BIO 1107, Exam 4, Dr. Abbott, UConn
1/190
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
191 Terms
Arteriosclerosis
Hardening of the walls of an artery
-Arterio = artery
-Sclerosis = Hardening
Atherosclerosis is a type of arteriosclerosis
Red blood cells are primarily produced in these types of bone
-High bone marrow, low density bone
-Vertebrae, hips, ribs, sternum
RNA polymerase I builds
Ribosomal RNA (rRNA)
What are the granulocytes and their functions?
Neutrophils
-Helps in phagocytosis
Eosinophils
-Fights infection, Anti-parasitic
Basophil
-Inflammation and allergic reactions
-release histamine and heparin
RNA polymerase II builds
messenger RNA (mRNA)
What are the covalent 6 modifications to proteins?
-Phosphorylation
-Glycosylation
-Hydroxylation
-Methylation
-Acetylation
-Ubiquitination
The disease Alkaptonuria is caused by a mutation in what gene.
HGD (Homogentisate 1,2-Dioxygenase)
-HGD is involved in the breaking down of phenylamine and tyrosine
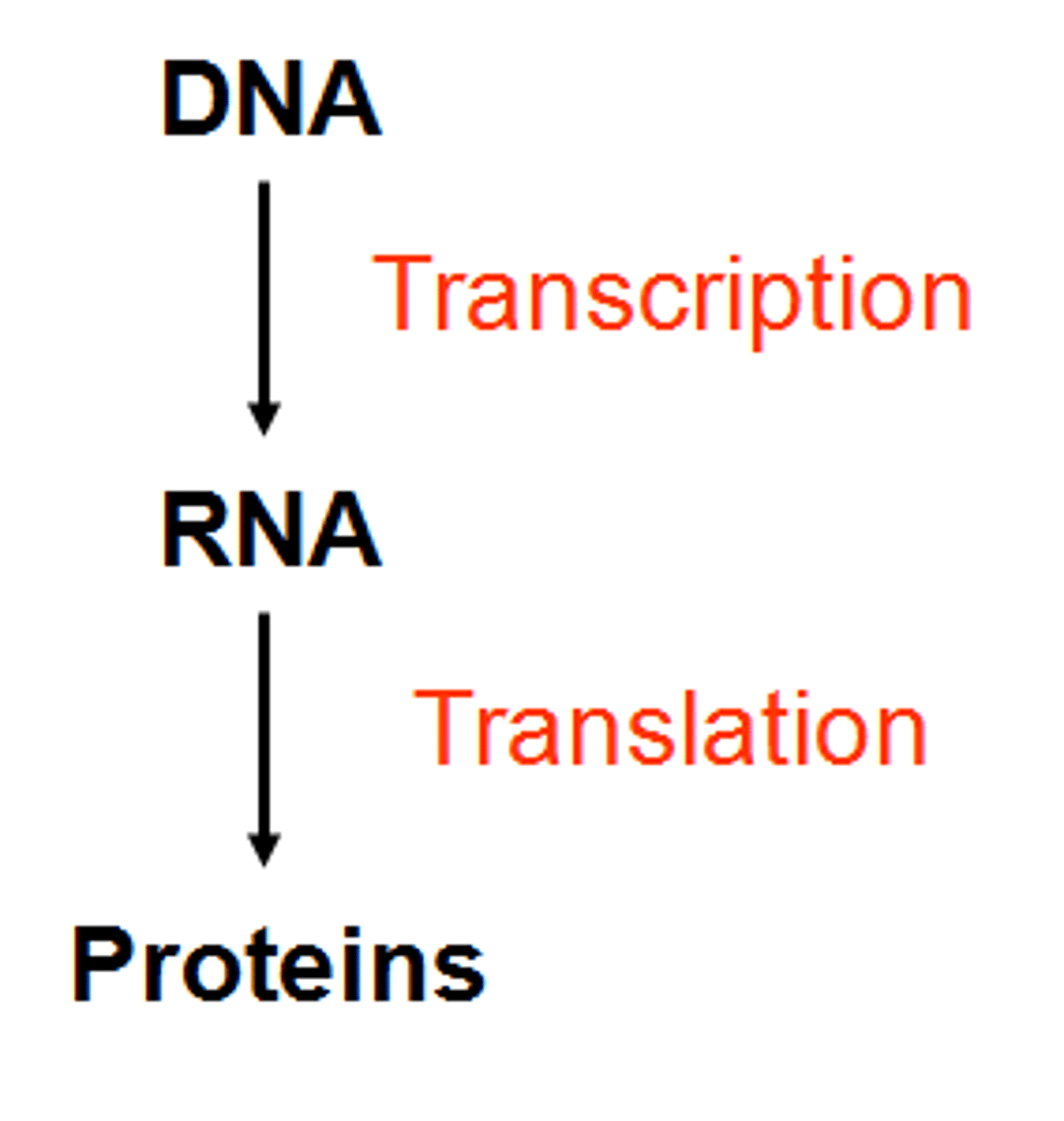
What is the central dogma of biology?
DNA -> RNA -> Protein
Monomers of lactose
glucose and galactose
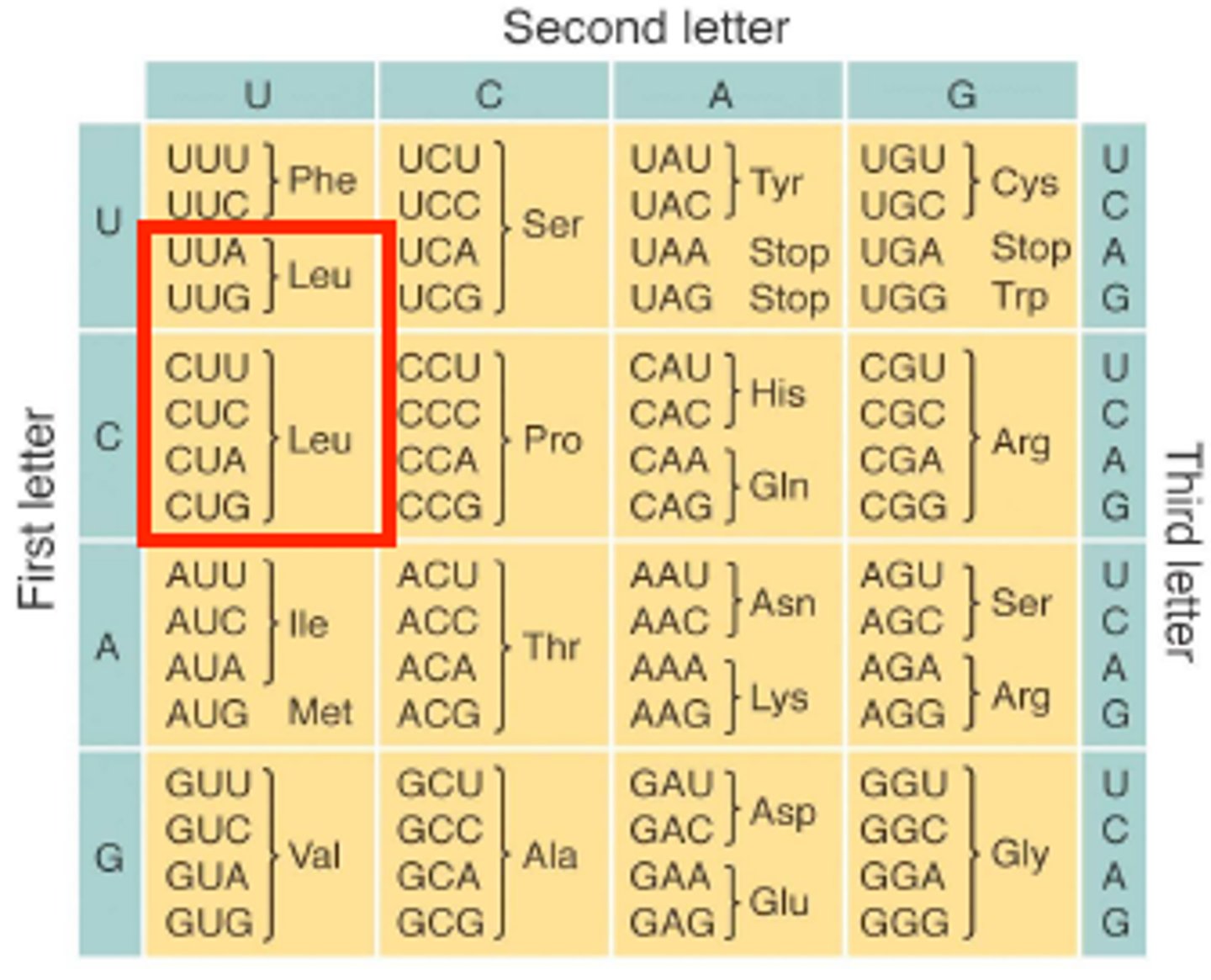
Start codon
AUG (methionine)
codon that signals to ribosomes to begin translation; codes for the first amino acid in a protein

How many stop codons are there?
what are they?
3 (UAA, UGA, UAG)
U Are Annoying
U Go Away
U Are Gone
How many different amino acids are there?
20 different amino acids
Redundant codons/ amino acid sequence definition
More than one possible three letter sequence to encode for a particular amino acid.
In RNA, Uracil base-pairs with?
Adenine
permeases are what kind of protein?
transmembrane transport proteins
-Allows lactose to get through the cell membrane
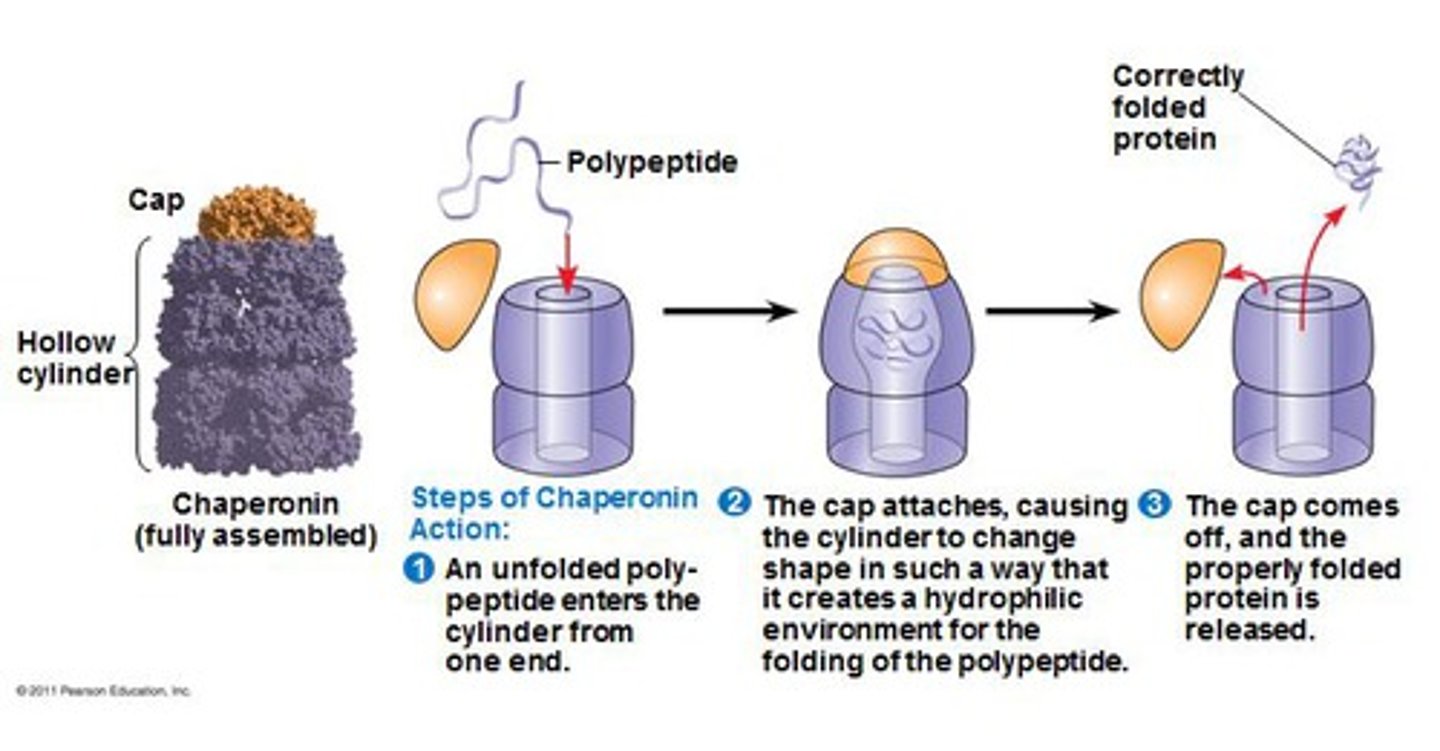
Chaperone proteins assist with
Protein folding
rRNA catalyzes what?
Peptide bonds between amino acids attached to tRNA
-Protein synthesis
Which tRNA structure recognizes the mRNA during translation
Anticodon
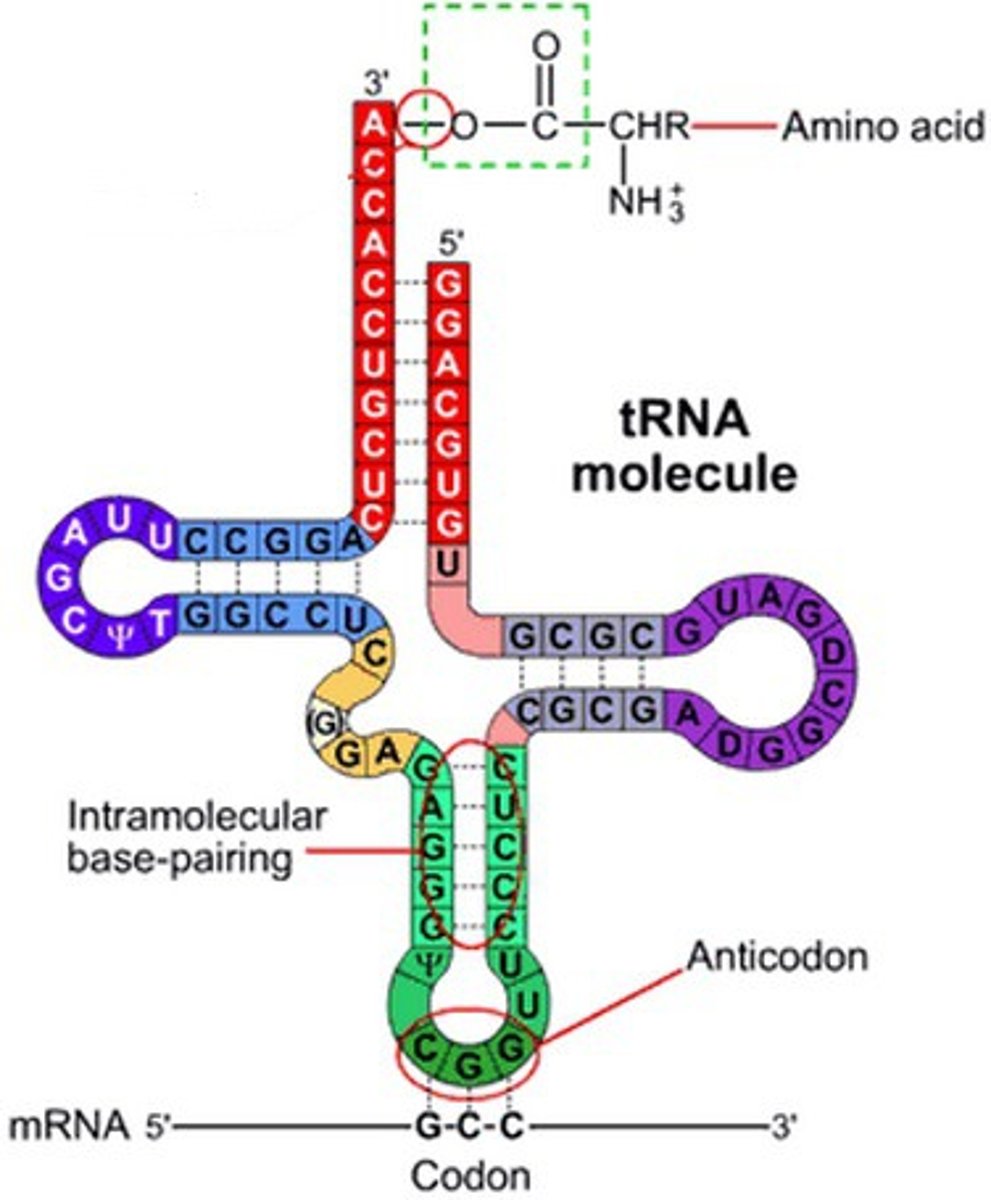
What is a charged tRNA?
tRNA bonded to an amino acid
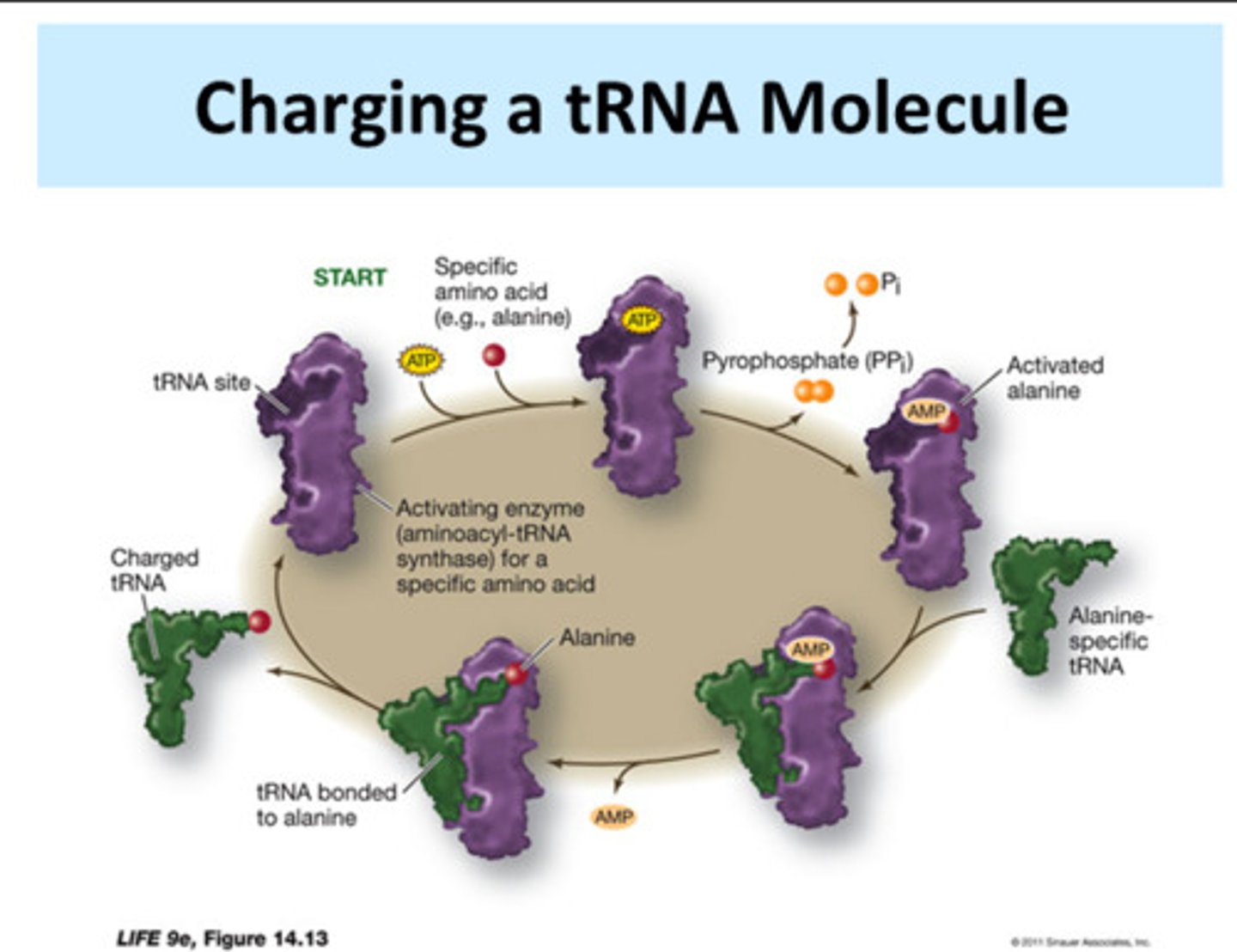
aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase
An enzyme that joins each amino acid to the appropriate tRNA.
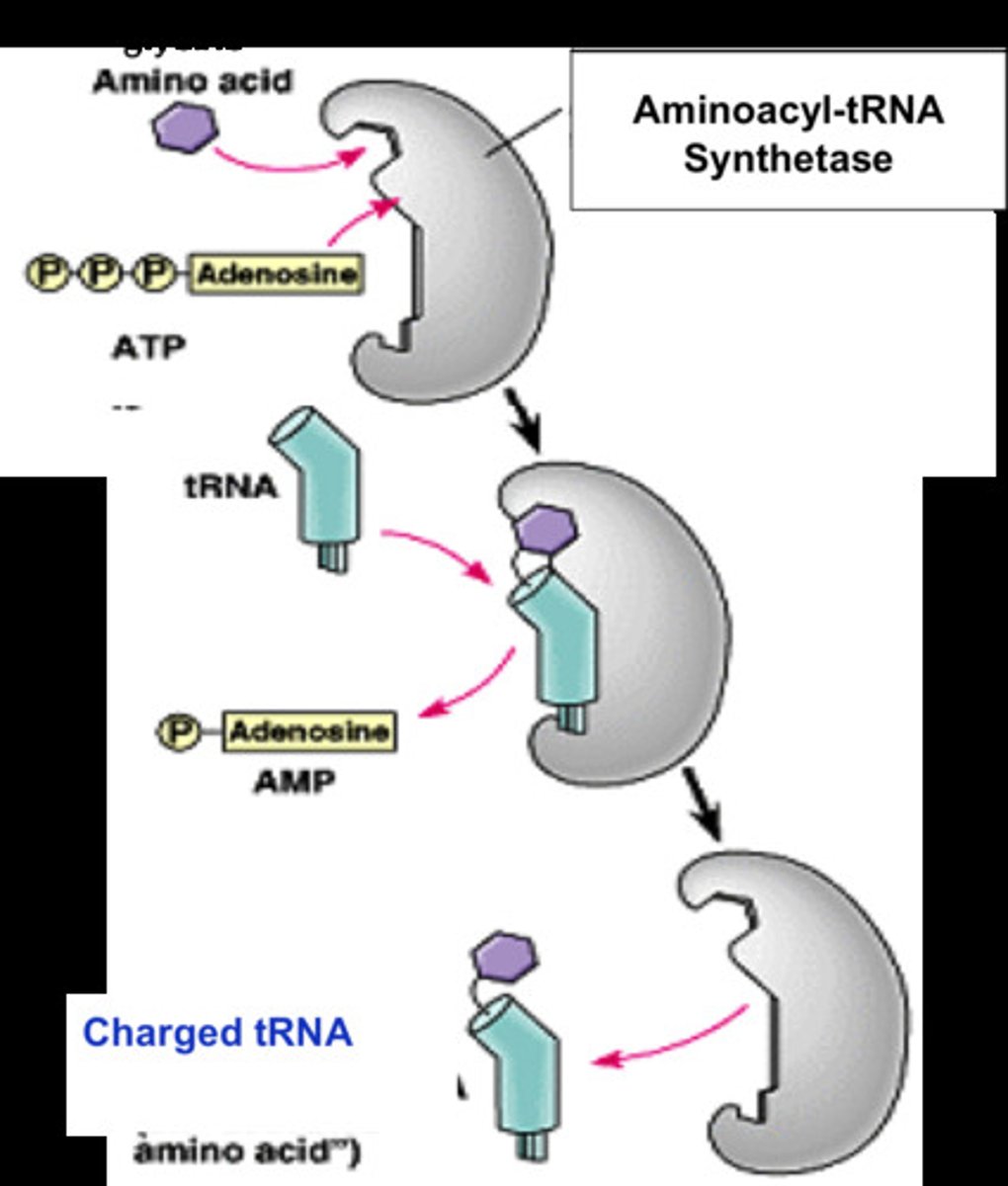
aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase recognizes which structure of tRNA
D-loop/D-arm
Which tRNA structure binds to the ribosome
T-loop/ T-arm
Remember: T-loop Tethers tRNA
The two parts of a ribosome are called
large subunit (60s) and small subunit (40s)
Describe the large subunit of the ribosome
-Contains catalytic Chambers
-Where transcription takes place
Describe the small subunit of the ribosome.
-Where initial binding to mRNA happens
Which amino acid codons are not degenerate/redundant.
Tryptophan- UGG
methionine - AUG
-only one codon encodes for these amino acids
A mutation in the gene HGD causes this disease
Alkaptonuria
Start and stop codons effect both.
Translation and transcription
What are the 3 sites on a ribosome?
E site, P site, A site
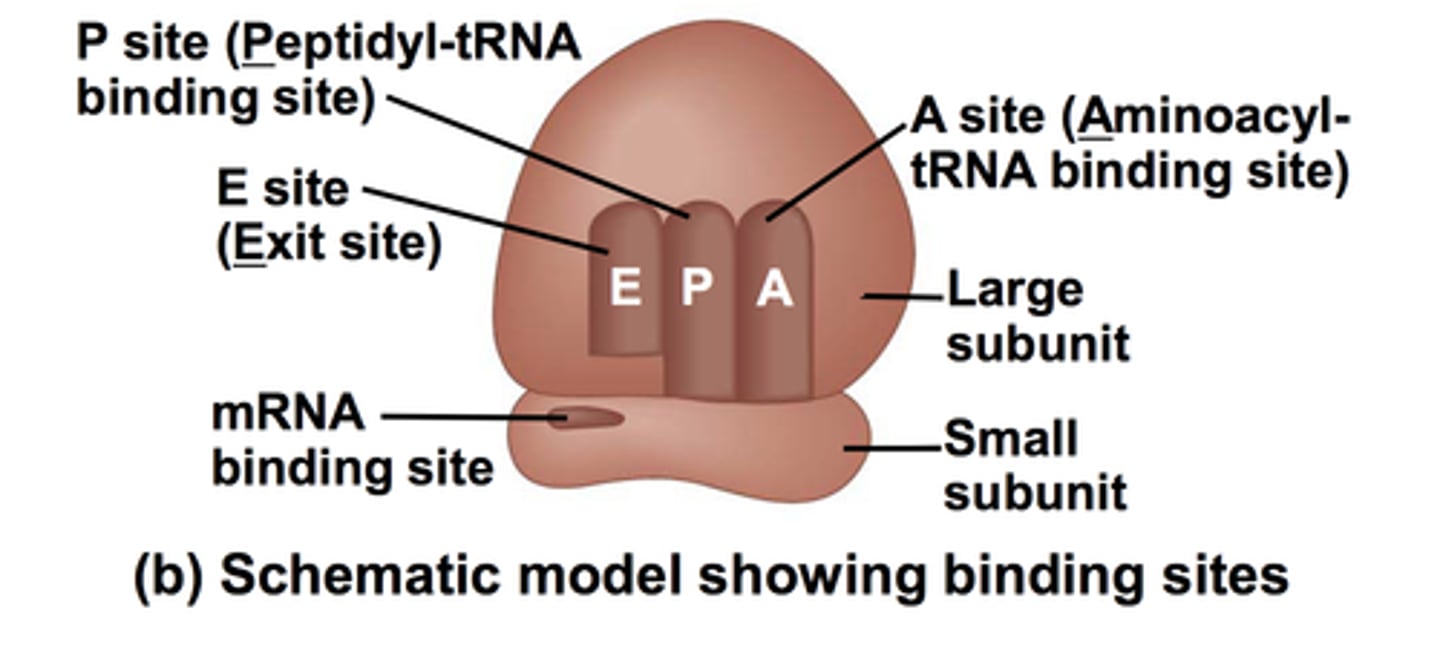
Ribosomal subunits are made of
rRNA and proteins
Auxotrophs
-Organisms that has lost ability to synthesize certain substances required for growth
-Used for mapping of different proteins involved in biochemical synthesis pathways and identification of mutagenic compounds
DNA complementary bases to the start codon
TAC
-Start codon: AUG
Levels of penetrants
How much expression is seen in the organism due to a mutation
codon degeneracy
More than one codon specific a specific amino acid
-The redundancy
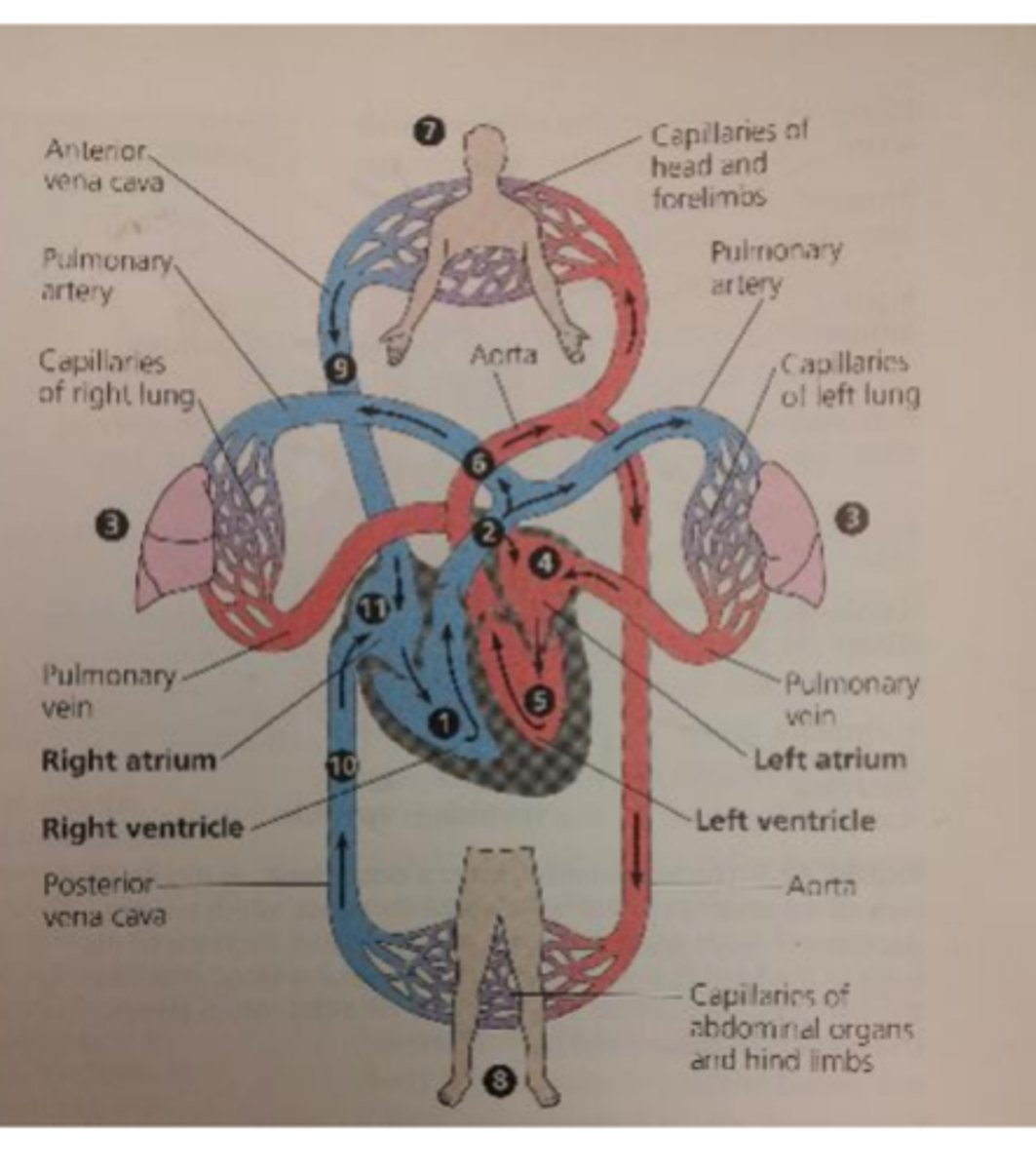
The left ventricle pumps oxygenated or deoxygenated blood and where?
-Oxygenated blood
-To the rest of the body though Aorta
Veins move blood _____ the heart
toward
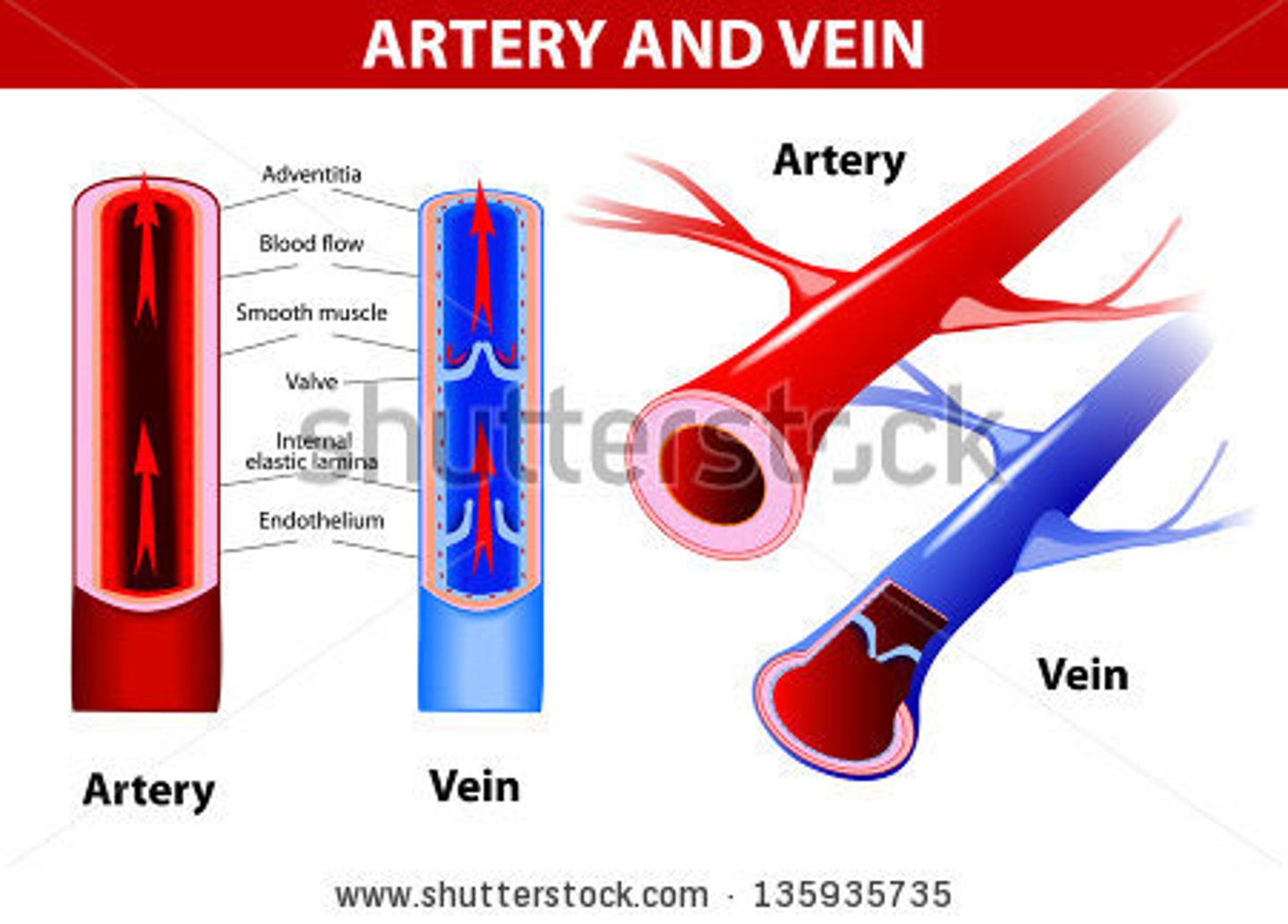
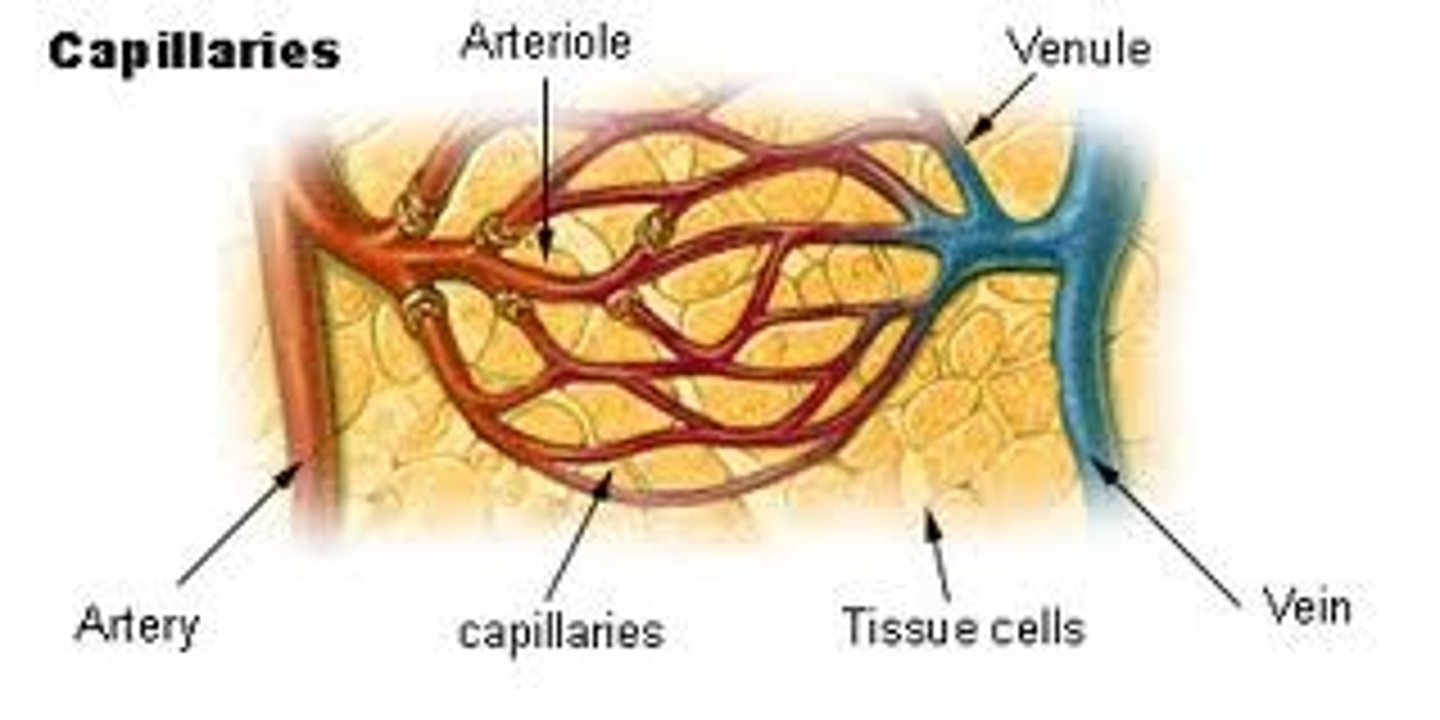
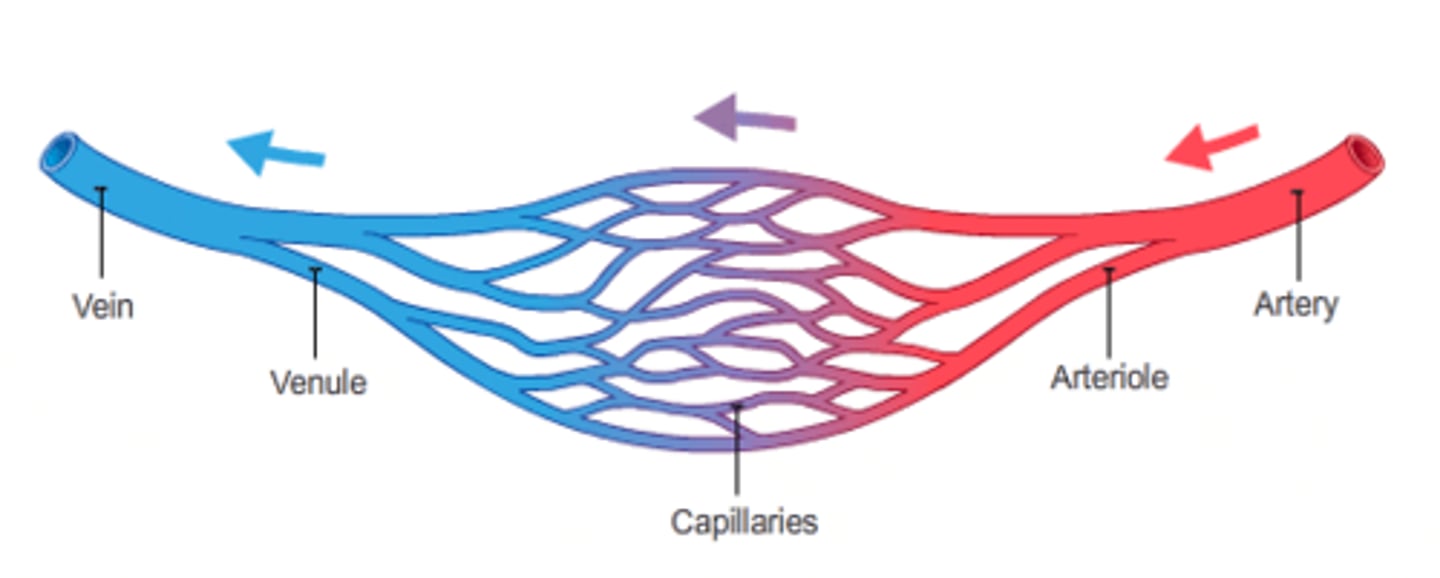
Capillaries
-Fine branching blood vessels
-Between arterioles and venules
-Deliver nutrients, remove waste
-Very thin membrane = +diffusion efficiency
-Large cross-sectional area, slows blood = +diffusion
Arteries move blood ______ from the heart
away
Diffusing rates are affected by
-thickness of membrane
-Concentration gradient
-Temperature
Erythrocyte
red blood cell
-most common type of bloodcell
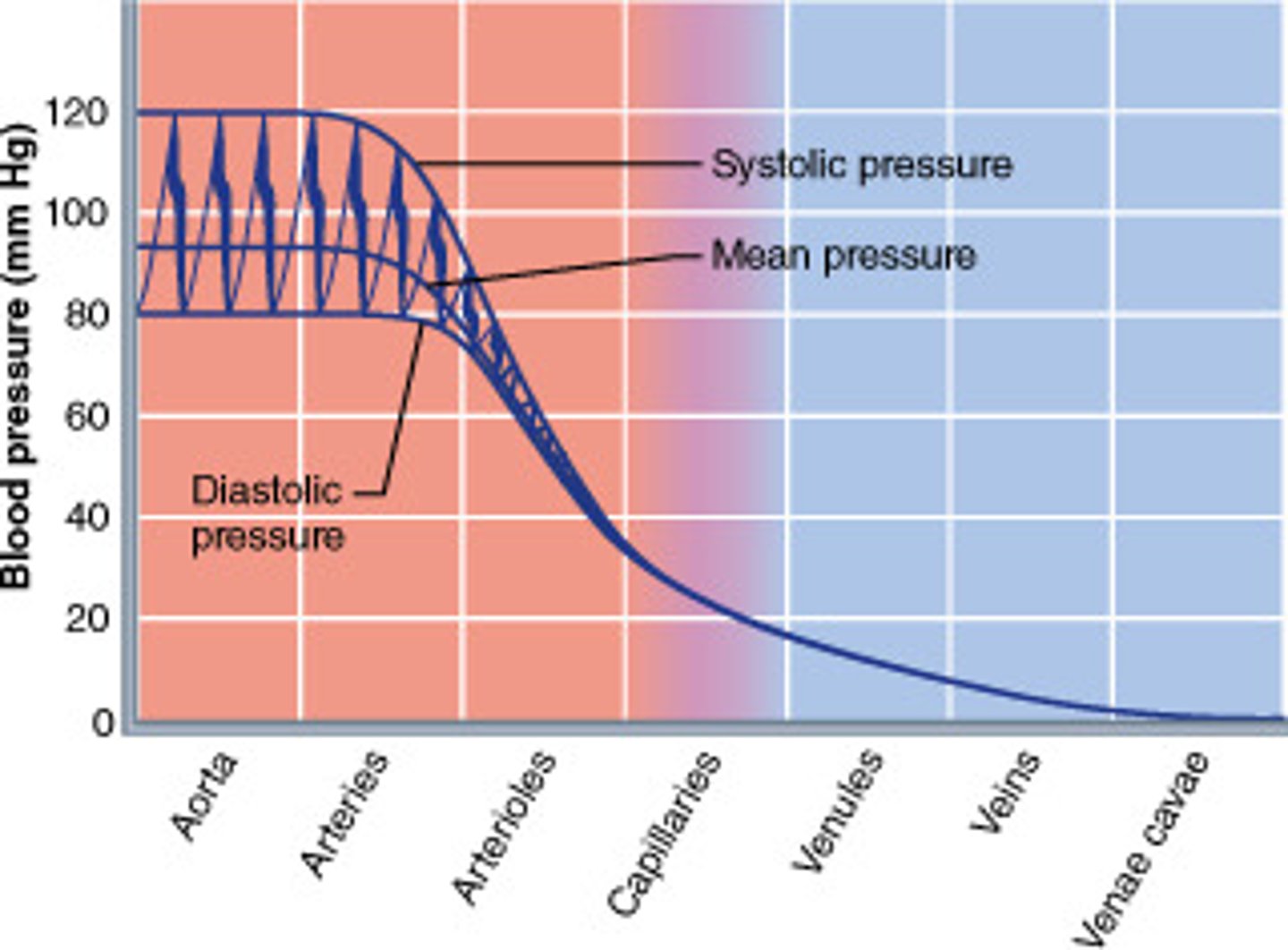
Blood pressure is highest in the arteries or veins.
Highest in the arteries
Arteries--> away from heart
-before capillaries
Lowest in the veins
Veins --> towards heart
-past capillaries
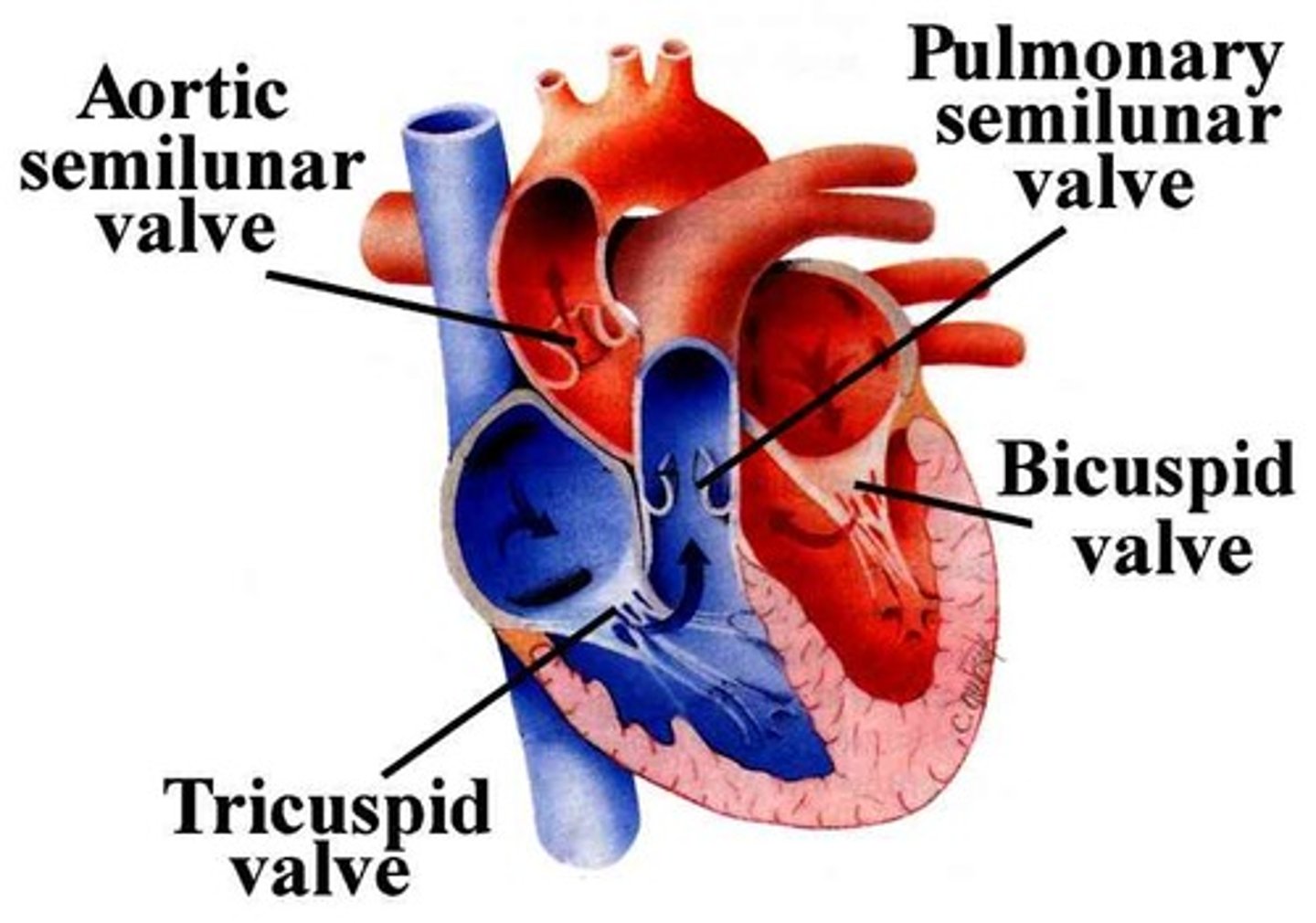
semilunar valves
pulmonary and aortic valves located between the right ventricle and the pulmonary artery and between the left ventricle and the aorta
AV node (atrioventricular node) function
region of the heart between the right atrium and right ventricle from which electrical impulses spread to the ventricles during a heartbeat
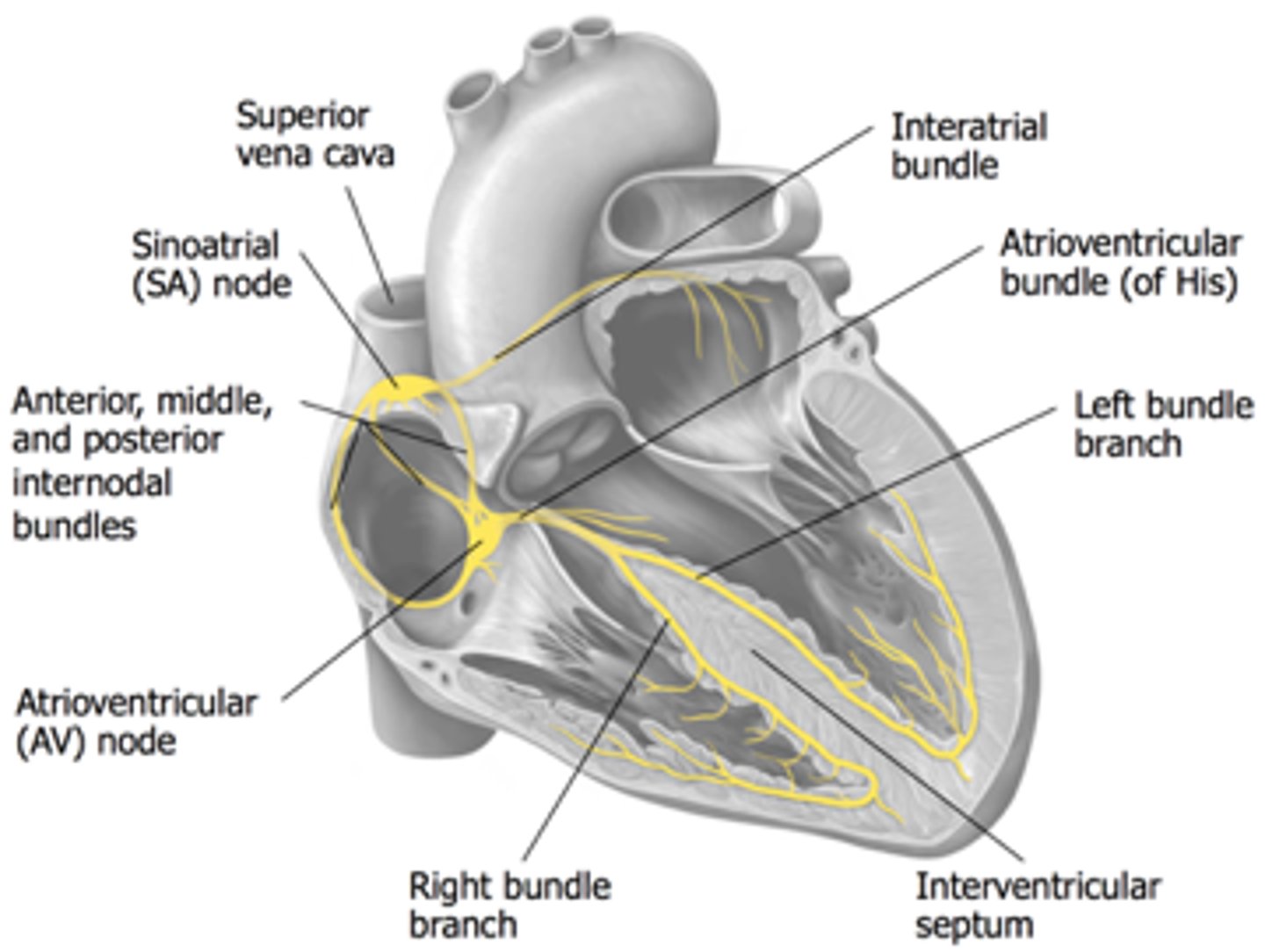
SA node (sinoatrial node)
-pacemaker of the heart
-sets the heartbeat rate
-located in the right atrium
-causes atria to contract
Function of platelets (thrombocytes)
Blood-clotting mechanism (coagulation)
What are the Agranulocytes and their functions?
Lymphocytes
-B lymphocytes -Makes antibodies
-T lymphocytes - Control immune response
-Natural killer cell - kills tumor and infected cells
Monocytes
-Fights off bacteria, fungi, and viruses
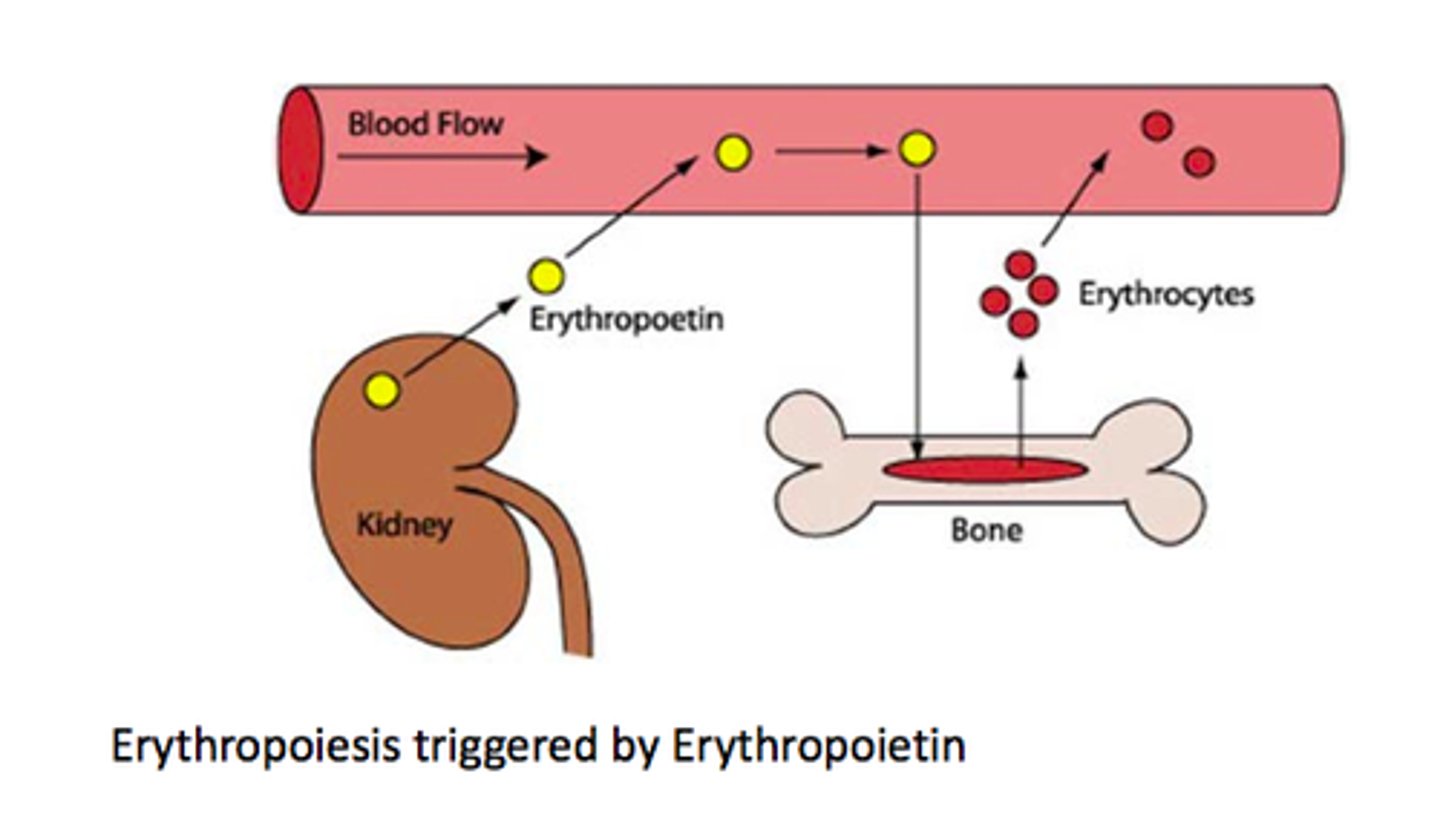
Erythropoietin (EPO) secreted by? Function?
-Secreted by kidneys
-Stimulates erythrocyte production
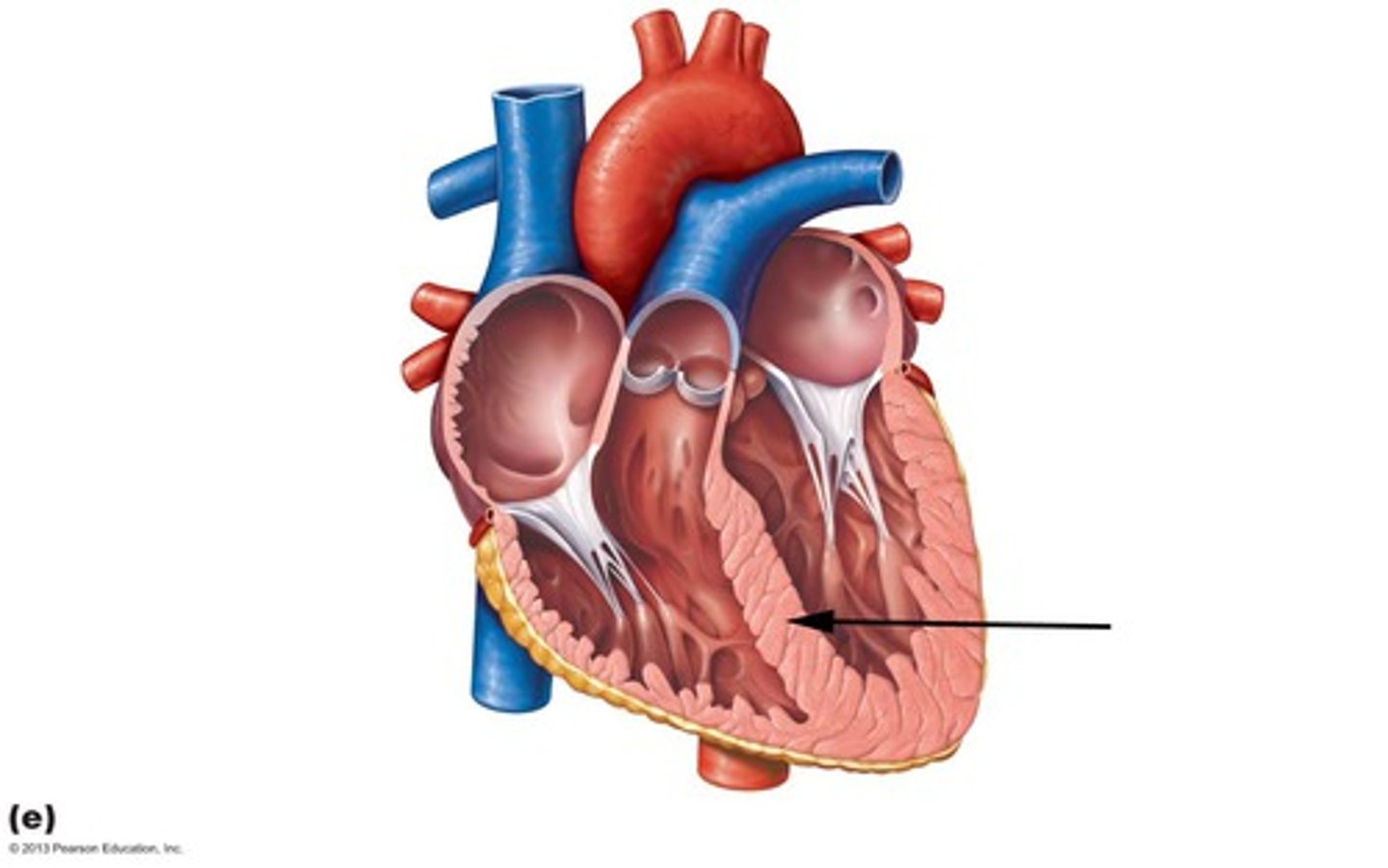
Name the structure that separates the heart into two distinct halves.
Septum
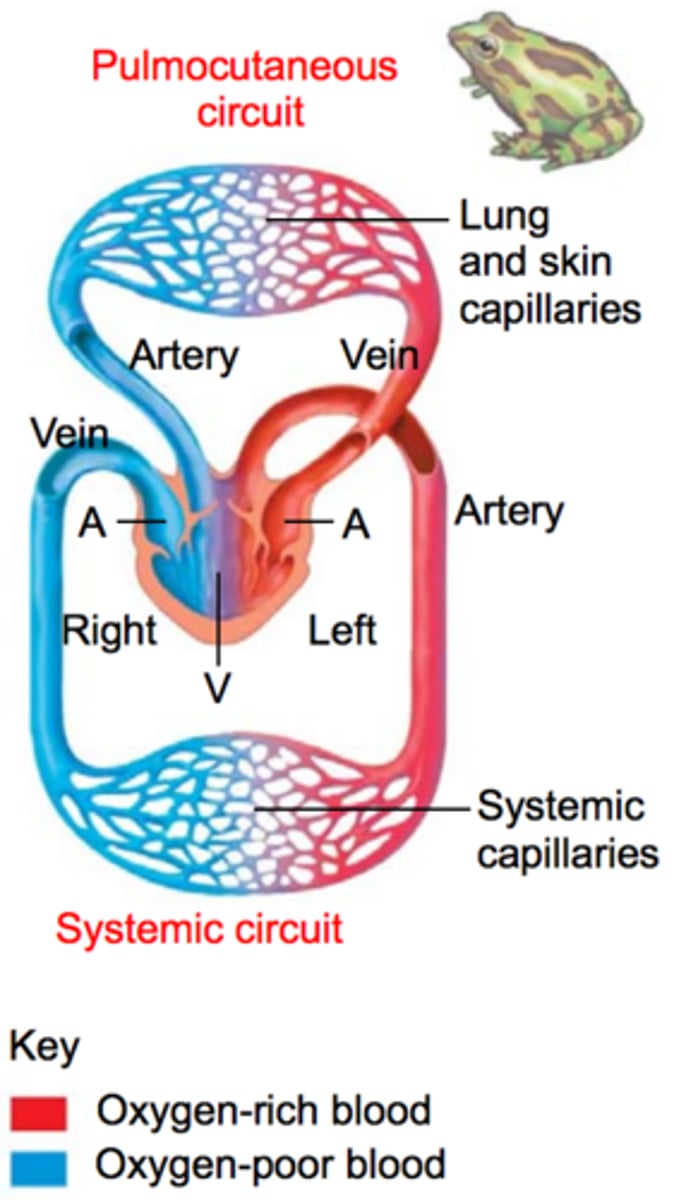
The combination of using skin and lungs for gas exchange is called?
pulmocutaneous
-only seen in amphibians
Artery -> arterioles -> capillary bed
Does blood flow rate increase or decrease?
Decrease
-larger cross-sectional volume
The right atrium receives oxygenated or deoxygenated blood from where
Deoxygenated blood from body tissue
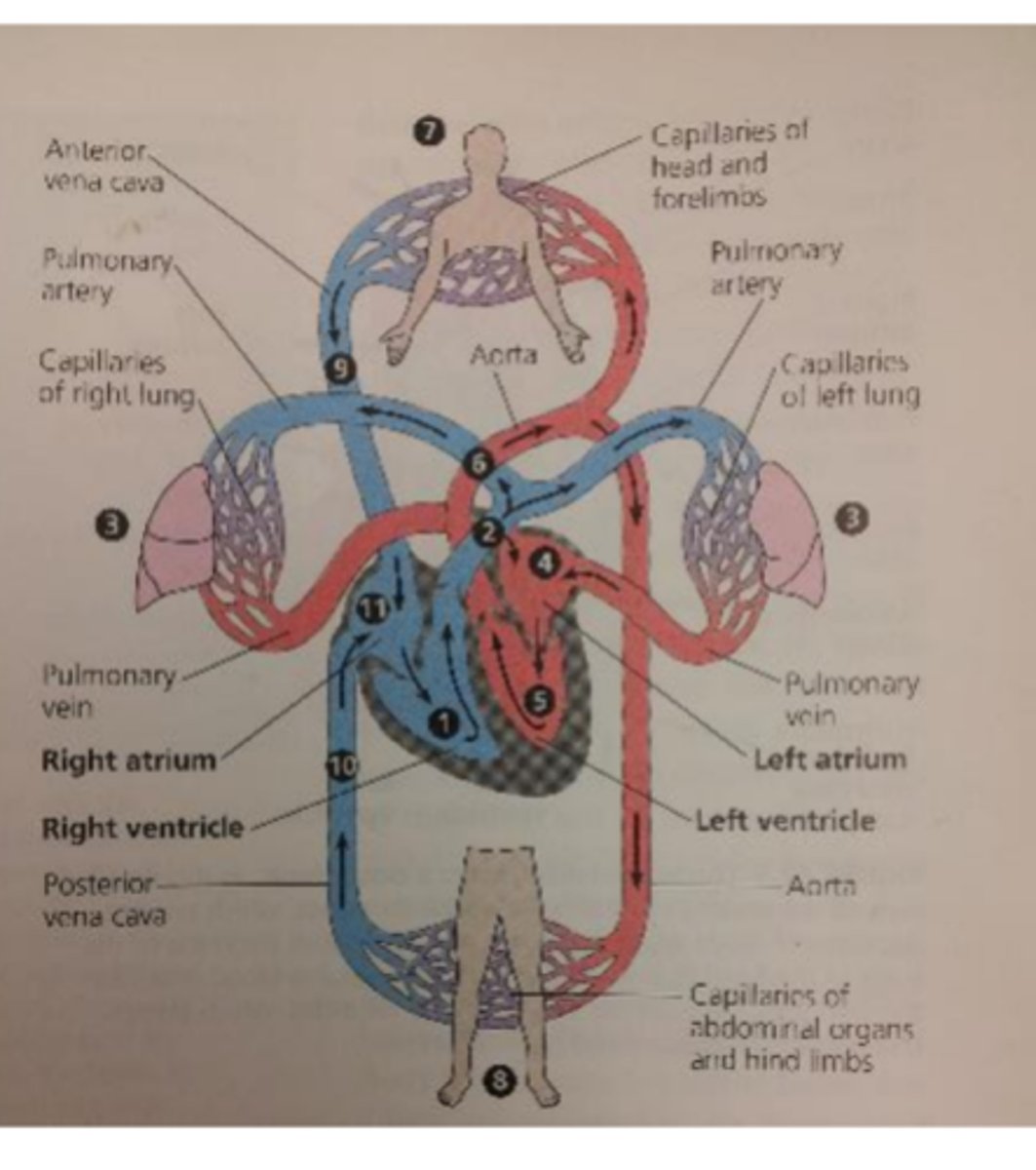
The right ventricle pumps oxygenated or deoxygenated blood to where?
Deoxygenated blood to the pulmonary loop though pulmonary arteries
Atrioventricular valve
-Valve between an atrium and ventricle in the heart
Diastole
Relaxation of the heart
Blood pressure = systolic pressure over diastolic pressure
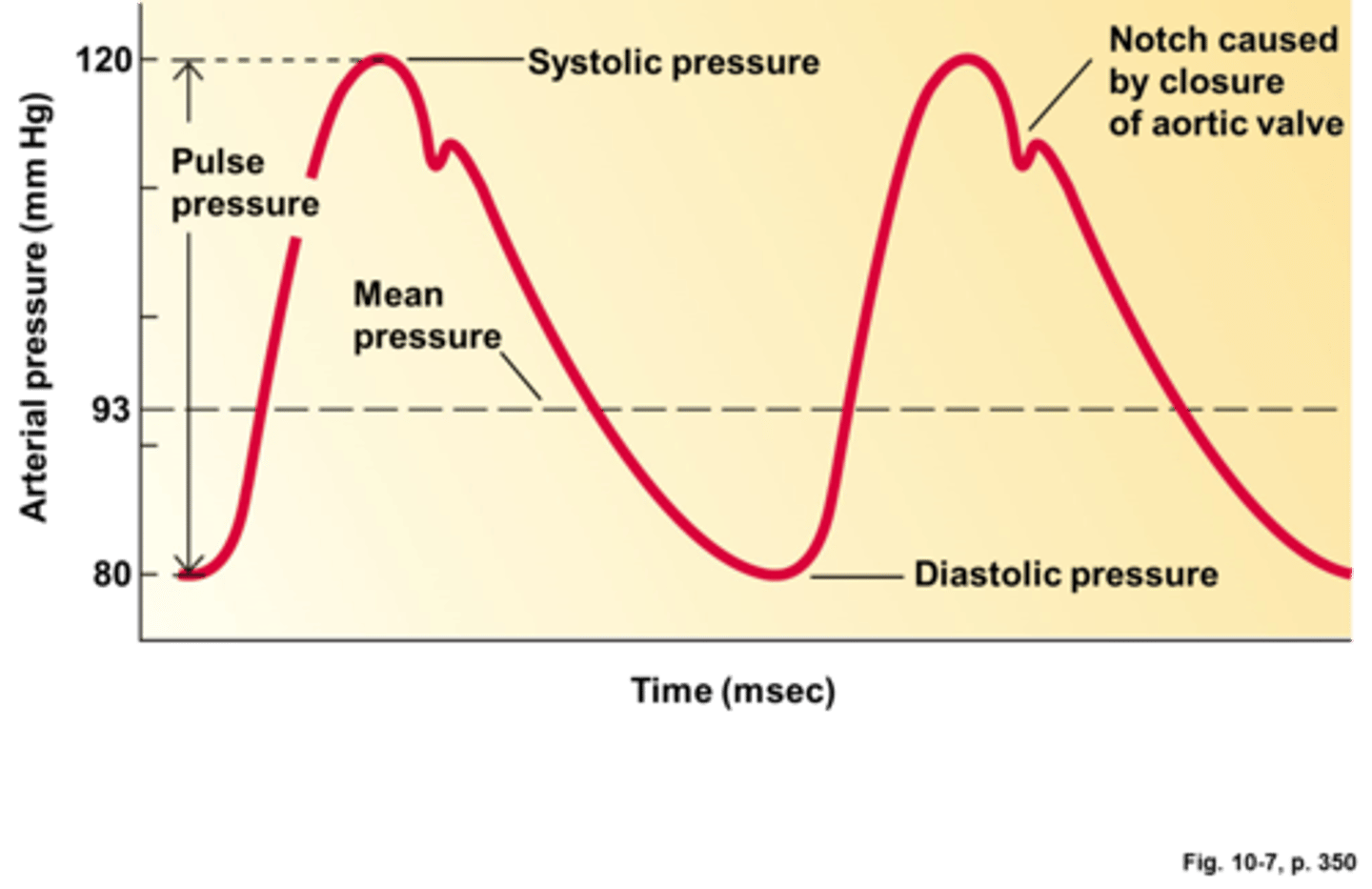
Systole
Contraction of the heart
pulmocutaneous
Combination of using skin and lungs for gas exchange
-only seen in amphibians
The left atrium receives oxygenated or deoxidated blood from where?
oxygenated blood from pulmonary loop
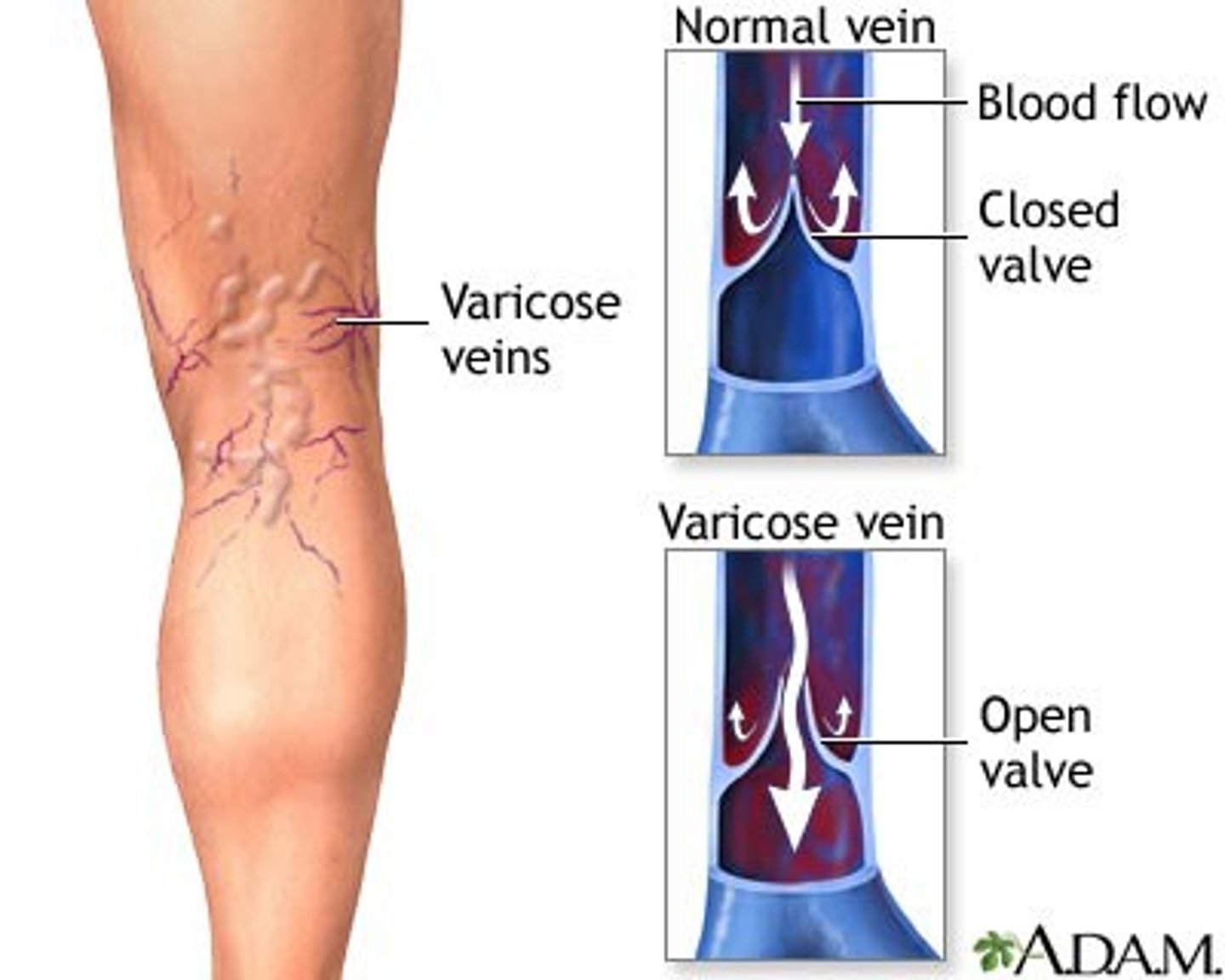
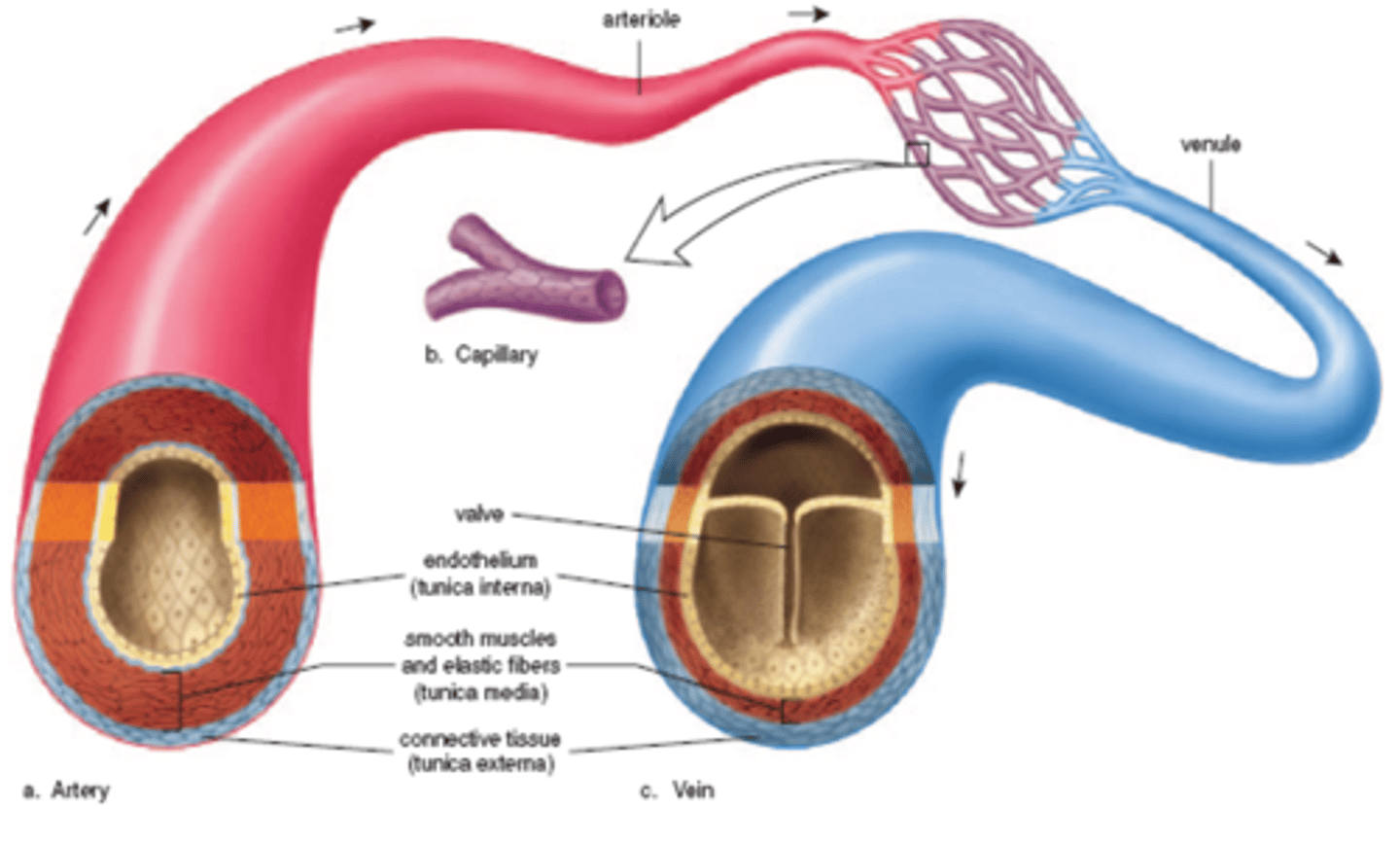
Veins have valves to prevent.
backflow of blood
-Arteries do not contain valves
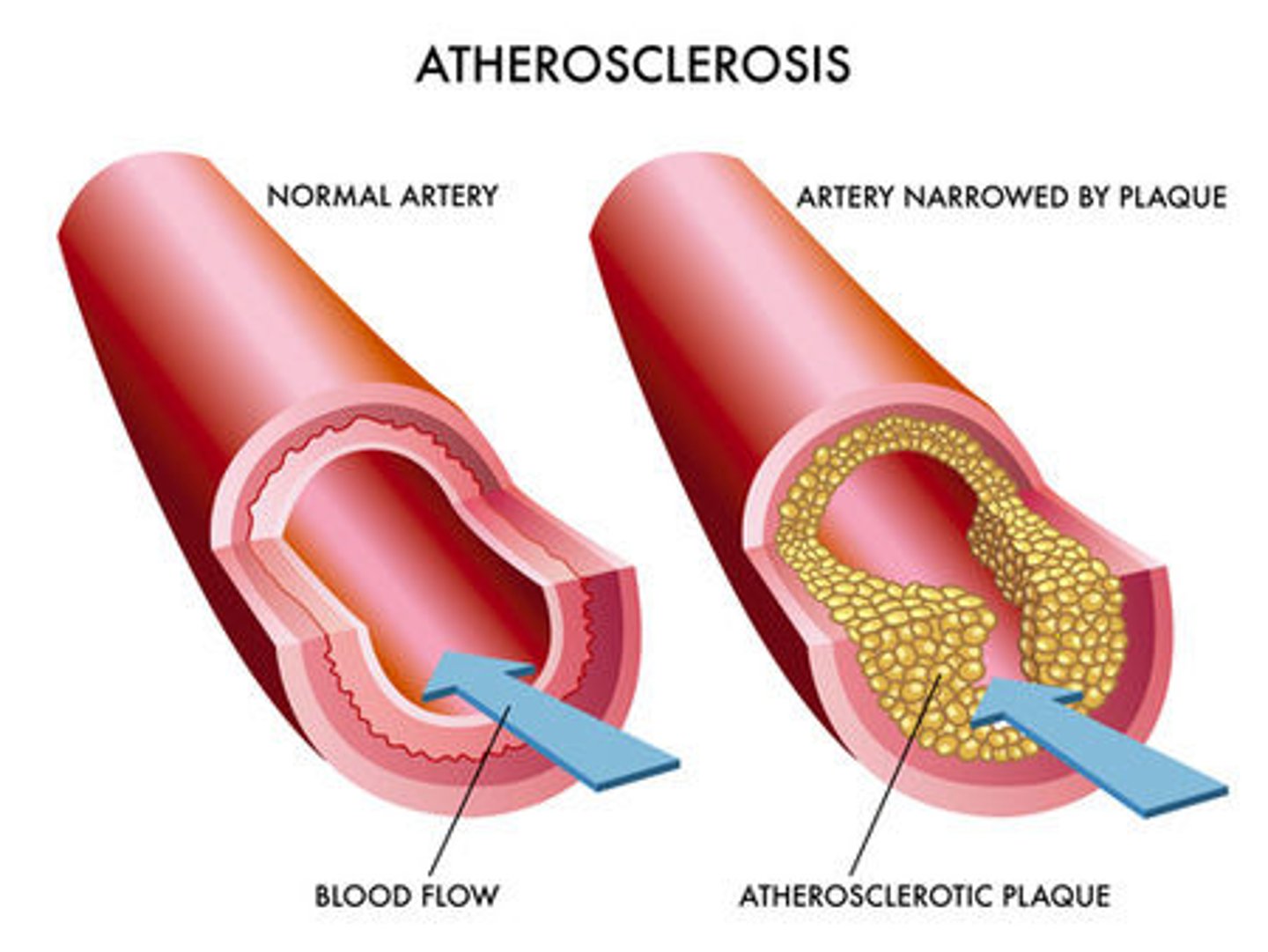
Atherosclerosis
condition in which fatty deposits called plaque buildup on the inner walls of the arteries.
Athero - pasty material / plaque
Sclerosis - hardening
Heart attack caused by
Sudden reduction in blood flow to cardiac/ heart muscle
-Myocardial infarction
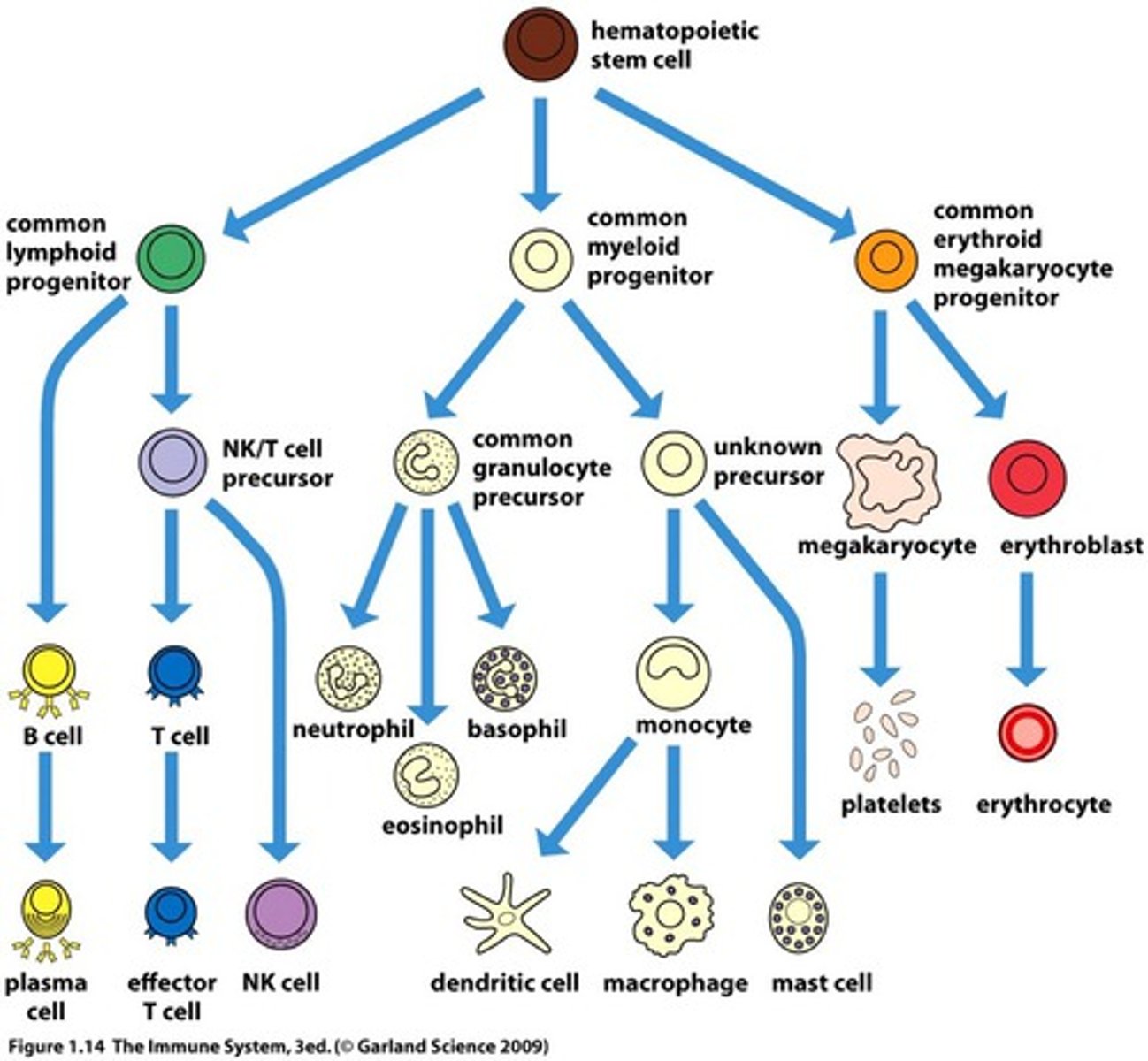
Progenitor cells are
A cell that has lost the capacity for self renewal and is committed to the generation of a particular cell lineage
Septum
Separates the heart into two distinct halves
Stroke is the
Sudden reduction of blood flow to the brain
Blocked artery = Ischemic stroke
Leaking or bursting of blood vessel = Hemorrhagic stoke
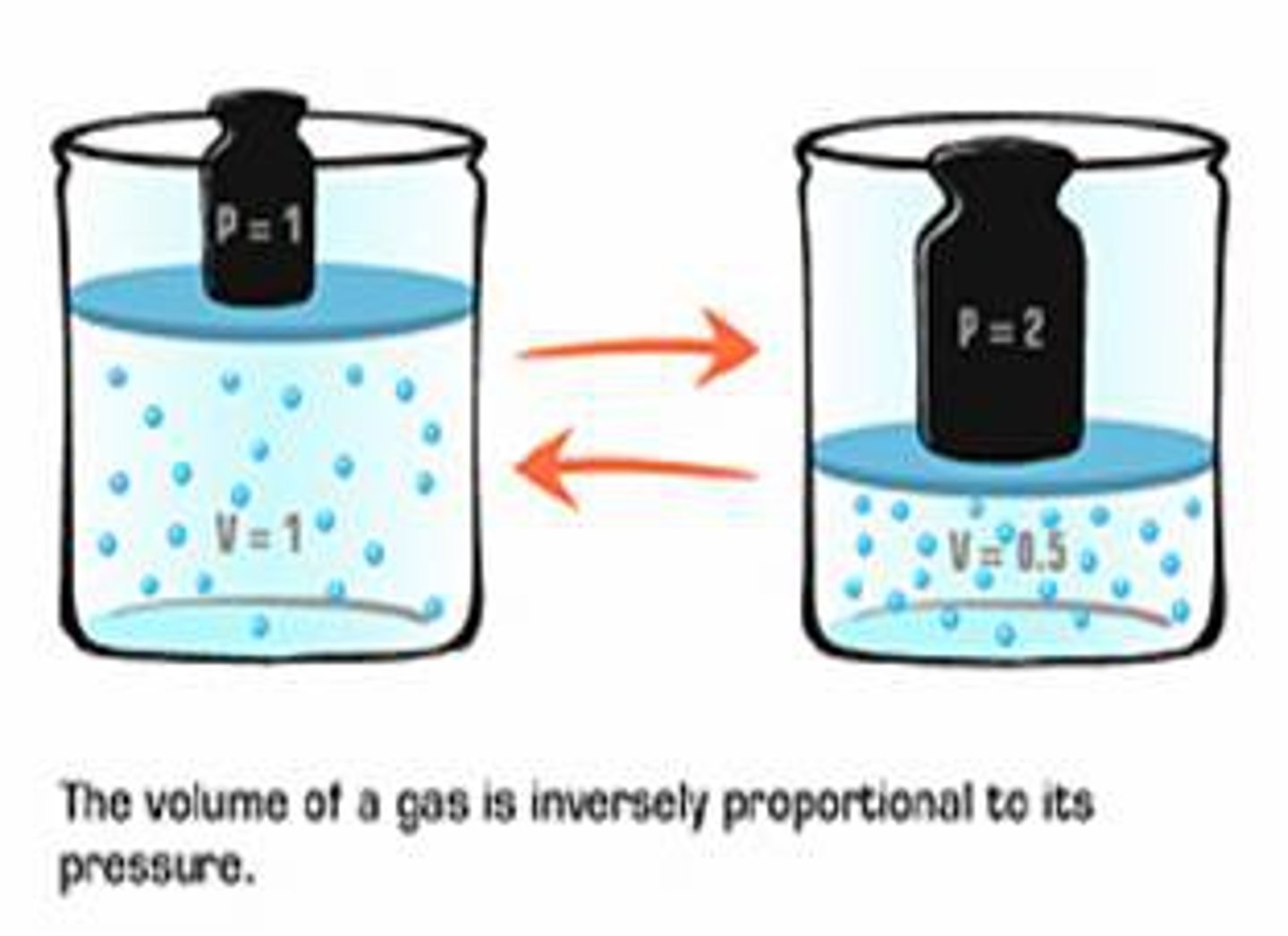
If the volume of the lungs increases, what happens to the air pressure inside the lungs?
Decrease
-Also, applies to blood pressure when entering capillaries (cross-sectional volume increases)
Hemolymph
circulatory fluid in invertebrates
-"invertebrate blood"
-Does not use hemoglobin to carry blood, some use copper compounds. "Blue blood"
Hemophilia
A hereditary disease where blood does not coagulate to stop bleeding
Type A - Factor 8
Type B - Factor 9
Type C - Factor 11
Rank from highest pressure to lowest: Capillaries, Arteries, veins
-Arteries
-Veins
-Capilaries
Do arteries or veins have thicker walls?
arteries have thicker walls
-Due to higher pressure
Globulins function
-Transport lips and fat soluble vitamins
-some are enzymes
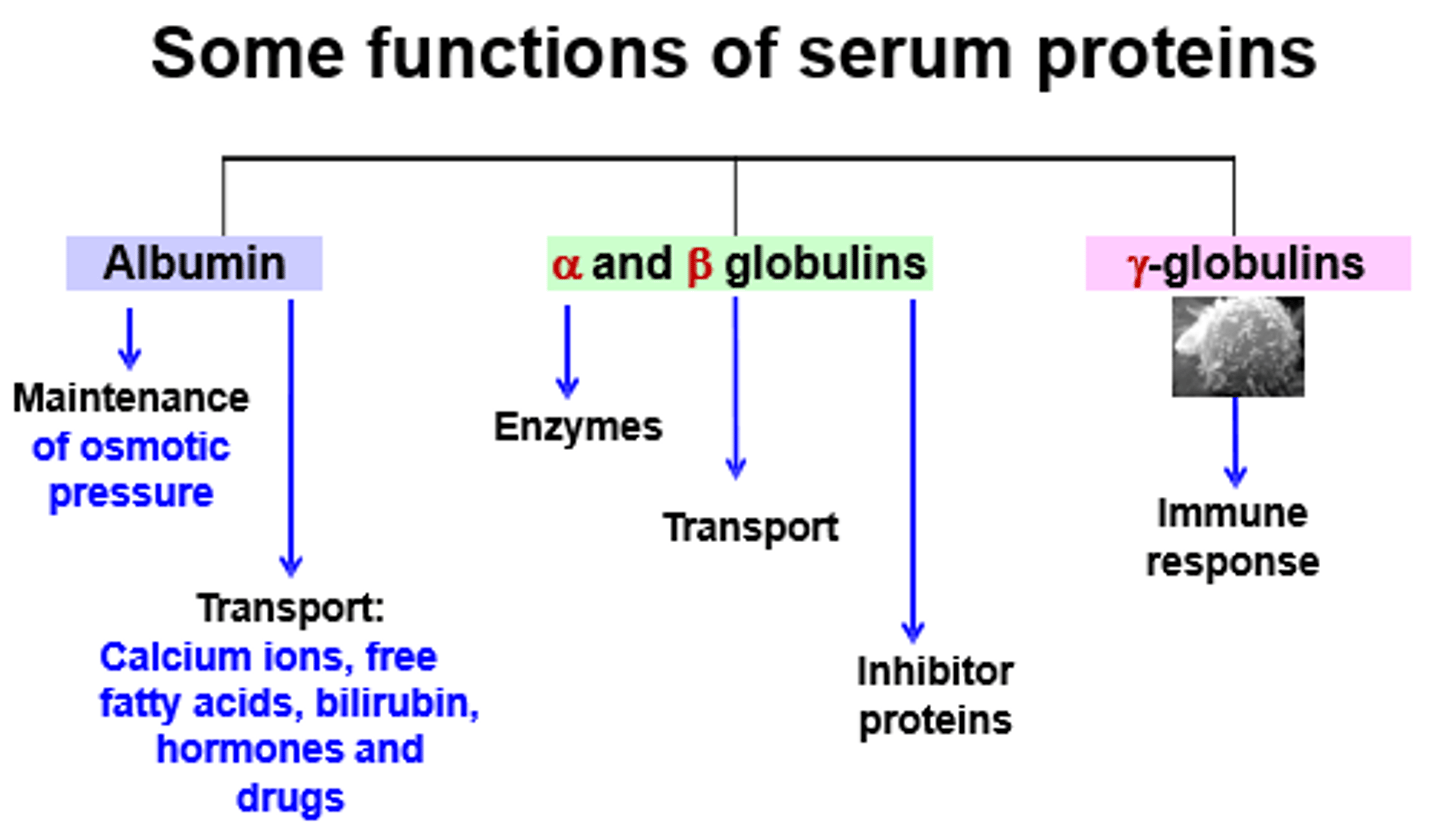
Albumins function
Osmotic balance, pH buffering, Transports wastes and hormones
If volume decreases then pressure
increases
Ischemia Vs. Infarction
Ischemia: term for not getting enough oxygen
Infarction: death of the tissue
-possible end result of too much Ischemia
Venous blood and arterial blood
-Venous blood is deoxygenated blood that enters the right atrium,
-Arterial blood is oxygenated blood that enters the left atrium
Aortic aneurism
-Bursting or splitting of the aorta
-Aorta stretches during ventricle contraction
Thrombin function
converts fibrinogen into fibrin, causing blood clotting
-enzyme
-aka clotting factor 2
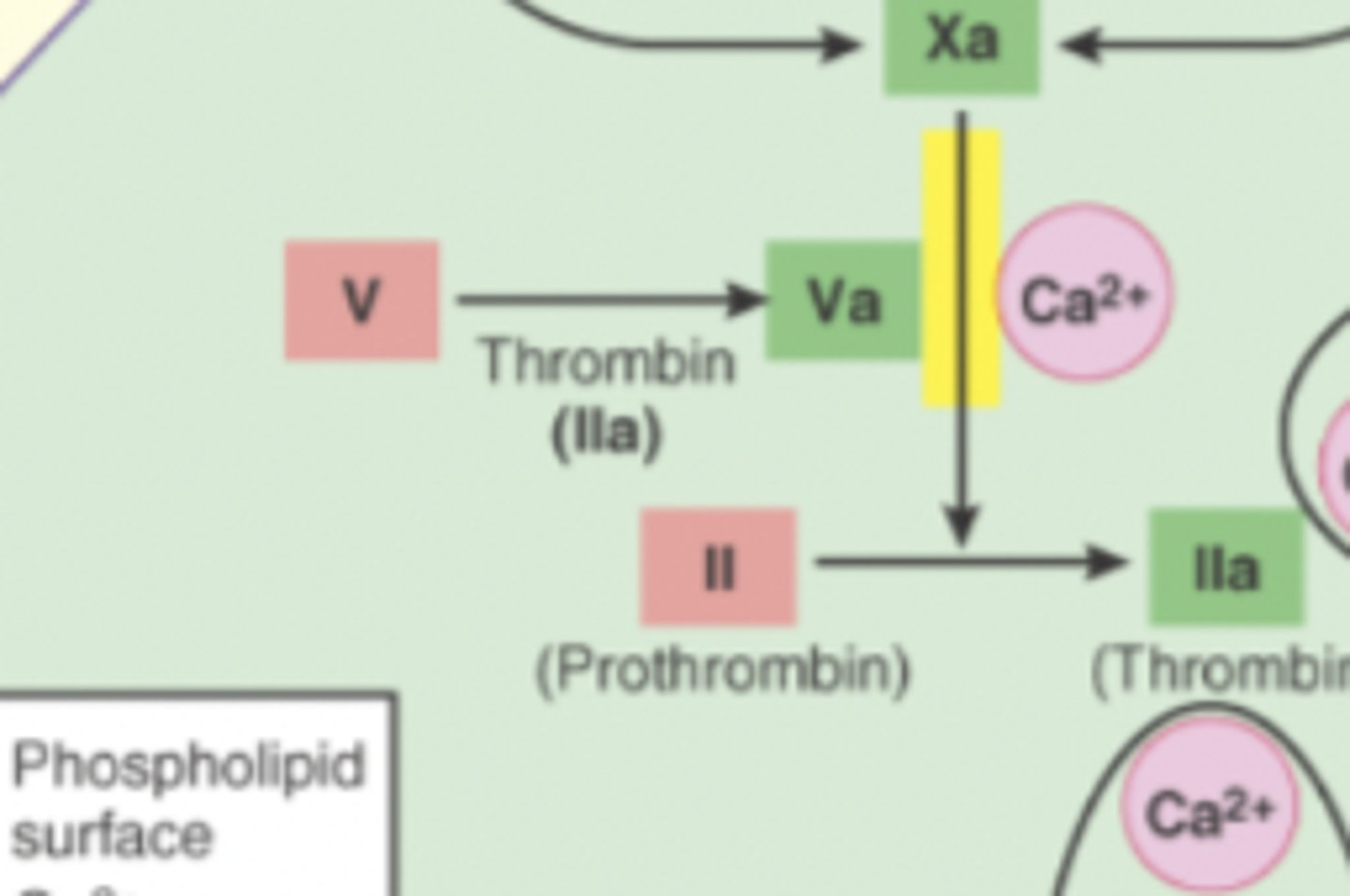
Fibrinogen function
blood clotting
-aka clotting factor 1
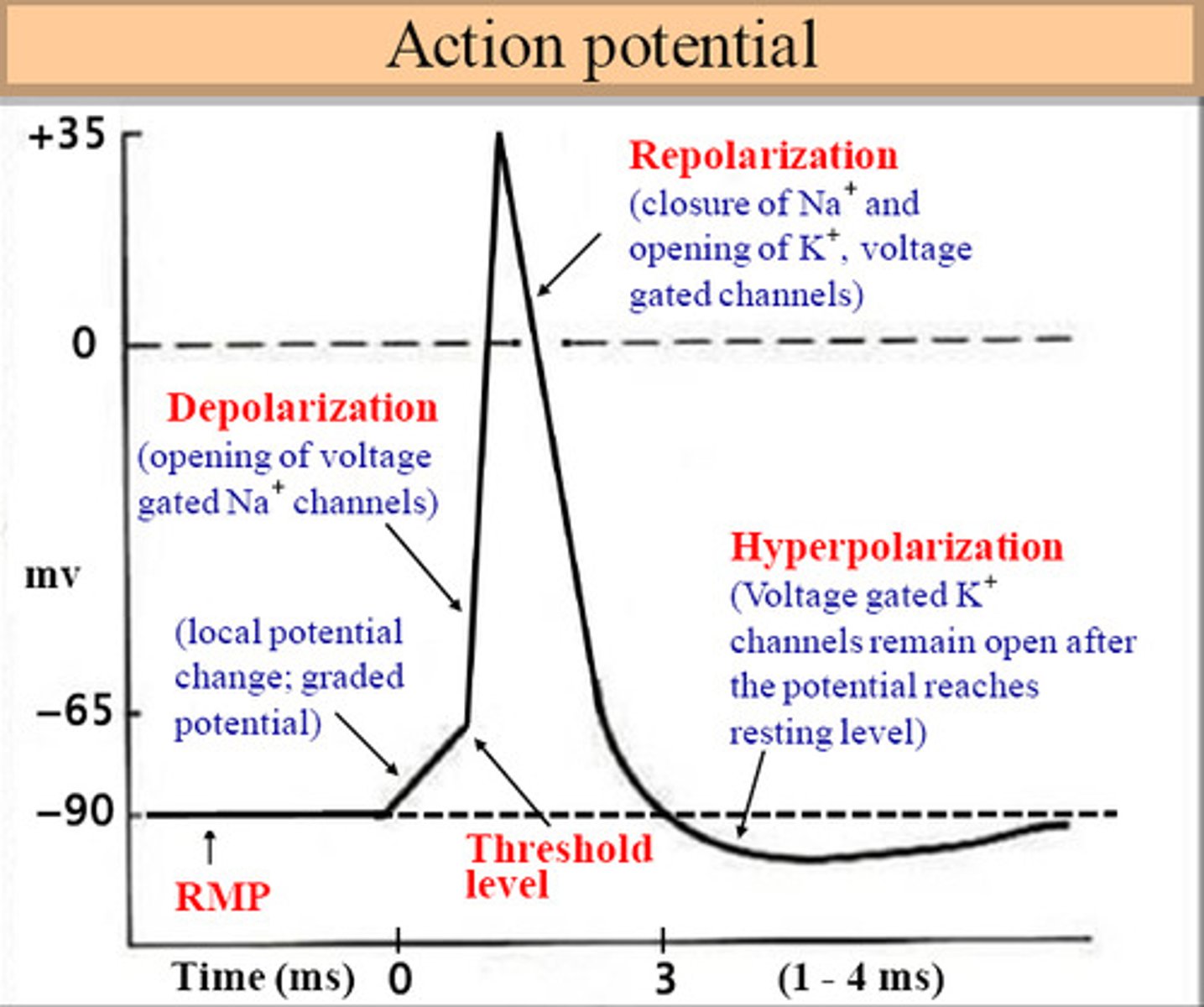
Action potential
the change in electrical potential associated with the passage of an impulse along the membrane of a muscle cell or nerve cell.
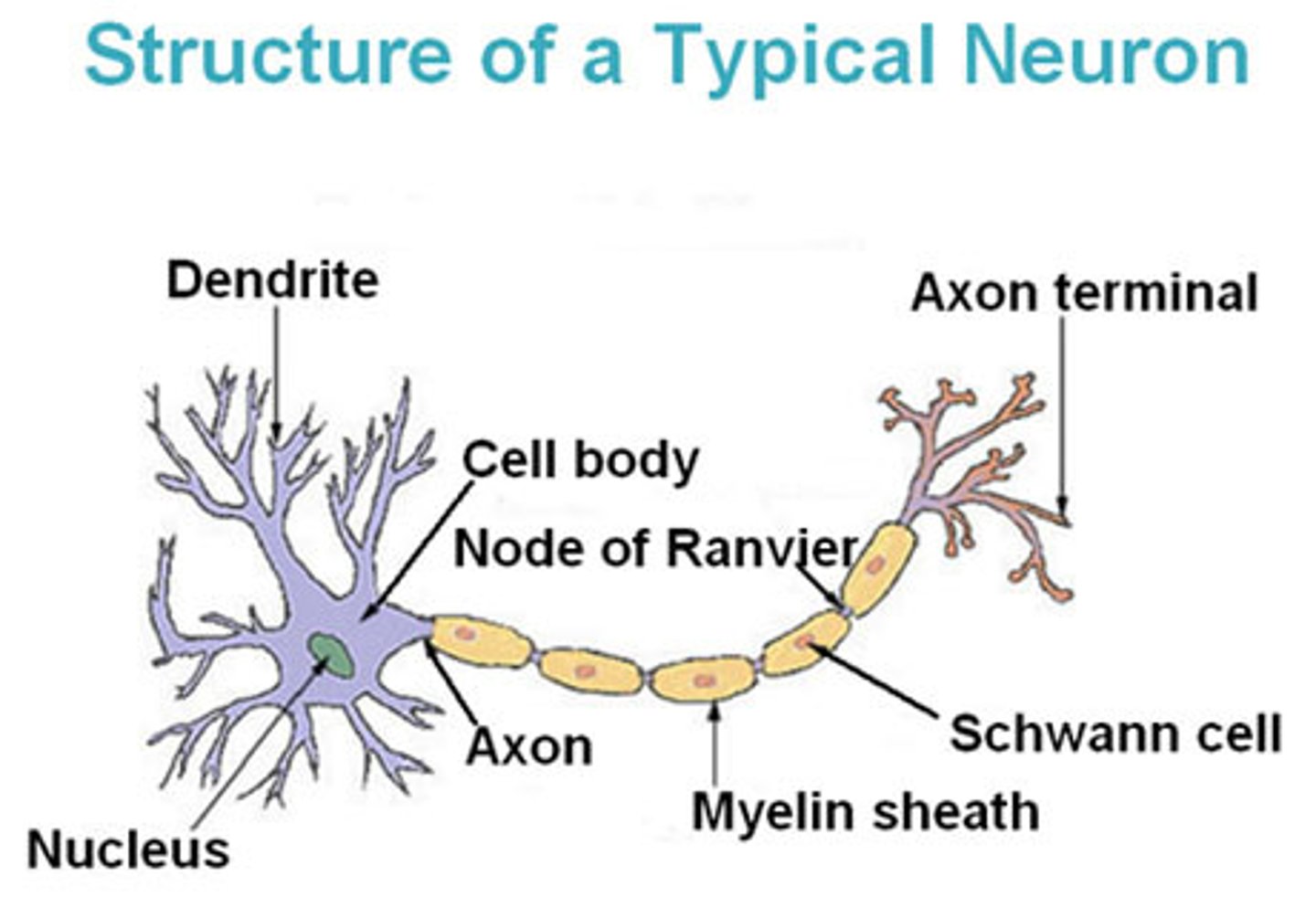
myelin sheath
A layer of fatty tissue segmentally encases the fibers of many neurons. Enables vastly greater transmission speed of neural impulses as the impulse hops from one node to the next.
-Insulates the axon
-Protects nerve cell
-Increase the rate of conduction
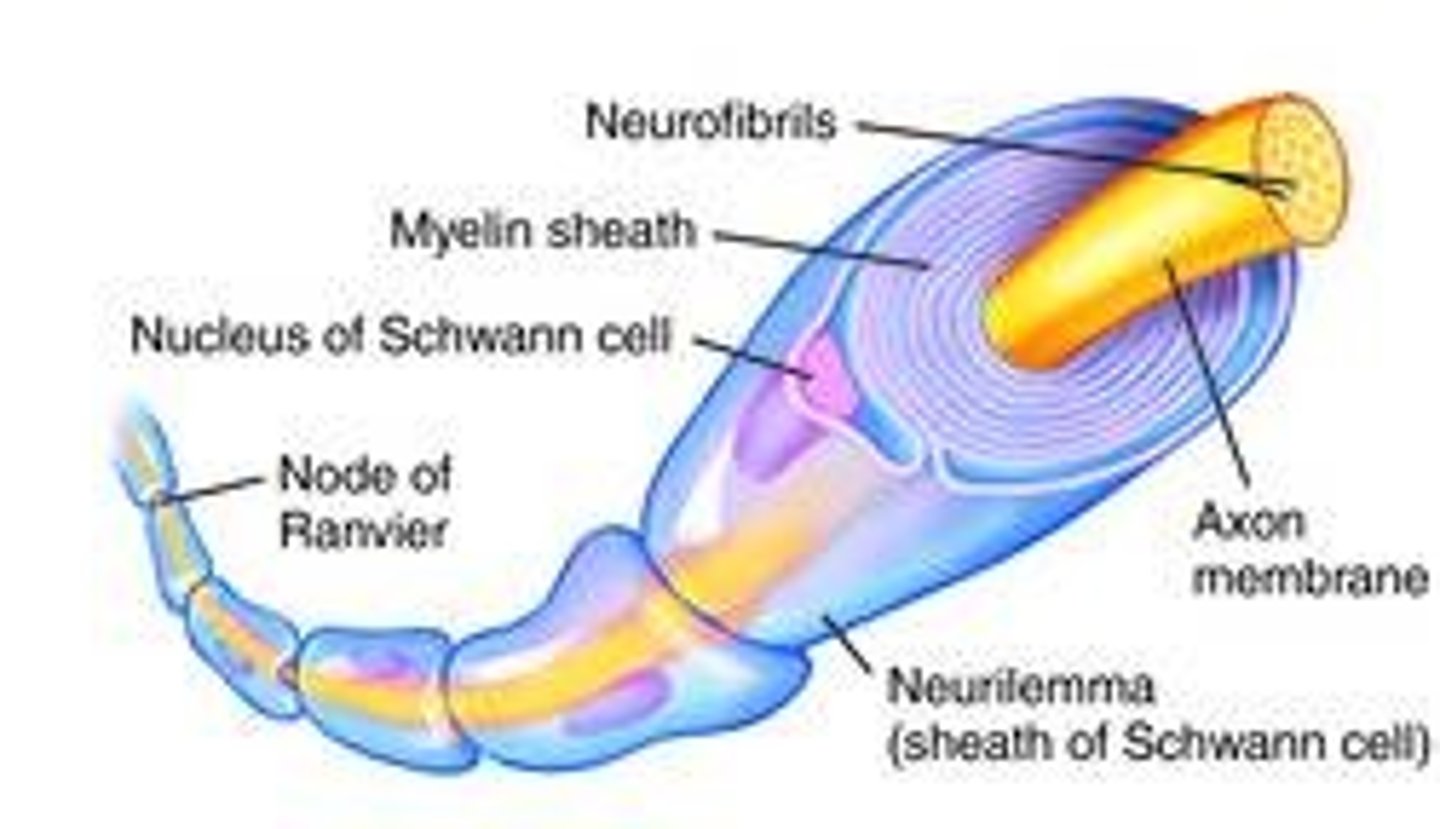
Receptor
protein that detects a signal molecule and performs an action in response
-Auditory receptors
-Olfactory receptors
-Photoreceptors
Nodes of Ranvier
Gaps in the myelin sheath to which voltage-gated sodium channels are confined.
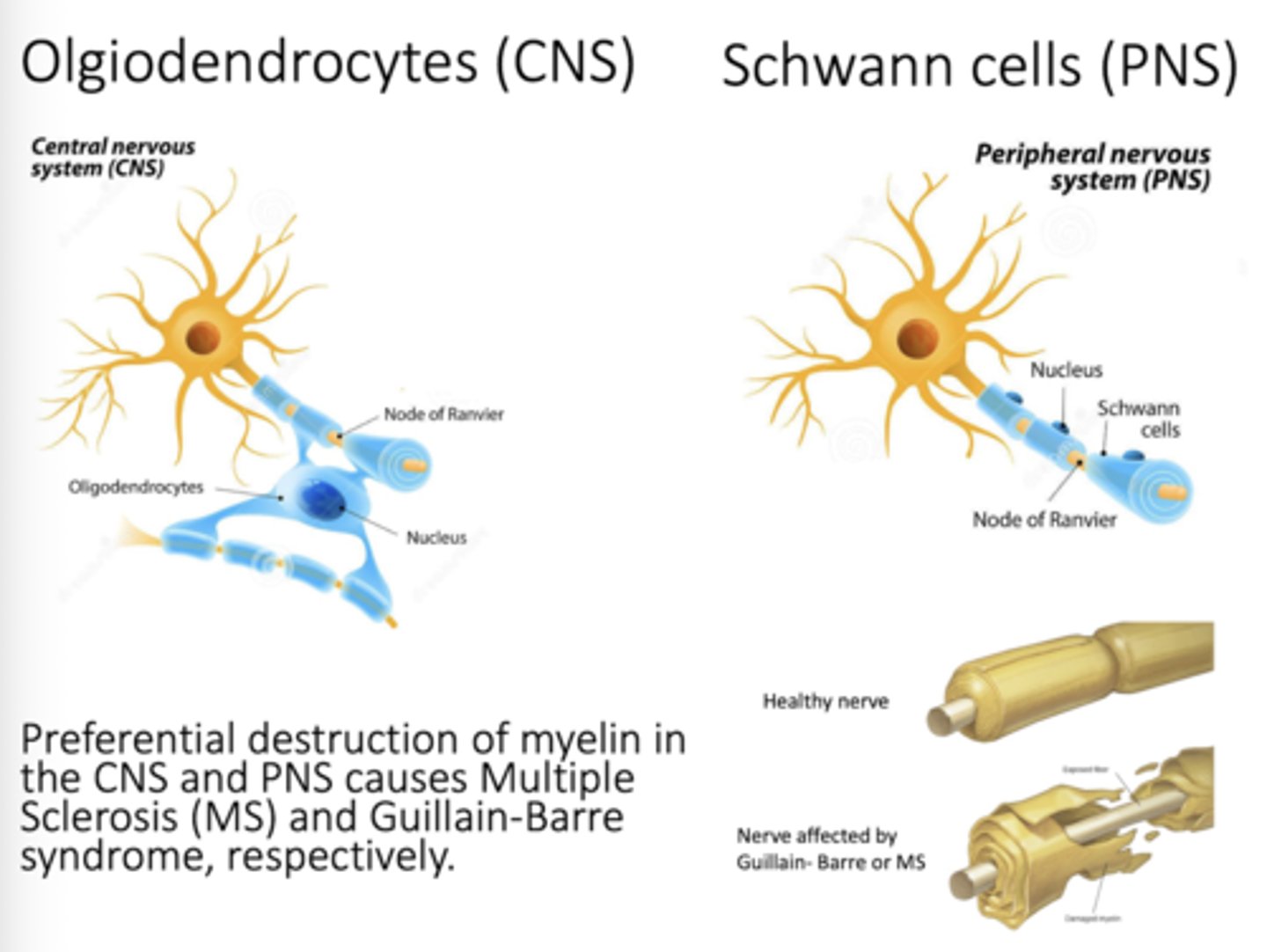
What produces myelin in the CNS? in the PNS?
Oligodendrocytes - CNS
Schwann cells - PNS
Glial cells
non-neuronal cells that are associated with and work with nerve cells
Ex: Astrocytes- CNS - support and maintain ion concentration of interstitial fluid (plays a role in the Blood Brain Barrier)
Oligodendrocytes - Produces myelin in the CNS
Schwann cells - produce myelin in the PNS
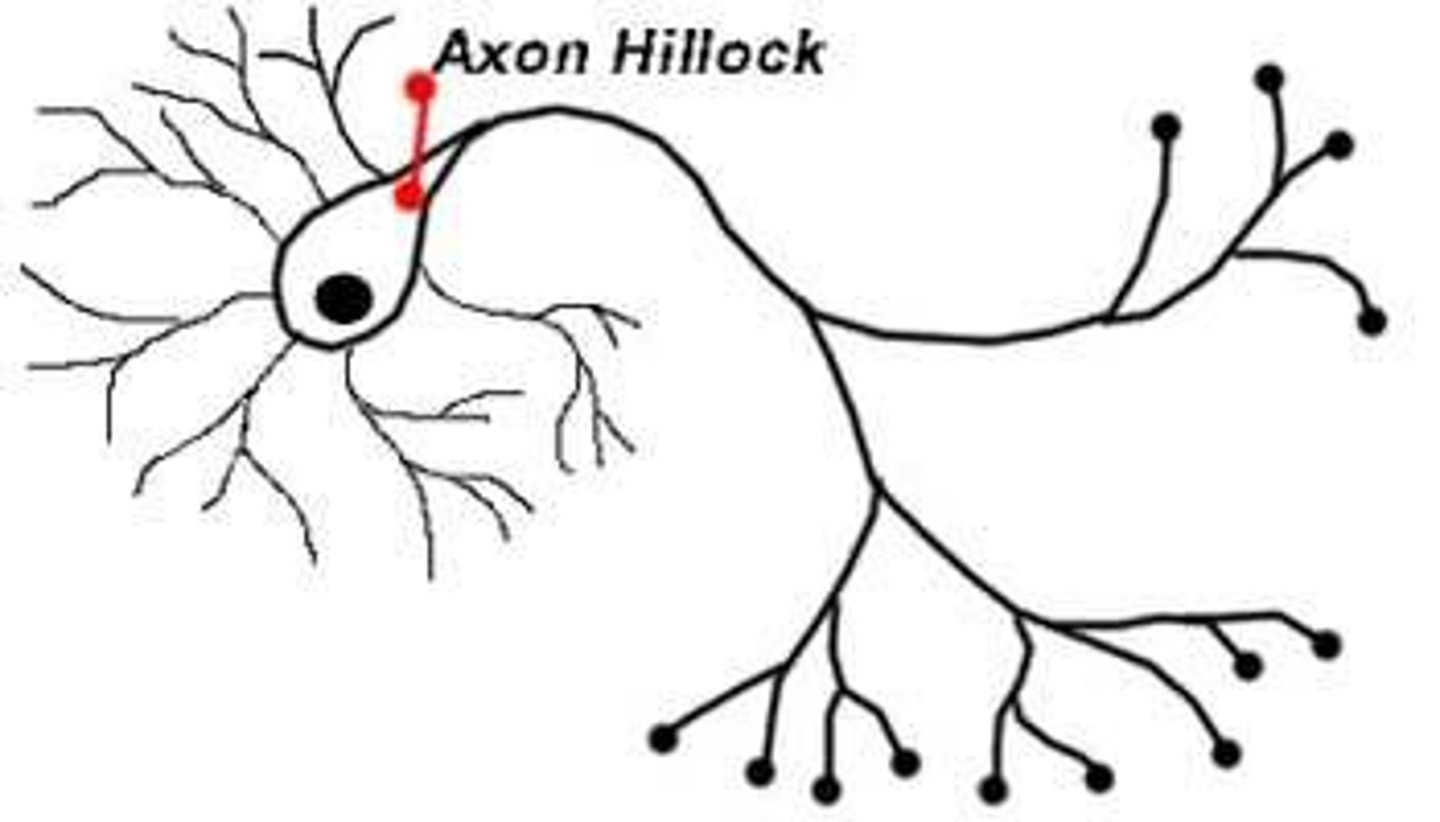
Axon hillock
A specialized part of the cell body (soma) of a neuron that connects to the axon
-Where action potential is generated
Presynaptic neuron
Neuron that transfers information from one cell to the other
sending neuron
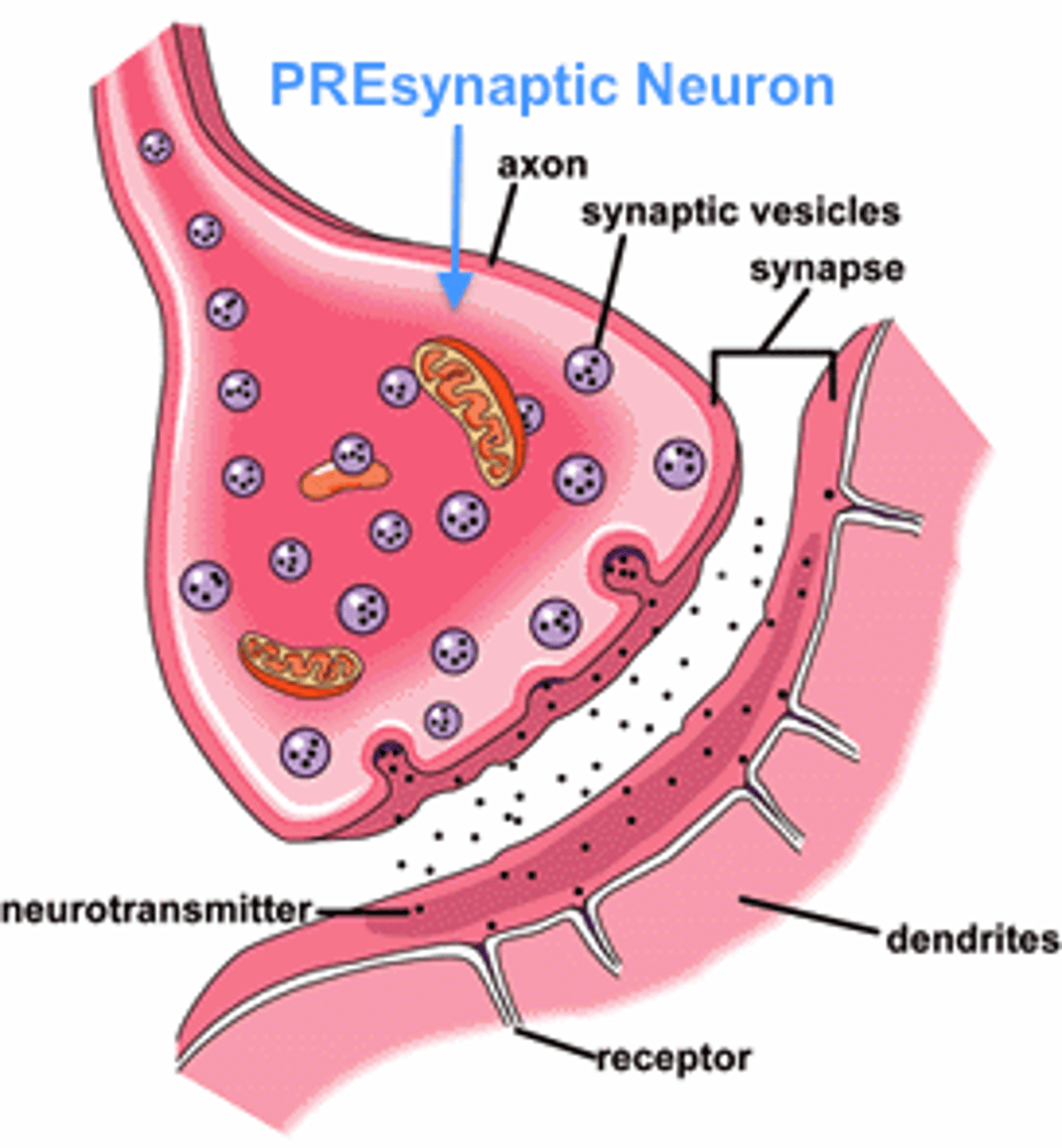
Ganglia and nuclei
ganglia - cluster of nerve cell bodies in the PNS
Nuclei - cluster of nerve cell bodies in the CNS
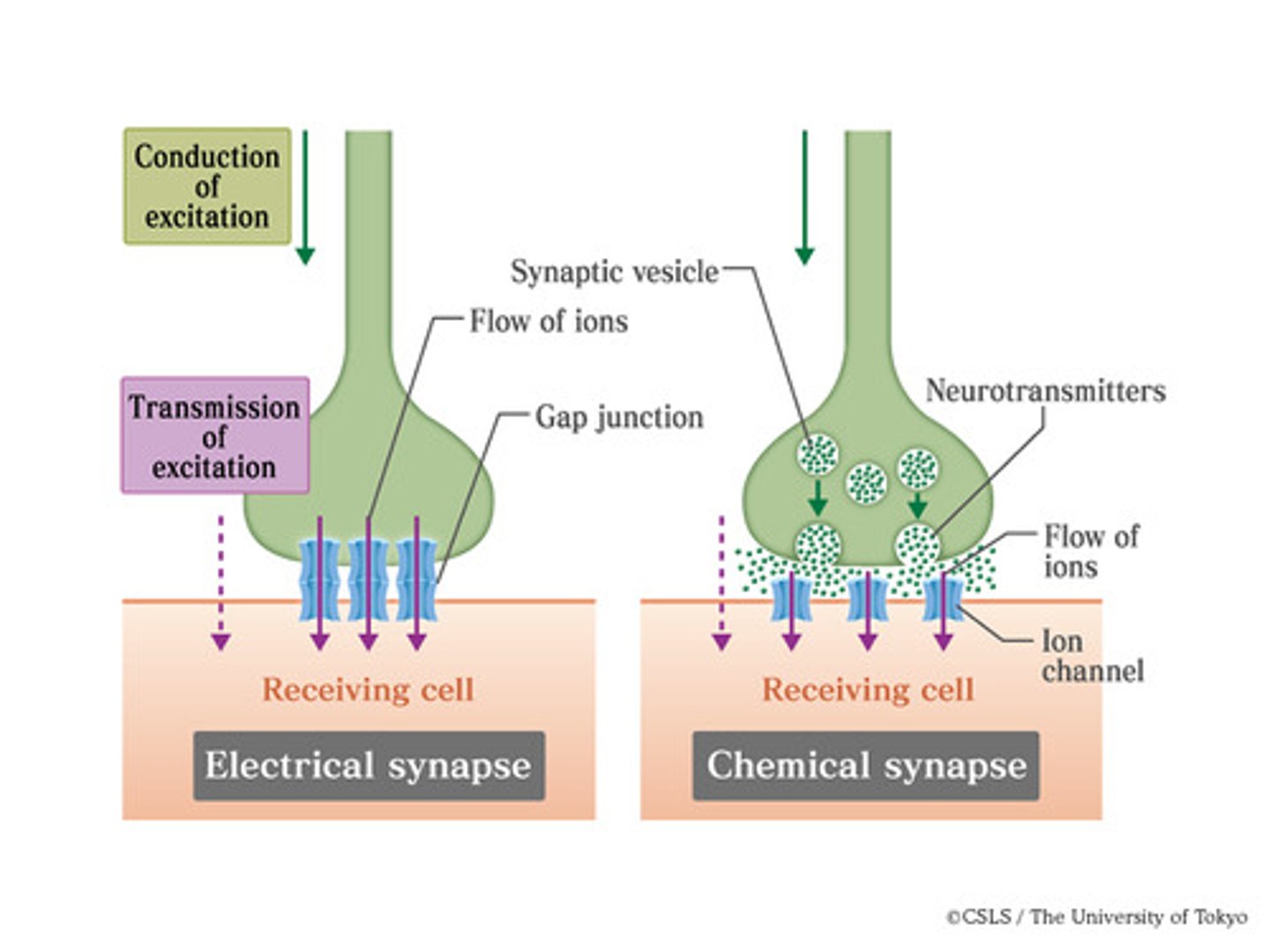
Of the two types of synapses?
1. electrical - Direct physical contact between pre and post neuron
2. chemical - Gap between neurons
-Use neurotransmitters
-Found in CNS and PNS
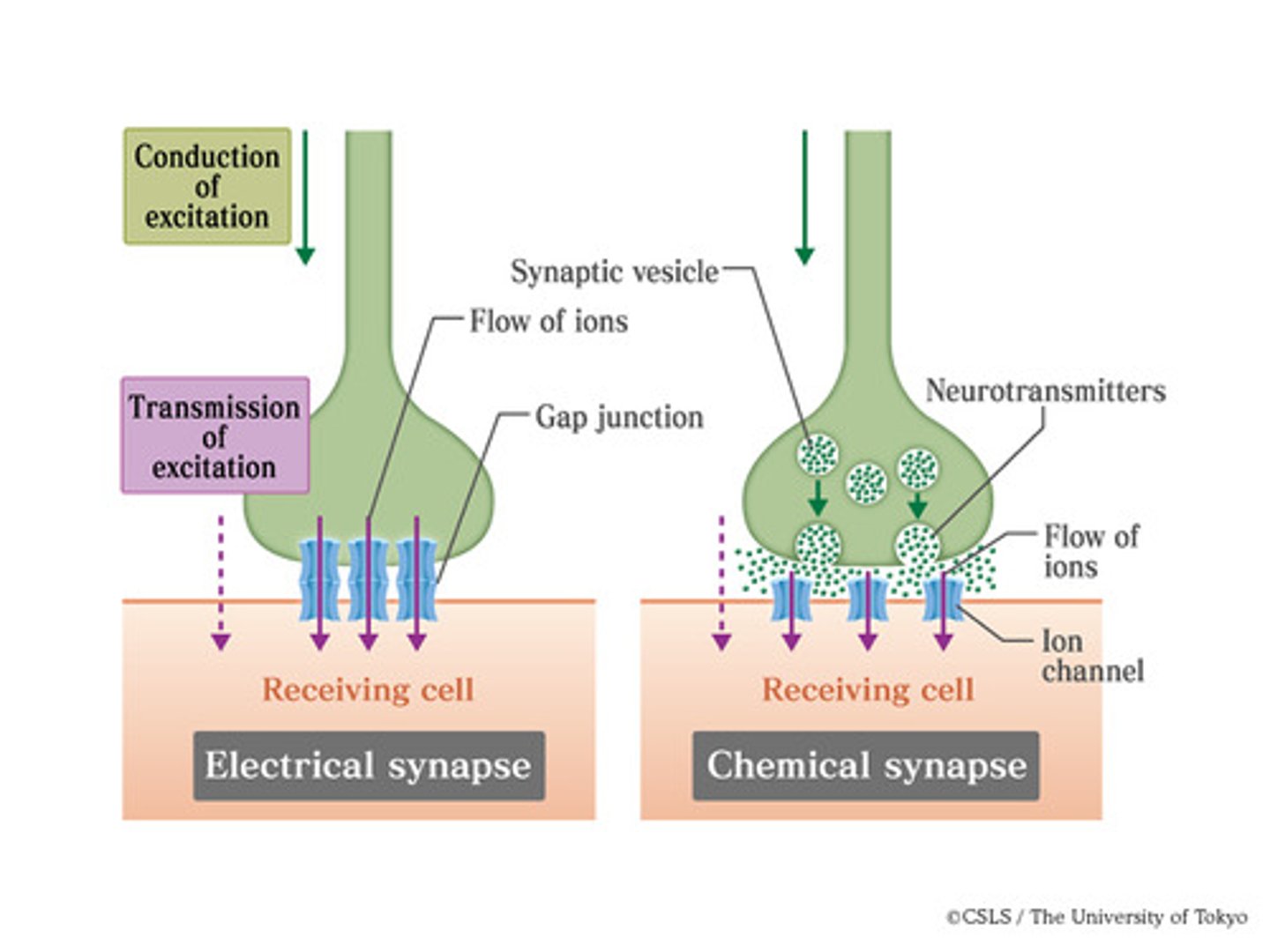
Which type of synapse evolutionarily came first?
Chemical came first
Electrical vs chemical synapses
electrical synapses occur when the cytoplasms of two cells are joined by gap junctions. If two cells are joined by an electrical synapse, an action potential will spread directly from one cell to another.
chemical synapses are found at the ends of axons where they meet their target cell; here an action potential is converted to a chemical signal.
refractory period
-Period of hyperpolarization, action potential cannot be generated
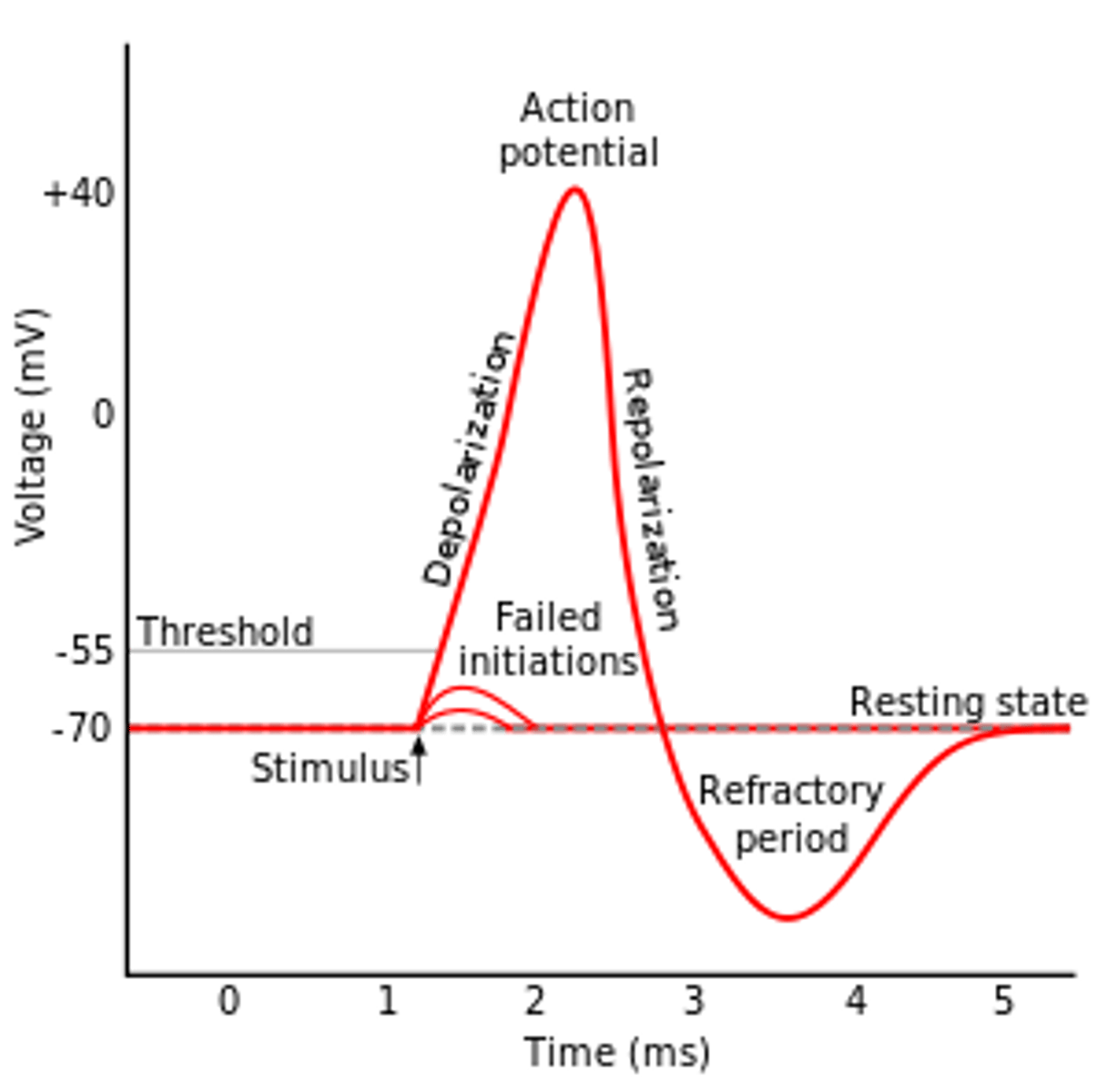
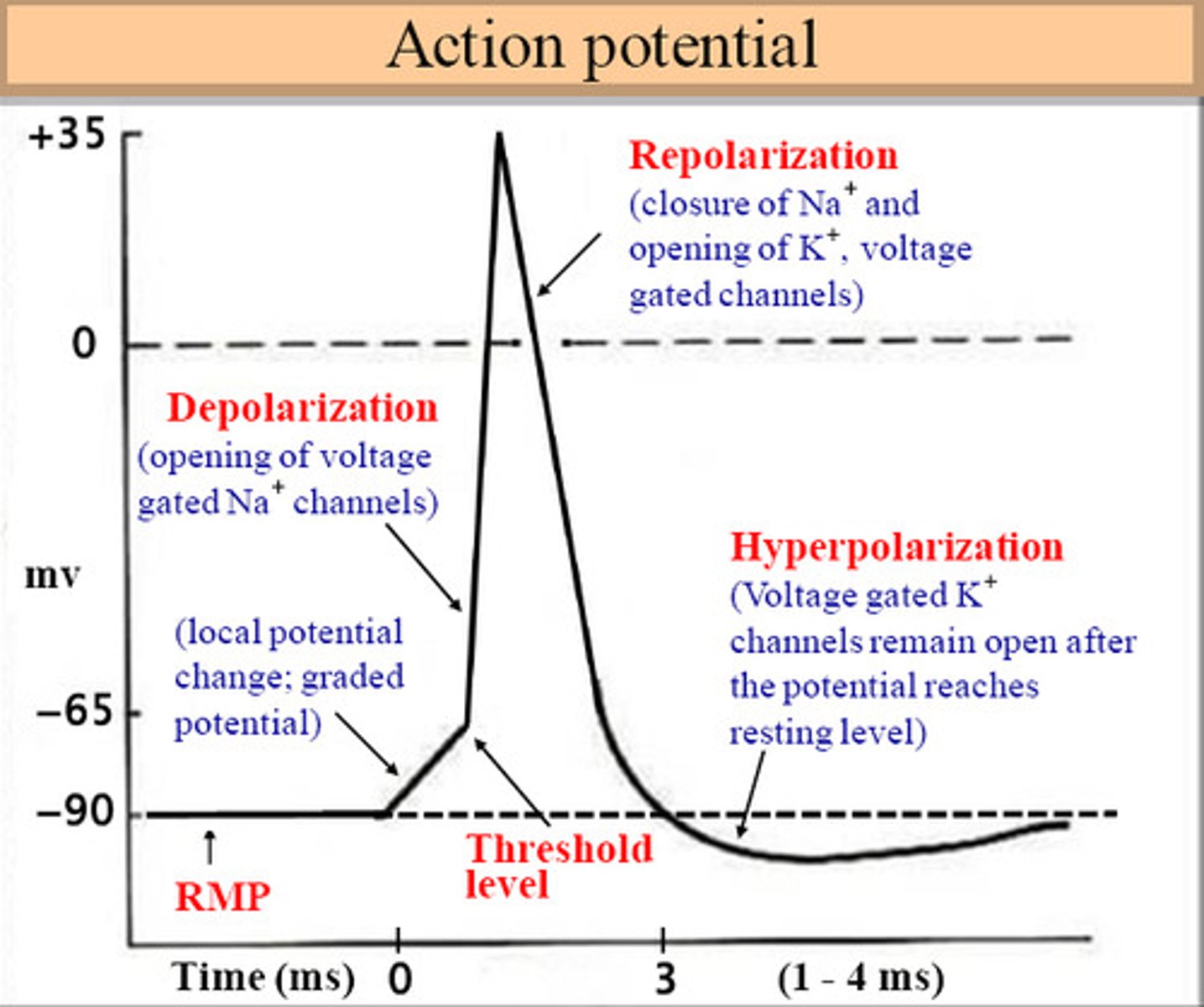
The "threshold" potential of a membrane is the
-Point where depolarization begins, the voltage needed for Na+ voltage-gated channels to open
-55mV
-70mV --> Na+ into cell slowly ---> -55mV ---> NA+ into cell quickly via voltage-gated channel = depolarization
Equilibrium potential of ions is based on
Concentration gradients
-Electrostatic forces
-Membrane permeability
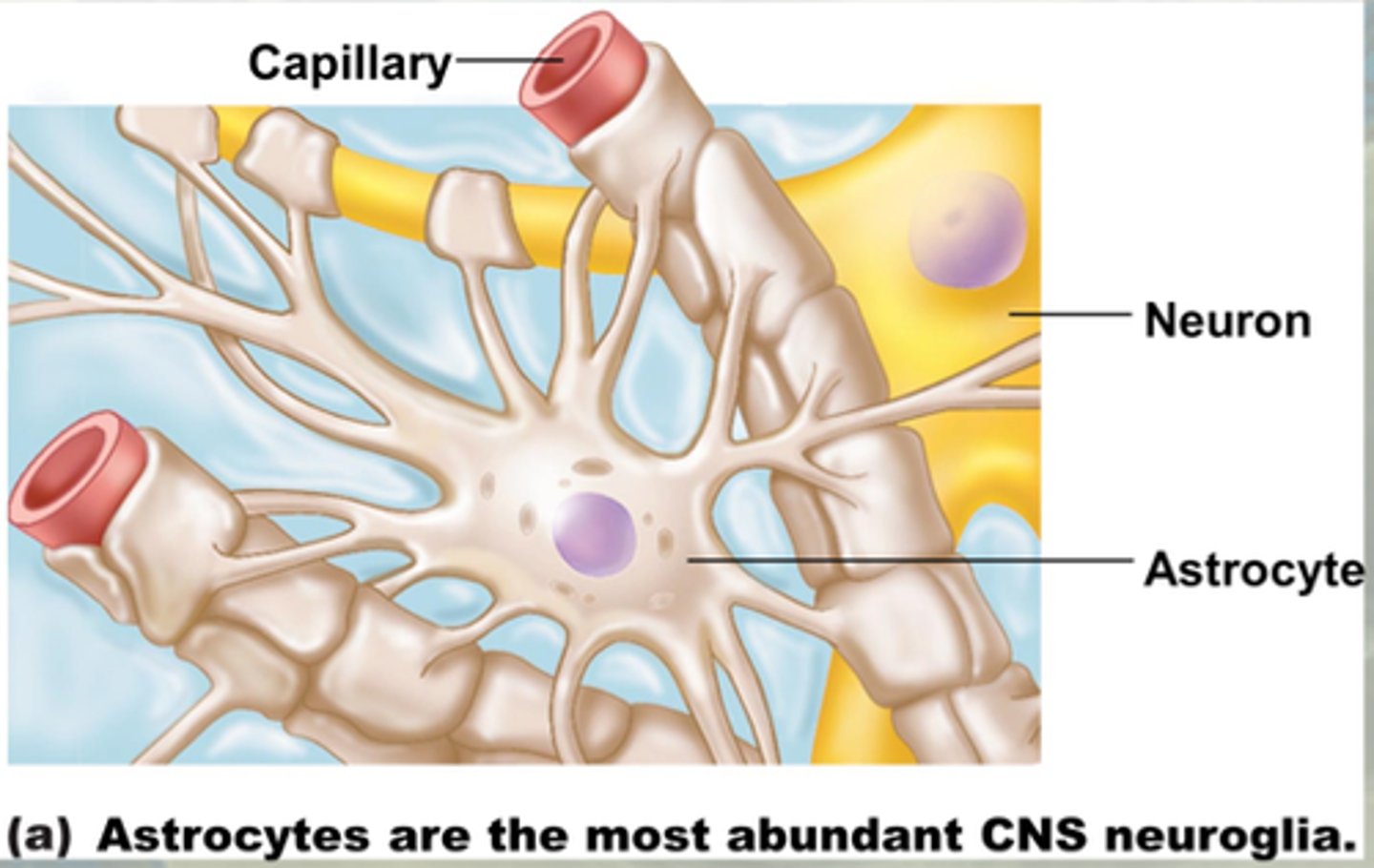
Astrocytes
-Closely cover the surface of blood vessels, provide physical support and maintain concentrations of ions in interstitial fluid
-Type of Glial cell
-Plays are role in the blood-brain barrier
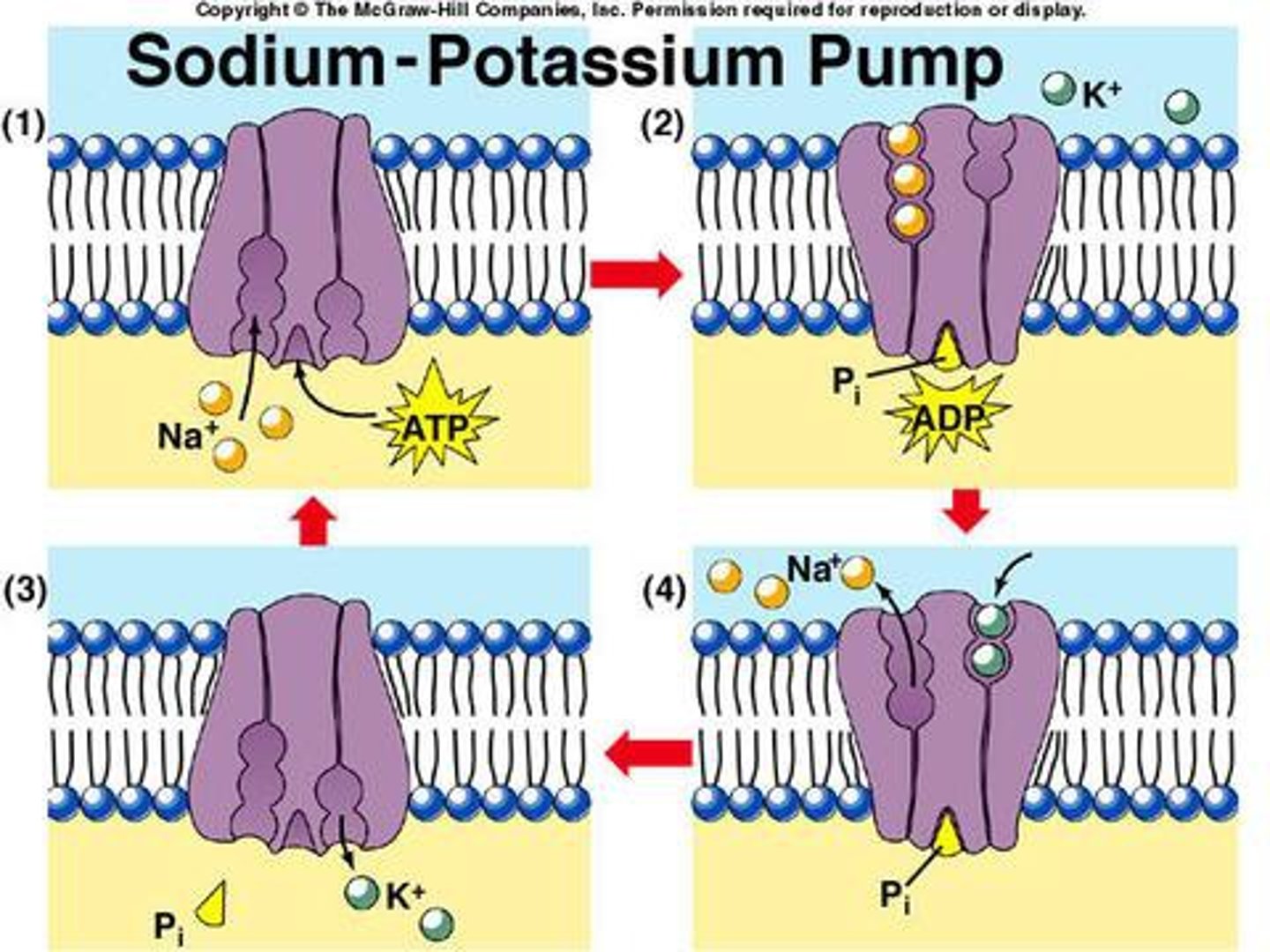
The sodium-potassium pumps how many K+? (into or out of the cell)?
How much Na+? (into or out of the cell)?
-2 K+ into the cell
-3 Na+ out of the cell
-Uses ATP
-Maintains resting potential
Remember: Salted Banana
Action potential phases
1. Resting potential (-70mV)
2. Depolarization Na+ --> cell
-voltage-gated sodium channels open
3. Repolarization K+ --> Out of cell
4. Hyperpolarization/overshoot
-Na+/k+ pumps begin charge back to resting potential
Oligodendrocytes
Produce myelin in CNS
-type of Glial cell
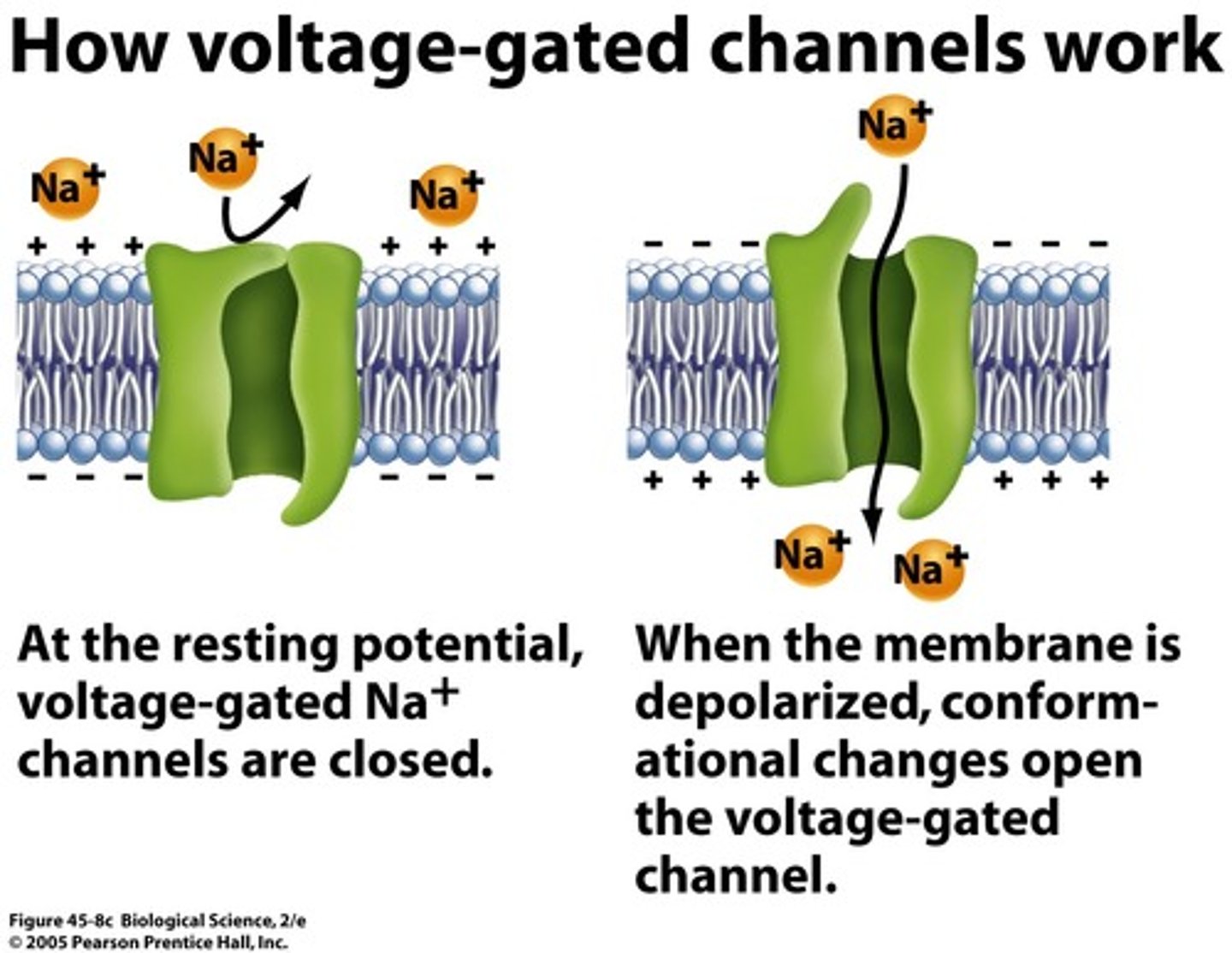
voltage gated channels
Open and close depending on membrane voltage
-passive transport
-Threshold --> Voltage-gated channels open --> depolarization
Afferent vs Efferent nerves
-Afferent (sensory): Receptor --> CNS
-Efferent (motor): CNS --> muscle, gland, or organ
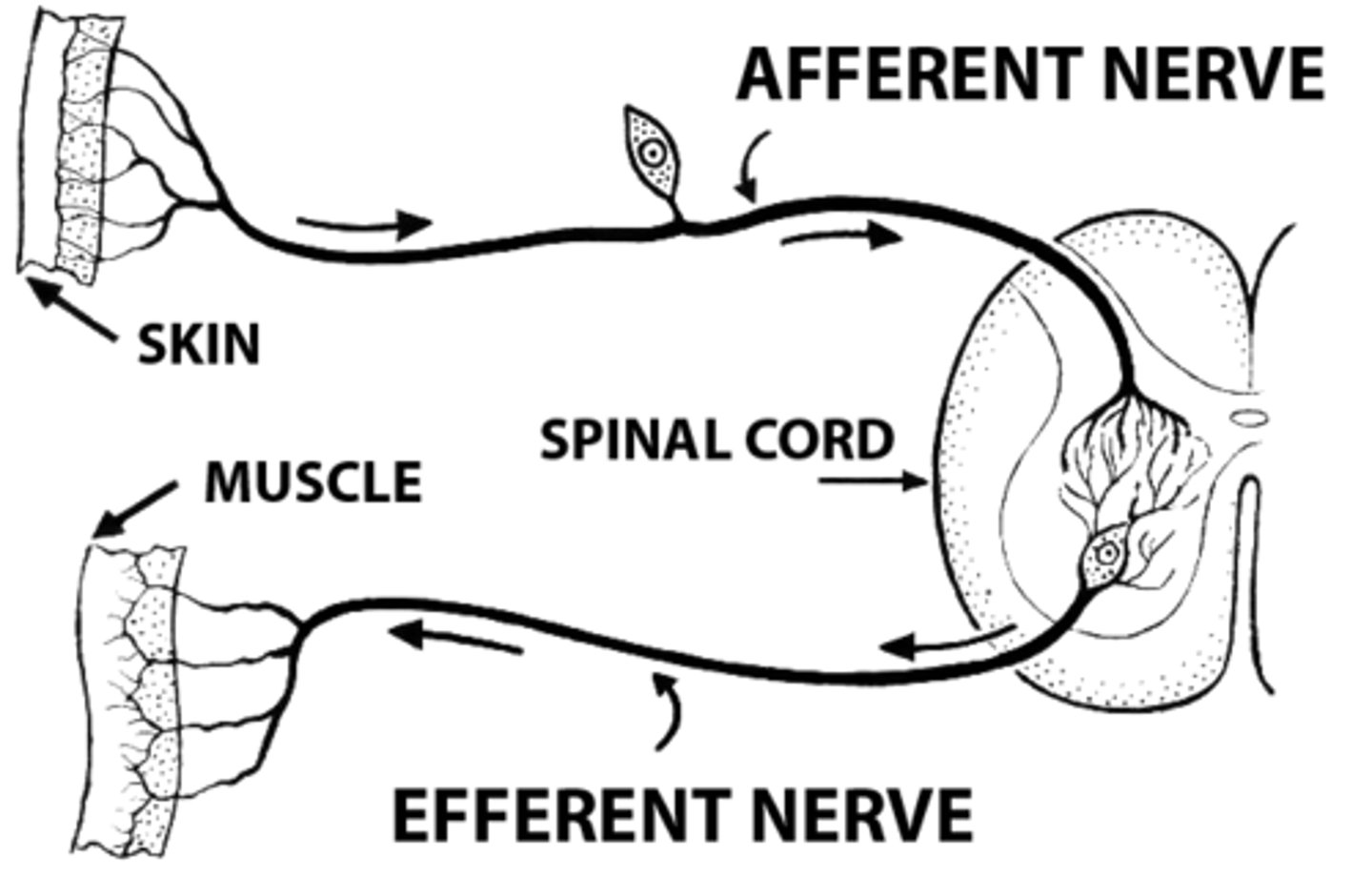
Non-neural cells that assist neurons are called
Glial cells
-Astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, Schwann cells
membrane potential
The voltage across a cell's plasma membrane.
-The imbalance/polarity
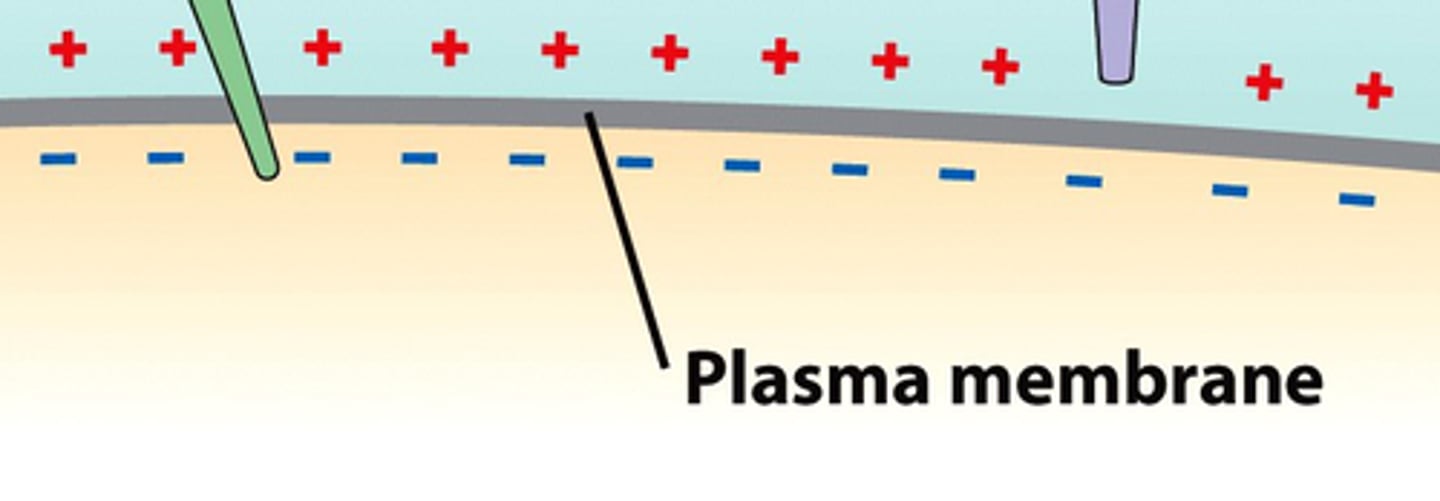
Diffusion vs Electrostatic forces
Diffusion based on concentrations
Electrostatic based on electrical charges
-forces counteract each other in neuron