Exam 3 (1/2)
1/102
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
103 Terms
Oral mucosa
The lining of the oral cavity.
What are the three divisions of the oral mucosa?
Masticatory
Lining
Specialized
Anatomic crown
Part of tooth covered by enamel
Clinical crown
Part of anatomical crown that is visible in the oral cavity and not covered by gingiva
Anatomic root
Part of tooth covered by cementum
Clinical root
part of anatomical root visible in the oral cavity and not
covered by gingiva. Recession
Masticatory Mucosa
Covers the gingiva and hard palate
Firmly attached to underlying tissue
Not attached to free margin of the gingiva
Keratinized
Lining Mucosa
Epithelium is not generally keratinized
Tissues not firmly attached
Covers inner surface of lips, cheeks, floor of mouth
Specialized Mucosa
Covers dorsum of tongue
Contains papillae and taste buds

Types of papillae
Filiform
Fungiform
Circumvallate
Foliate
Where is filiform located & function?
Cover most of the dorsal (top) surface of the tongue.
Provide texture and friction to help with chewing and moving food; do NOT contain taste buds.
Fungiform papillae
Scattered on the anterior 2/3 of the tongue, look like red dots
Contain taste buds
Papillae circumvallate?
Arranged in a V-shaped line in the posterior tongue (just in front of the sulcus terminalis).
Contain many taste buds; involved in bitter taste.
Where is foliatae located?
On the lateral (side) borders of the tongue in vertical folds.
Contain taste buds; sensitive to sour.
Periodontium
Tissues surrounding and supporting the teeth in two sections; Gingival unit & attachment apparatus
What are the two sections that make up the periodontium?
Gingival unit
Attachment apparatus
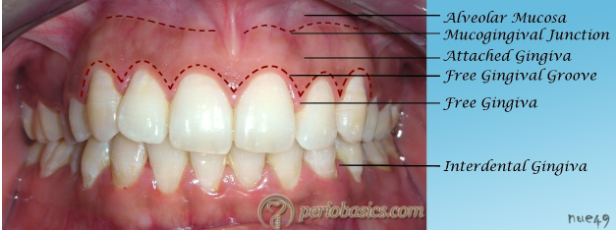
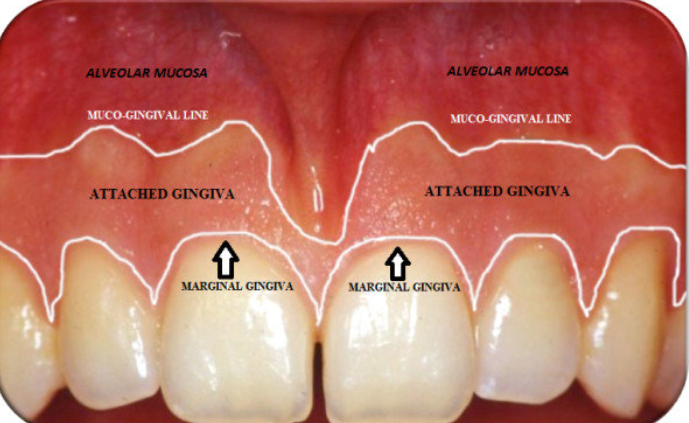
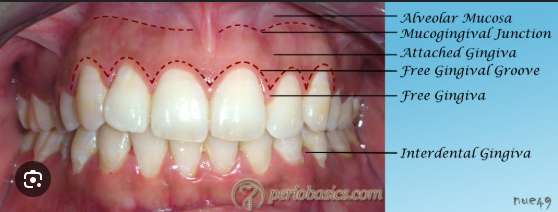
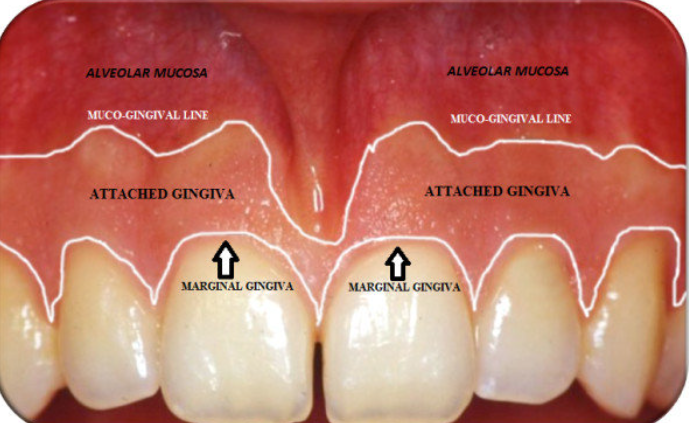
Gingiva
Masticatory mucosa that surrounds the neck of the teeth and is attached to teeth and alveolar bone
What does the gingiva consist of?
Free gingiva
Attached gingiva
Interdental papilla
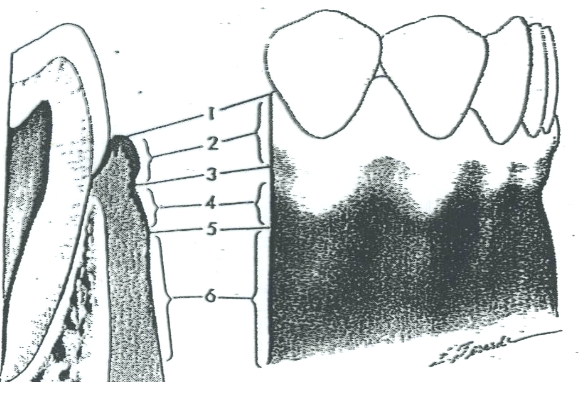
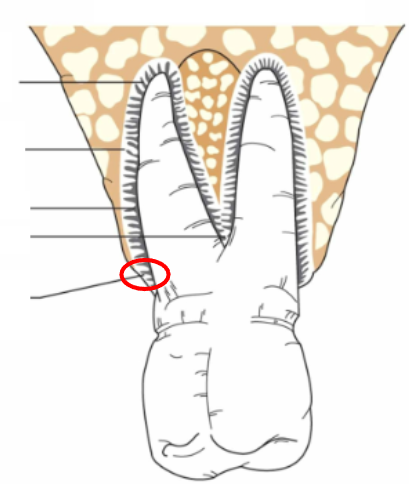
What is 1?
Free gingival margin
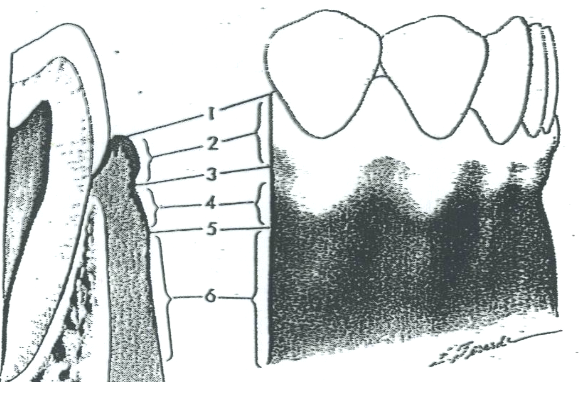
What is 2?
Free gingiva
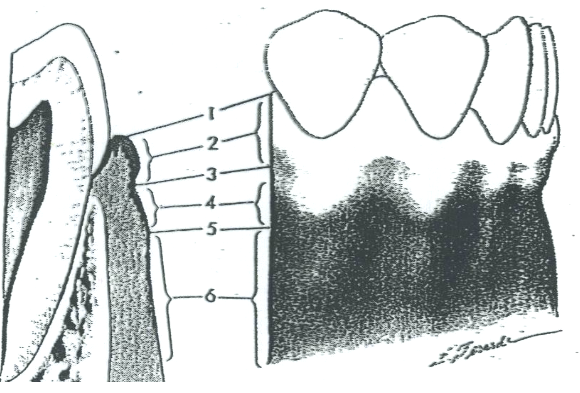
What is 3?
Free gingival groove
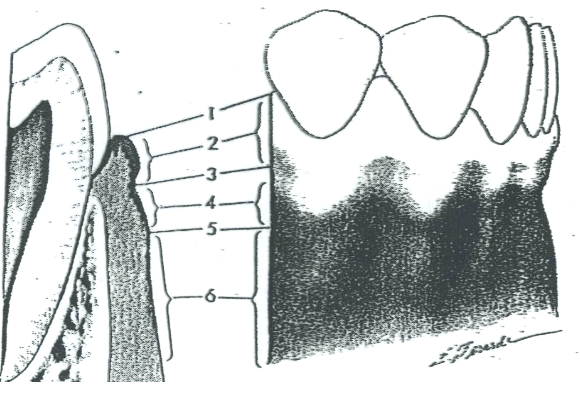
What is 4?
Attached gingiva
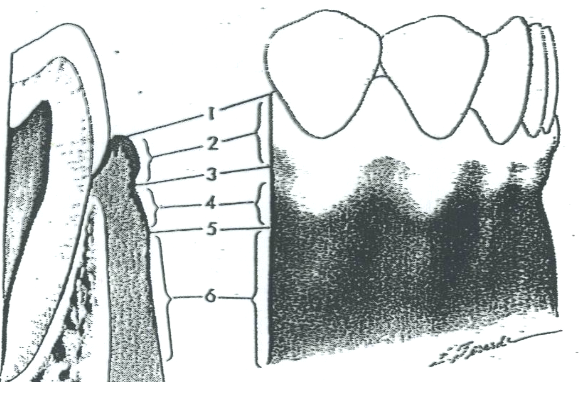
What is 5?
MGJ (Mucogingival junction)
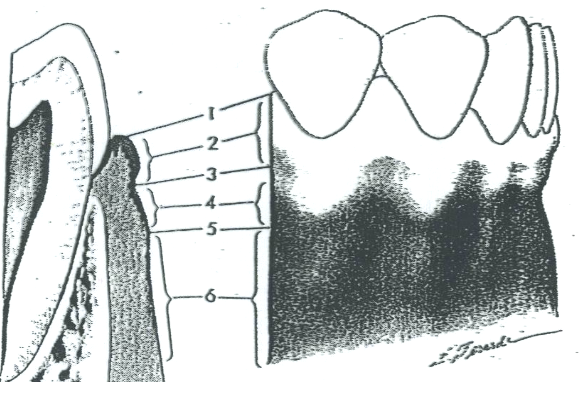
What is 6?
Alveolar mucosa
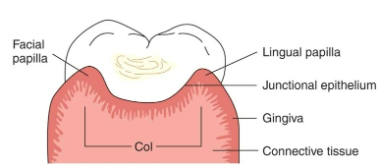
Papillary
Pointed part of gingiva located between the teeth
Marginal (free)
Most coronal portion of gingiva
Col
Connects facial and lingual gingiva
non-keratinized, concavity; susceptible to disease
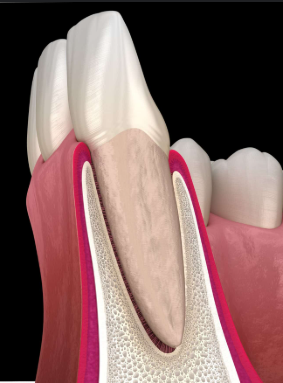
Gingival sulcus (gingival pocket)
Space between the tooth and internal portion of the free gingiva
Attached gingiva
Extends from free gingival groove to alveolar mucosa
width varies, not movable, firmly attached to underlying bone and cementum
Free gingival groove
shallow linear groove, demarcating the free gingiva from attached
Sulcular Epithelium
Non-keratinized epithelial tissue lining the gingival sulcus
Alveolar mucosa
Lining mucosa
Non keratinized
Movable, loosely attached
MGJ-mucogingival junction-separated
alveolar mucosa and attached gingiva
Darker red in color
Highly vascularized
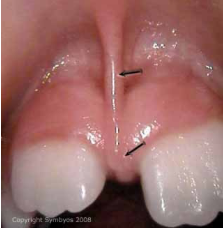
Frena
Fold of mucus membrane, attached to movable tissue to more fixed
tissue.
Junctional Epithelium
Specialized tissue that attaches the gingiva (gums) to the tooth, forming the base of the gingival sulcus
Gingival Crevicular Fluid (GCF)
a fluid that flows from the gingival sulcus, part of “defense system”
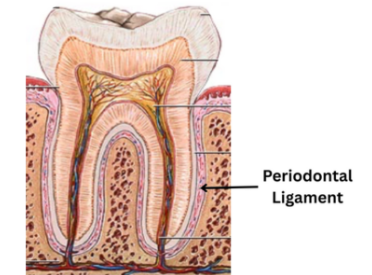
Periodontal Ligament
The fibrous connective tissue that surrounds and attaches the tooth’s root to alveolar bone
What is the Gingival Fiber Group
fibers that hold the gingiva tight to the teeth and keep the tissue stable.
What makes up the Gingival Fiber Group
Dentogingival
Dentoperiosteal
Transeptal
Alveologingival
Circumferential
Dentogingival fibers
Attach from tooth → gingiva. Help keep the gingiva snug around the tooth.
Alveologingival fibers
From alveolar bone → gingiva. Help attach the gingiva to the bone.
Circumferential (circular) fibers
Wrap around the tooth like a belt. Help keep the gingiva firm and in place.
Dentoperiosteal fibers
From tooth → periosteum (bone covering). Help anchor the tooth to the bone area.
Transseptal fibers
Stretch from the cementum of one tooth across the interdental space to the cementum of the neighboring tooth. Keep teeth aligned and close together.
Principal Fiber Group (Dentoalveolar Fibers)
Fibers that anchor the tooth in the socket and resist forces.
Alveolar Crest fibers
From cementum → alveolar crest. Resist sideways (lateral) movement.
Horizontal fibers
From cementum → bone in a horizontal line. Resist lateral forces.
Oblique fibers
From cementum → bone, angled upward. Absorb chewing pressure.
Apical (Periapical) fibers
From cementum → bone at the root tip. Resist tipping of the tooth.
Interradicular fibers
From bone → cementum in furcations. Resist tooth loosening and tipping.
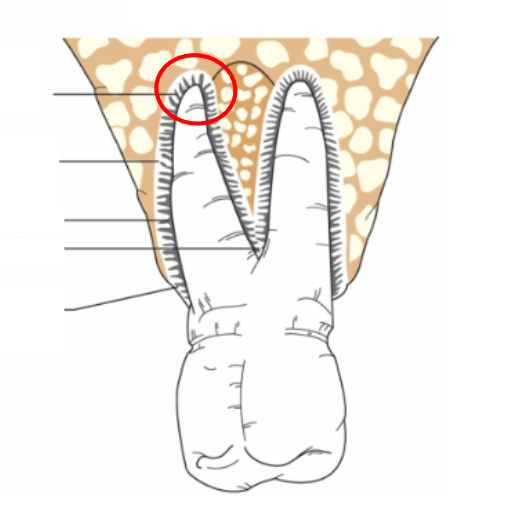
What is this?
Apical (Periapical) fibers
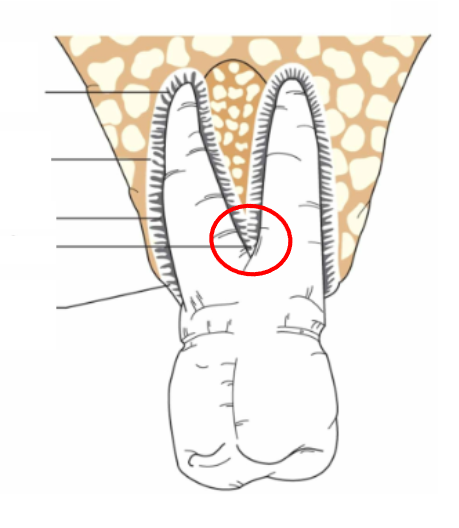
What is this?
Interradicular fibers
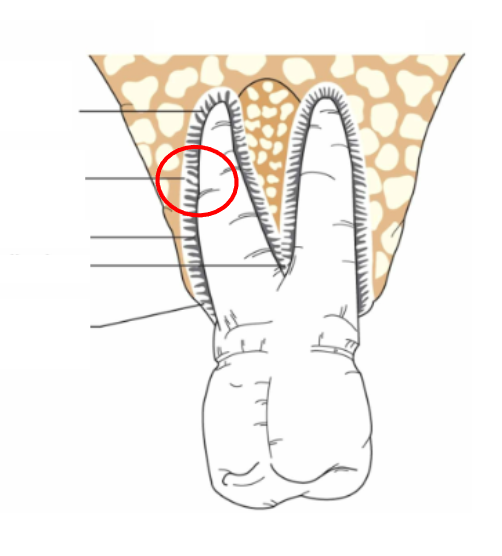
What is this?
Oblique fibers
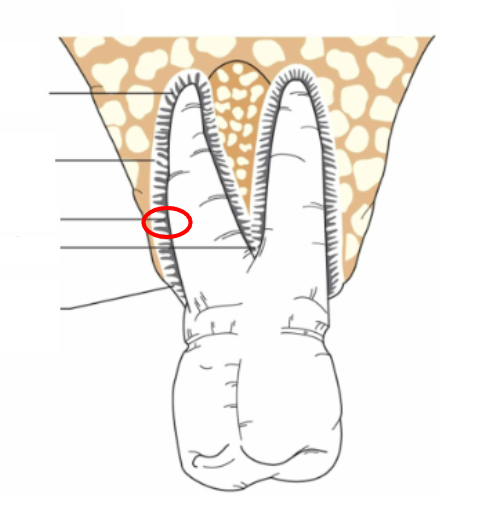
What is this?
Horizontal fibers
What is this?
Alveolar crest fibers
Cementum
Thin, mineralized, bone-like substance (conn. tissue) covering roots from CEJ to apex; outer most layer of the roots
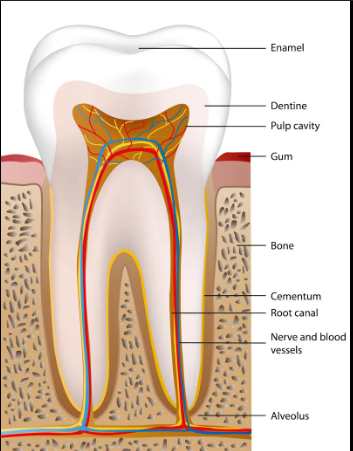
Function of the cementum
Seals dentinal tubules
Provides attachment for fibers of periodontal ligament
Alveolar Bone
Surrounds the tooth socket and supporting bone
Support the teeth
Provide attachment for PL fibers
What should you look for during a gingival exam?
Color
Size
Contour (shape)
Consistency
Surface texture
Position
Exudate (fluid leakage)
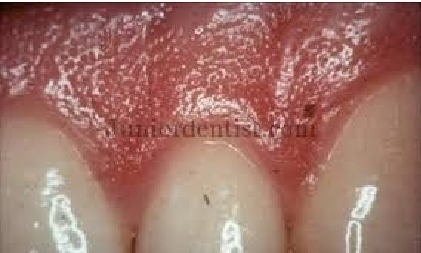
Stippling
Orange peel texture of attached gingiva
Resiliency
When pressed with side of probe, how much indentation you get
Sponginess
Deeper impression left
What are some symptoms of a diseased periodontium?
Bleeding
Tender, sensitive gingiva
Food traps
Bad taste in mouth
Bad breath
What is the main cause of periodontal disease?
microorganisms in bacteria plaque (biofilm) that produce enzymes
and toxins that breakdown tissue
What are the 2 forms of periodontal disease?
Gingivitis & Periodontitis
Gingivits
Inflammation of the gingiva with no apparent attachment loss. Only the marginal gingiva involved
Periodontitis
Inflammation and infection involving supporting structures; apical
migration of junctional epithelium w/ loss of alveolar bone
Stages of Periodontal Development
Gingivitis - Initial lesion within 2 to 4 days (no clinical signs)
Early lesion - 7 to 14 days (reversible, first clinical sign)
Established Lesion, gingival pocketing
Periodontitis, advanced legion
Pocketing
Formation of deep spaces between the gums and teeth
A pocket is a diseased sulcus
Pocket refers to ‘soft tissue’, not bone.
Periodontal pocket
Pocket formed by disease causing the junc. epithelium to migrate apically
Pocket refers to ‘soft tissue’, not bone.
Suprabony pockets
Pocket bottom (junctional epithelium) is above the alveolar bone.
Usually seen with horizontal bone loss
Infrabony pockets
Pocket bottom is below the alveolar bone.
Usually seen with vertical bone loss.
True or False: All gingival pockets are suprabony; periodontal
pockets can be either
True
Process of Pocket Formation
Bacteria destroy the junctional epithelium → PDL fibers detach → junctional epithelium moves down → cementum becomes exposed and rough → demineralization, calculus, and biofilm build up.
Class I Furcation
early, can probe anatomy of furcation entrance <3mm
Class II Furcation
moderate, probe can enter furca but can not pass thru
Class III Furcation
Severe, probe can pass thru
Class IV Furcation
Same as III, but furcation is exposed due to recession
Tooth Mobility
Degree to which tooth is able to move in a horizontal or vertical direction
Modifiable risk factors of periodontitis
Tobacco use
Diabetes Mellitus
Psychosocial factors
Medications
Poor home care
Possibly nutrition, alcohol, socioeconomic status
Non modifiable risk factors of periodontitis
Genetics
Host response
Osteoporosis
Immune deficiencies
Old Paradigm (Linear Theory)
Bone loss happens slowly, steadily, and at a constant rate.
Current Paradigm (Burst Theory)
Bone loss happens in short bursts of activity, with periods of no progression in between.
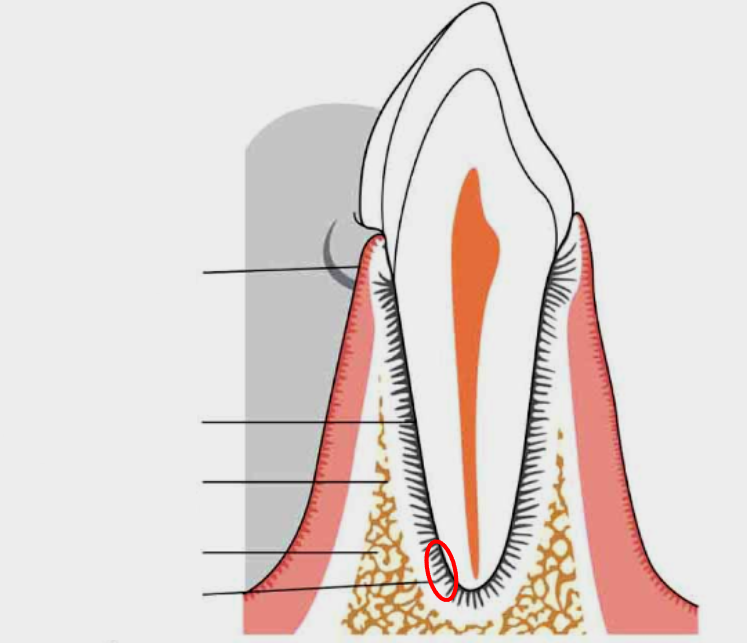
What is this?
Periodontal ligament
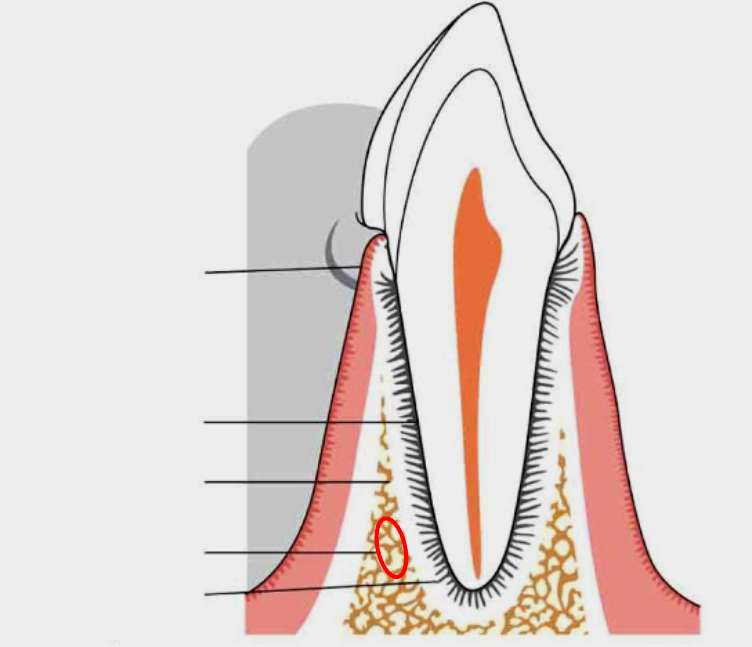
What is this?
Alveolar process
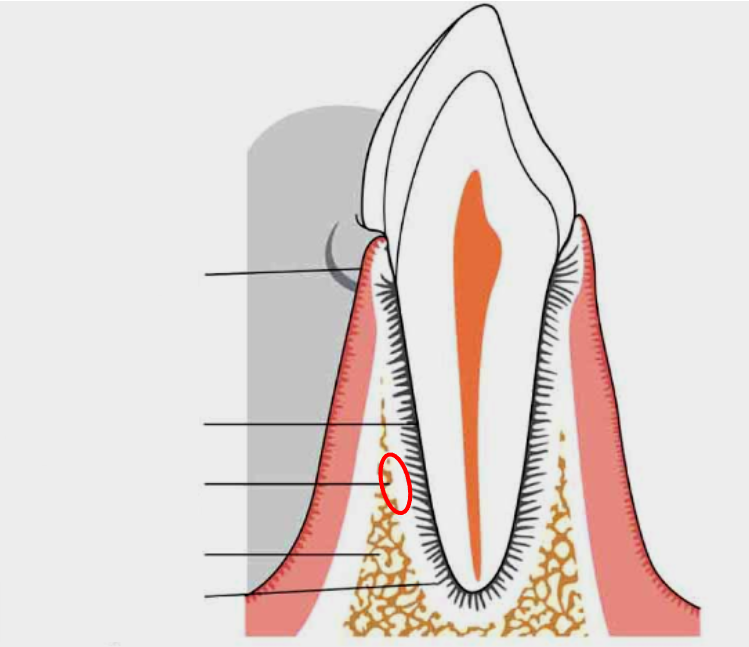
What is this?
Alveolar bone proper
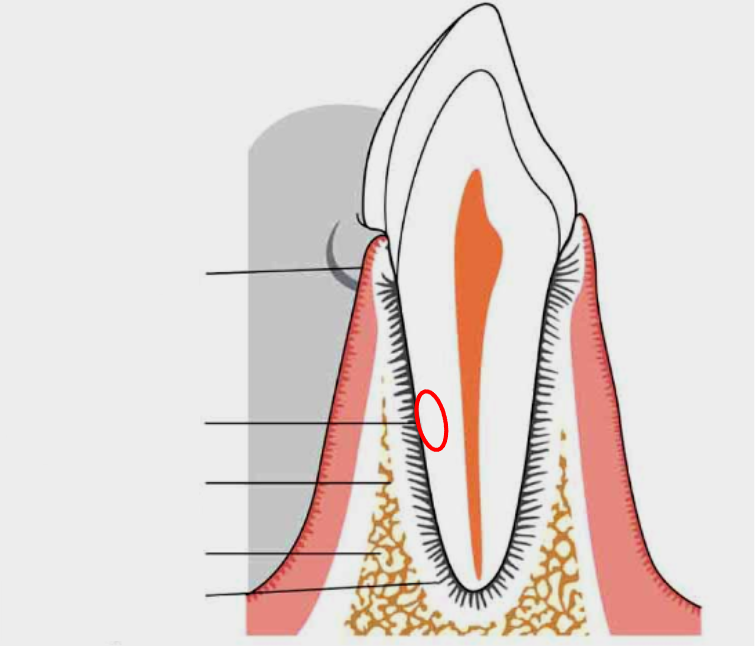
What is this?
Root cementum
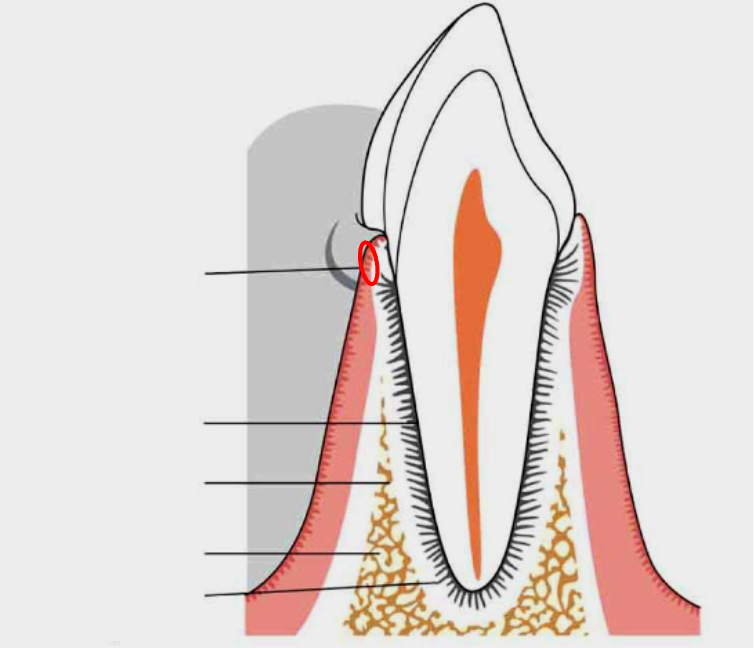
What is this?
Gingiva
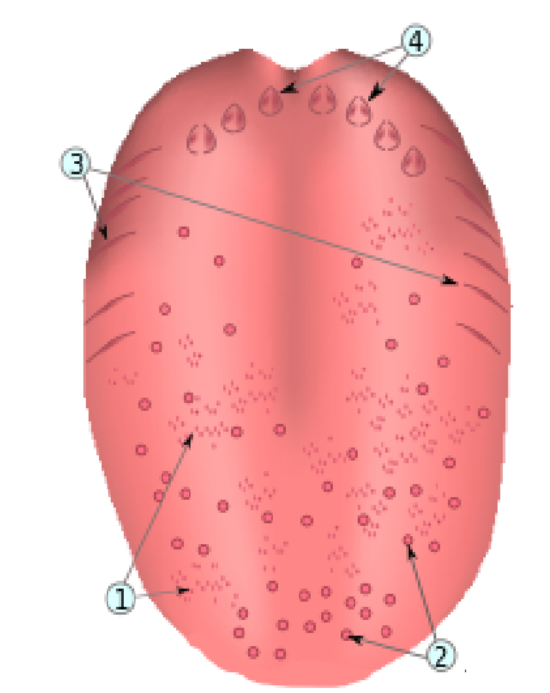
What is number 4?
Papilla circumvallatae
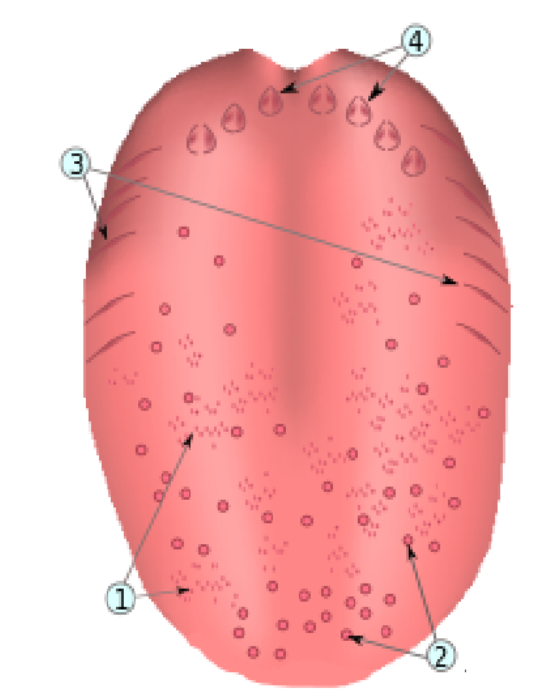
What is number 3?
Papillae foliatae
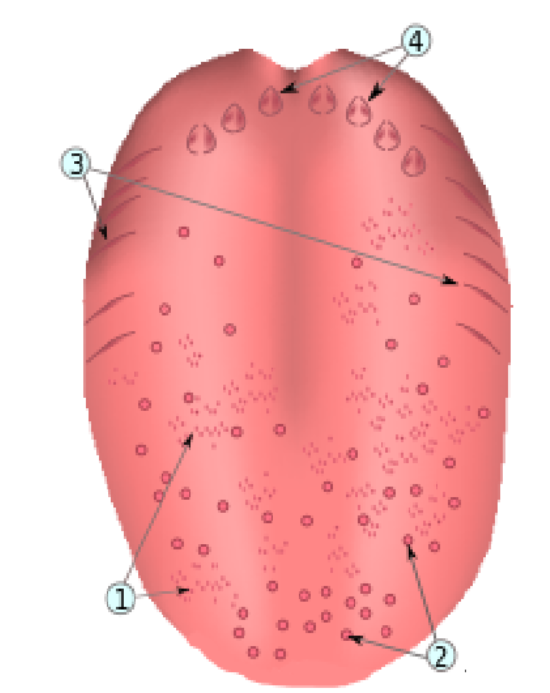
What is number 1?
Papillae filiforms
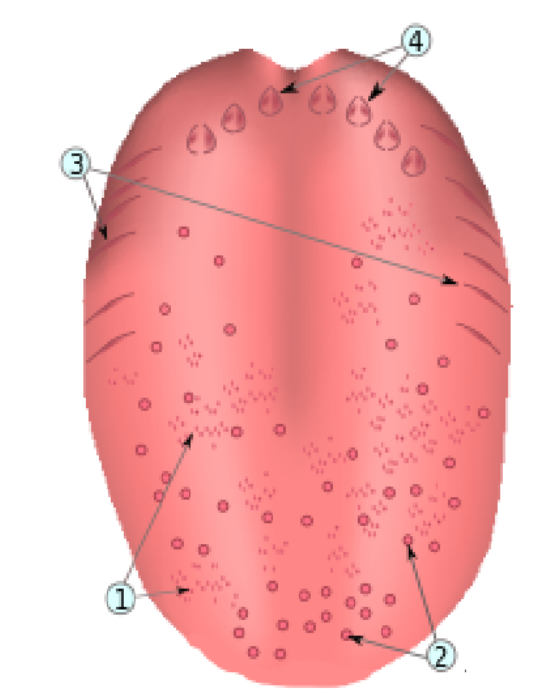
What is number 2?
Papillae fungiforms
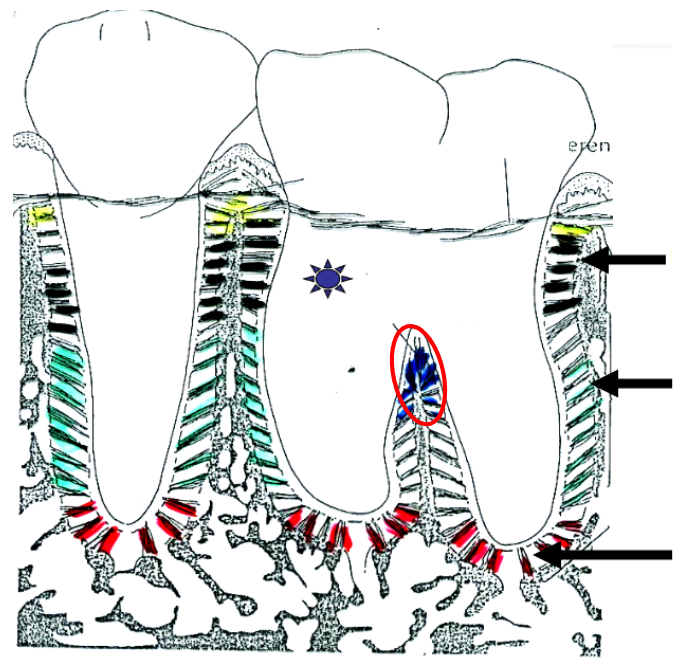
What is this?
Interarticular fibers
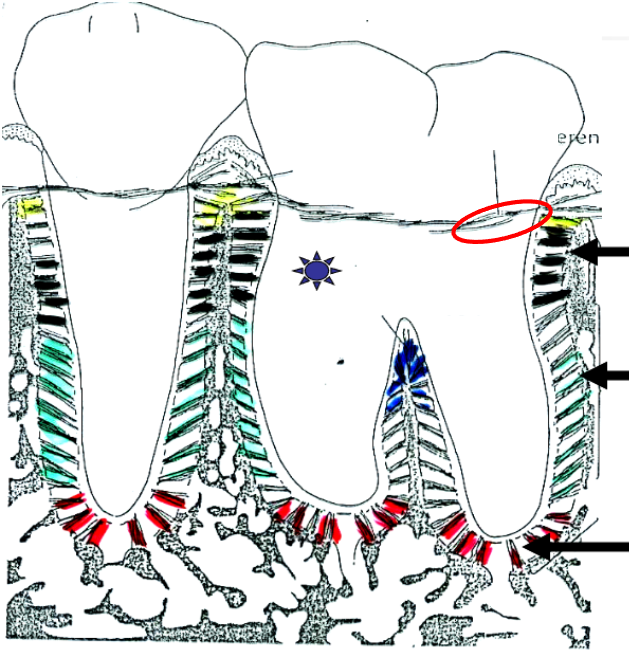
What is this?
Circumferen
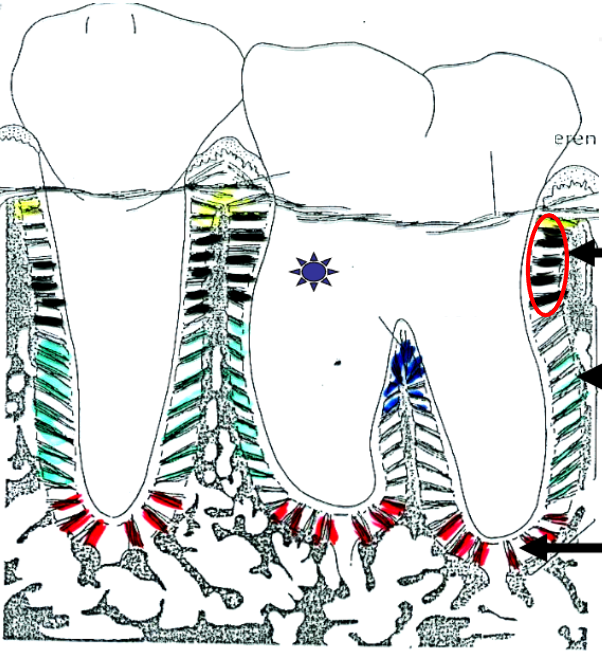
What is this?
Horizontal fibers
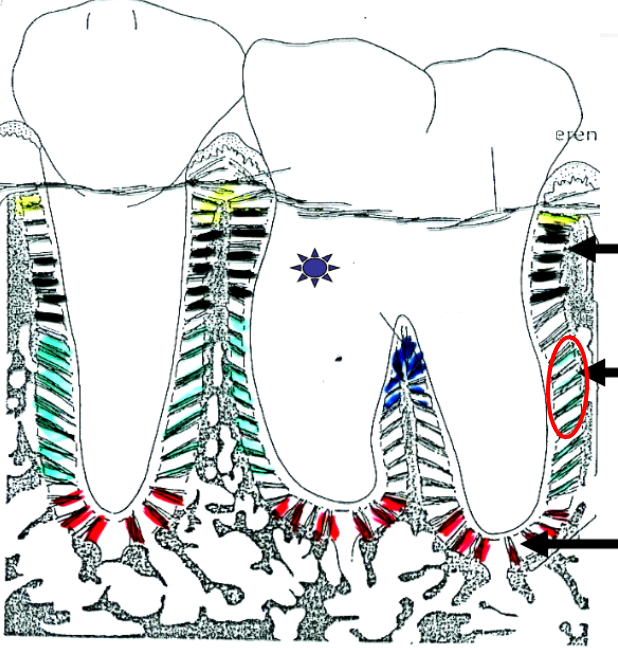
What is this?
Oblique fibers
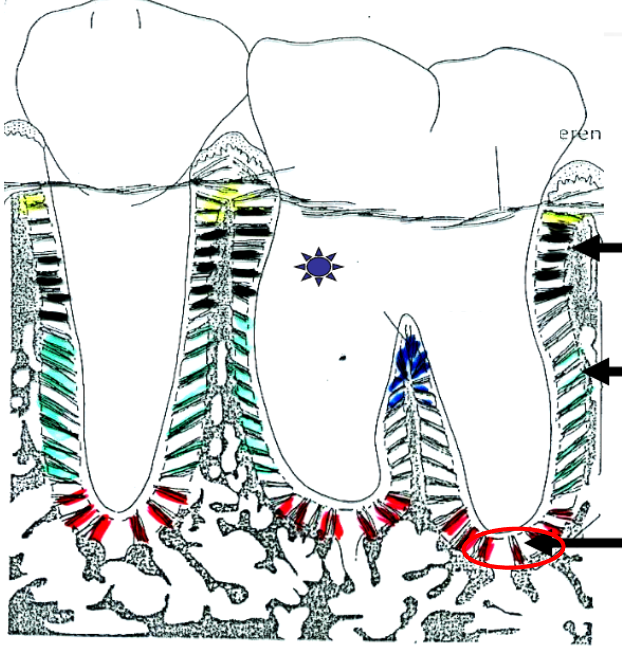
What is this?
Apical fibers
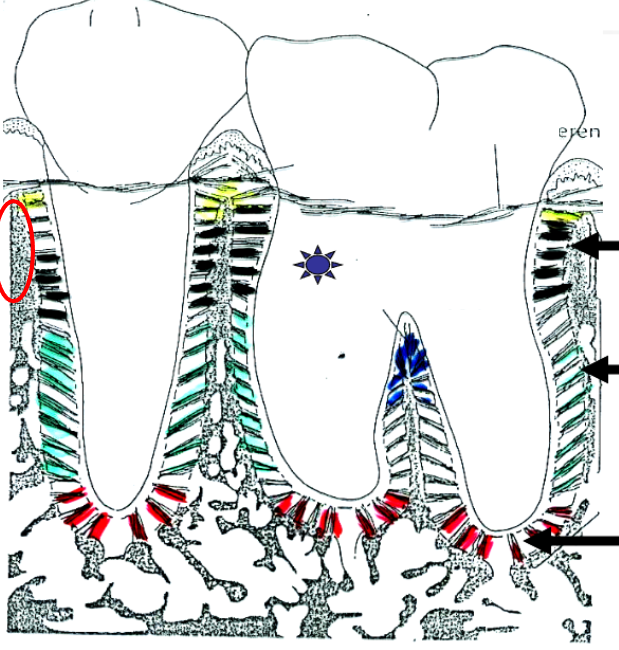
What is this?
Transseptal fibers
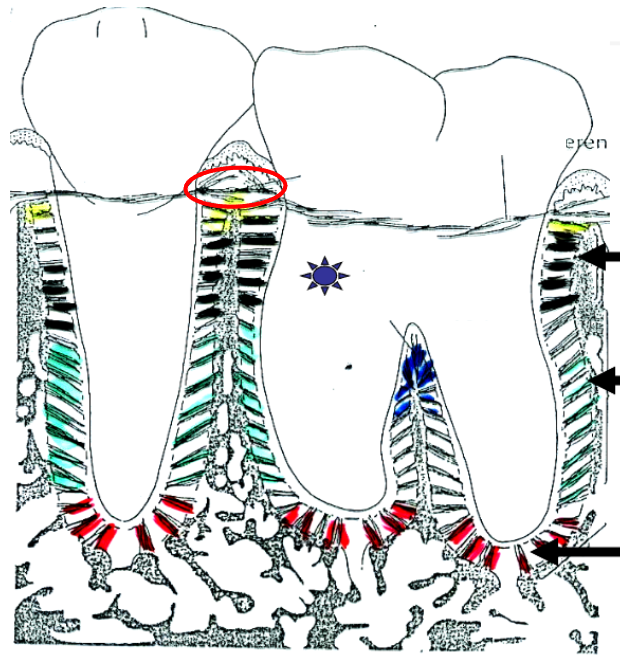
What is this?
Alveolar crest
What is rolled gingiva?
A rounded, thickened gingival margin caused by inflammation or edema, often from plaque or improper brushing.
Bulbous
What is festooned gingiva?
Gingiva with a “scalloped” or exaggerated, swollen collar shape around the tooth, often seen in chronic inflammation.