4. Endo/Repro - Medicine: Dental Care in Pregnancy
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
what are two positive outcomes of good oral health and control of oral disease in pregnant women?
- Protects woman's health and quality of life
- Potential to reduce transmission of pathogenic bacteria from mother to child
T or F: treatment of infection or sources of sepsis should only happen in the 3rd trimester of pregnancy
FALSE
- Treat infection or sources of sepsis at any stage of pregnancy
T or F: there is an increased risk of miscarriage or preterm delivery when dental treatment is performed in the 1st trimester of. pregnancy
FALSE
- No increased risk of miscarriage or preterm delivery by treating (there is risk to not treating!)
what are the 3 barriers to dental care in pregnancy?
- patients
- oral health professionals
- prenatal care providers
what proportion of people who gave birth reported having a dental cleaning during the last 12 months before pregnancy?
slightly more than half, 52.7%
how many people who gave birth reported getting cleaning during pregnancy?
55.1%
What percentage of pregnant patients with acute oral health problems attempted accessing dental care? what explains why some did not?
only 50%
- Believed poor oral health was normal
- Believed dental treatment harmful
what is the biggest barrier cited (in a survey of oregon dentists) regarding treating pregnant women?
perceived lack of time and compensation
what are some barriers to dental care for pregnant women in which dentists are the cause?
- Many thought x-rays, periodontal surgery,amalgam fillings, pain meds dangerous
- Dentists less comfortable than OBs with meds/procedures
- High rates of incorrect knowledge of routine & emergency procedures in pregnant women
- Biggest barrier cited: Perceived lack of time and compensation
what are some barriers to dental care for pregnant women in which OBs are the cause?

what pregnancy test is positive 2 weeks after conception and is qualitative?
urine hcg
what pregnancy test is positive 9 days after conception and is quantitative
serum hcg
early signs and symptoms of pregnancy
- Amenorrhea (period stops)
- Nausea, vomiting
- Urinary frequency
- Breast tenderness and enlargement
- Fatigue
conception happens when usually?
14 days into cycle
when pregnancy is discovered at the first missed menses, what is the estimated gestational age and embryonic age?
- Gestational age of 5 weeks
- Embryonic age of 3 weeks
dating of pregnancy begins on what day?
1st day of last menstrual cycle
how do you get a pregnant women's due date?
- 1st day of period + 280 days
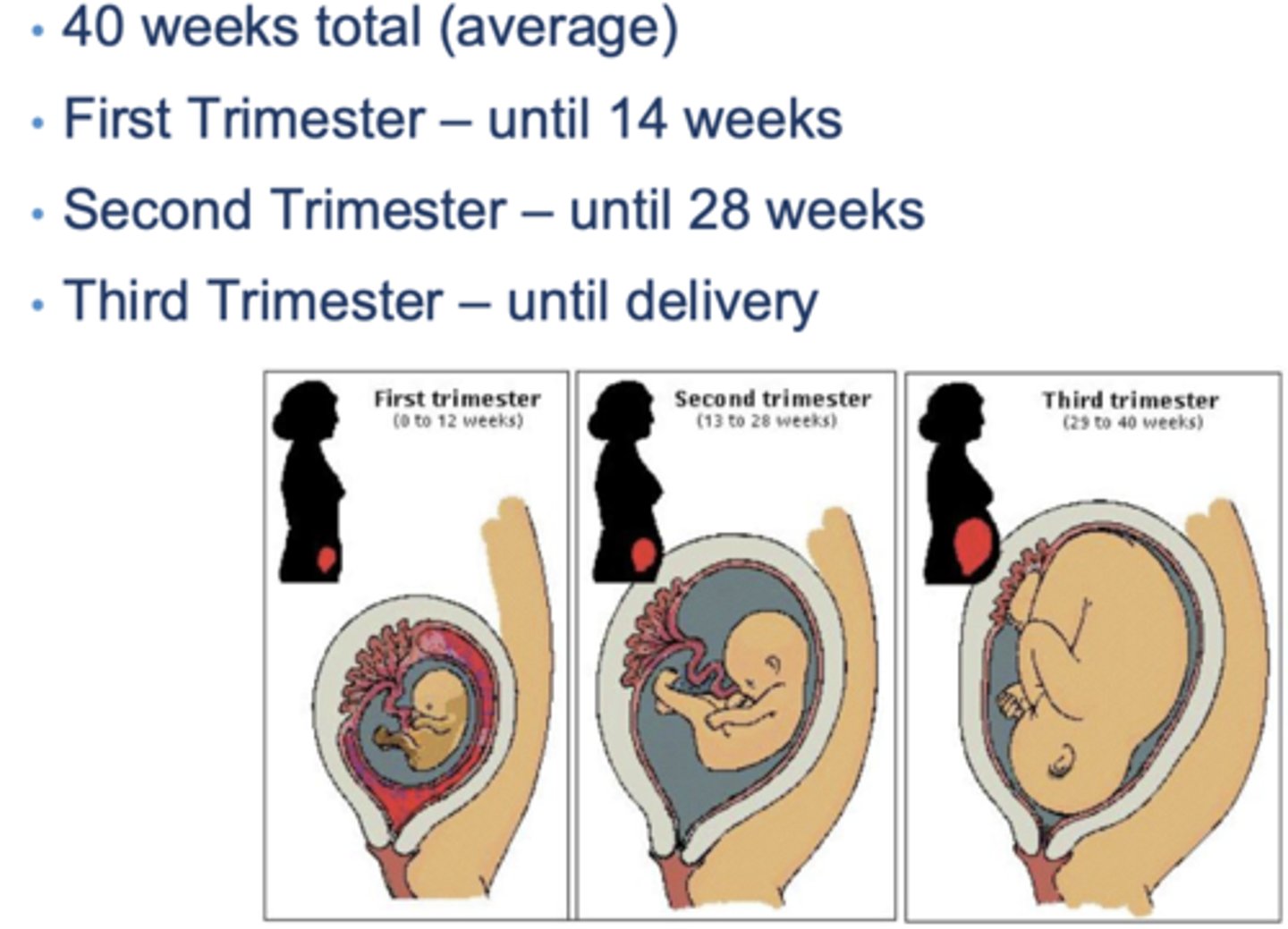
the average pregnancy lasts how many weeks?
40
the ideal weight gain in pregnancy for non-obese women is...
25-35 lbs

cardiovascular changes to plasma volume, cardiac output, peripheral vascular resistance and blood pressure:
increased:
- plasma volume
- cardiac output
decreased
- peripheral vascular resistance
- blod pressure

respiratory changes during pregnancy:
increase
- minute ventilation
- tidal volume
what can happen to gums during pregnancy?
hyperemic
- increase in blood flow
GI changes in pregnancy;
• Decreased motility of GI tract
---–- constipation, reflux, heartburn
• Relaxed esophageal sphincter
----– GERD
----– Increased aspiration risk, especially in surgery
• Nausea/vomiting – Hyperemesis Gravidarum
----– 70% experience some N/V
----- 2% with hyperemesis (associated with weight loss, dehydration,+/-electrolyte abnormalities)
hyperemesis gravidarum is usually limited to which trimester of pregnancy
1st
what can be done to reduce the risk of aspiration in pregnant women during surgery due to relaxation of the esophageal sphincter?
• Regional anesthesia during cesareans
• Pre-op prophylaxis with antacid (e.g., Bicitra)
perio affects what percentage of women of childbearing age and pregnant women?
• Affects about 15% childbearing age
• Up to 40% of pregnant women
risk factors associated with pregnant women/women of childbearing age developing perio disease:
- low-income
- older age
- smokers
- diabetics
pregnancy gingivitis peaks in what trimester?
3rd
what increases susceptibility of pregnancy gingivitis?
Hormonal changes can cause shift in bacterial flora
a pyogenic granuloma is also known as?
pregnancy tumor
- not purulent
- Lobular capillary hemangioma
pyogenic granuloma is most often found where in oral cavity?
Usually anterior & maxillary
what fits this description?
• Soft, painless
• Smooth or lobulated red-purple
• A pedunculated outgrowth from interproximal gingiva
• Up to 2cm in diameter
pyogenic granuloma
pyogenic granuloma is seen in what percentage of pregnant women?
5%
treatment for pyogenic granuloma
- Expectant management
- Surgical excision
T or F: the increased mobility associated with pregnancy leads to tooth loss
FALSE
- increased tooth mobility but normally no tooth loss
is supine position recommended in pregnant women during dental procedures? why or why not?
NO
- compression of the IVC can occur in supine position causing supine hypotension
- use semi-reclined position and encourage frequent position changes
- • Place small pillow under right side to tilt patient to the left
what is the benefit of the left lateral tilt position?
moves the weight off the aorta and IVC
what should you do in the case of supine hypotension?
- Sit patient up
- Fully recline chair and roll patient to left side
are dental caries increased by pregnancy?
no
(pre-existing dental disease may become exacerbated due to pregnancy influences (increased acidity, more sugary cravings)
Any agent or factor to which fetal exposure produces a permanent alteration in form or function of the offspring defines what?
teratogen
what can be said about treating periodontal disease and reducing the rate of preterm birth rate?
If treatment is successful, there is a 6-fold decrease in the preterm birth rate
at which gestational period do you expect to see structural malformations as a result of teratogens?
embryonic period:
- weeks 3-8
- organogenesis - structural malformations
- highest risk in first trimester
in which gestational period is there no susceptibility to teratogens?
pre-implantation period
- 1-2 weeks from fertilization thru implantation
what are some things that determine teratogenicity?

what are some meds that are contraindicated in pregnancy?

antibiotics with potential toxicity:

what antibiotics are safe for use in pregnant patients, including for cardiac prophylaxis?

what analgesics should be avoided in pregnant women?
aspirin and NSAIDs
- low dose aspirin is used for preeclampsia prevention
what are some airway changes to be aware of in pregnancy?
- Increased swelling and friability of oropharyngeal tissues
- Reduced size of glottis
- Worse at end of pregnancy
- Can lead to difficulty ventilating and intubating
in the case of nitric oxide, chronic exposure (occupational) without proper scavenging of exhaled gases associated with:
- Reduced fertility
- Increase in miscarriages
which imaging studies are NOT safe?
• Radioactive iodine for therapeutic purposes
– Crosses the placenta; Can affect fetal thyroid
– Especially if used after 10-12 weeks
– Contraindicated in pregnancy
– Treat patients AFTER delivery
• nuclear medicine tests
- paramagnetic contrast agents
- radiopaque contrast agents (for CT/X-rays)
- radionuclide testing
what is the limit for radiation exposure in pregnant patients?
less than 5 rads
adverse effects of high-dose radiation exposure:
• Embryonic death - all or none phenomenon
• Teratogenic effects
• Carcinogenesis
• Genetic effects or germ cell mutations
• ?? Adverse genetic effects on future generations
• Intrauterine fetal growth restriction
teratogenic effects of radiation exposure:
• Data from atomic bomb survivors
• Fetal growth restriction
• Microcephaly
• Mental retardation
• CNS effects greatest if exposed 8-15 weeks
• Threshold may be 20-40 rad
carcinogenesis associated with radiation exposure:
• Unclear risk, but probably small
• Estimated 1-2 rad fetal exposure may increase incidence of leukemia by 1.5-2x
• Estimated 1 in 1,000 cases per rad
• Background risk is 1 in 3,000
• Non-irradiated siblings also have higher incidence
benefits of breastfeeding:
• Colostrum aids digestive system
• Antibodies that help immune system
• Lower risk of asthma, obesity,allergies
• Protein/fat better used than formula
• Less gas, feeding issues,constipation
• Less SIDS (sudden infant death)
for how long should infants be exclusively breastfed?
first 6 months
- breastfeeding should continue until 1 year of age with supplementation of solid food after 6 months
U.S. breastfeeding rates:

how should meds be timed considering breatsfeeding?
May use meds with relative contraindications by timing doses immediately after a feeding
what should be done if wondering the effects of meds on breastfeeding?
• Best to look up effects in reliable source
- Reprotox
medications safe for breastfeeding:

when is breastfeeding contraindicated?
• Antineoplastic, thyrotoxic and immunosuppressive agents
• Radioactive isotopes• Undergoing chemotherapy or radiation therapy
most effective contraceptive?
IUD, implant
ranks different contraceptive methods and their effectiveness
Most Effective (LARCs)
- IUD (intrauterine device), implant
Less Effective
- injection, pills, ring, patch
Even Less Effective
- condoms, withdrawal, sponge, cap, diaphragm
Worst
- fertility awareness, spermicides