Body Quadrants, body regions and quadrants, Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 1, Anatomy & Physiology - Abdominal Regions of the Body and Underlying Organs, Anatomical Terminology and Body Cavities
1/193
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
194 Terms
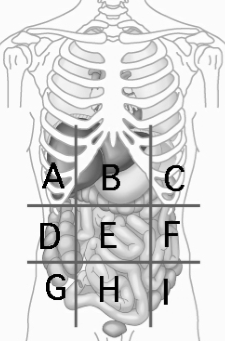
Right Hypochondriac Region
contains liver and gallbladder A
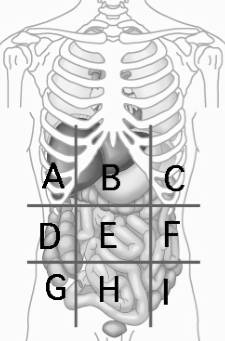
Epigastric Region
Contains the stomach B
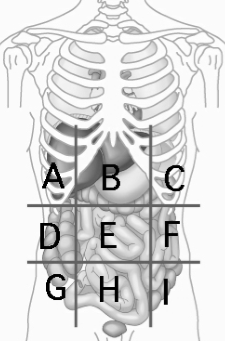
Left Hypochondriac Region
Contains the Diaphragm, Spleen, and Stomach C
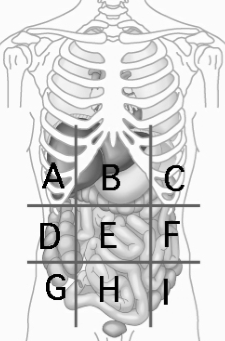
Right Lumbar Region
Contains Ascending colon of large intestine D
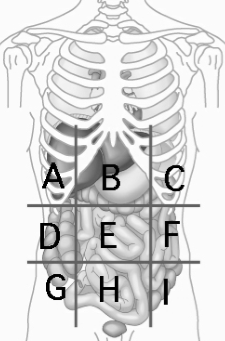
Left Lumbar Region
contains descending colon of large intestine F
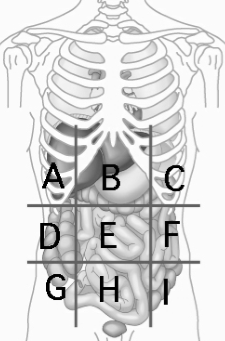
Right Iliac (Inguinal) Region
Contains cecum and appendix G
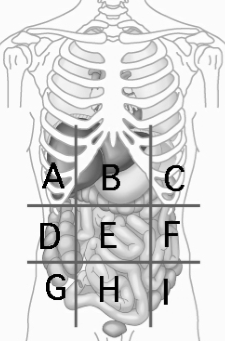
Hypogastric (Pubic) Region
contains urinary bladder H
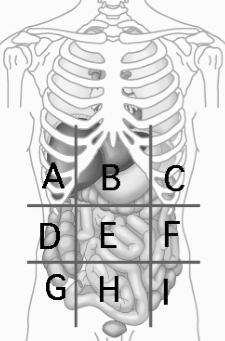
Left Iliac (inguinal) Region
Contains initial part of sigmoid colon I
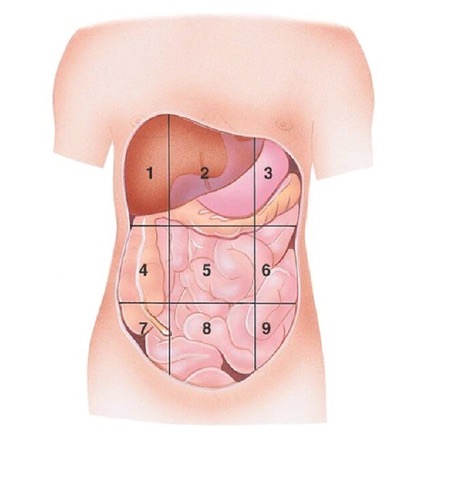
Right Hypochondriac region
what region is 1?
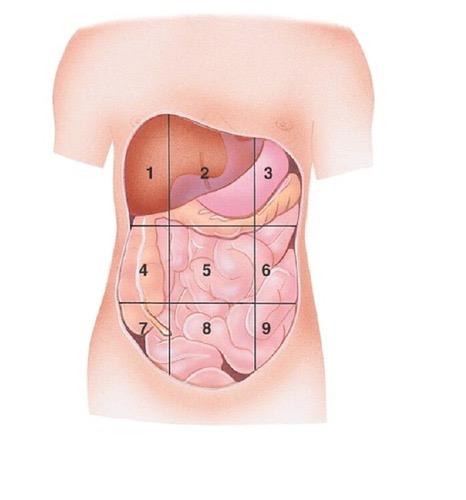
Epigastric Region
what region is 2?
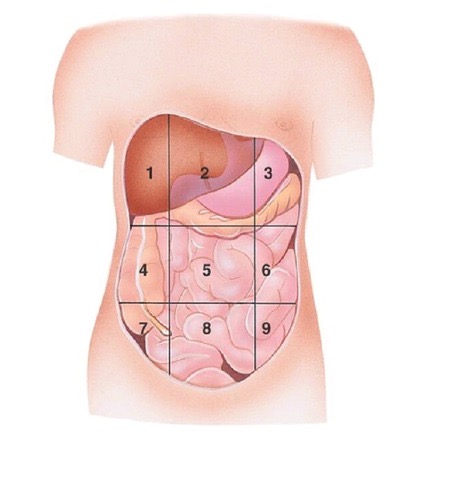
Left Hypochondriac Region
what region is 3?
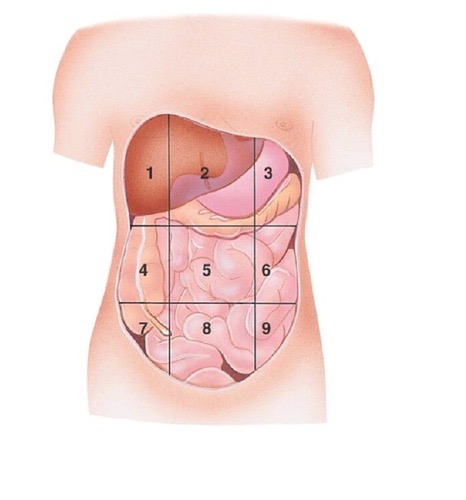
Right Lumbar Region
what region is 4?
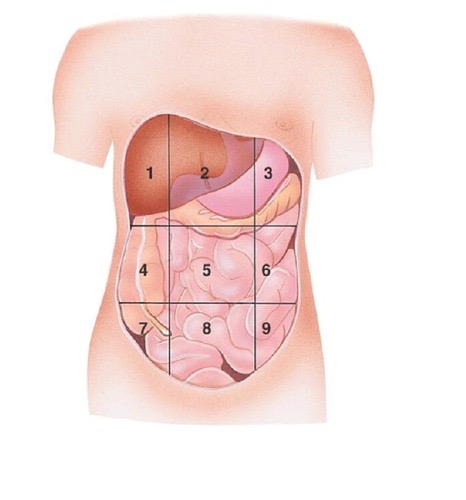
Umbilical region
what region is 5?
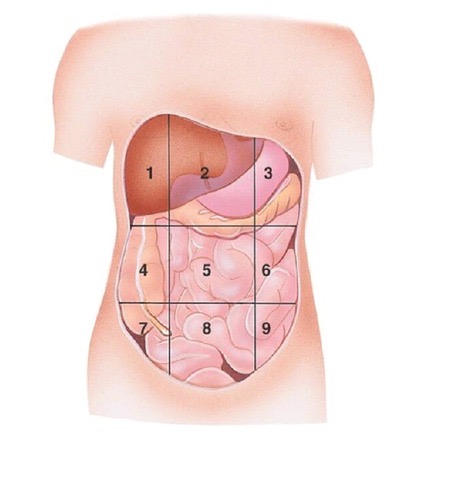
Left Lumbar region
what region is 6?
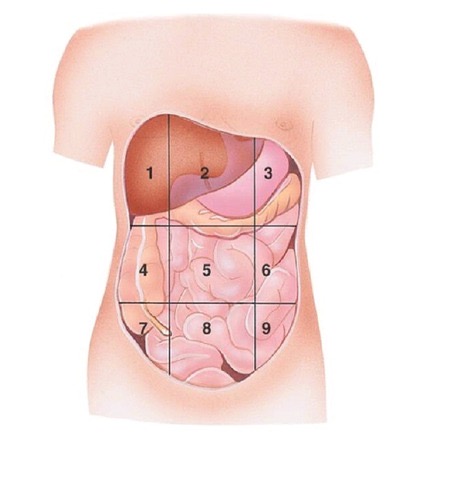
Right Iliac (Inguinal) region
what region is 7?

Hypogastric region
what region is 8?

Left Iliac (Inguinal) region
what region is 9?
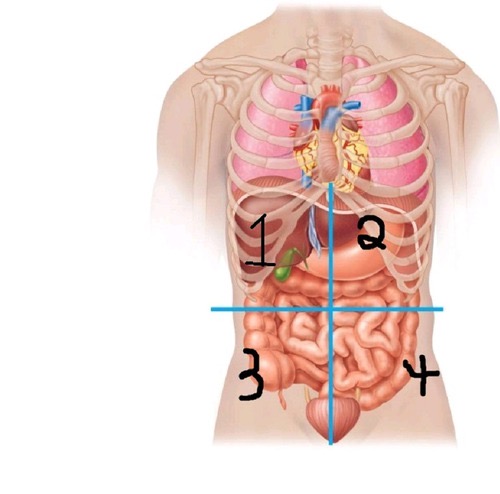
Right Upper quadrant (RUQ)
what quadrant is 1?
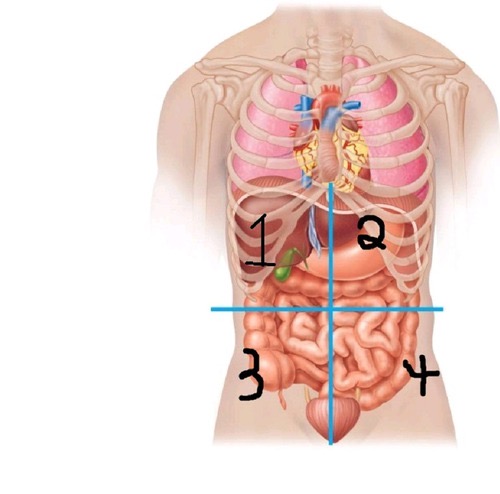
Left Upper quadrant ( LUQ)
what quadrant is 2?
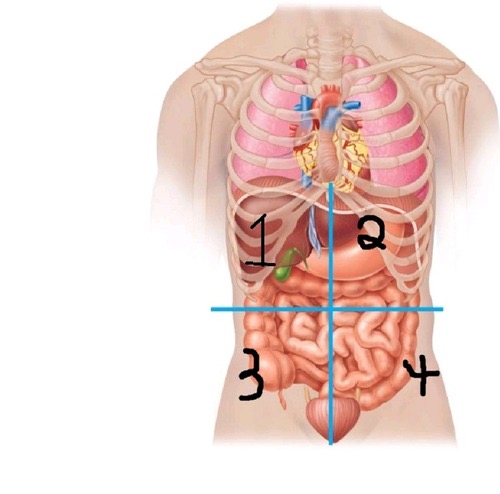
Right Lower quadrant (RLQ)
what quadrant is 3?
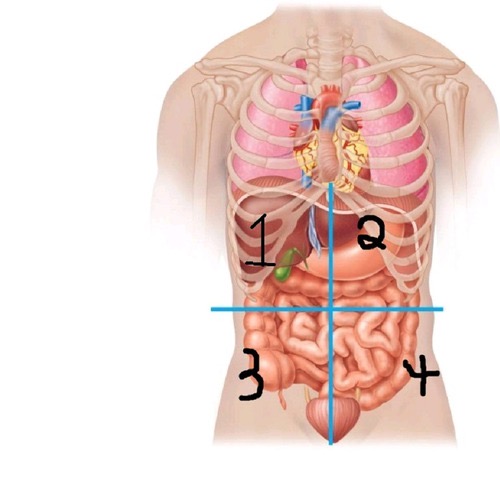
Left Lower quadrant (LLQ)
what quadrant is 4?
Superior
toward the head end or upper part of a structure or the body; above
Inferior
away from the head end or toward the lower part of a structure or the body; below
Ventral (anterior)
toward or at the front of the body; in front of
Dorsal (posterior)
Toward or at the back of the body; behind

Medial
toward or at the midline of the body; on the inner side of

Lateral
away from the midline of the body; on the outer side of
Superficial
toward or at the body surface
Deep
away from the body surface; more internal
Anatomical Position
erect, feet forward, arms at side with palms facing forward, head facing forward, internationally know
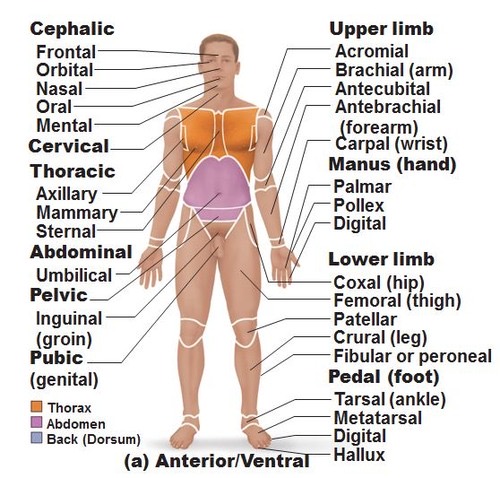
Anterior/Ventral Body
front

Posterior/Dorsal Body
back of body
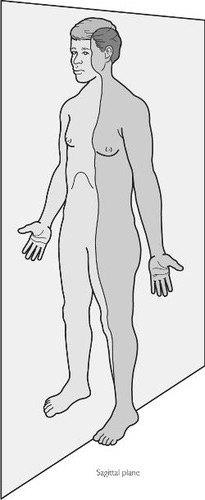
Sagittal
a vertical plane that divides the body into right and left parts

Frontal Planes (Coronal Plane)
like sagittal plane lie vertically, divide body into anterior and posterior parts

Transverse/Horizontal Plane
runs horizontally from right to left, dividing the body into superior and inferior parts. (Transverse is perpendicular to long axis of an organ, horizontal is from front to back)
Oblique Sections
cuts made diagonally between the horizontal and the vertical planes
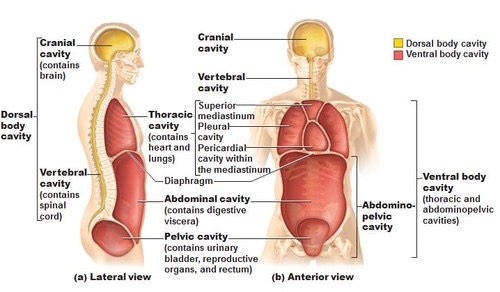
Dorsal Body Cavity
protects the fragile nervous system organs, has 2 subdivisions
Cranial Cavity
in the skull, encases the brain
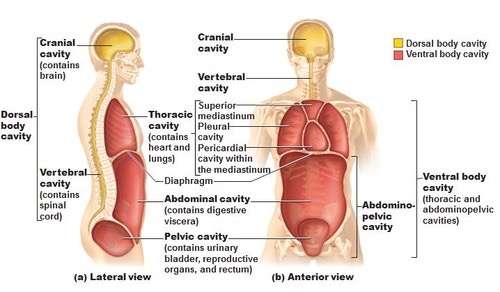
Vertebral Cavity (Spinal Cavity)
runs within the bony vertebral column, encloses the delicate spinal cord
Ventral Body Cavity
the more anterior and larger of the closed body cavities, has 2 major subdivisions, houses internal organs called Viscera
Thoracic Cavity
surrounded by the ribs and muscles of the chest
Pleural Cavities
lateral subdivision of Thoracic Cavity, enveloping a lung, and the Medial Mediastinum
Pericardial Cavity
encloses the heart and also surrounds the the remaining thoracic organs (esophagus, trachea, and others)
Abdominopelvic Cavity
seperated from thoracic cavity by the diaphram, a dome shaped muscle important in breathing. Has abdominal and pelvic cavities
Abdominal Cavity
Contains stomach, intestines, spleen, and liver, and other organs
Pelvic Cavity
Contains urinary bladder, reproductive organs, and rectum
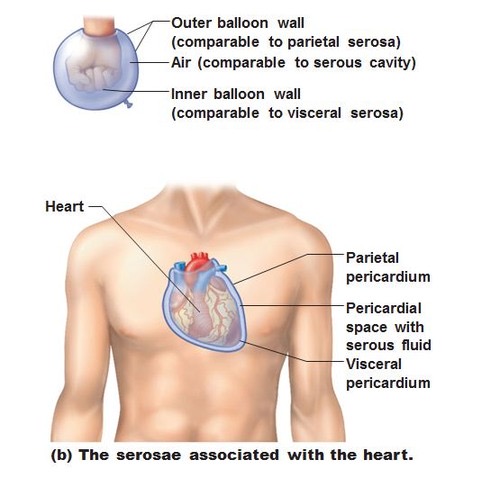
Serosa (Serous Membrane)
the walls of the ventral body cavity and the outer surfaces of the organs it contains are covered by this thin double layered membrane
What is anatomy?
the study of structure
What is physiology?
the study of function at many levels
Would you be studying anatomy or physiology if you investigated how muscles shorten? If you explored the location of the lungs in the body?
Muscle shortening is a topic of physiology. The body location of the lungs is an anatomy topic.
What are the levels of structural organization?
chemical, cellular, tissue, organ, organ system and organismal level
What does the digestive system do?
takes in nutrients, breaks them down, and eliminates unabsorbed matter (feces)
What does the respiratory system do?
takes in oxygen and eliminates carbon dioxide
What does the urinary system do?
eliminates nitrogenous wastes and excess ions
What does the cardiovascular system do?
via the blood, distributes oxygen and nutrients to all body cells and delivers wastes and carbon dioxide to deposal organs
What does the integumentary system do?
protects the body as a whole from the external environment
What are the main parts of the integumentary system?
hair, nails and skin
What are the main parts of the Skeletal System?
bones and joints
What is the main part of the muscular system?
skeletal muscles
What are the main parts of the nervous system?
the brain, nerves and spinal cord
What are the main parts of the endocrine system?
pineal, pituitary, thyroid and adrenal gland, thymus, pancreas, ovaries and testis, hypothalamus, and pancreas
What are the main parts of the cardiovascular system?
blood vessels and heart
main parts of lymphatic system/ immunity
red bone marrow, thymus, lymphatic vessels, thoracic duct, spleen, and lymph nodes
main parts of respiratory system
nasal cavity, pharynx, larynx, trachea, lungs and bronchus
main parts of digestive system
oral cavity, esophagus, liver, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum , and anus
main parts of urinary system
kidney, ureter, urinary bladder, and urethra
main parts of male and female reproductive systems
male: prostate gland, penis, testis, scrotum, ductus deferens. female: mammary glands, ovary, uterine tube, uterus, and vagina
What are some functions of the lymphatic system?
it picks up fluid leaked from blood vessels and returns it to blood; disposes of debris in the lymphatic stream; houses white blood cells involved in immunity;
What is homeostasis?
the ability to maintain a relatively stable internal environment in an ever-changing outside world
What are control mechanisms for homeostasis?
receptor is a sensor that monitors the environment and responds to changes, called stimuli and then sends info via the afferent pathway to the control center where it is analyzed and determines the appropriate response or course of action and then to the effector via the efferent pathway which provides the means for the control centers output
What is negative feedback within homeostasis? and example
the response reduces or shuts off the original stimulus regulation of body temp (nervous mechanism) regulation of blood volume by ADH (endocrine mechanism)
What are positive feedback examples?
the response enhances or exaggerates the original stimulus; exhibits an amplifying effect; usually controls infrequent events ex: enhancement of labor contractions by oxytocin, platelet plug formation and blood clotting
the head is _ to the abdomen
superior
the navel is to the chin
inferior
the breastbone is _ to the spine
anterior (ventral)
the heart is _ to the breastbone
posterior (dorsal)
the heart is _ to the arm
medial
the arms are _ to the chest
lateral
the collarbone is _ between the breastbone and shoulder
intermediate
the elbow is _ to the wrist
proximal
the knee is ___ to the thigh
distal
the skin is to the skeletal muscles
superficial
the lungs are _ to the skin
deep
What process allows us to adjust to either extreme heat or extreme cold?
Negative feedback mechanisms allow us to adjust to conditions outside the normal temperature range by causing heat to be lost from the body and retained or generated by the body.
When we begin to get dehydrated, we usually get thirsty, which causes us to drink fluids. Is thirst part of a negative or a positive feedback control system?
thirst is part of a neg. feedback control system because it prods us to drink which ends the thirst stimulus and returns body fluid volume to the normal range
Why is the formation of platelet plug called positive feedback? What event ends it?
This is a pos. feedback mechanism because it enhances the change set into motion by the stimulus. The response ends when the platelet plug has plugged the hole in the blood vessel.
The two fundamental divisions of our body
Axial part - head, neck and trunk. Appendicular part- appendages or limbs
Regional terms are used to ……
designate specific areas within major body divisions
The most frequent planes
Sagittal, Frontal, Transverse
Sagittal plane
vertical plane- divides the body into right and left parts
Midsagittal plane
median for the sagittal plane
Parasagittal plane
offset from the midline or midsagittal plane
Frontal plane
vertically divide the body into ventral and dorsal parts
transverse or horizontal plane
horizontal from right to lfet dividint eh body into superior and inferior parts
What cavity is the brain in?
cranial cavity
what cavity contains the spinal cord
vertebral cavity
what cavity contains the heart and lungs
thoracic cavity
what is between the thoracic cavity and the abdominal cavity
diaphragm
what cavity contains the digestive viscera
Abdominal cavity
what cavity contains the urinary bladder, reproductive organs and rectum
pelvic cavity