LDSP FINAL
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
Assigned Leadership
people who are leaders due to their formal position or job title
Emergent Leadership
people who become leaders based on how others perceive them and how others respond regardless of title
Managers
Kotter planning/budgeting, controlling/problem solving
Zaleznik – unidirectional authority, reactive, lower emotional involvement, give instruction
Leaders
Kotter – establish direction, aligning ppl, motivating
Zaleznik – multidimensional influence, shapes ideas, emotionally involved, influence followers
Northouse Leadership
a process whereby an individual influences a group of individuals to achieve a common goal
Great Man Theories
Focused on identifying innate qualities and characteristics of great social, political, and military leaders
5 major leadership traits
1. Intelligence
2. Self confidence
3. Determination
4. Integrity
5. Sociability
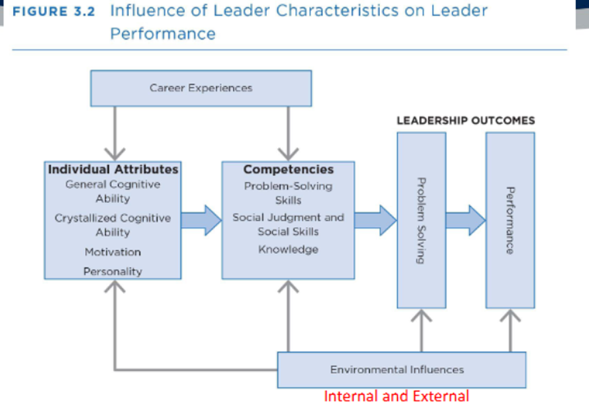
Intelligence and leadership
o Linear increases in intelligence and associated with increase in perceived ldsp
o Curvilinear increases in intelligence are associated with increases in perceived ldsp only to a point after which further increases in intelligence are associated with decreases in perceived leadership
Three Types of Skills
Technical – having knowledge about being proficient in a specific type of work or activity (working with things)
Human- having knowledge of about and being able to work with people
Conceptual – the ability to do the mental work of shaping the meaning of organizational policy or issues (what company stands for and where its going)
Skills model
skills can be learned and developed
Markman’s (2017) Harvard Business Review article “Can You Be a Great Leader without Technical Expertise?”
o What is the key argument
o Leadership education needs to evolve
o Challenges of generalist leadership
o Implications for training future leaders
o Organizational risks
o Today professionals switch jobs and industries more often than in the past
o This mobility makes it harder to develop deep expertise in any one field which can weaken leadership effectiveness
Task relationship
focuses on getting the job done
Behavior relationship
focuses on relationships with subordinates and their wellbeing
Ohio State Studies
o Leadership behavior description questionnaire
o Initiating structure
Task behavior – organizing work, giving structure to the work context
o Consideration: leaders nurture subordinates
Relationship behavior
Michigan Studies
o Two types of leadership behaviors
Production orientation
· Stresses the technical aspects of job
· Similar to Ohio initiation structure
Employee orientation
· Strong human relations
· Similar to Ohio consideration
Blake and Mouton Leadership Grid
country club
team management
Middle of the road
Impoverished management
Authority Compliance Co
Country Club
thoughtful attention to the needs of the people for satisfying relationship levels to a comfortable friendly organization atmosphere
Team Management
work accomplishment is from committed people. Interdependence through a common stake in organization purpose leads to relationship of trust and respect
Middle of the Road
balancing the necessity to get work in such a way that human while maintaining morale of people at a satisfactory level
Impoverished Management
exertion of minimum to get required work done as appropriate to sustain organization membership
Authority Compliance
Efficiency in operations results from arranging conditions of work in a such a way that human elements interfere to a minimum degree
LMX Theory
o Leadership is a process
o Leaders treat followers in a collective way
In Group / out group
o In group – group who identify with each other based on demographics, race, gender, age, religion and geography
o Out- group – people not in the ingroup
Leadership Making
a prescriptive approach to leadership that emphasizes that a leader should develop high-quality exchanges with all of her/his followers, rather than just a few
Leadership Making Stages
Stranger phase
rule bound
Acquaintance phase
testing period
Mature partnership phase
mutual trust, respect and obligation toward each other
Found relationship dependable
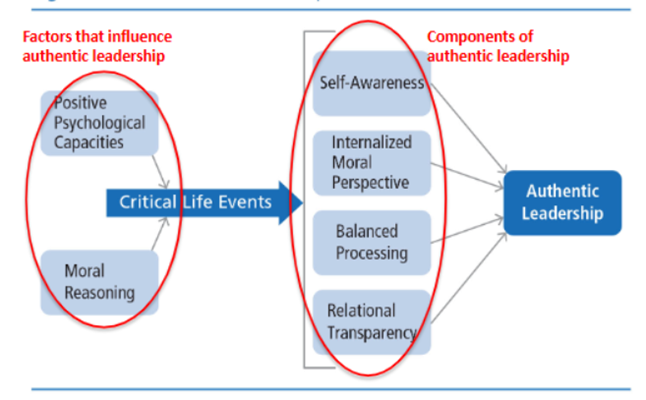
Three definitions of authentic leadership
o Intrapersonal – focuses on leader and what goes on inside the leader
o Interpersonal – created by leaders and followers together/ reciprocal process
Developmental – behavior grounded in leaders good ethics and positive psychological qualities / leadership can be developed/ impact of major life events
Practical approach to authentic ldsp
Five characteristics of authentic leaders
· Understand their purpose
· Strong values
· Trusting relationships
· Self-discipline
· Act from the heart
Theoretical approach to authentic leadership
Followership
a process whereby an individual or individuals accept the influence of others to accomplish a common goal
Perspective on followership
o Role-based – examines the typical roles followers enact while occupying a formal or informal position within a hierarchical system
o Relational-based
§ Social constructivism: people create meaning about their reality as they interact with each other
§ Co created by leader and follower
typologies of followership
o Zeleznik – withdrawn, masochistic, compulsive, impulsive
o Kelley – Alienated, passive, conformist, pragmatist, exemplary
o Chaleff- resource, individualist, implementer, partner
Kellerman – isolate, bystander, participant, activist, diehard
Kelly’s (1988) Harvard Business Review article “In Praise of Followers”
followers can assume one of five different roles based on their degree of active engagement and independent critical thinking. These roles range from exemplary, conformist, passive, alienated, an pragmatist followership
Ethical pluralism (moral pluralism)
notion that there are different values that exist and they could conflict with each other
Two axes create ethical lenses in ethics game
rationality
sensibility
equality
autonomy
Biases that may effect leaders ethical behavior
“Instant entitlement bias”
- Member of team à divide the resources equally
- Selected as the “leader” of team à keep a much larger share of the resources for oneself
Social networks
– People are more likely to inaccurately believe that others agree with them re
- what is ethical when they are in the center of a social network
CEO’s and leaders = center of social networks
• Leaders may have self-serving rationalizations for unethical behavior that focus on their own rights at the expense of others’ rights
How can leaders/managers encourage their employees to behave ethically
leaders must establish their organizations ethical norms
ask “what does our organization stand for”
Set high expectations
Communicate content of norms
Employment practices
hire ethical people
reward ethical behavior
Theranos (Elizabeth Holmes, Tyler Shultz)
medical startup company
exaggerated claims about its blood tests
Tyler was an employee, recent graudate
whistleblower - someone who informs on behavior that is unethical or illegal
Elizabeth was the founder & CEO
Common Information effect
o Team members spend too much time focusing on shared (common) information and neglect unique information
Asymmetrical Information
o Information is distributed unequally among team members
Asymmetrical Interests
Team members have partially conflicting goals
Bob Mckenna CEO of Peninsula Chamber of Commerce
o Seek continual improvement
o Do something each day to improve yourself
o Know ur job
o Be decisive
o Take care of other
o Set standards
o Build a team