2.1 Cell Structure
1/30
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
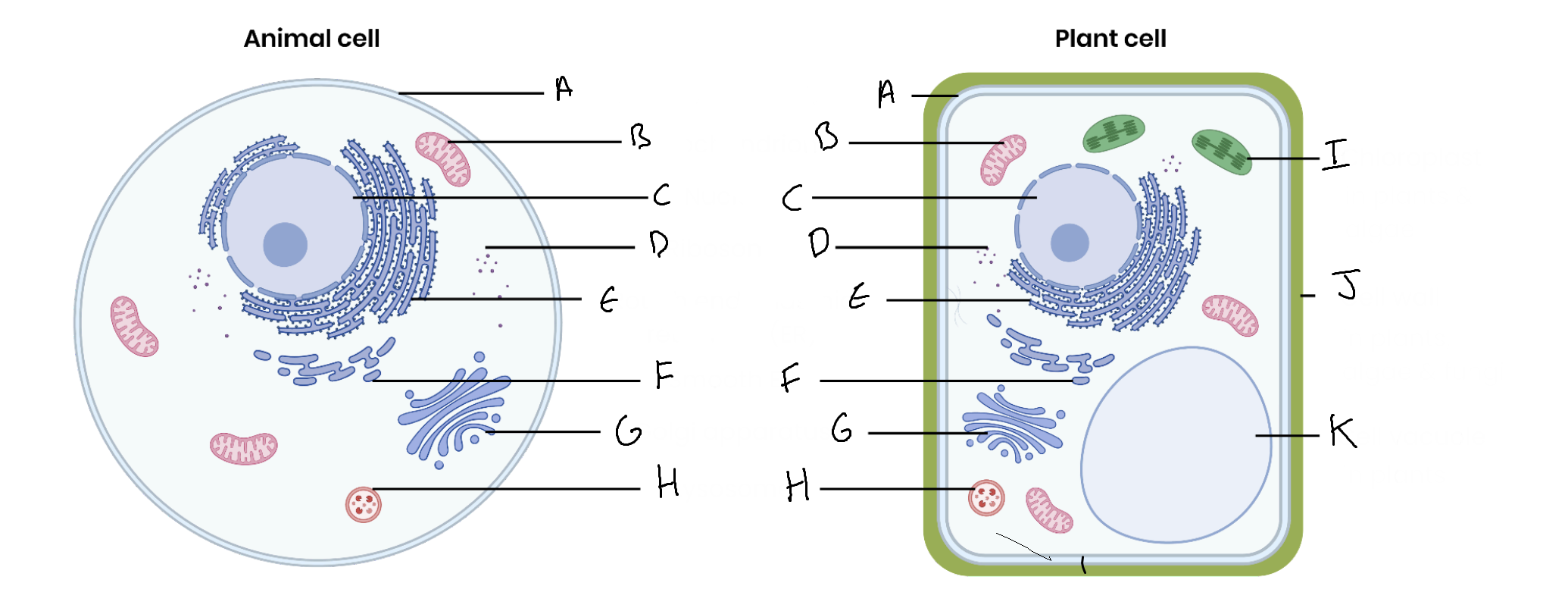
What is the organelle labelled A?
Cell surface membrane
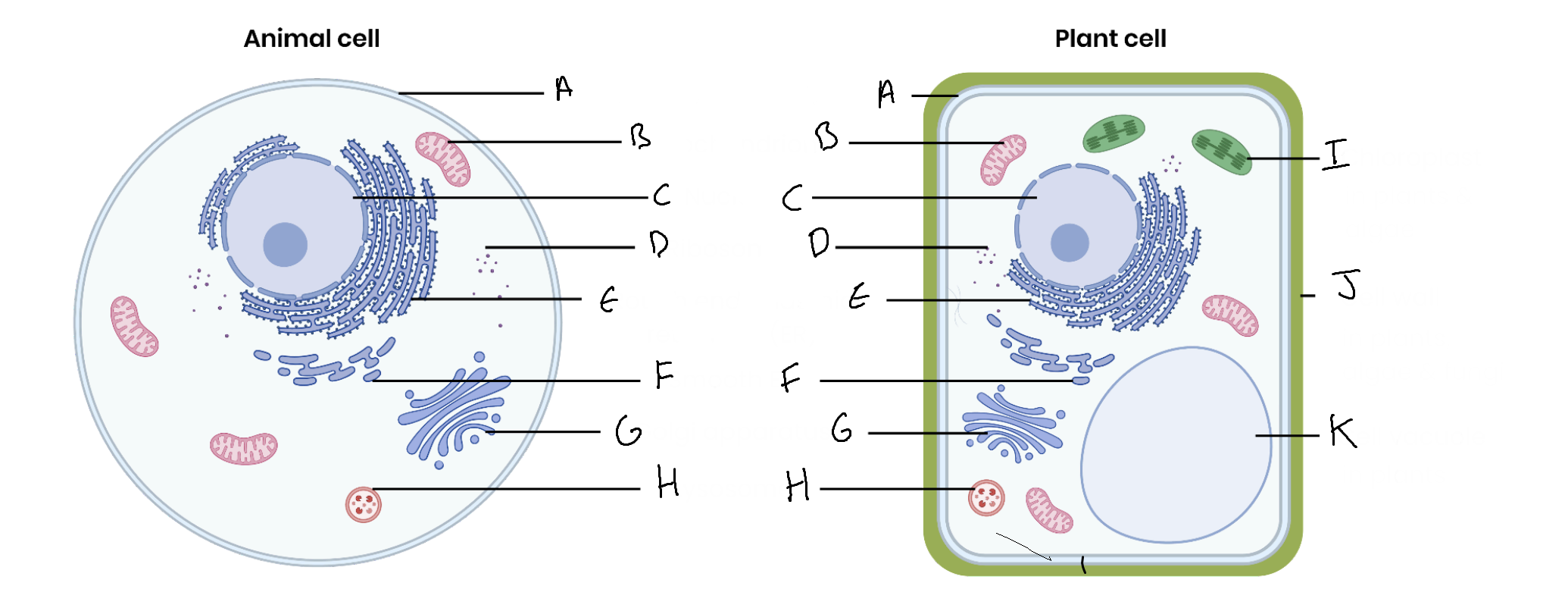
What is the organelle labelled B?
Mitochondrion
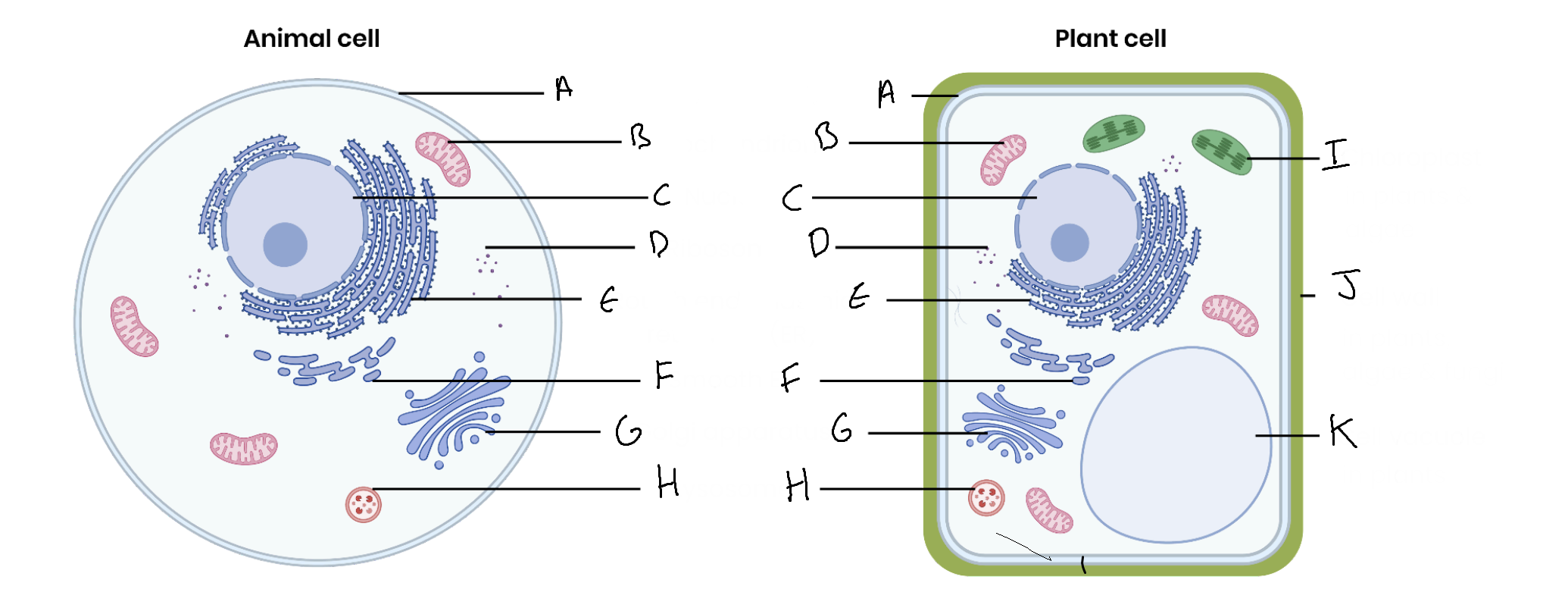
What is the organelle labelled C?
Nucleus
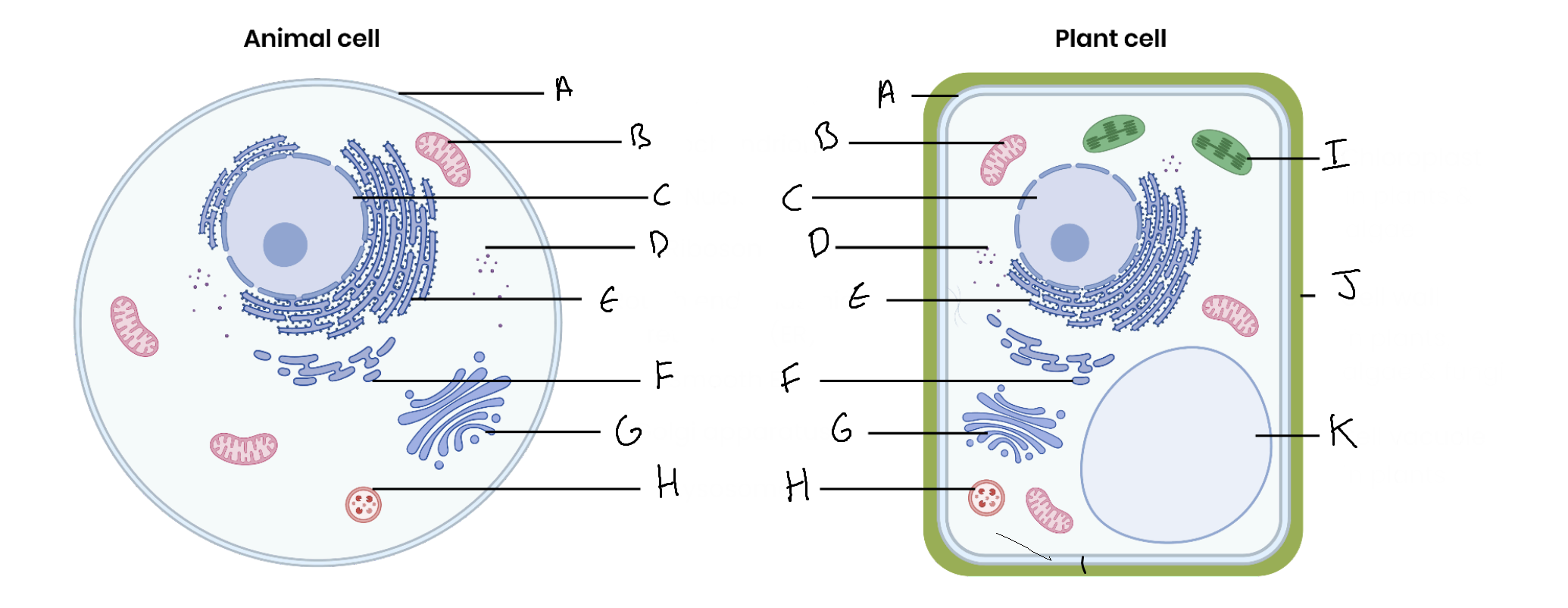
What is the organelle labelled D?
Ribosomes
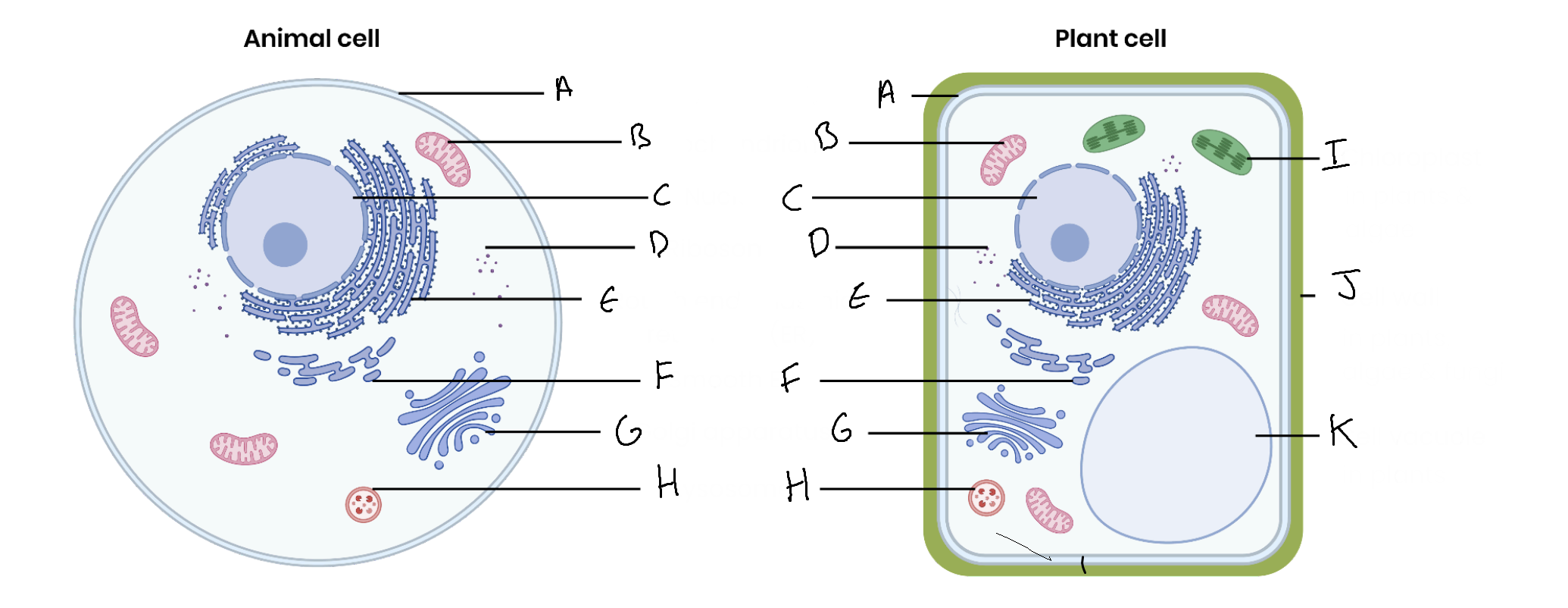
What is the organelle labelled E?
Rough endoplasmic reticulum
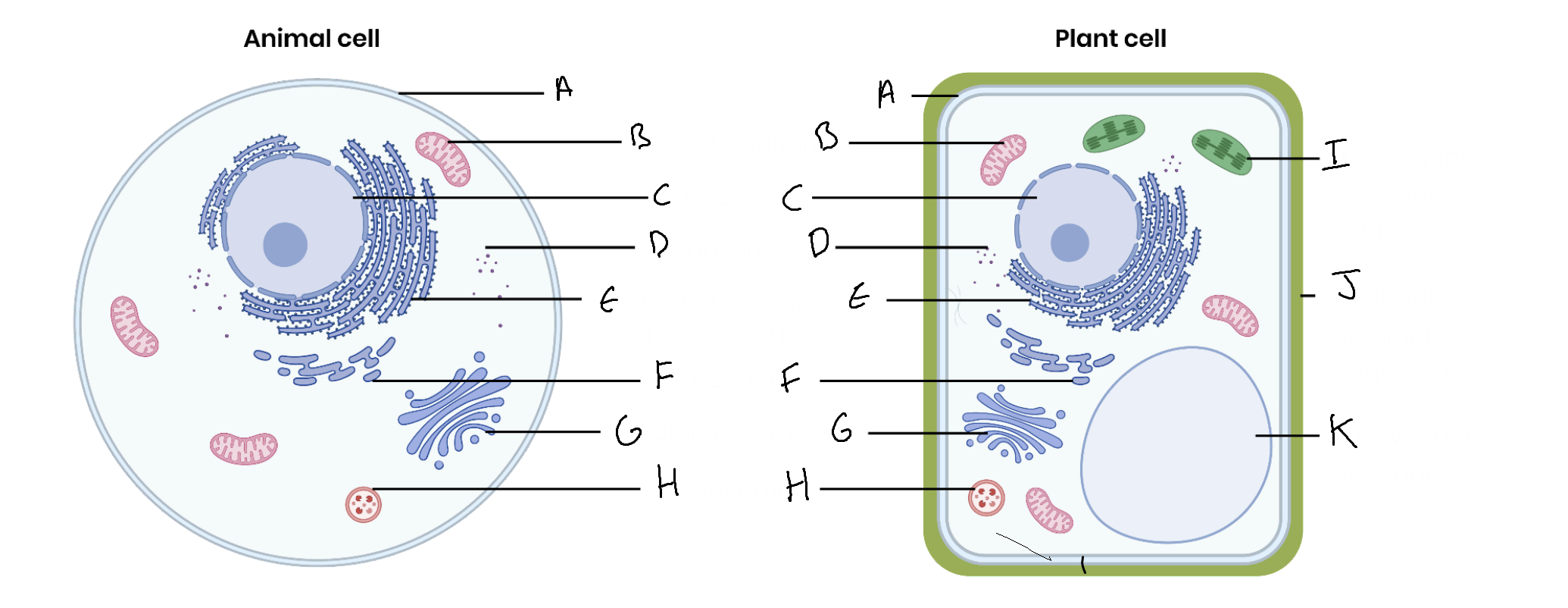
What is the organelle labelled F?
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
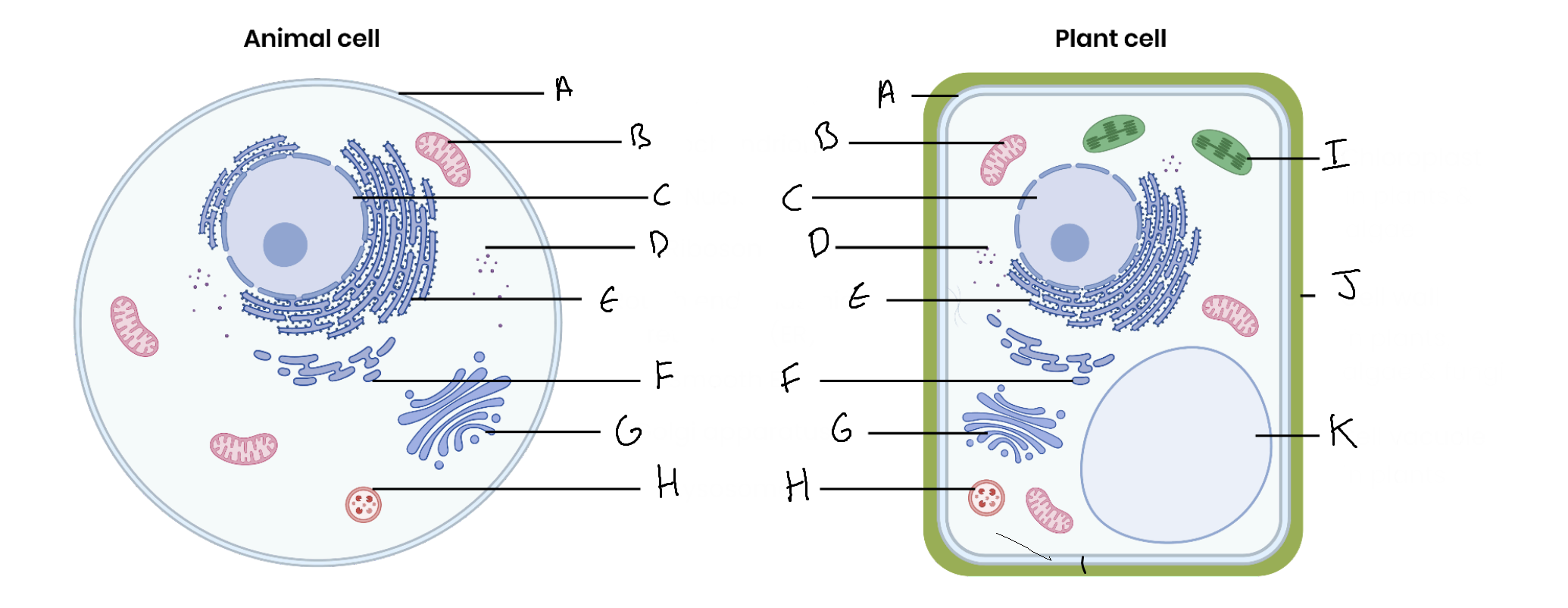
What is the organelle labelled G?
Golgi apparatus
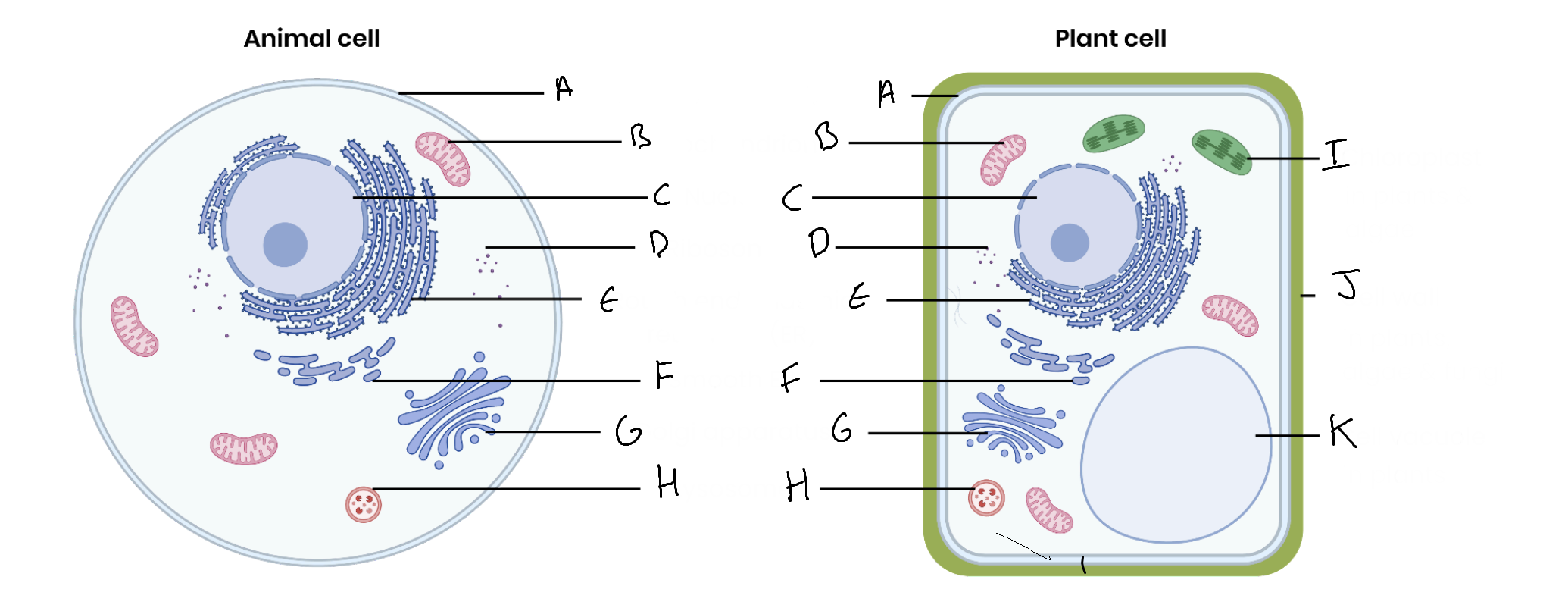
What is the organelle labelled H?
Lysosome
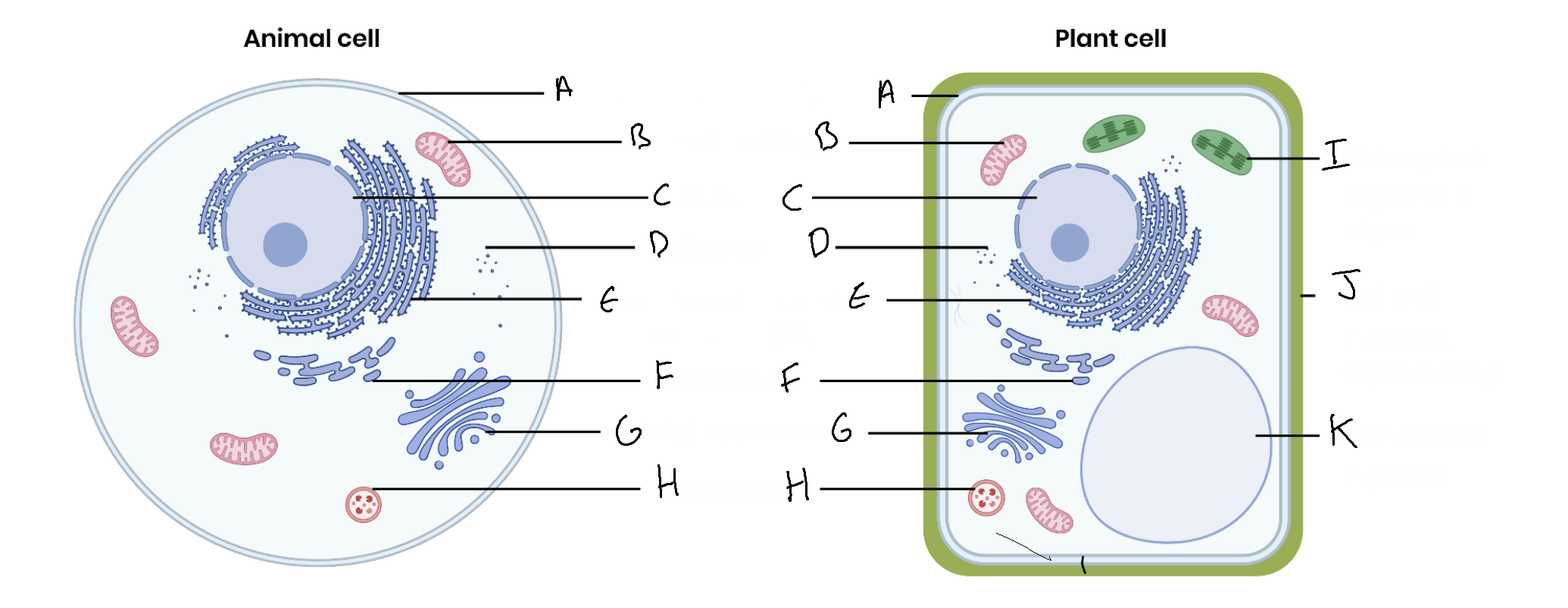
What is the organelle labelled I?
Chloroplast
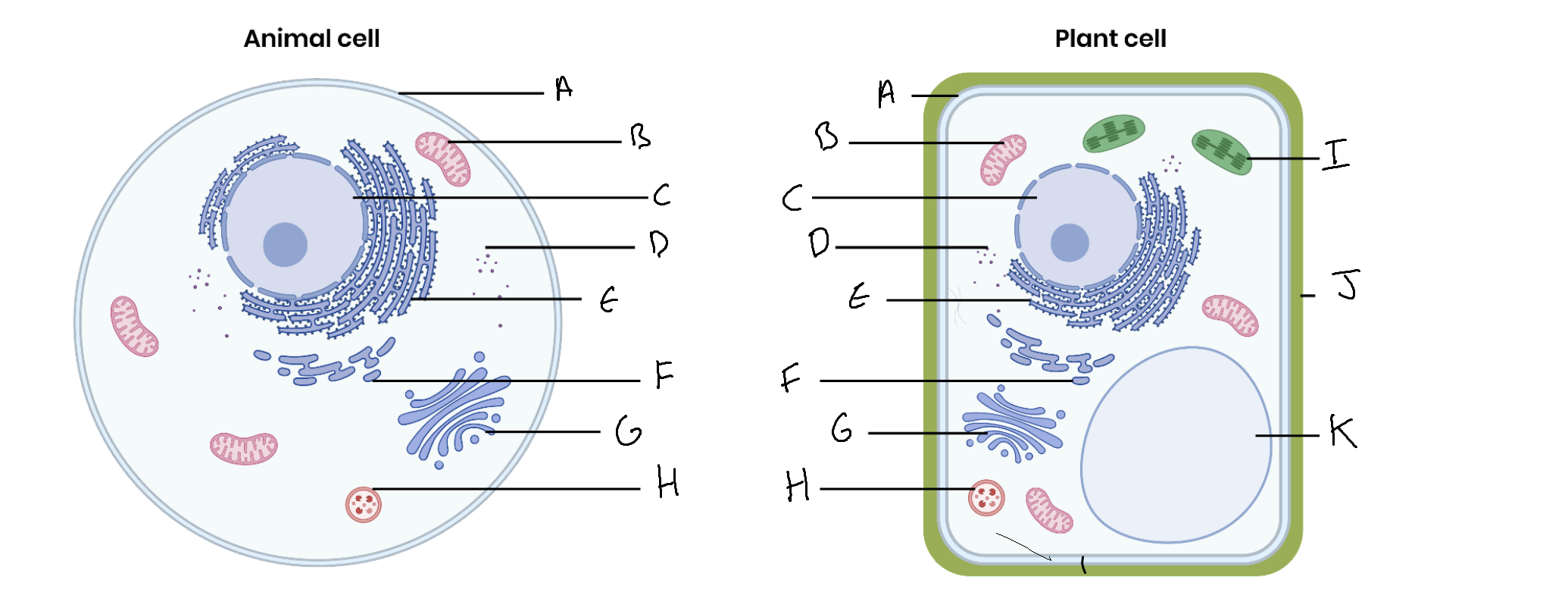
What is the organelle labelled J?
Cell wall
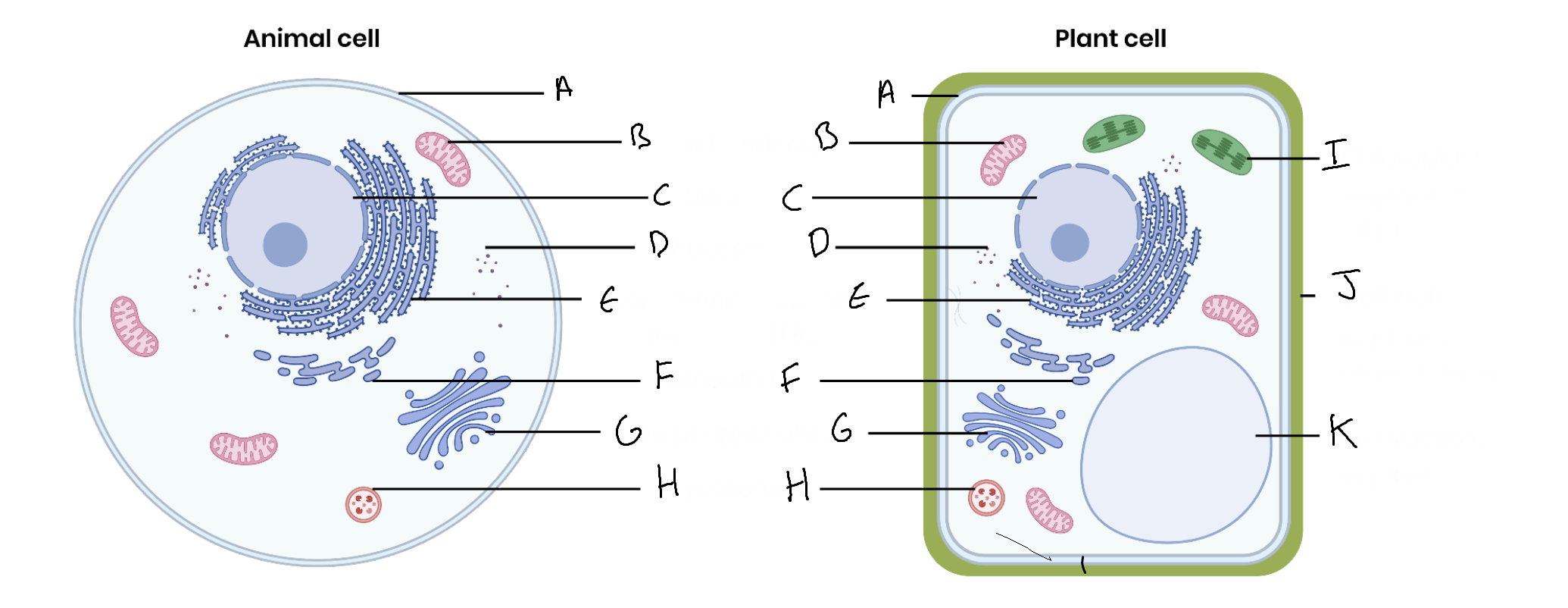
What is the organelle labelled K?
Vacuole
Describe the structure of the nucleus
Nuclear envelope
- double membrane
- has nuclear pores
Nucleoplasm
Nucleolus (inner region)
Protein linear DNA
- histone-bound
- chromatin → condensed
Chromosome → highly condensed
Function of the nucleus
carries genetic information which codes for polypeptides (proteins)
site of transcription
nucleolus makes ribosomes/ rRNA
Describe the structure of a ribosome
Made of ribosomal DNA and protein
Function of a ribosome
site of protein synthesis - translation
Function of sER
synthesises and processes lipids e.g. cholesterol and steroid hormones
Function of rER
ribosomes on surface synthesise proteins. proteins packages into vesicles for transport
Function of Golgi apparatus
modifies protein e.g. adds carbohydrates to produce glycoproteins
modifies lipids e.g. adds carbohydrates to make glycolipids
produces lysosomes
Function of Golgi vesicles
transports proteins and lipids to their required destination
Structure of lysosomes
Has a membrane and hydrolytic enzymes
Function of lysosomes
release hydrolytic enzymes (lysozymes) to hydrolyse pathogens
Structure of mitochondria
Outer membrane, inner membrane folded to form cristae, matrix containing ribosomes and circular DNA
Function of mitochondria
site of aerobic respiration
to produce ATP for energy release
Structure of chloroplasts
double membrane, stroma containing thylakoid membrane, ribosomes, circular DNA and starch granules, lamella and grana.
Thylakoids stack up to form ___ in chloroplasts
grana
function of chloroplasts
absorbs light energy for photosynthesis
Structure of cell walls in plants
composed of cellulose in plants/ algae but composed of chitin in fungi
function of cell wall
provides mechanical strength to cell to prevent bursting under pressure due to osmosis
Definition of a tissue
Group of specialised cells with a similar structure working together to perform a specific function, often with the same origin.
Definition of an organ
Aggregations of tissues performing specific functions.
Definition of organ system
Group of organs working together to perform specific functions.