Cell Bio Lab Mindterm
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
What is Elisa?
A laboratory technique used to detect and test for the presence of antigens quantify proteins, antibodies, or hormones in a sample using enzyme-linked antibodies.
What Does Elisa Stand For.
Elisa stands for ENZYME LINKED IMMUNOSORBMENT ASSAY
Types of Elisa
Direct Elisa: Is the presence of certain antigens in the patient's blood.
Indirect Elisa: testing the presence of antibodies in a patient's blood signifies a that there was an infection and their body launched immune response.

Antigen/antibody complex
Antibodies are proteins with different antigen binding sites for specific antigens aka lock and key, have different binding sites at their end. Designed to fit the shape of antigens.
Antigen antibody complex: signal for antigen destructions for infection prevention and immune system stimulation. Marks the invading organism/antigen for destruction and stimulates and additional immune response.

Innate Immune System
function regardless of the type of pathogen, physical barriers in mucous, skin, and lysozymes in tears. Nonspecific immune responses like fevers, inflammation, complement system and antiviral infections. Knows the difference between self and non-self cells so it can destroy.
Adaptive Immune System
Adaptive: specific immune response tailored to the type of pathogen. Dendritic cells like Macrophages, and white blood cells called B cells, and T cells

Antibody
Serum proteins, immunoglobulins that have a Y shaped structure with binding site on the end. Has heavy chains and constant regions which make the base of the Y. it branched out and is connected by the disulfide chain. The hinge protein is connected to the light chain via disulfide bonds. There are green variable regions at end which make the antibody. This is where the antigen binds.


Phagocytosis
Macrophages perform phagocytosis to engulf bacteria. The bacterium enters the macrophage through phagocytosis (a form of endocytosis) and binds to a receptor. It is enclosed in a phagosome, which then fuses with a lysosome. The lysosomal enzymes digest the bacterium. Finally, the degraded material is expelled from the cell via exocytosis as soluble debris.

Triplicates
We did all of the tests in triplicate to ensure the reproducibility of the results, a lighter shade indicates that our tests were done correctly.
Positive and negative control show us what the colors looks like if they have the disease or not

Function of ELISA
A secondary antibody is added to the wells and recognizes and looks for the antigen/antibody complexes and it binds to the primary antibody from the patient's serum. It is then attached to the enzyme to form a conjugate. Chromagen comes in and if the enzyme linked to the secondary antibody is present, it causes a chemical reaction that changes color if present. Purple positive and green negative,

ELISA LAB Summarized
Step 1: genetically engineered enzymes are added to the well and forms hydrophobic interactions with plastic, it is washed to remove any unbound material.
Step 2: patients blood serum is added and will from antibody complex with antigen, wells are washed again
Step 3: secondary antibody is added
Step4: chromagen added

What Is Bioinformatics?
Using databases and stimulation for experiments.
Interdisciplinary field, the storage, manipulation and interpretation of biological data of nucleic and amino acids, molecular rules and systems, and sequence genomes of extinct species. used for viruses as well
Hold sequences of amino and nucleic acids
Applications of Bioinformatics
analysis of genomic data and molecular sequences genome annotation, gene and protein prediction. Molecular folding, modeling, and design. Build biological networks and develop databases and data managements systems, developing software and analysis tools.

What does NCBI stand for?
t is the National Center of Biotechnology Information and provides access to biomedical and genomic information to advance science and health. It is a part of the National Library of Medicine.
It organizes and classifies information on data sequences, evolutionary relationships, and scientific publications.

Databases
Some include Chemicals and Bioassays; Data and Software; DNA and RNA; Domains and Structures; taxonomy; Proteins, And Sequence Analysis.

What does BLAST stand for?
Basic local alignment search tool

What is the E-Value
Number of expected hits of similar quality that can be found by chance. It described the random background noise. Less that E-10 is favorable.To have the best, lowest and most accurate search, the longer the sequence the better

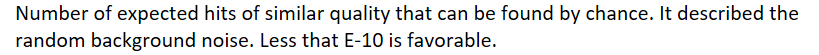
Organism of Interest
Wolfbachia which is a genus of intracellular bacteria that infects mainly arthropods and Libanorhinus succunis.

Do reactions Depend on enzymes?
Without enzymes, the chemical reactions they speed up can still occur , but at a slower rate without .

Lock and Key Analogy
Each type of enzyme has a specific shape that fits into the structure of the substrate. Enzymes have specificity for certain substrates.

Factors that Affect Enzymes
Temp: Low temps can usually slow down a reaction and higher temps usually speed them up due to an inc in kinetic energy for more molecule interactions. Very high temps denature enzymes.
PH: all enzymes have optimum pH ranges. Outside of range can slow down activity and extreme pH denatures.
Cofactors: helper molecule that can cause a confirmational change in enzyme for induced fit or activation. (e.g. ADH=NAD+)
Inhibitors: block active site

Function of Enzyme
Enzymes act as biological catalysts. Speed up a vast majority of processes in the cells, those that break down (e.g. Digestion), and build up ( e.g. Photosynthesis). Enzymes do not get consumed and can do their job again like a matchmaker. They stabilize the transition states which is what requires the most energy.

Substrate
The substrate is the molecule(s) that the enzyme will convert into product. It fits into an indentation in the globular protein called the active site.
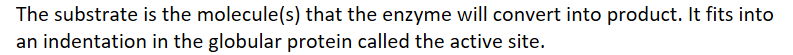
Active Site
the part of the enzyme the substrate binds. It also releases the modifies product and staying open for more substrate. Shape and chemical properties are critical to its function.

Transition State
Transition state is the is the structure with the highest energy.
Reaction Rate: (V) is the change in concentration over time.
Can also be rate of product formation (P) and substrate formation (S)

Activation Energy
Activation energy is the energy needed for a reaction to occur. Reactions proceed at a much higher rate.

How does an enzyme lower activation energy?

Substrate->Transition->Product
In transition state, a species can: lose energy and move towards substrate lose energy and move towards product. Enzymes catalyze forward and reverse reactions
Lowering activation energy accelerates both reactions
In the presence of an enzyme:
The equilibrium of products & substrates does not change
The amount of time necessary to reach equilibrium is shorter

What did we Graph in Enzyme Lab?
Dark yellow meant more p-nitrophenol=more product
We are trying to figure out how effective cellobiase was in breaking down the substrate p-Nitrophenul glucopyranoside into glucose and p-Nitrophenol

Standard Curve
Know that y=mx+b and use this formula for the standard curve and
y=absorbance at 410 nm and x is the amount of p-nutropheno;l
