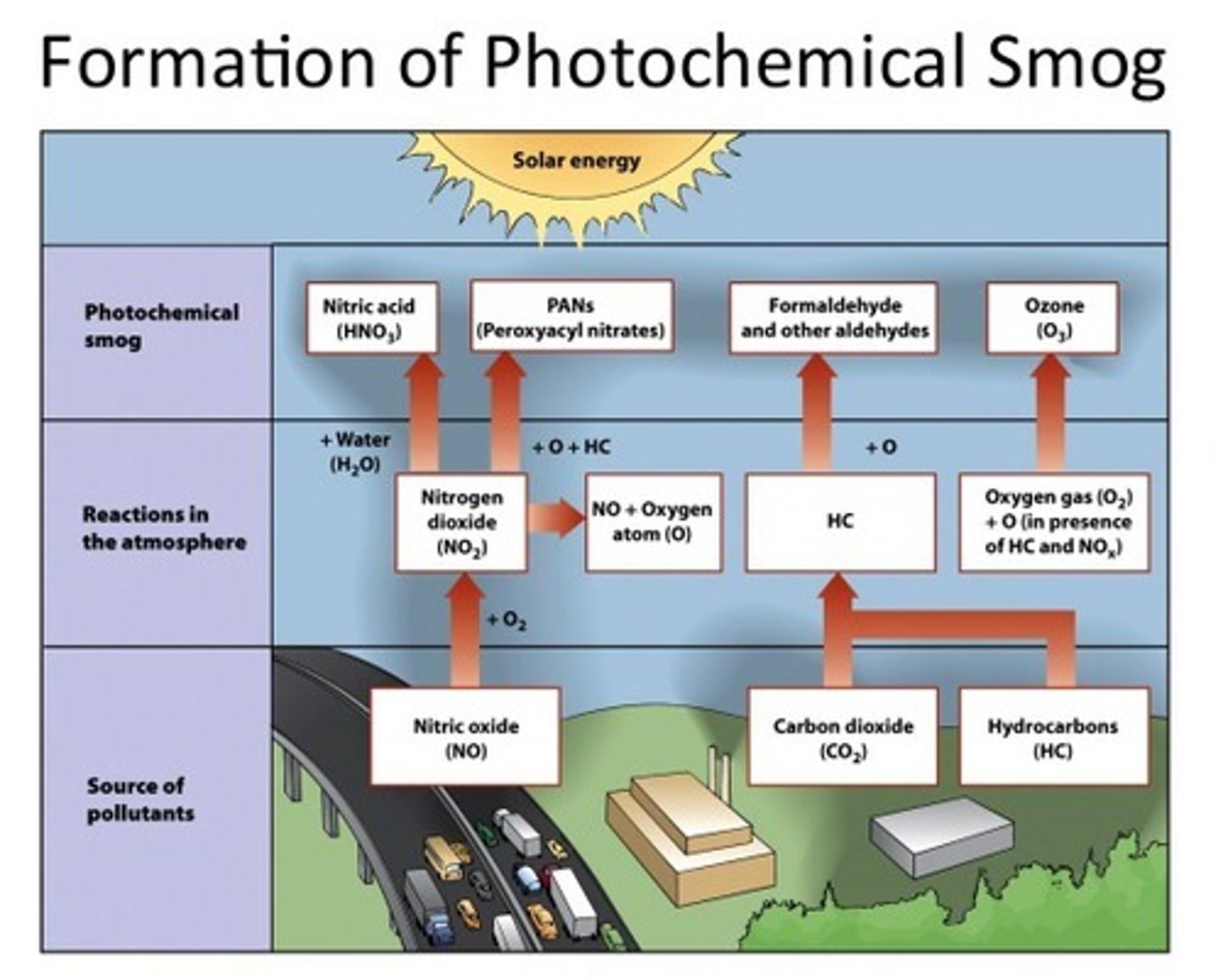
photochemical smog reactants
NOx, VOCs, sunlight
VOCs (volatile organic compounds)
group of primary pollutants that comes from gas, solvents, and evaporating chemicals; component of photochemical smog
- volatile: easily evaporates
- organic: hydrocarbon
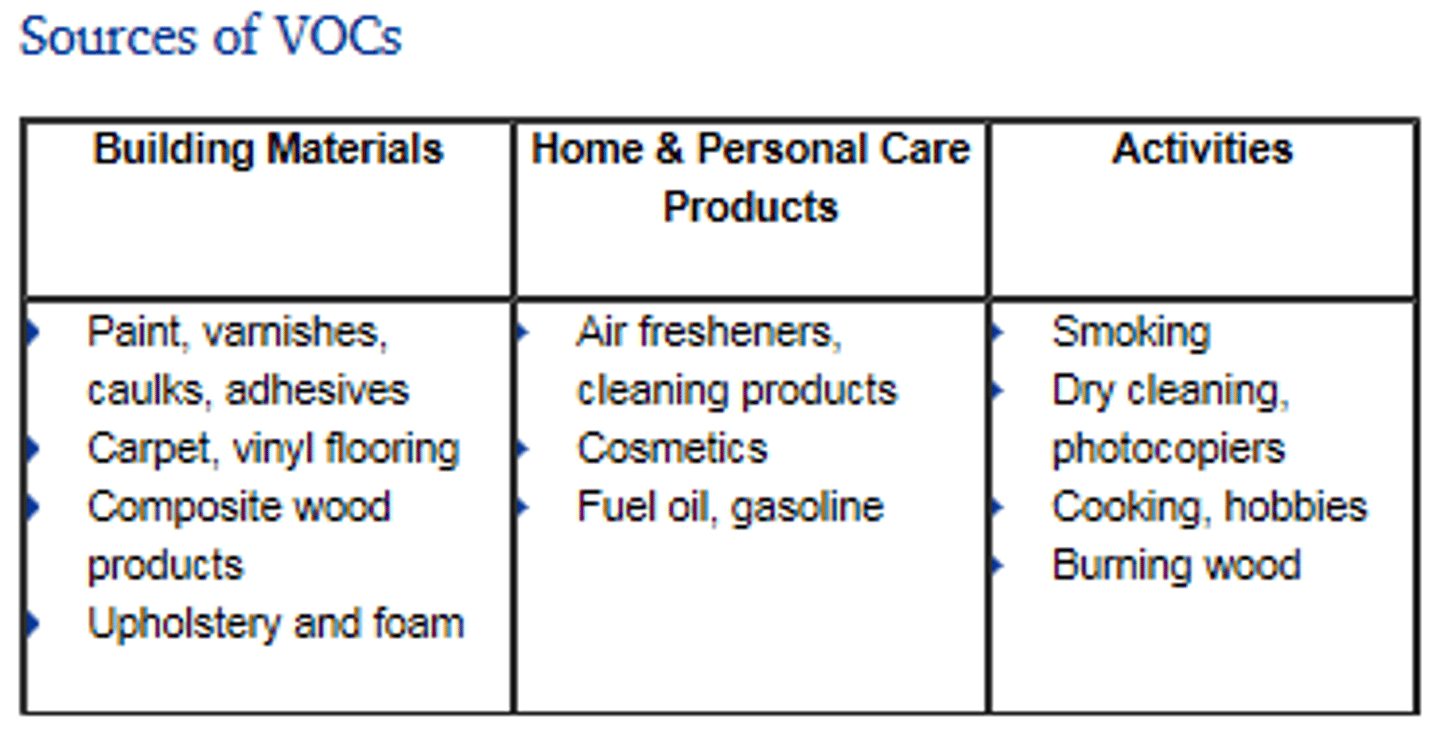
hydrocarbon
An organic molecule consisting only of carbon and hydrogen.
VOC health effects
eye, nose, throat, irritation, headaches, loss of coordination, nausea, damage to liver and kidney and central nervous system, can cause cancer in animals and humans
VOC solutions
avoid products, purchase low VOC building materials, ventilation/air filtration
Clean Air Act of 1970
The law aimed at combating air pollution, by charging the EPA with protecting and improving the quality of the nation's air
- CO2, O3, lead, N2, PM, SO2

O3
ozone
tropospheric ozone
ground level ozone; is considered bad because it is closer to the earth making it more likely for someone to breathe it in. It is also more dangerous because it is made up of particulate matter.
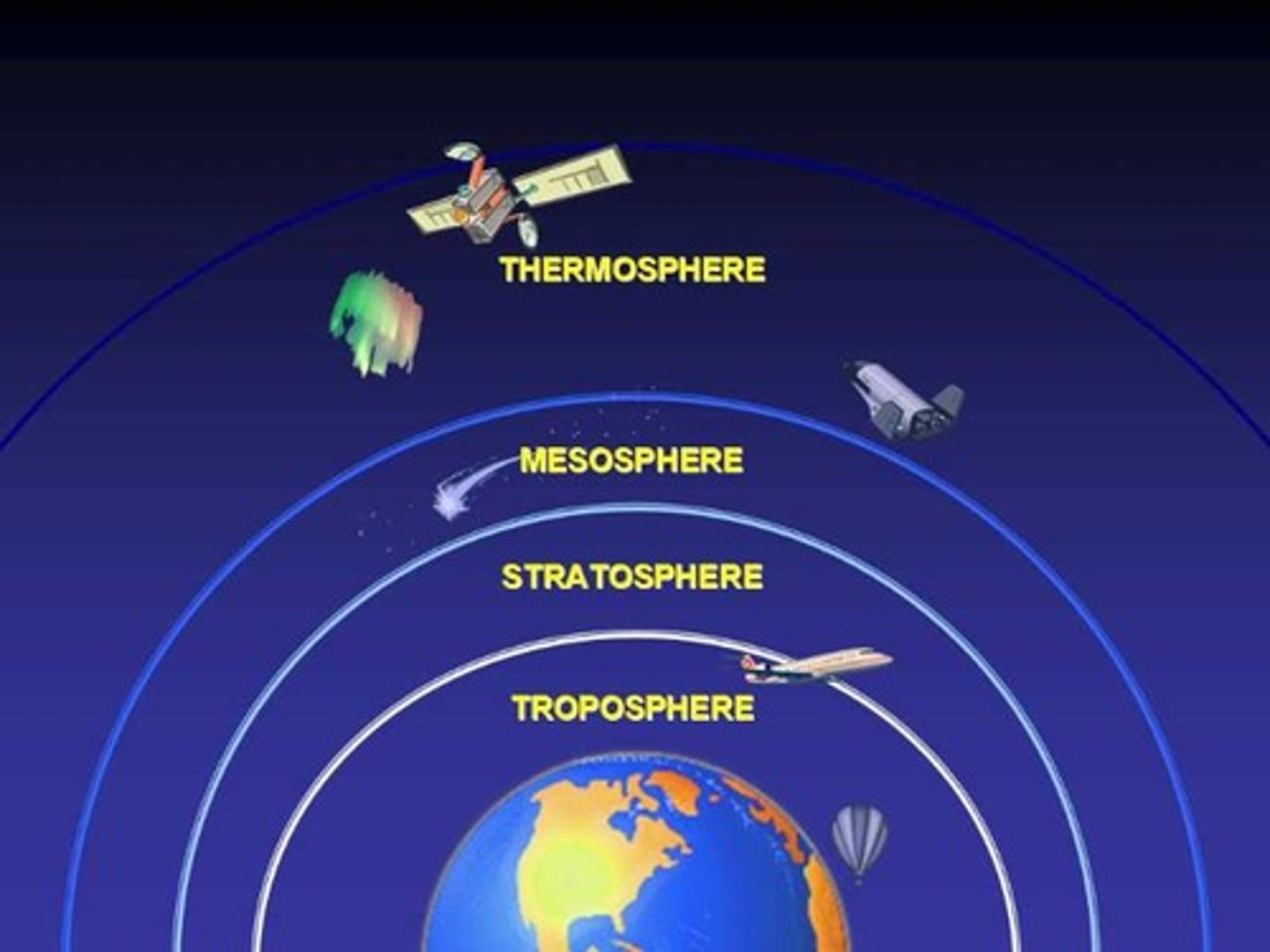
stratospheric ozone
good ozone, produces oxygen molecules to interact with UV radiation and prevent 95% of it from reaching the surface

particulate matter (PM)
a small discrete mass of solid or liquid matter that remains individually dispersed in gas or liquid emissions (usually considered to be an atmospheric pollutant)
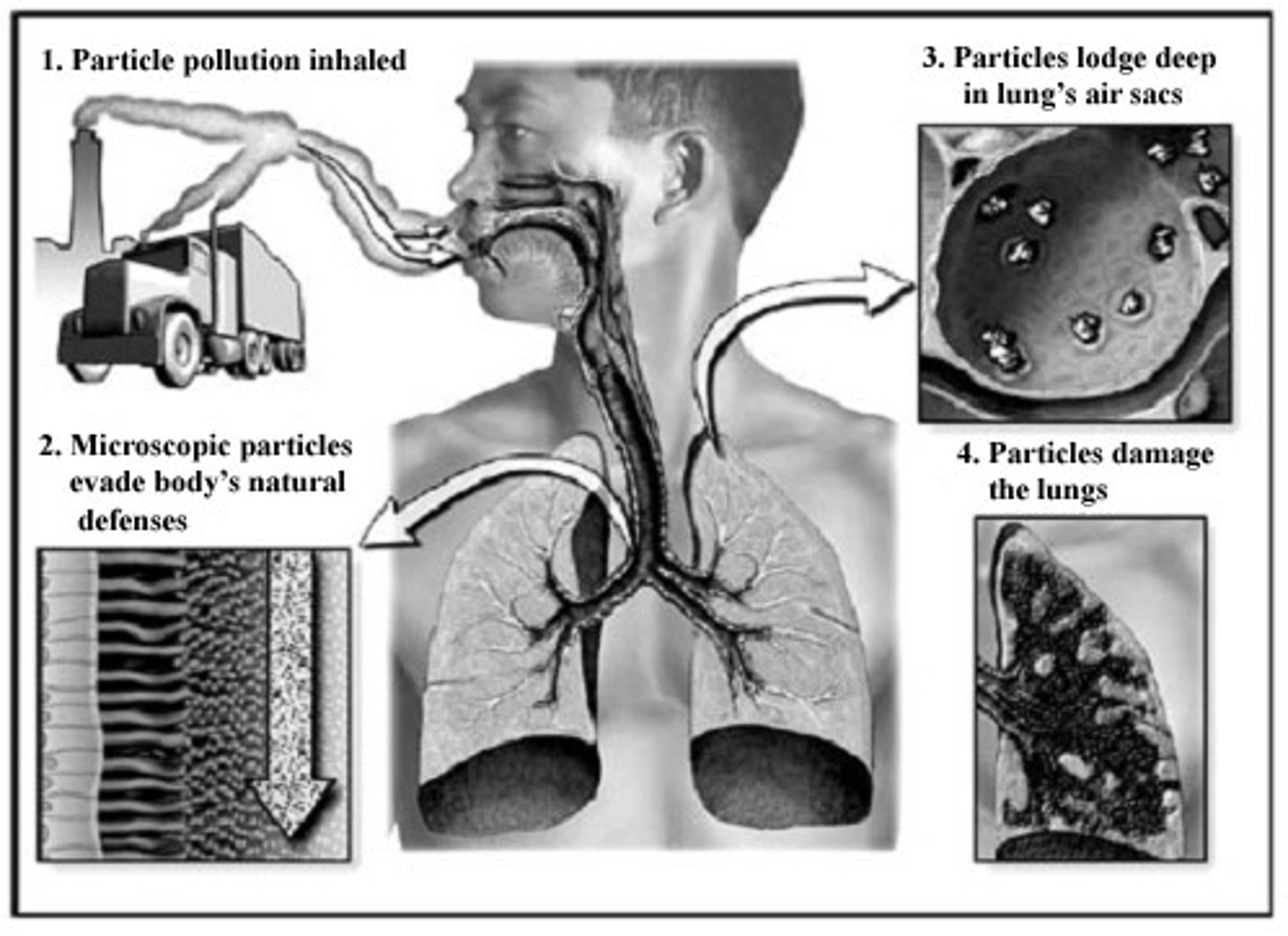
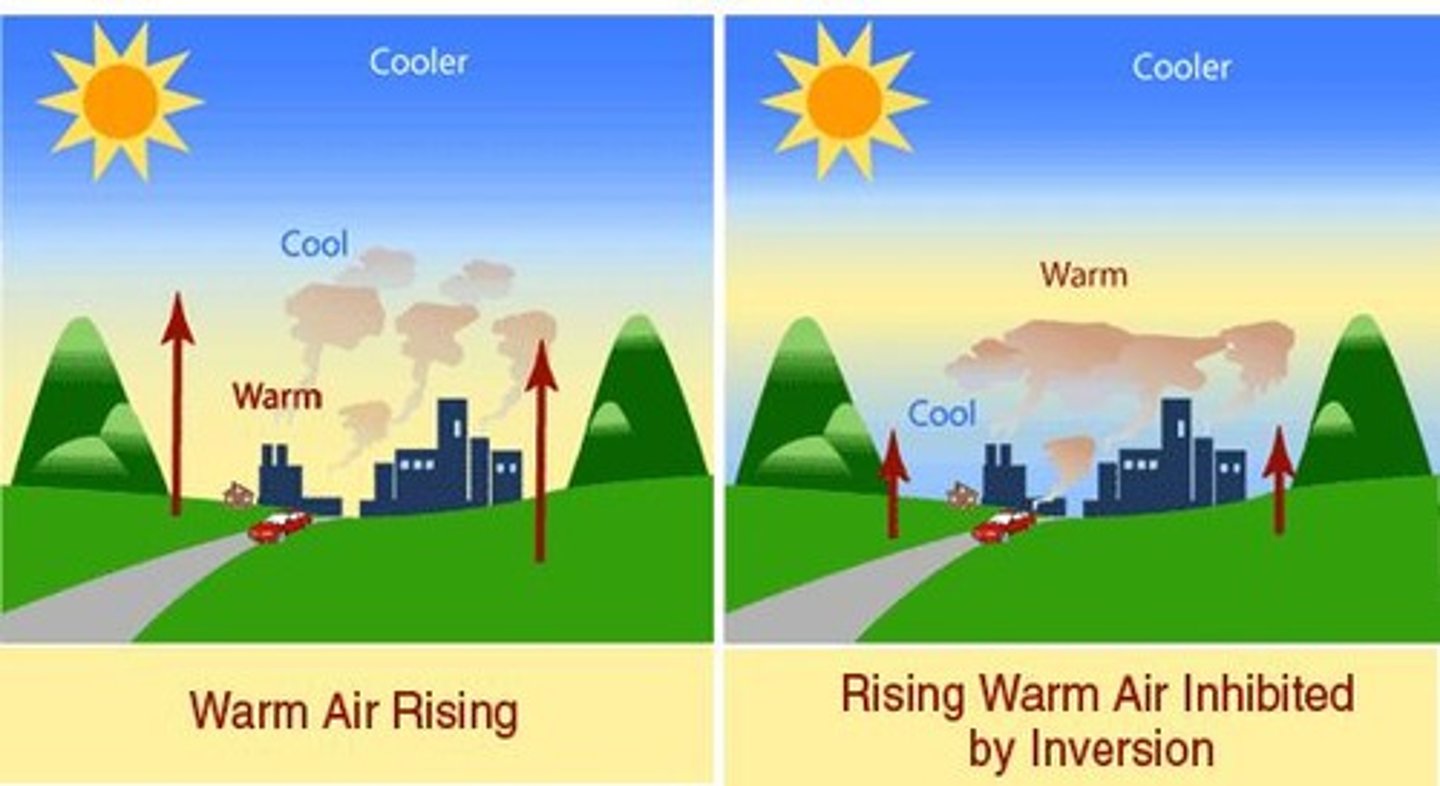
thermal inversion
The temperature inversion in which warm air traps cold air and pollutants near the earth
- creates poor air quality
acid rain
rain containing nitric and sulfuric acids
- can occur naturally or by secondary air pollutants
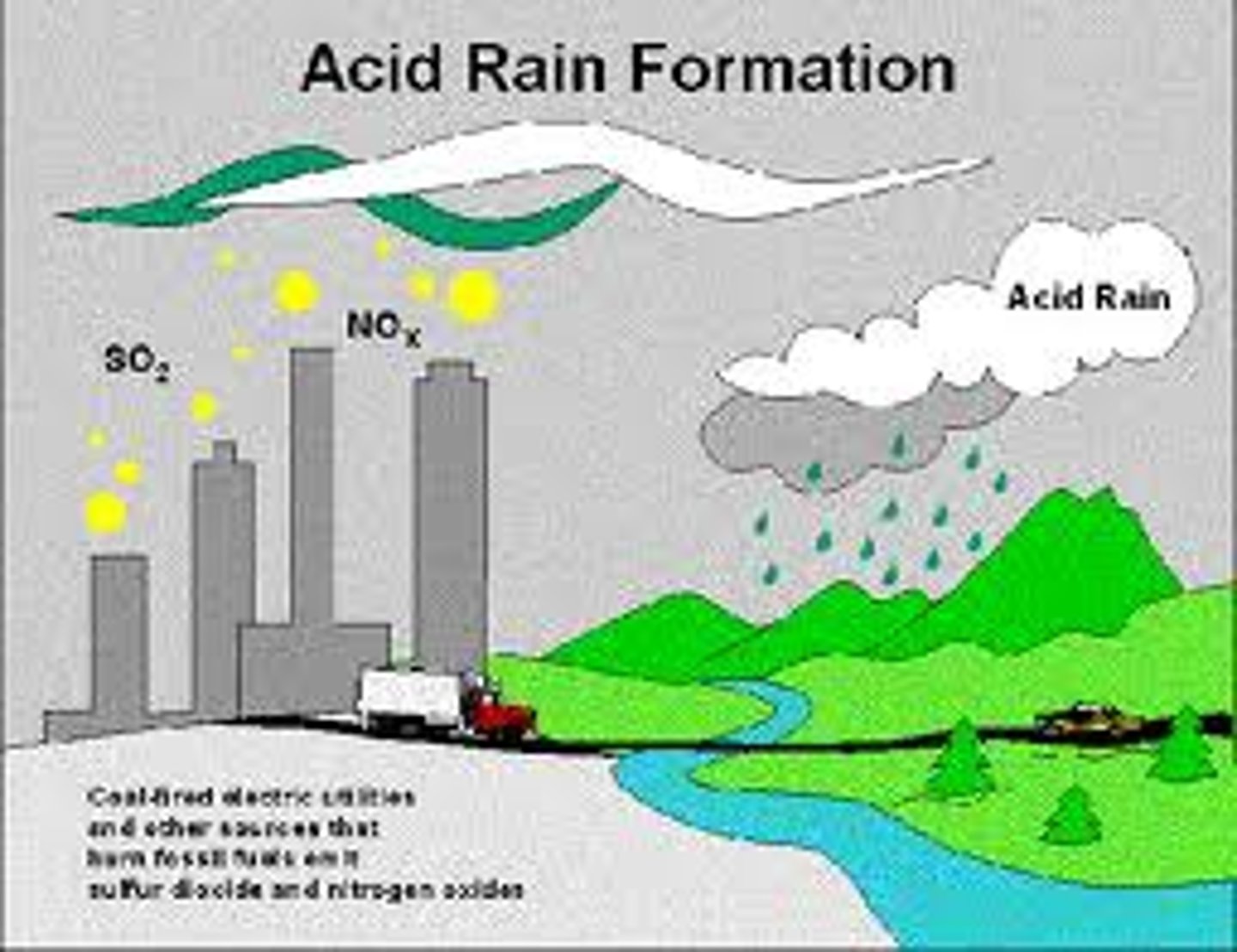
anthropogenic source of SOx
coal burning power plants
anthropogenic source of NOx
motor vehicles and burning of coal power plants
acid rain effects
- corrosion of human made structure
- limestone structures deteriorate
- damage to tree leaves/needles
- infiltrate groundwater
- runoff into surface waters
- acidic soils increase Al toxicity to plant and affect availability of some nutrients
methods to reduce air pollution
scrubbers, electrostatic precipitator, catalytic converter, vapor recovery system
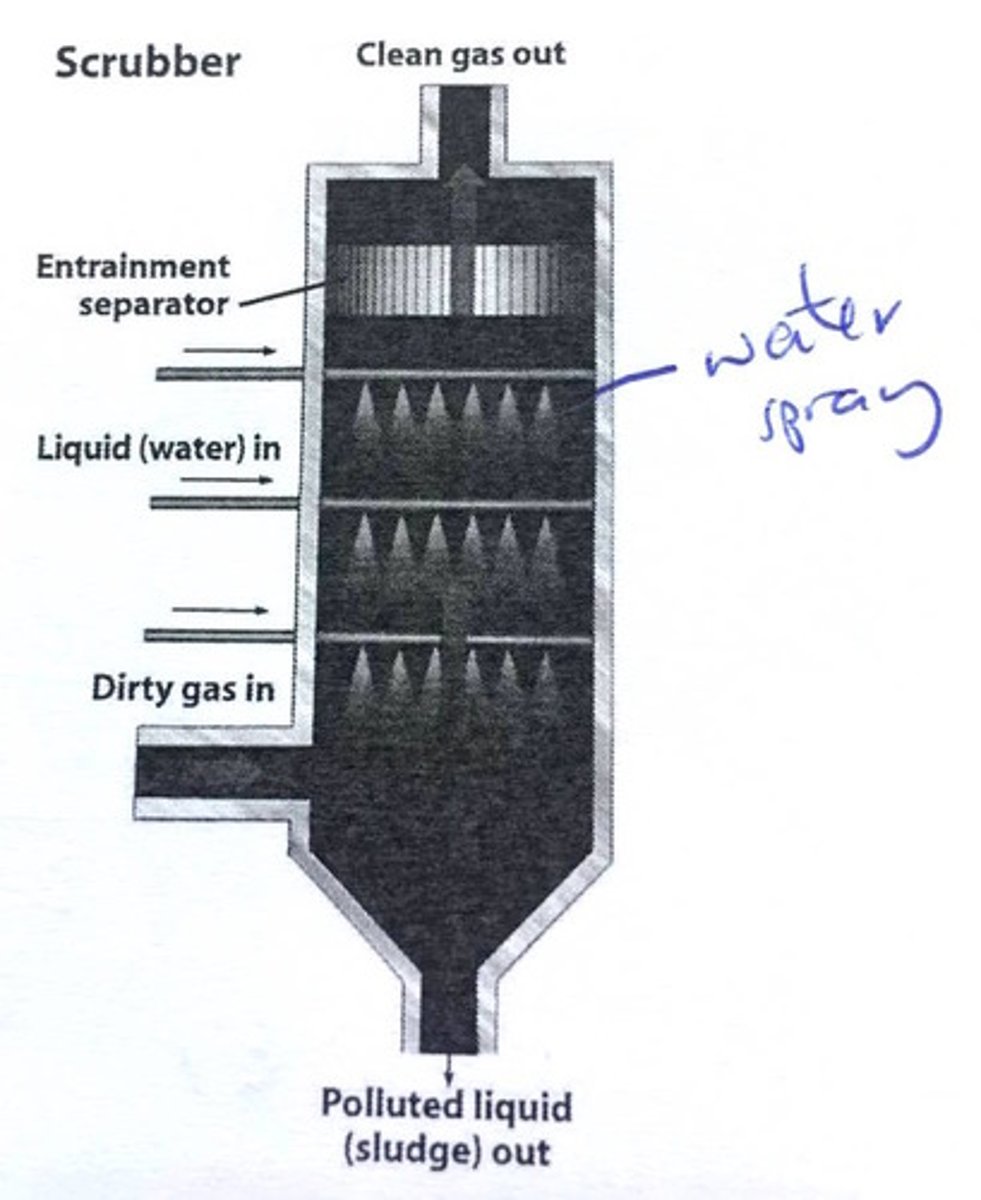
scrubber
A device that is used to remove some pollutants before they are released by smokestacks
- scrubs SOx and PM emissions
Vapor recovery system
Process used to capture and recover vapors
- nozzle on gas pumps prevent fuels (VOCs) from escaping
indoor air pollutants
Substances that contribute to poor indoor air quality and may lead to health problems or other undesirable effects
- nitrogen dioxide (NO2); carbon monoxide (NO); asbestos; volatile organic compounds (VOCs), including formaldehyde; allergens produced by dust mites; environmental tobacco smoke (ETS); fine particles; and radon (Rn), particulate matter (PM)
mold
common in poor ventilated areas, damp/humid areas in homes
- allergic reactions/asthma/respiratory issues
- use ventilation to control

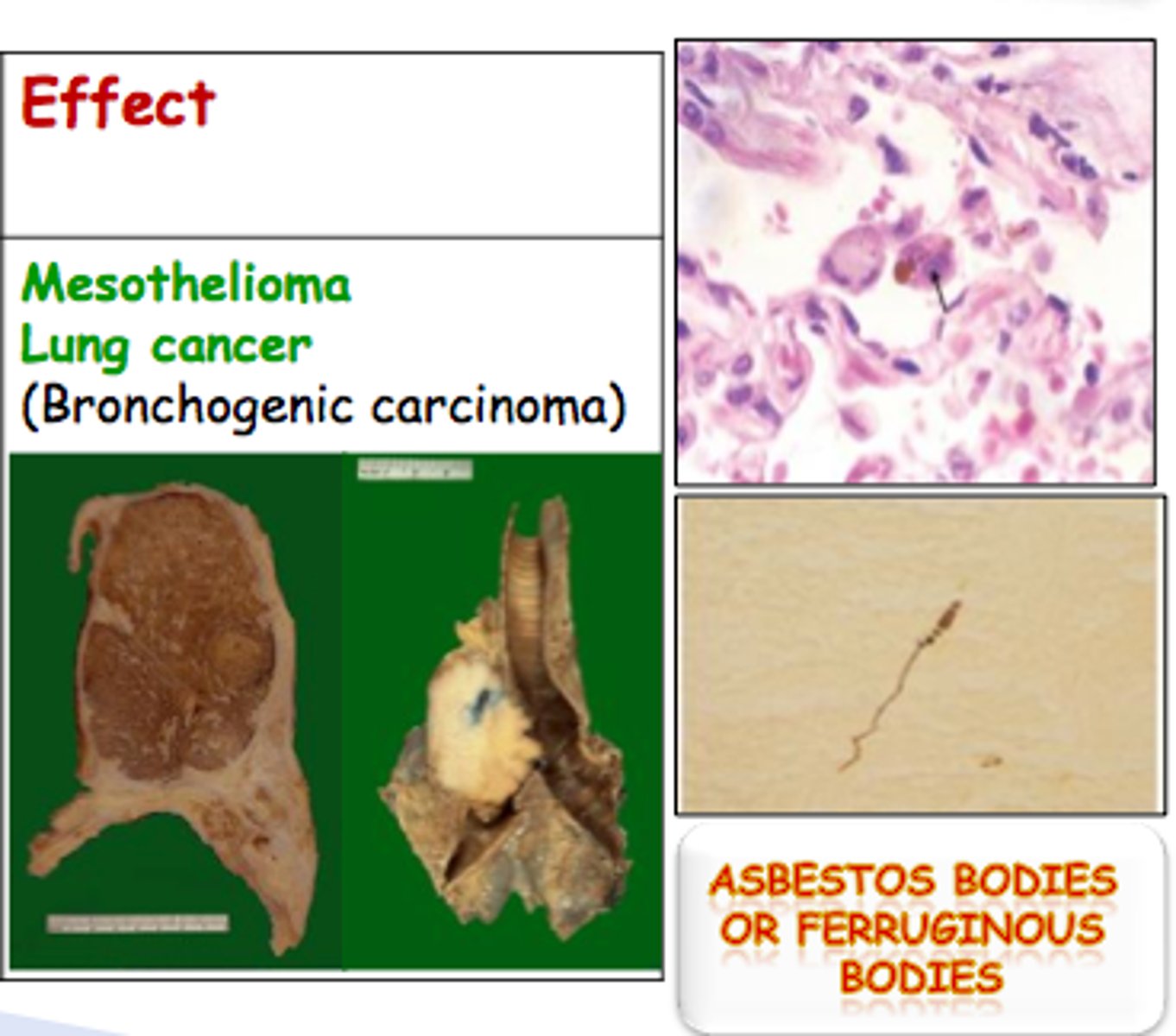
Asbestos
a heat-resistant fibrous silicate mineral that can be woven into fabrics, and is used in fire-resistant and insulating materials such as brake linings
- PM pollution
- naturally composed mineral
- cancers/diseases like mesothelioma
Lead (air pollution)
found in old paint, chipped/deteriorating paint can create dust particles
- remodeling, dry scraping
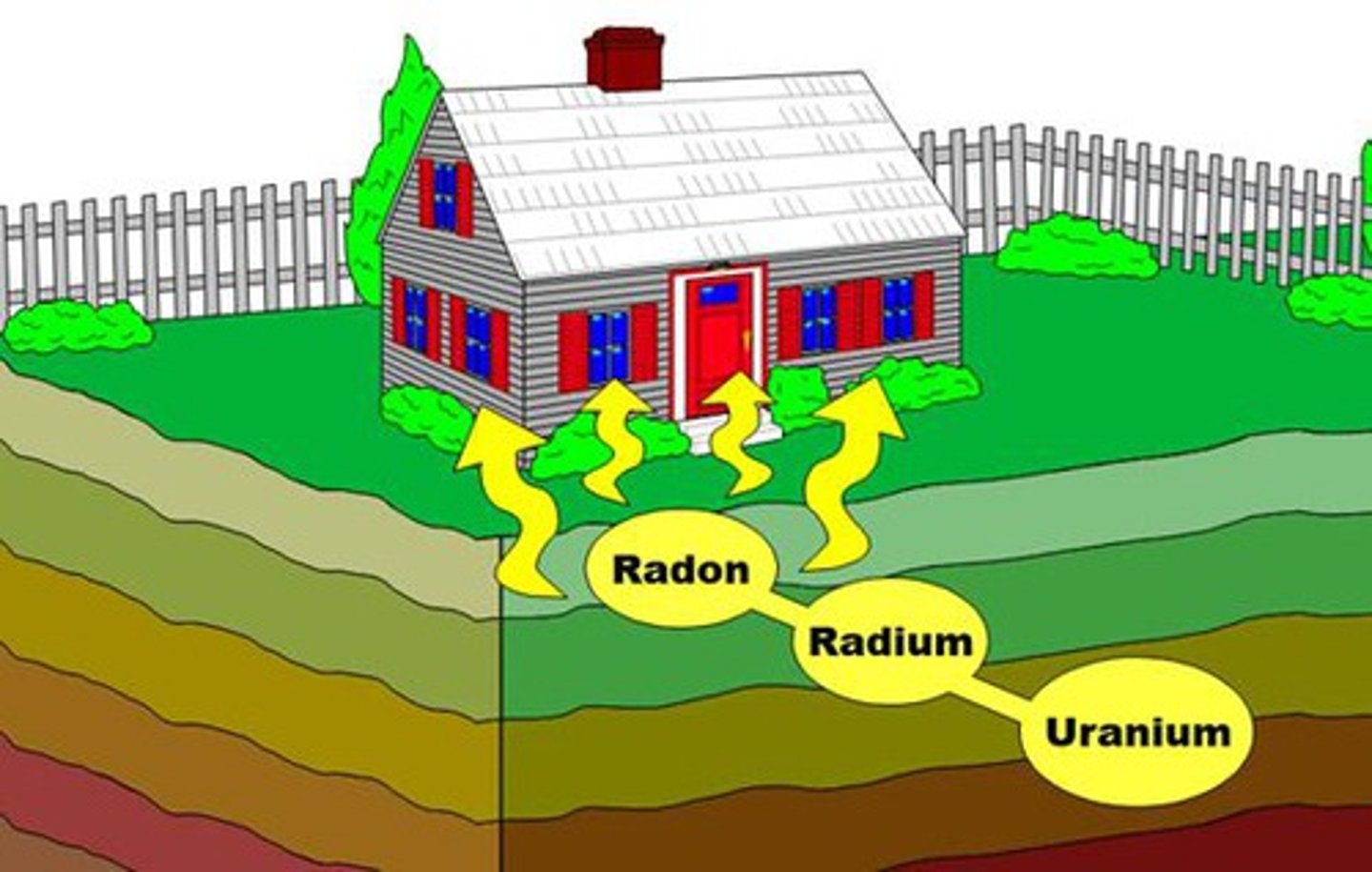
radon
A gas that arises from the earth where radioactive materials are present
- produced with decay of uranium
- moves into home though cracks/holes
- dissolves into ground water
- second leading cause of lung cancer
noise pollution
Any unwanted, disturbing, or harmful sound that impairs or interferes with hearing, causes stress, hampers concentration and work efficiency, or causes accidents
- higher in urban areas
- masks sounds for animal communication/hunting
- damages ecolocation
- changes migratory routes