Unit 7 - Articulations
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
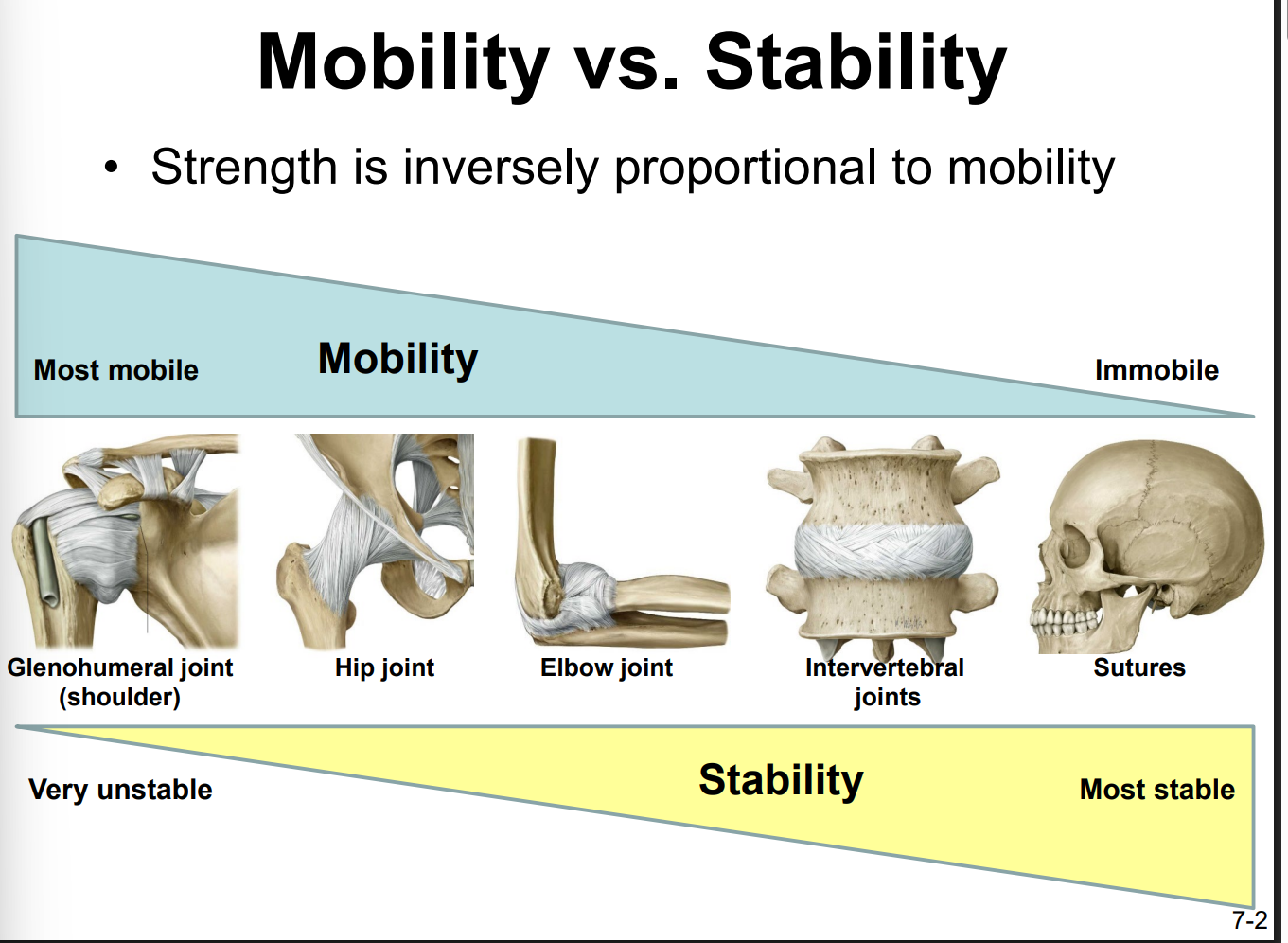
Describe the relationship between the degree of joint mobility and joint stability
they are inversely proportional
the more mobile a joint is → the less stable it is
Most to least mobile:
1) Glenohumeral joint (shoulder)
2) hip joint
3) elbow joint
4) intervertebral joints
5) sutures
Explain how to classify joints functionally and structurally
Functional Classification
1) synarthrosis (immovable)
2) amphiarthrosis (slightly movable)
3) diarthrosis (freely movable)
Structural Classification
1) Fibrous (connected by fibrous tissue)
2) Cartilagenous (connected by cartilage)
3) Synovial (contains a fluid-filled joint cavity)
Describe the relationship between structural classifications and functional classifications of joints.
joint:
any place where adjacent bones or bone and cartilage come together to form a connection
The amount of movement available at a particular joint of the body is related to the functional requirements for that joint
immobile or slightly moveable joints serve to protect internal organs, give stability to the body, and allow for limited body movement. In contrast, freely moveable joints allow for much more extensive movements of the body and limbs
Define synarthrosis and give examples
synarthrosis: immobile/nearly immobile joint
strong union b/t articulating bones
ex. sutures, manubriosternal joint, gomphosis (tooth peg-in-socket joint), synchondroses (bones connected by hyaline cartilage)
amphiarthrosis and give examples
limited mobility
ex. cartilaginous joint that unites the bodies of adjacent vertebrae (fibrocartilage intervertebral disc), pubic symphysis of pelvis
diarthrosis and give examples
freely mobile joint
ex. elbow joint, knee joint, synovial joint
Name and describe the three subtypes of fibrous joints. Give examples of each subtype.
1) suture
narrow fibrous joint b/t bones of the skull
2) syndesmosis joint
bones are widely separated, but held together by a narrow band of fibrous connective tissue called ligament or wide sheet of connective tissue called interosseous membrane (b/t shafts of long bones in the forearm & leg)
3) Gomphosis
narrow fibrous joint b/t the roots of a tooth & the bony socket in the jaw into which the tooth fits
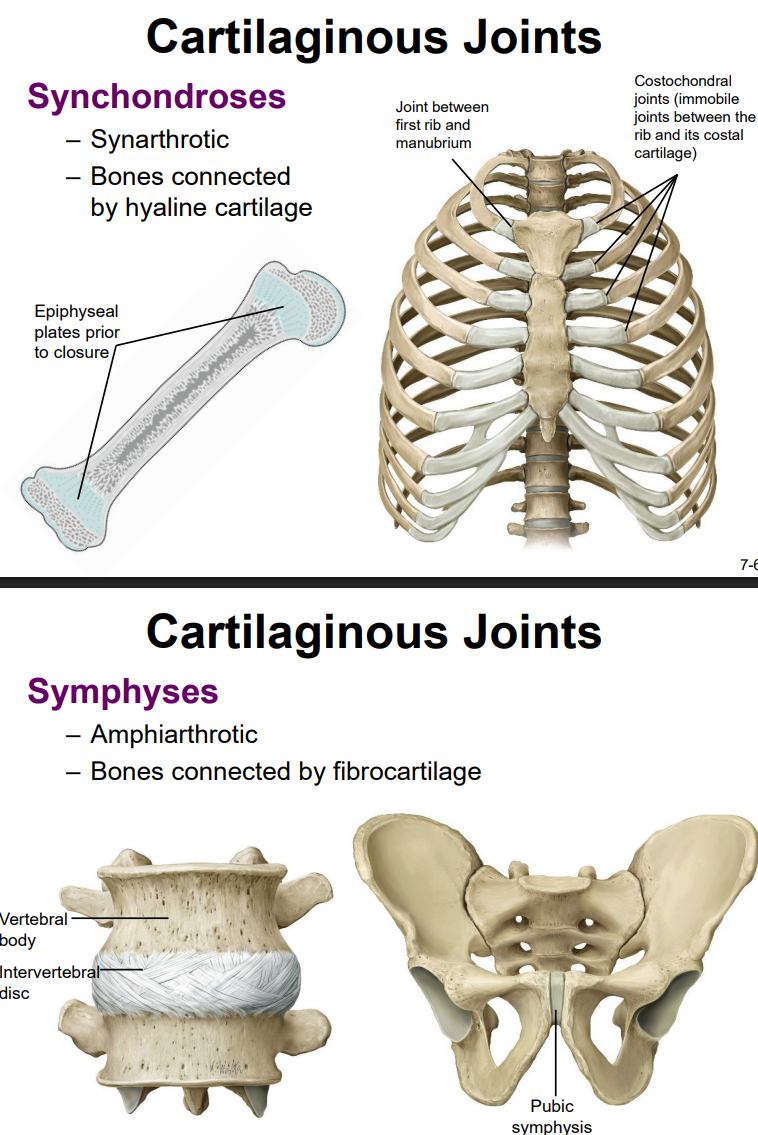
Name and describe the two subtypes of cartilaginous joints. Give examples of each subtype.
1) Synchondrosis joint (bone is united by a hyaline cartilage structure)
ex. sternocostal joint, epiphyseal plate, joint b/t first rib & manubrium, costochondral joints (joints b/t the rib & its costal cartilage)
2) symphysis (bones joined by fibrocartilage)
ex. vertebral body’s intervertebral disc, pubic symphysis
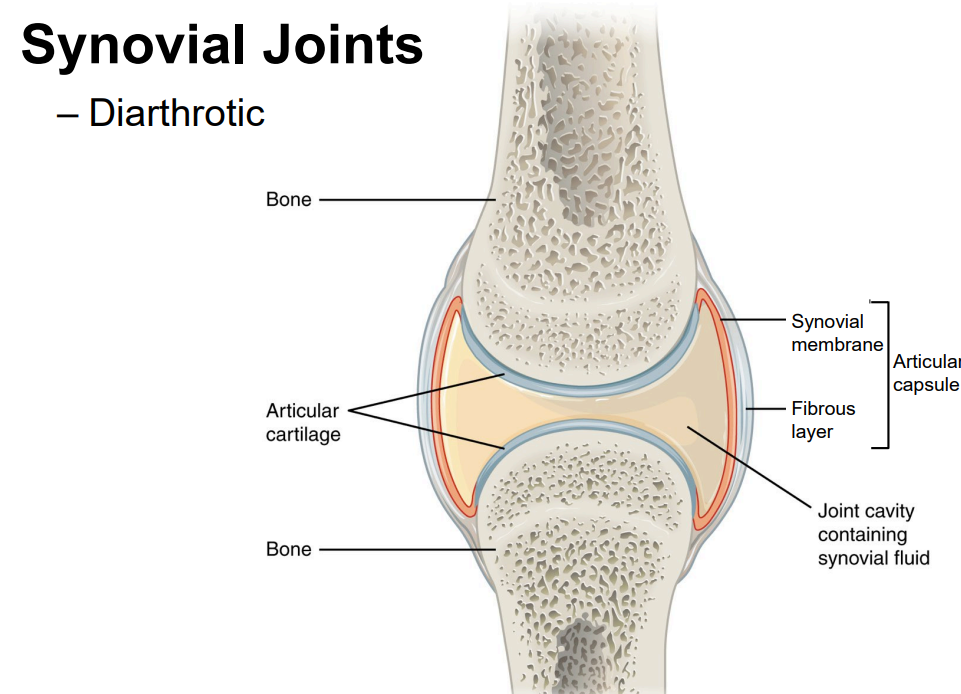
Draw a typical synovial joint, labeling the following: bone, articular cartilage, articular capsule, fibrous layer, synovial membrane, joint cavity, synovial fluid. State the function of each of the labeled structures.
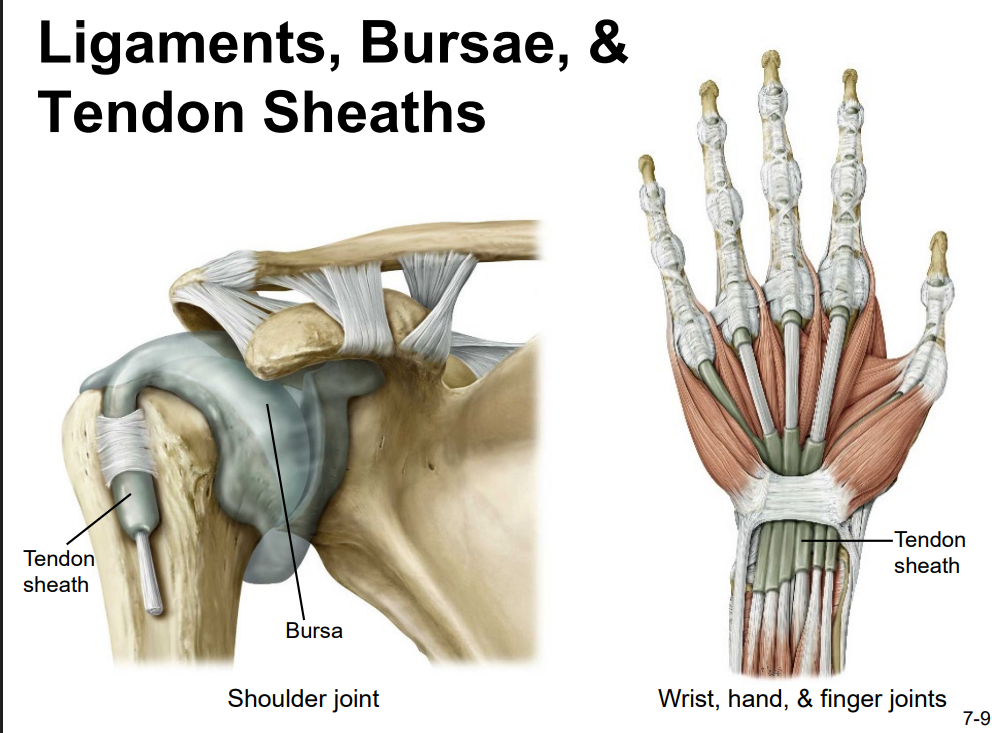
State the location and function of the following in relation to joints: ligaments, bursae, tendon sheaths, menisci, articular discs, muscles, and tendons.
bursa: thin connective tissue sac filled w/ lubricating liquid
located in regions where skin, ligaments, muscles, or muscle tendons can rub against each other
reduce friction by sep’ing the adjacent structures, preventing them from rubbing directly against each other
classified by location: subcutaneous bursa = located b/t the skin and an underlying bone
tendon sheath:
similar in structure to a bursa
connective tissue sac that surrounds a muscle tendon at places where the tendon crosses a joint
contains a lubricating fluid that allows for smooth motions of the tendon during muscle contraction and joint movements
menisci:
c-shaped fibrocartilage structure located b/t the articulating bones
can unite the bones of the joint to each other, provide shock absorption and cushioning between the bones, can smooth the movements b/t the articulating bones
articular disc:
like minisci, but small and oval-shaped
same functions as menisci
tendon:
dense connective tissue structure that attaches muscle to bone
works with muscle to resist forces & support the joint
stabilize the joint
esp. important for shoulders
Name and describe the six types of synovial joints. Give examples of each type.
Synovial joints subdivided based on the shapes of the articulating surfaces of the bones that form each joint
1) Pivot joints
a rounded portion of bone is enclosed within a ring formed partly by the articulation w/ another bone and partly by a ligament. The bone rotates within this ring
Uniaxial diarthrosis (bc joint rotates around single axis)
ex. C1 (atlas) & C2 (axis)
ex. radius articulates with ulna = allows for forearm movements
2) Hinge joints
convex end of one bone articulates with concave end of adjoining bone
bending and straightening along a singe axis (elbow, knee, ankle)
3) Condyloid joints
the shallow depression at the end of one bone articulates with a rounded structure from an adjacent bone/bones
interphalangeal joint
biaxial (forward-backward, side-to-side)
4) Saddle joints
both articulating bones have saddle shape (concave in one direction, convex in another)
biaxial
5) Plane Joints
articulating surfaces = flat/slightly curved → allow bones to slide against each other
b/t carpal bones of wrist & tarsal bones
multiaxial joint
6) Ball & Socket Joints
head of one bone fits into concave articulation of adjacent bone
hip joint (acetabulum) and glenohumeral joint
multiaxial joints
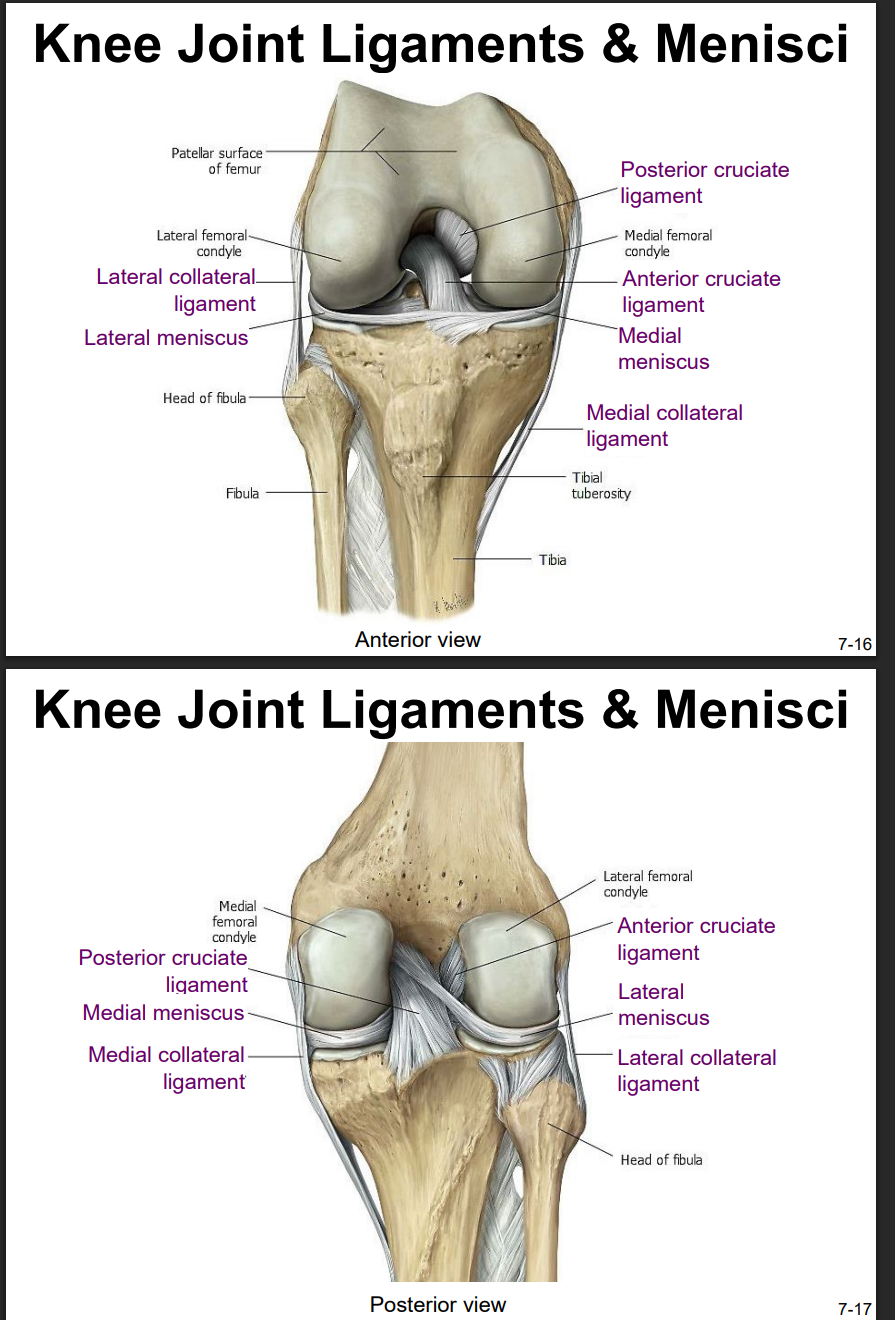
Explain the location and functions of following structures associated with the knee joint: Anterior cruciate ligament
intracapsular ligament
anchored inferiorly to tibia at intercondylar eminence
supports knee when flexed and weight bearing (like walking downhill)
becomes tight when knee is extended and resists hyperextension
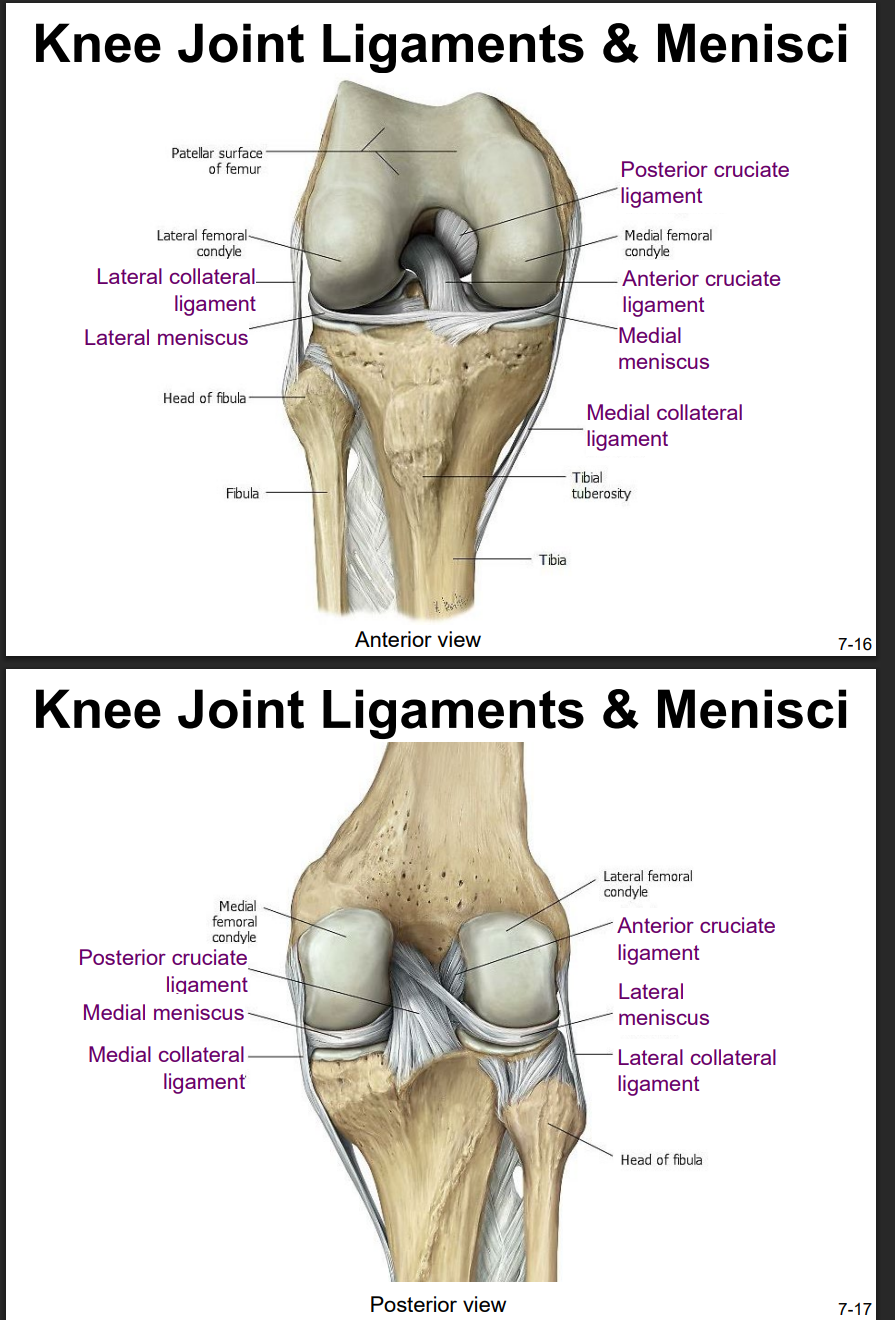
Explain the location and functions of following structures associated with the knee joint: Posterior cruciate ligament
anchored posteriorly to tibia
the stronger ligament (compared to anterior)
supports knee when flexed and weight bearing (like walking downhill)
prevents femur from sliding anteriorly off the top of tibia
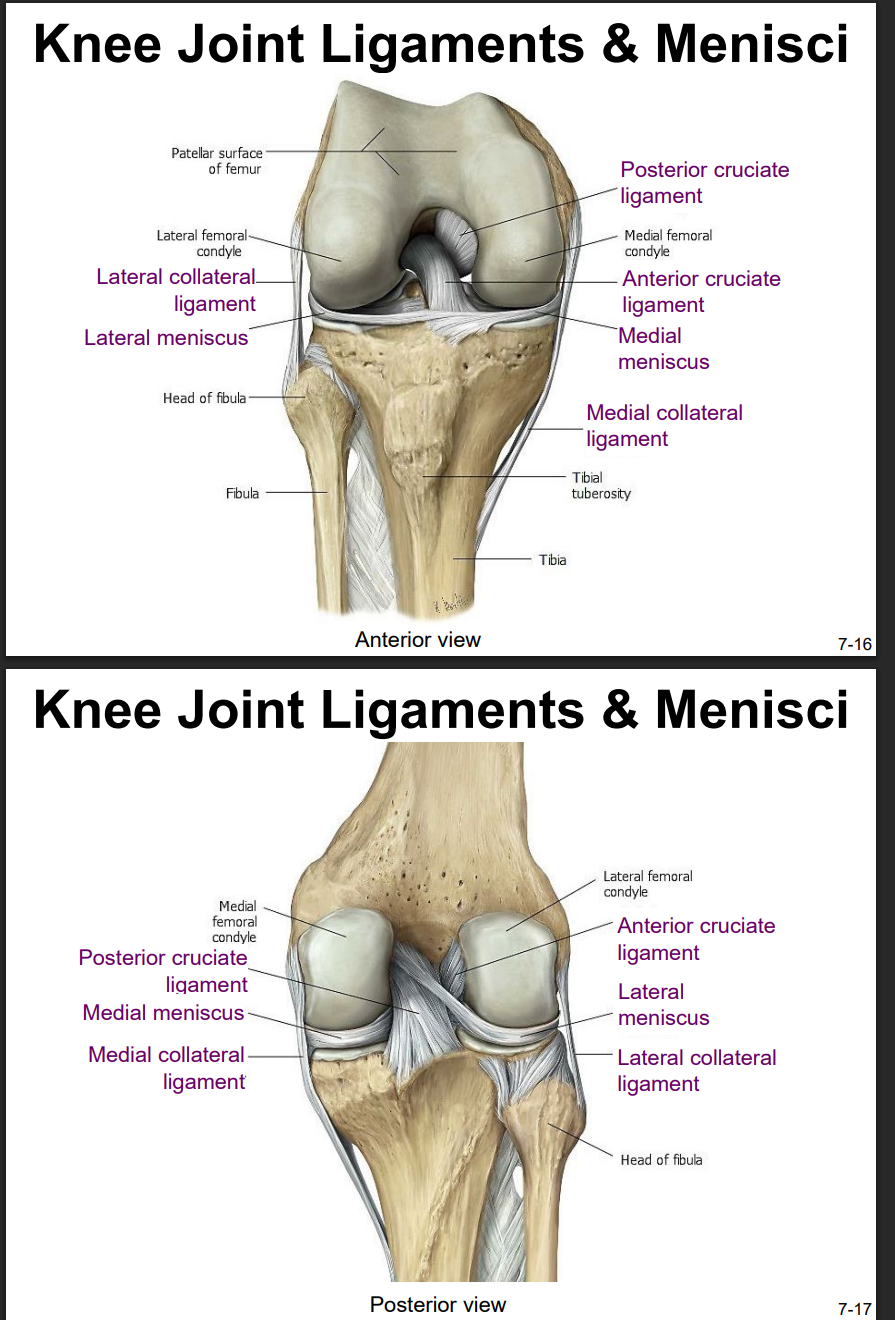
Explain the location and functions of following structures associated with the knee joint: Medial collateral ligament
runs from medial epicondyle of the femur to the medial tibia
as it crosses the knee → firmly attached on its deep side to the articular capsule and media meniscus
taut when knee’s extended = helps stabilize and support the extended → prevents side-to-side or rotational motions b/t femur & tibia
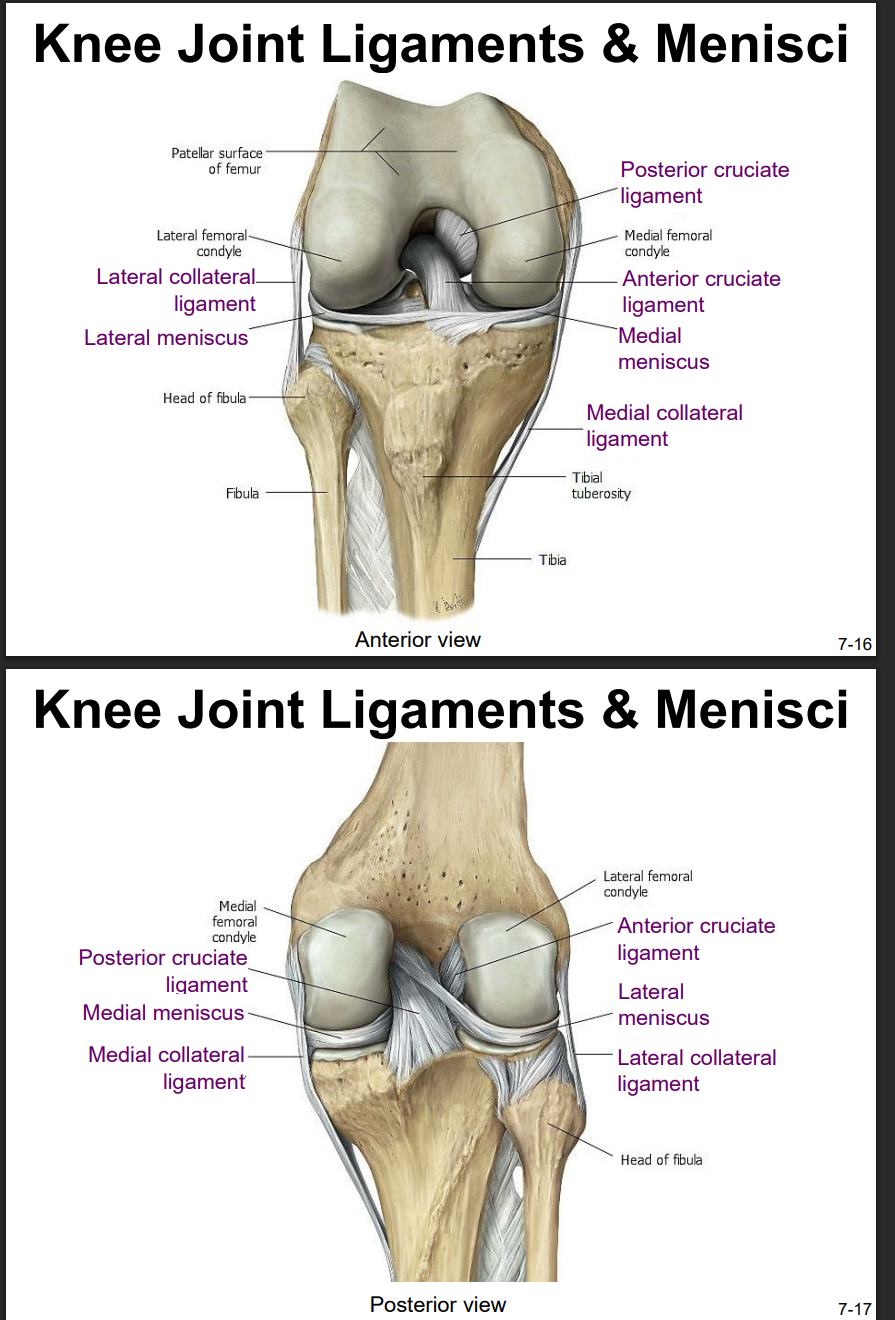
Explain the location and functions of following structures associated with the knee joint: Lateral collateral ligament
on lateral side
spans from lateral epicondyle of femur to head of fibula
stabilize & support extended knee, prevent side-to-side or rotational motions b/t tibia & femur
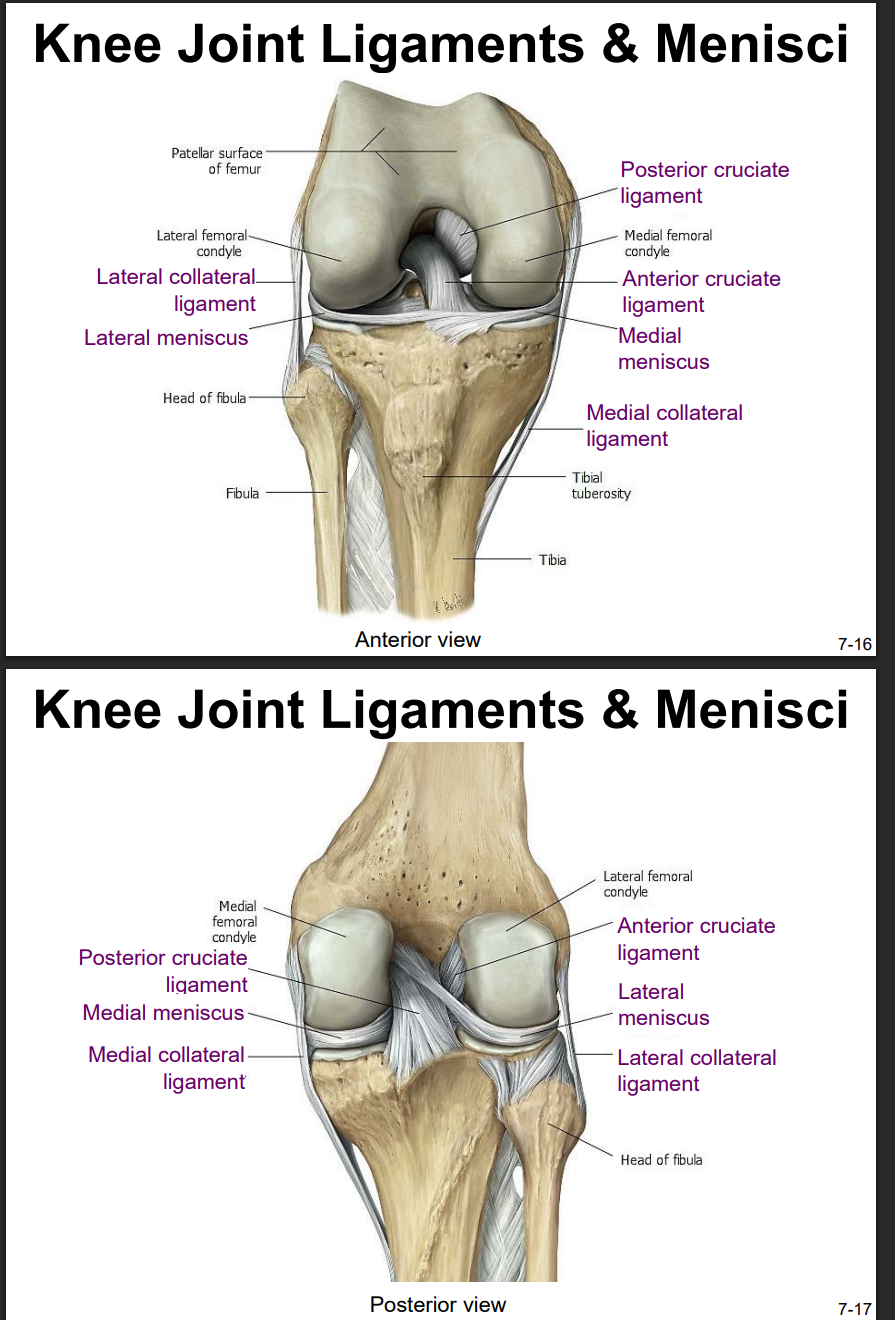
Explain the location and functions of following structures associated with the knee joint: Lateral meniscus & medial meniscus
C-shaped fibrocartilage structure that is thin along its inside margin and thick along the outer margin.
attached to their tibial condyles, do not attach to femur
provide padding b/t the bones & help to fill the gap b/t the round femoral condyles & flattened tibial condyles
some areas lack an arterial blood supply & heal poorly if damaged
Explain the location and functions of following structures associated with the knee joint: Patella
slides vertically within a groove on the distal femur
sesamoid bone incorporated into the tendon of the quadriceps femoris muscle (the lg. muscle of the anterior thigh)
protects the quadriceps tendon from friction against the distal femur
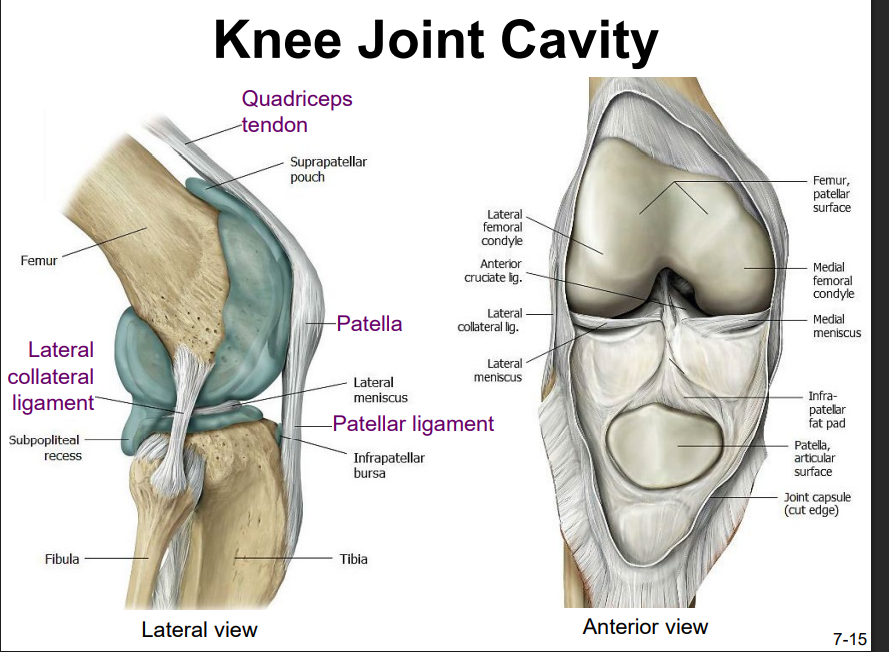
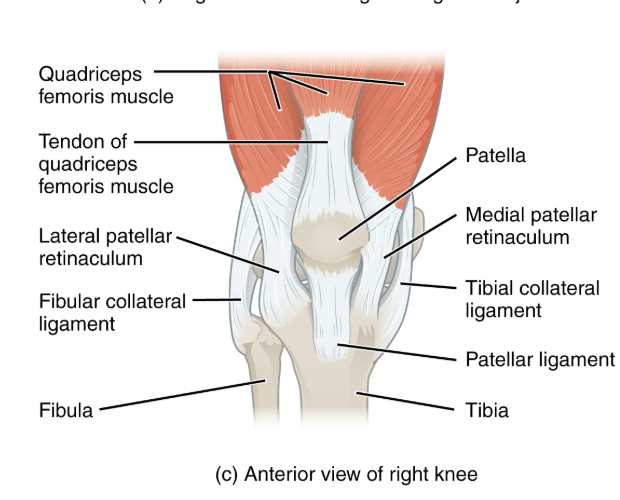
Explain the location and functions of following structures associated with the knee joint: Patellar ligament
the quadriceps femoris is a powerful muscle that acts via the patella & patellar ligament to extend the leg at the knee
dynamic ligament that provides important support & stabilization for the knee joint
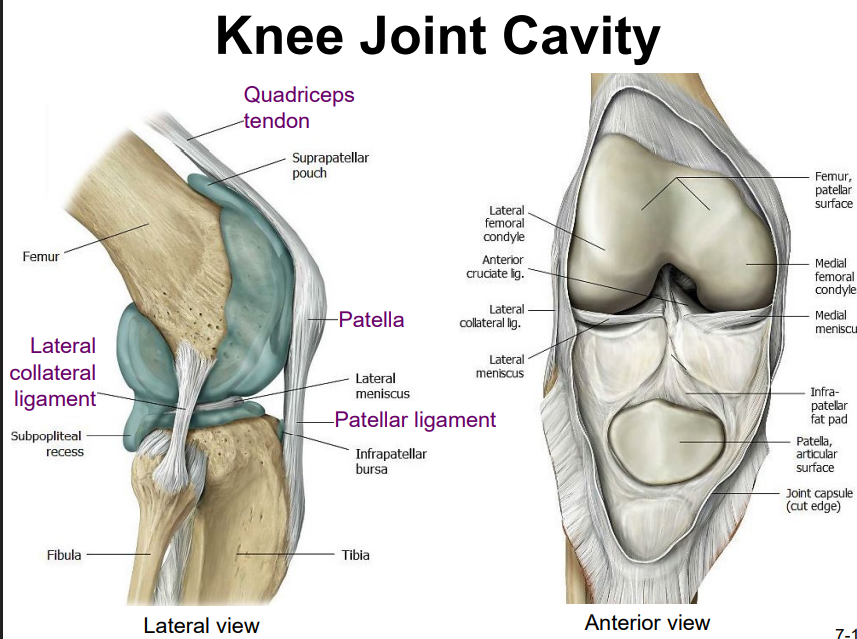
Explain the location and functions of following structures associated with the knee joint: Quadriceps tendon
contains the patella
helps extend the knee with quadriceps femoris muscles
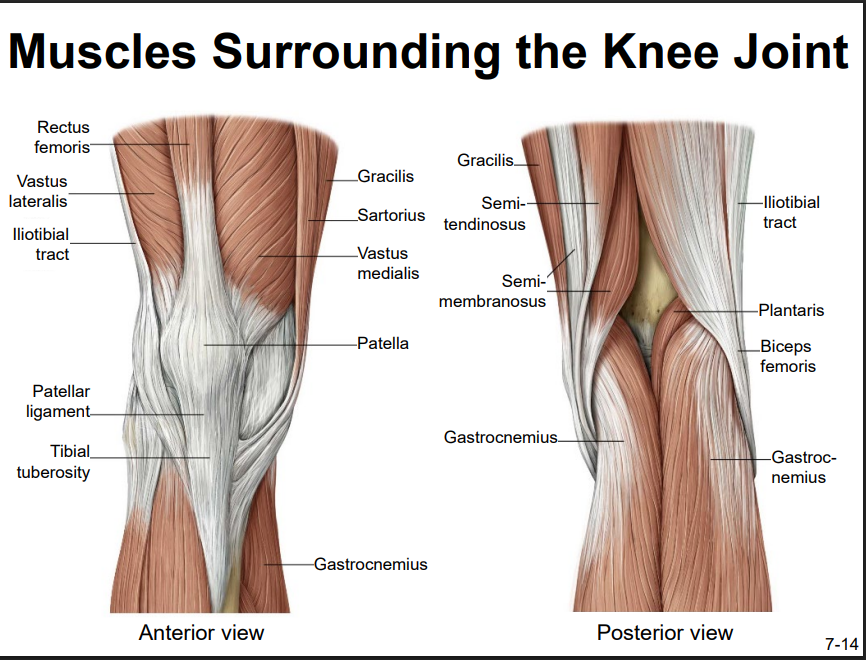
Explain the location and functions of following structures associated with the knee joint: Muscles that stabilize the knee joint
Anterior:
gracilis (side)
sartorius
vastus medialis
vastus lateralis
rectus femoris
gastrocnemius
Posterior:
Gracilis
semitendinosus
semimembranosus
plantaris
biceps femoris
gastrocnemius
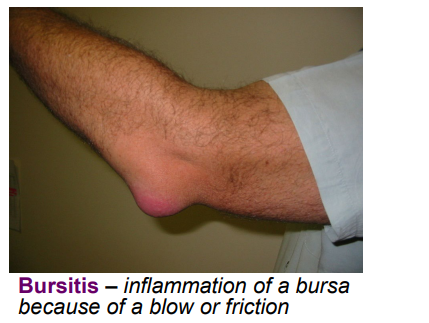
Define the following and give common causes of each: Bursitis
overuse
cure: antibiotics for infected bursa, anti-inflammatory agents
Define the following and give common causes of each: Tendinitis
caused by repetitive movements
stretch
may need surgery

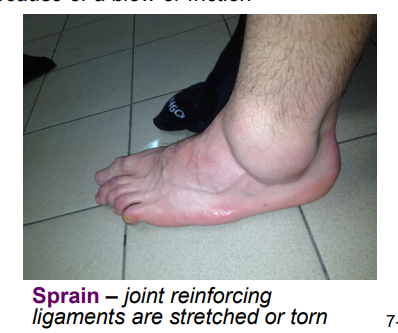
Define the following and give common causes of each: Sprain
stretching or tearing of supporting ligaments
can be treatead using RICE: rest, ice, compression, elevation
using a brace or cast may be req’d.
more severe injuries involving ligament tears or bone fractures may req. surgery
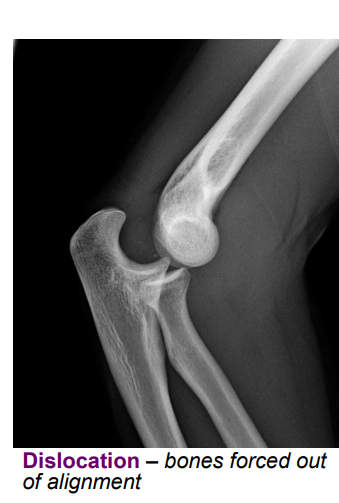
Define the following and give common causes of each: Dislocation
reduction = moving bones back into alignment
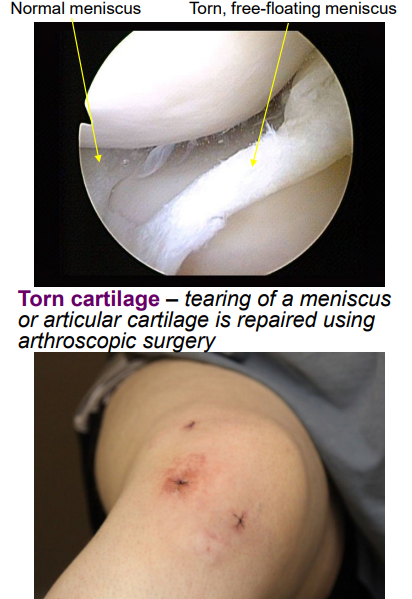
Define the following and give common causes of each: Torn cartilage
can be torn at a meniscus or articular cartilage
cartilage = avascular, cannot heal on its own
fixed using arthroscopic surgery
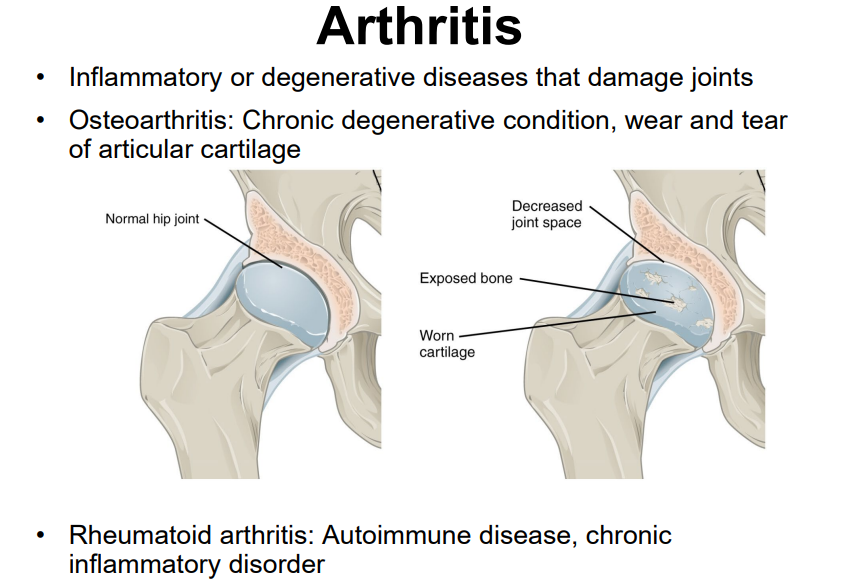
Explain the causes and symptoms of osteoarthritis
a lot of use of articular cartilage, aging, autoimmune diseases, bacterial infections, unknown (genetic) causes
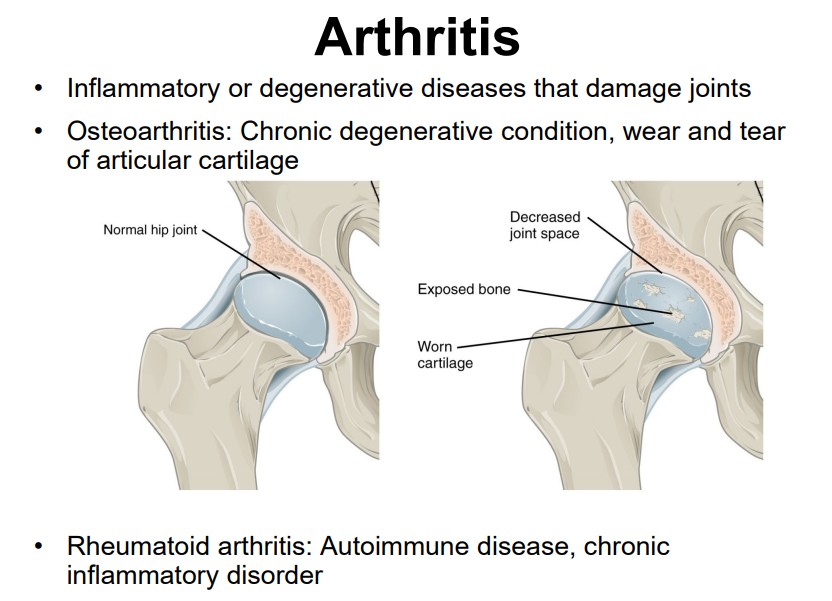
Explain the causes and symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis