Biomes
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
What are regions with common environmental characteristics?
biomes
What is the temperature and humidity of the tropical rain forest?
high, but stable temperature and humidity
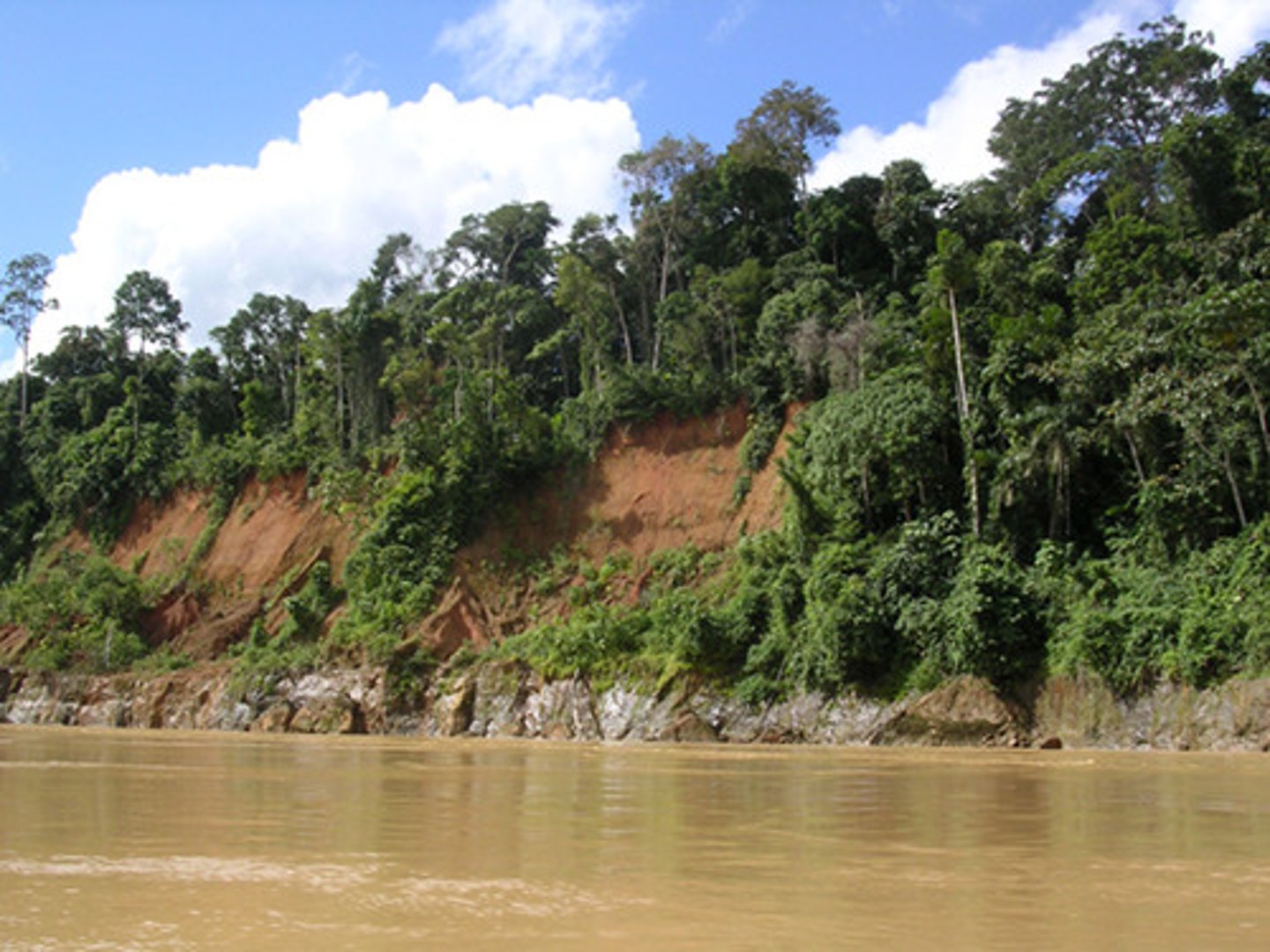

What is the rainfall of the tropical rain forest?
heavy rainfall

Which biome is filled with tall trees with branches at the tops that allow little light to enter, and vines (epiphytes)?
tropical rain forest

What is the most diverse biome?
tropical rain forest

which biome contains tropical grasslands with scattered trees?
savanna

What is the temperature of the savanna?
high temperature

What is the rainfall of the savanna?
little rainfall (~25 inches
a year to prevent the
regions from turning into deserts)

In which biome can you find ungulates (large-hoof/plant-eating mammals) like giraffes?
savanna

Which biomes are subject to seasonal droughts and fires?
savanna and
temperate grassland

Savannas cover many tropical and subtropical parts of which continents?
Australia and Africa
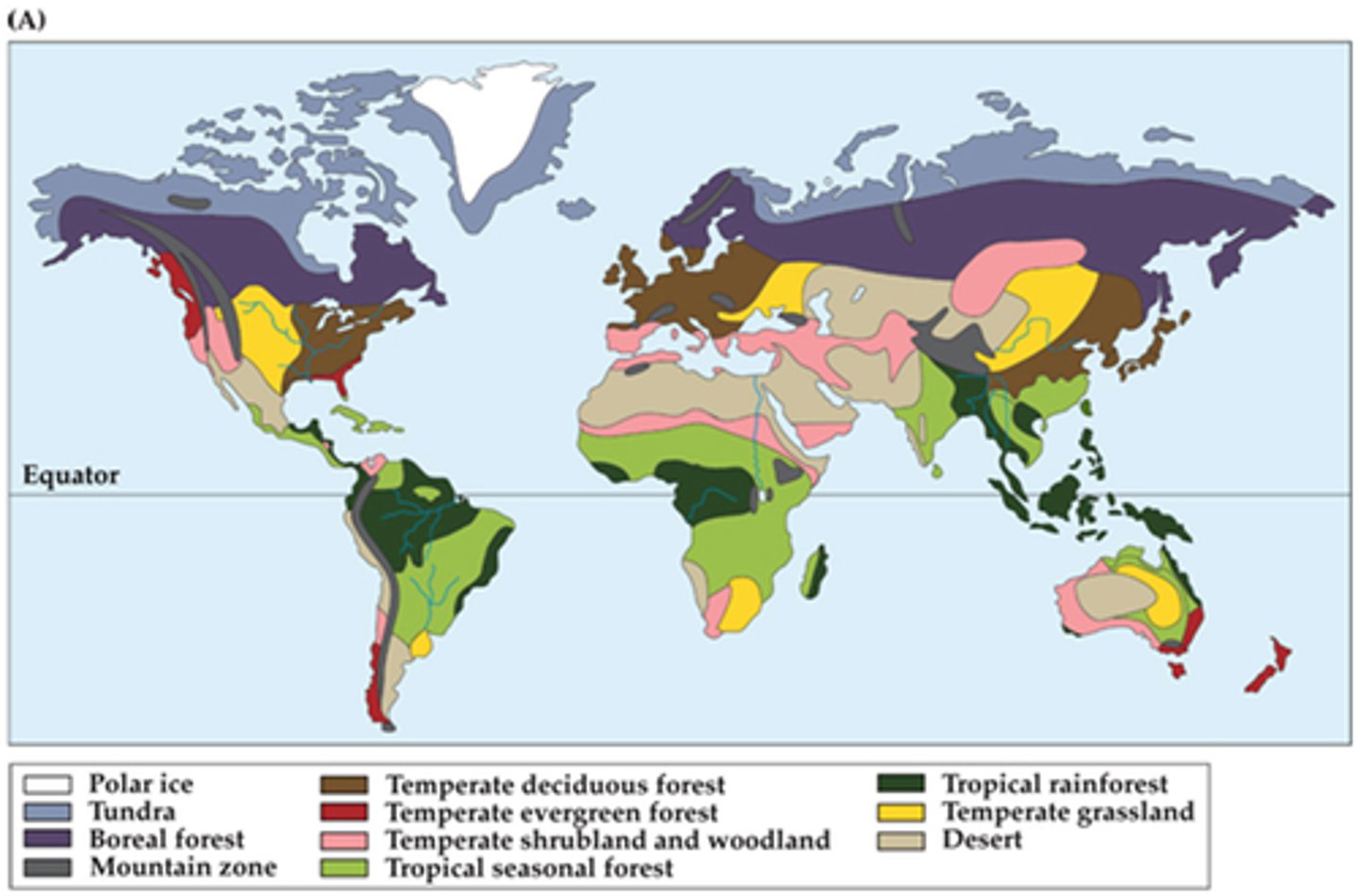
What is the rainfall of temperate grasslands?
low rainfall
(Note: uneven
seasonal occurrences
of rainfall)

What is the temperature of temperate grasslands?
vary seasonally
(Note: but lower than savannas)

Which biome contains the most fertile grassy soil in the world?
temperate grassland

Which biome contains large grazers?
temperate grassland

Which biome has warm summers, cold winters, and moderate precipitation?
temperate deciduous forest

Which biome contains large trees that shed leaves during winter, and the soil that is rich due to leaf shed?
temperate deciduous forest

What type of stratification does temperate deciduous forests exhibit?
vertical stratification
(Note: different types
of plants and animals
live depending on the
strata, or "layer")

What action do principal mammals perform during the cold winters of the temperate deciduous forests?
hibernation

Which biome contains forests that are cold and sometimes dry?
temperate coniferous

vegetation in temperate coniferous forests have adapted to conserve which resource?
water
(Note: such as
through needle leaves)

Which biome is hot and dry and has the most extreme temperature fluctuations from day to night?
desert

What factor is the growth of annual plants in the desert limited to?
rare rain

In deserts, plants and animals adapt to conserve which resource?
water
(Note: infrequently
urinate, cacti spines, etc.)

Which biome exists south of the tundra and consist of coniferous forests filled with trees like spruce, fir, and pine?
taiga

What are the winters like in the taiga?
long, cold winters with
low precipitation (snow)

What is the largest terrestrial biome?
taiga
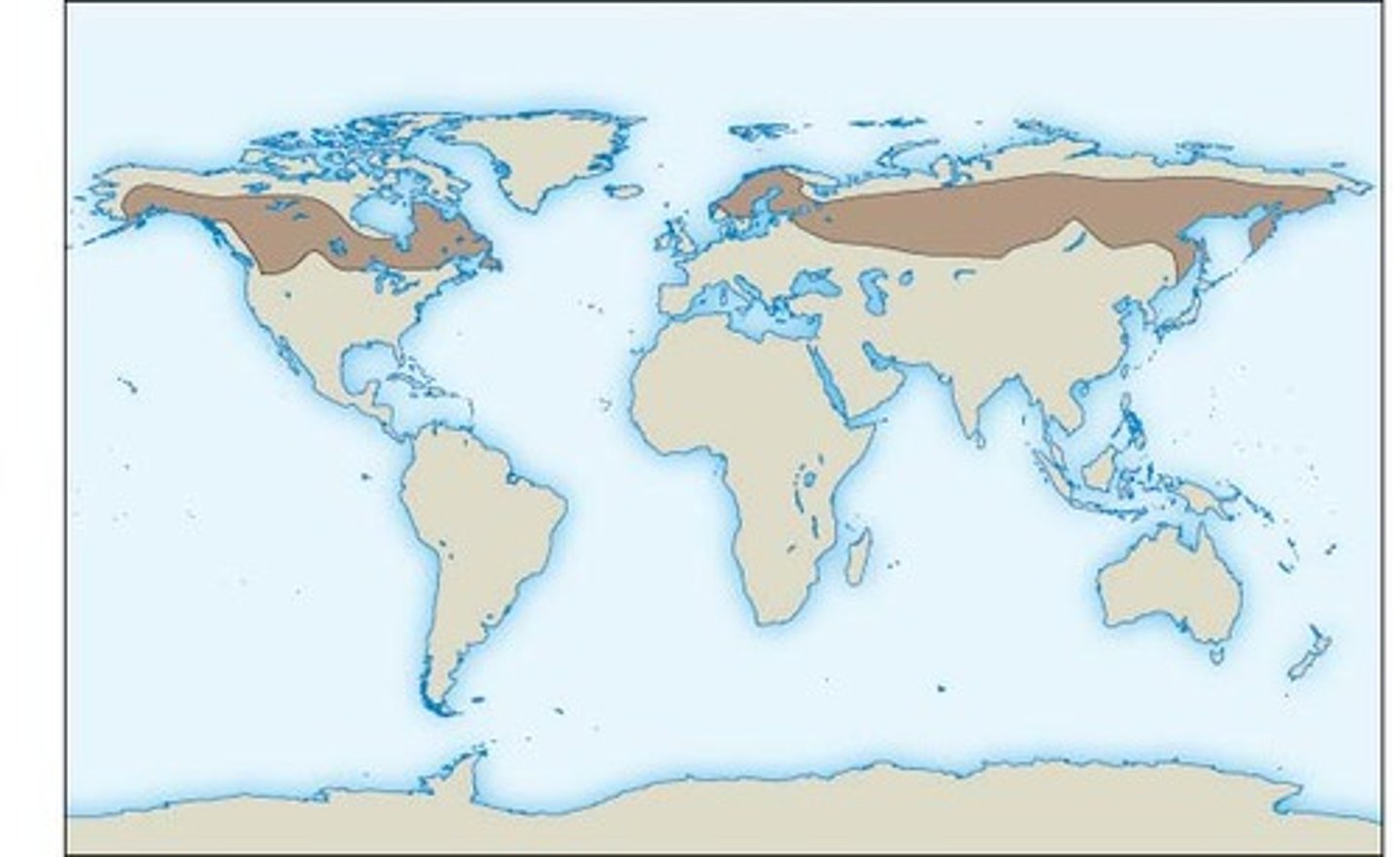
Which biome has cold winters where the ground freezes?
tundra

In which biome does the top layer thaw during summer to support minimal vegetation such as moss, lichen, and shrubs?
tundra

What is the term for the deeper soil of the tundra that remains permanently frozen?
permafrost

What is the rainfall of the tundra?
very little
(Note: short
growing season)

What is the biome along the California coastline is characterized by wet winters, dry summers, and scattered vegetation?
chaparral
(Note: California
fires happen here)

What is the region that is frozen with no vegetation or terrestrial animals?
polar region

What percentage of the earth's surface is covered by aquatic biomes?
over 75%

Which biome includes ponds, lakes, streams, and rivers?
fresh water biomes
How does the osmolarity of freshwater biomes compare to organisms?
hypotonic to organisms

Which biomes cover 3/4th of the world's surface?
marine biomes
Which biomes provide most of the earth's food and oxygen?
marine biomes
What specific biomes are included in marine biomes?
1. estuaries (meeting of ocean and river)
2. intertidal zone
3. continental shelves/littoral zones
4. coral reefs
5. pelagic oceans
Why do marine biomes have a relatively constant temperature?
water's high heat capacity and volume
How are marine biomes divided into regions?
1. amount of sunlight
2. distance from shore
3. depth
4. open water vs. ocean bottom
what is the lowest layer of a body of water, including the sediment surface and sub-surface layers?
benthic zone
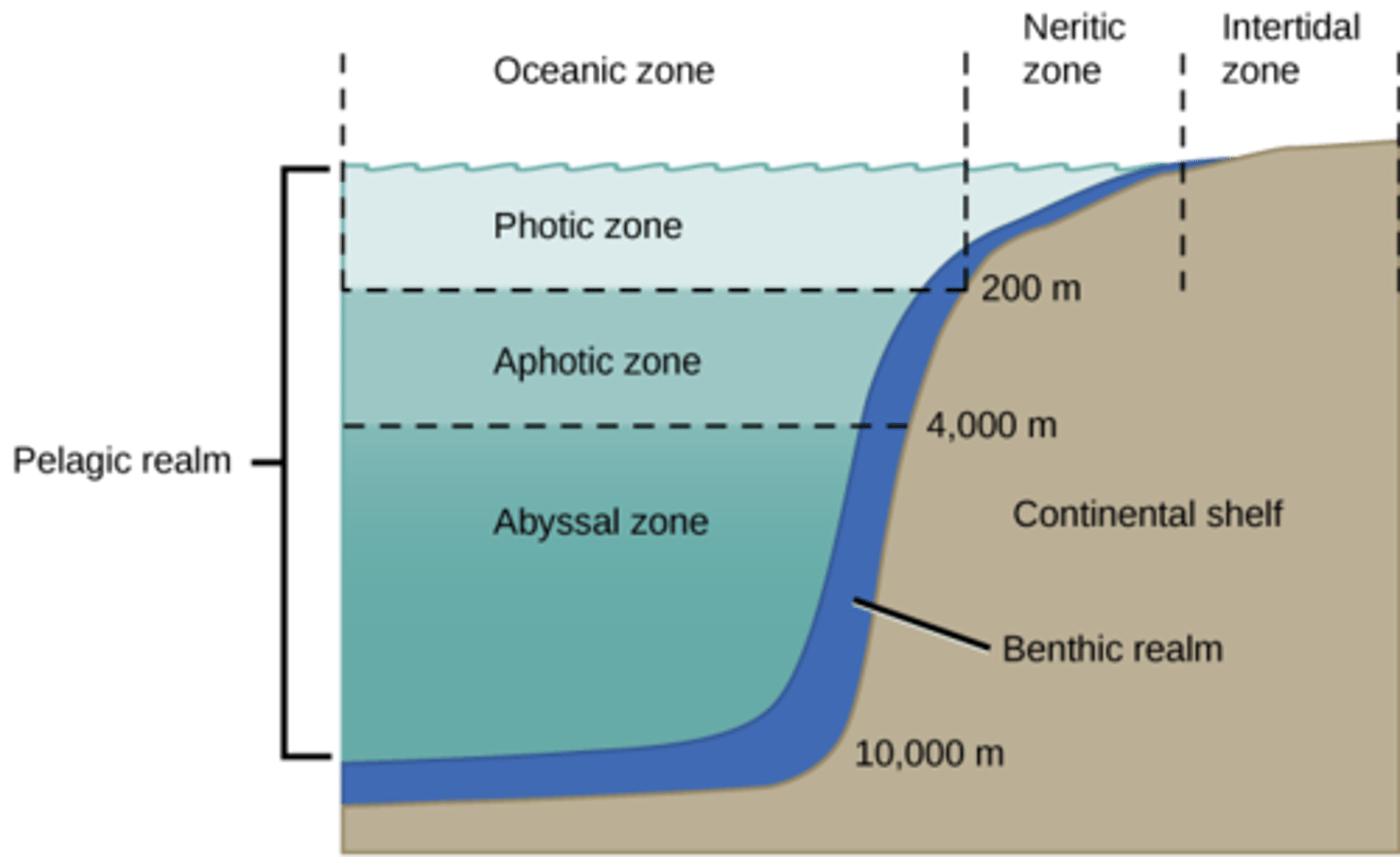
because light does not penetrate deep ocean water, how do most organisms obtain food?
most are scavengers and detritivores
What zone of ocean describes the water that is neither close to shore nor close to the very bottom?
pelagic zone
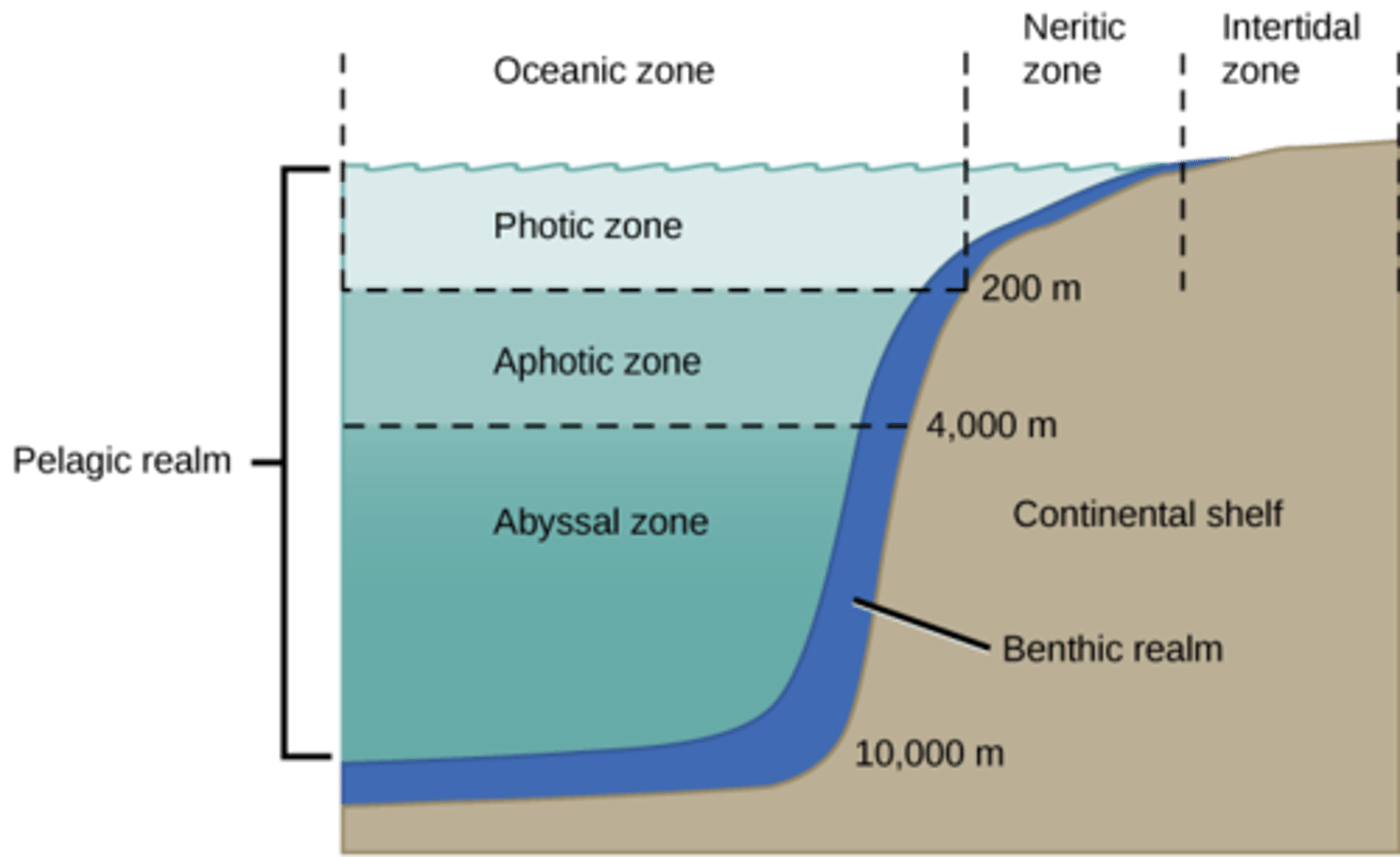
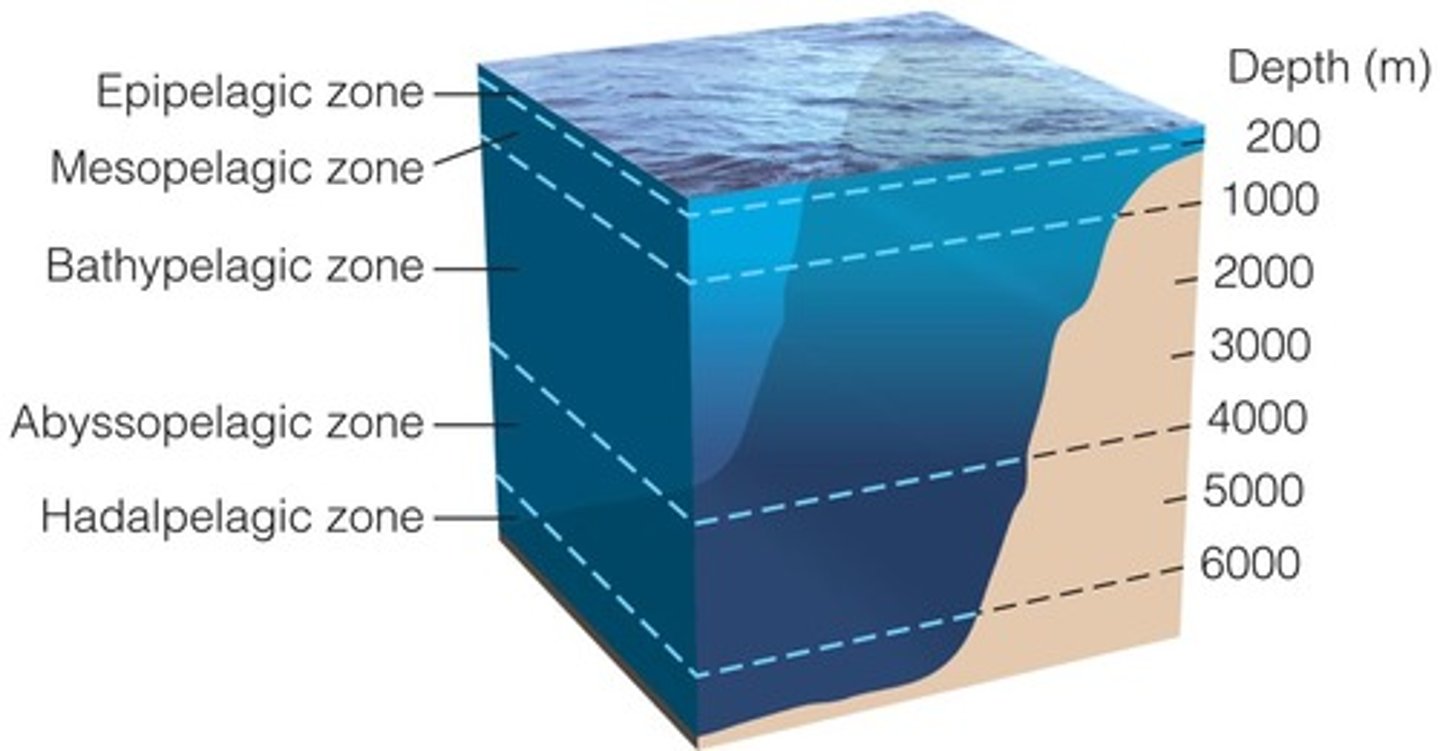
What are the layers of the pelagic zone from top to bottom?
1. epipelagic
2. mesopelagic
3. bathypelagic
4. abyssopelagic
5. hadopelagic
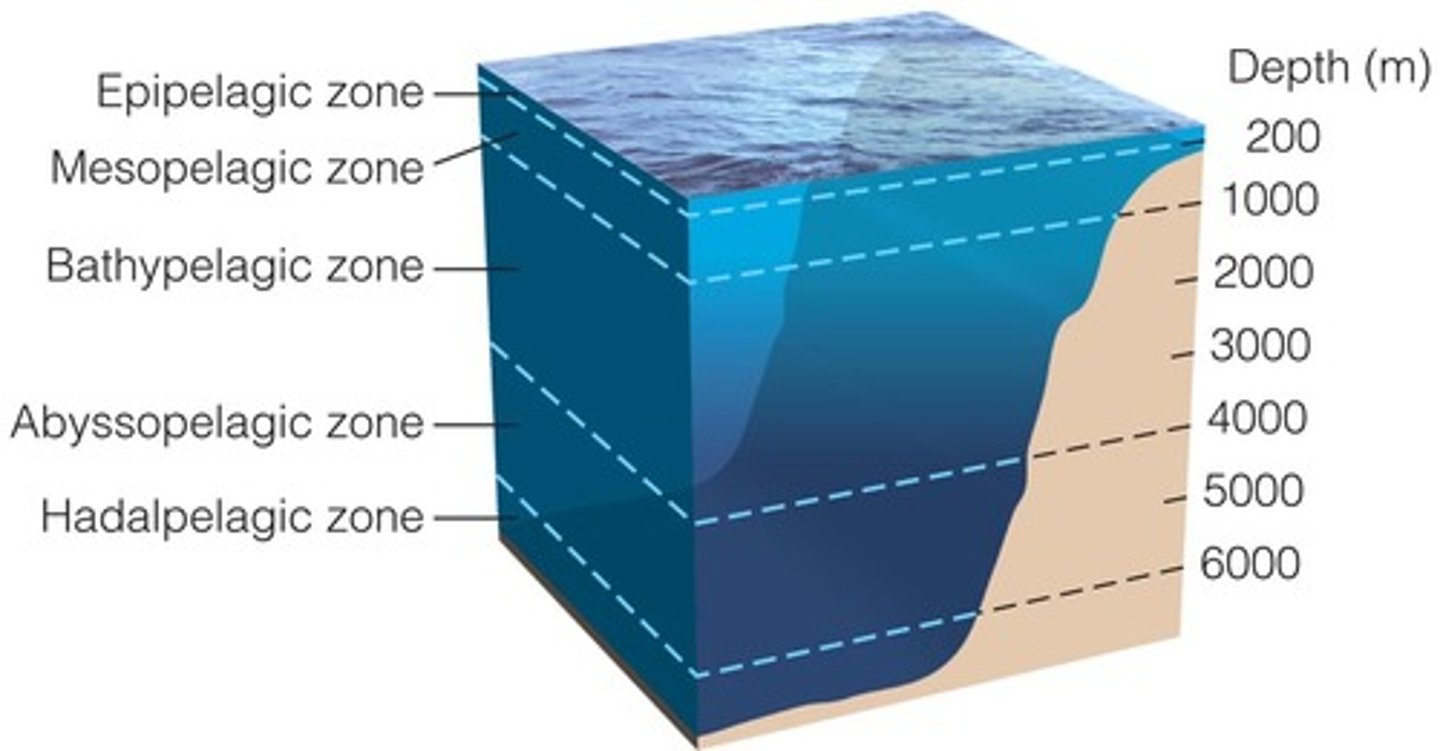
Which layer of the pelagic zone is the surface layer of water and the only photic zone?
epipelagic
(Note: nearly all
primary production
of the ocean occurs here)
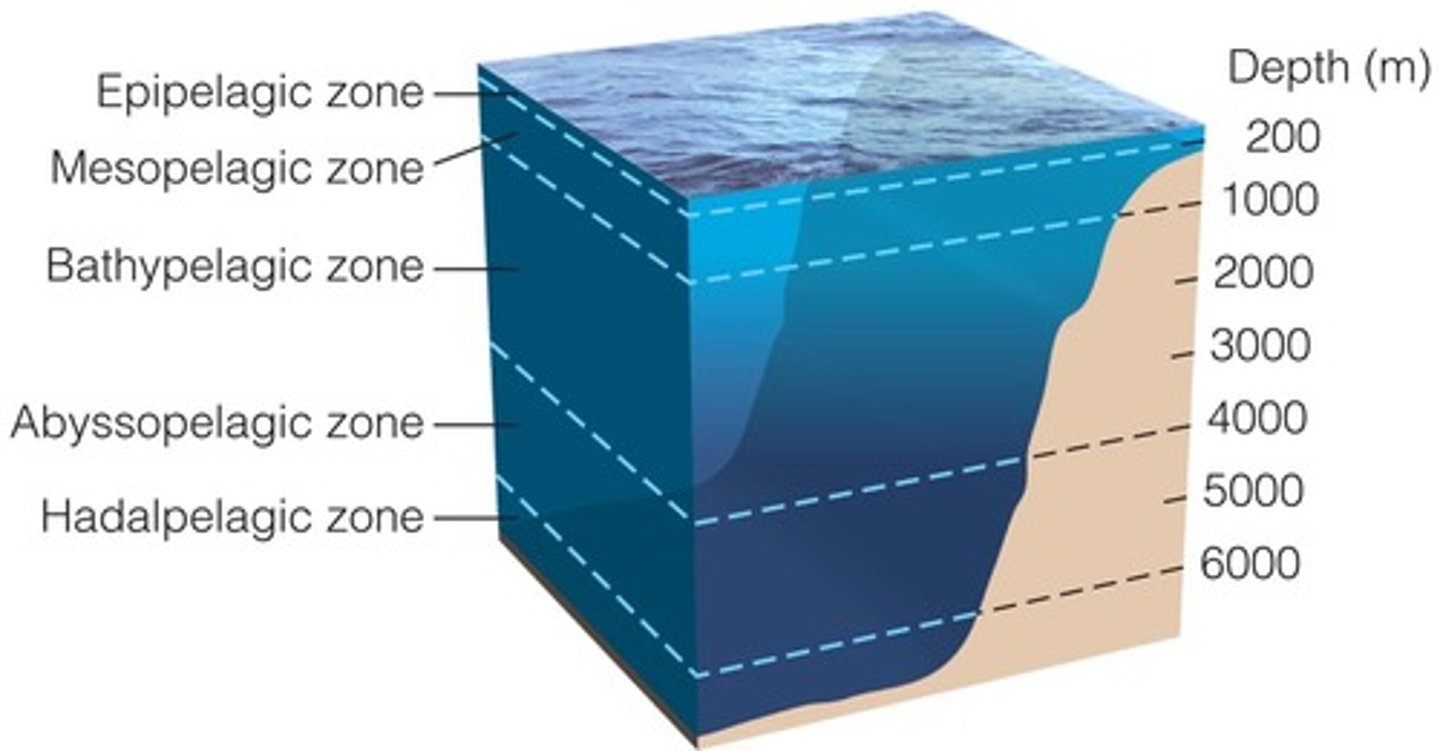
Which layer of the pelagic zone is an aphotic zone with minimal oxygen?
mesoplagic
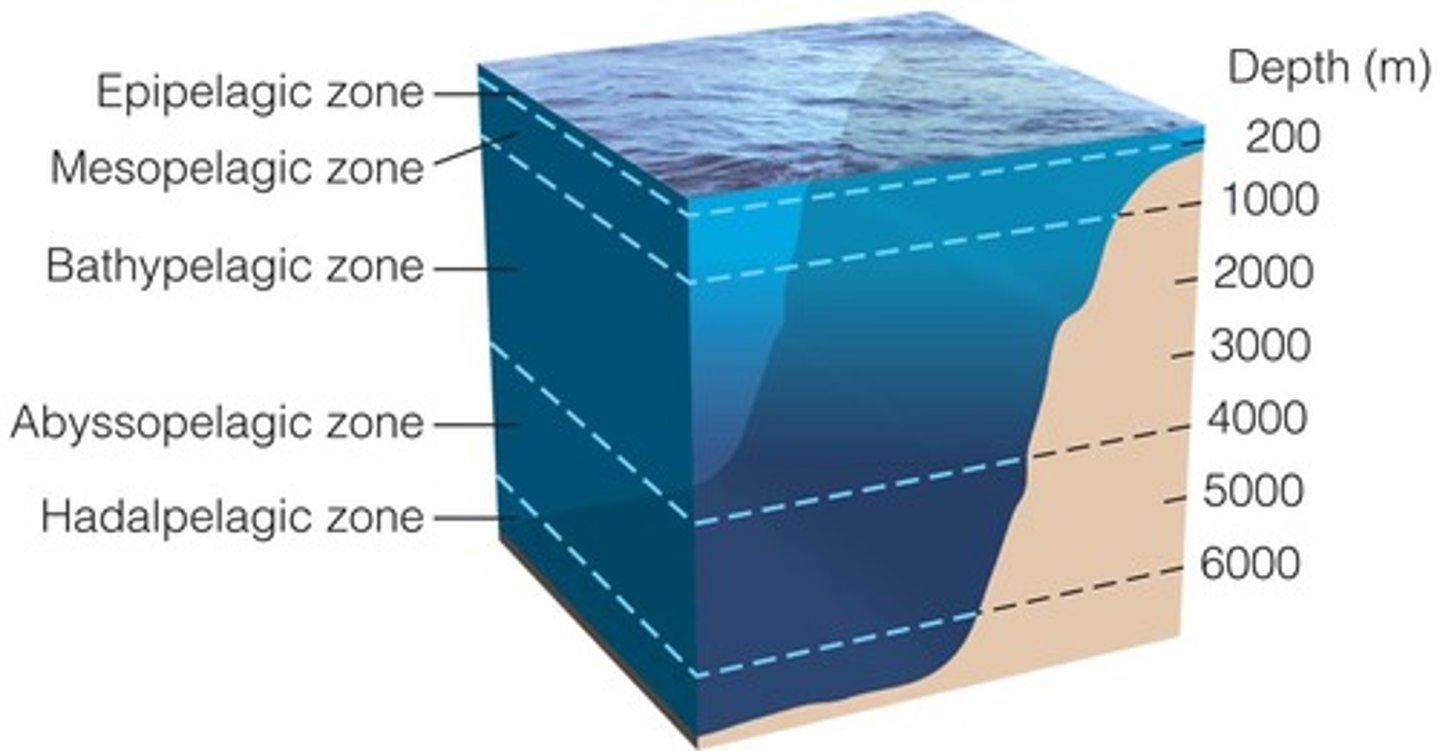
Which layer of the pelagic zone is an aphotic, pitch-black zone with no plant life where most organisms consume detritus?
bathypelagic
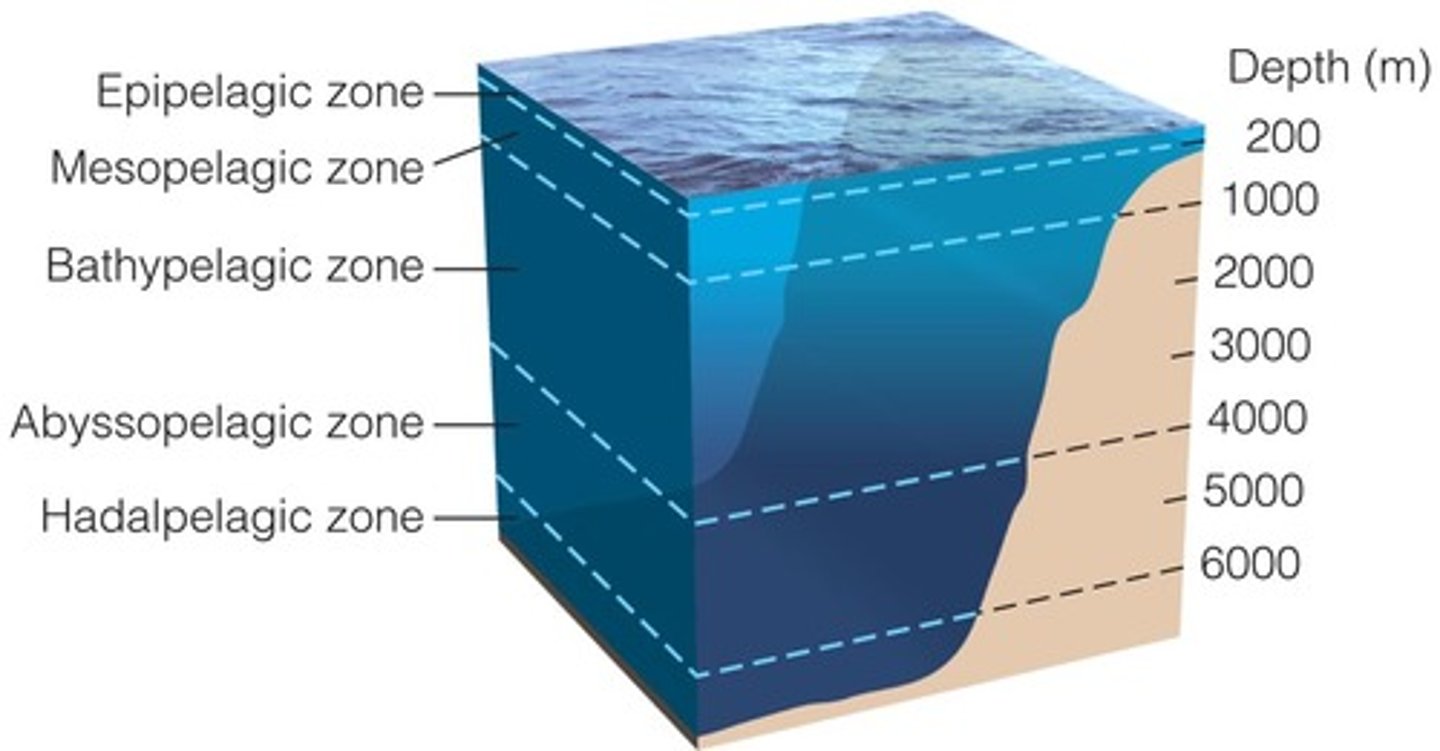
Which layer of the pelagic zone is an aphotic, cold, high-pressure zone where most species have no eyes from lack of light?
abyssopelagic
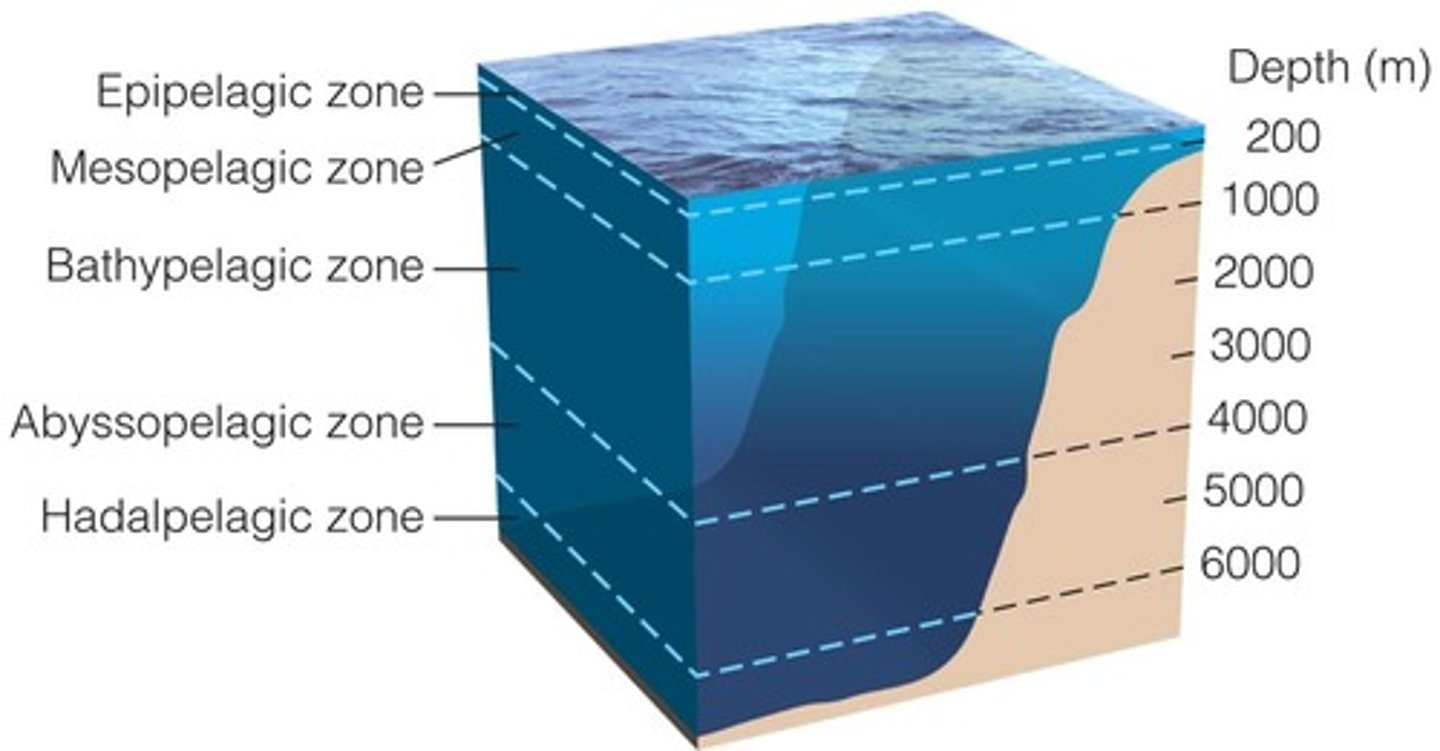
Which layer of the pelagic zone is aphotic and has life that almost only exists in hydrothermal vents?
hadopelagic
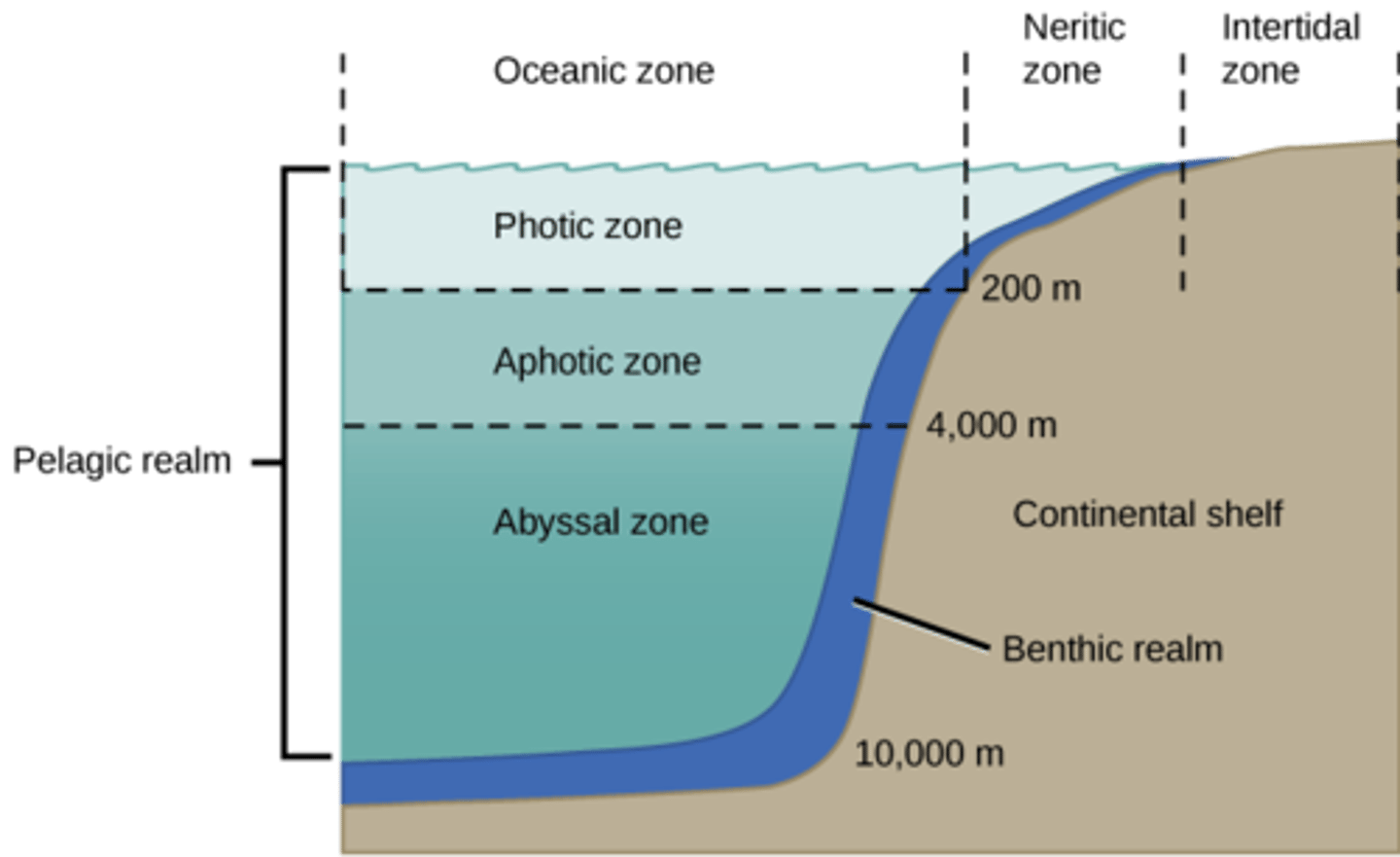
Is the benthic zone aphotic or photic?
the benthic zone
can be aphotic or
photic depending
on the depth
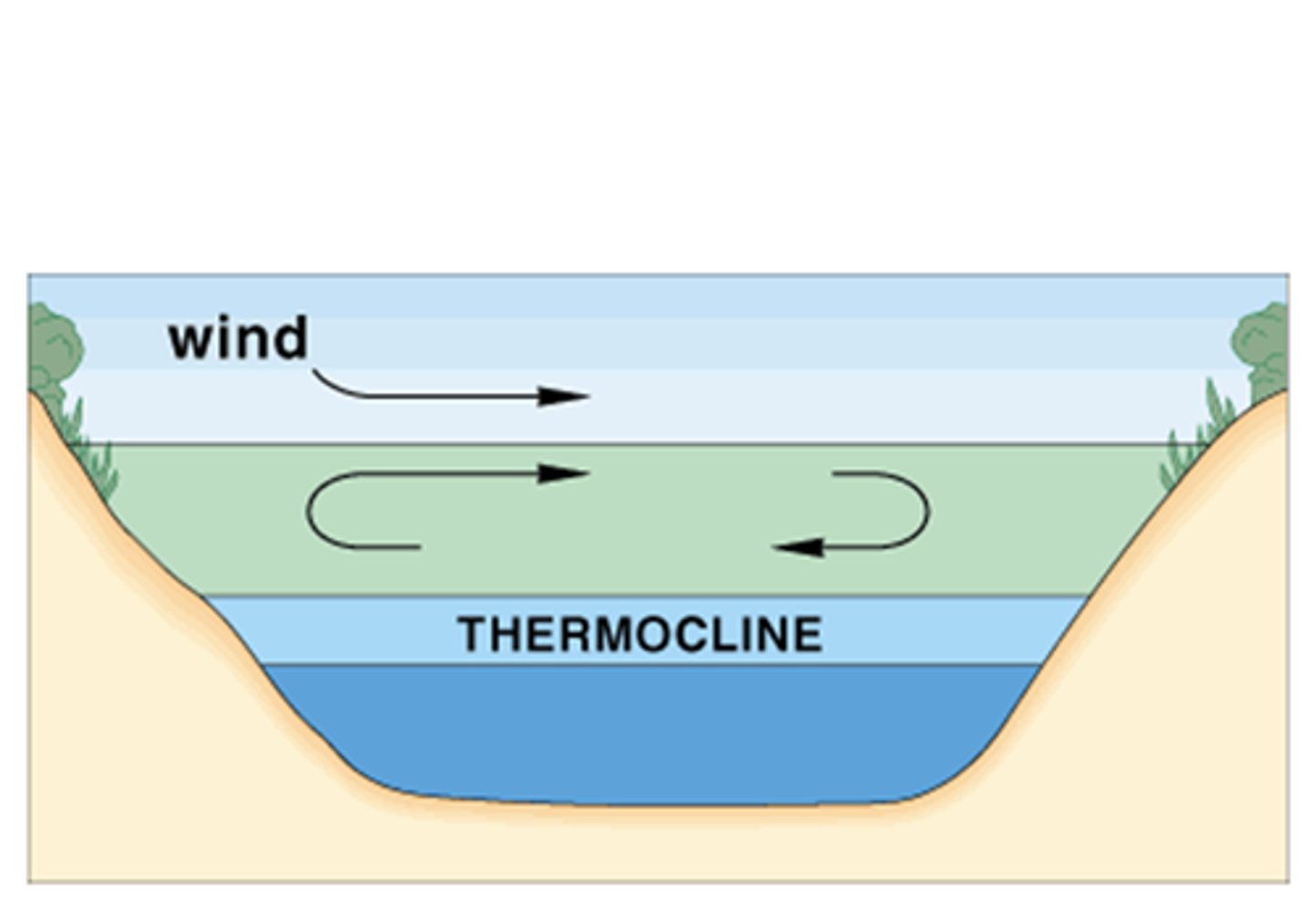
In winter and summer, by what metric are lakes stratified?
temperature
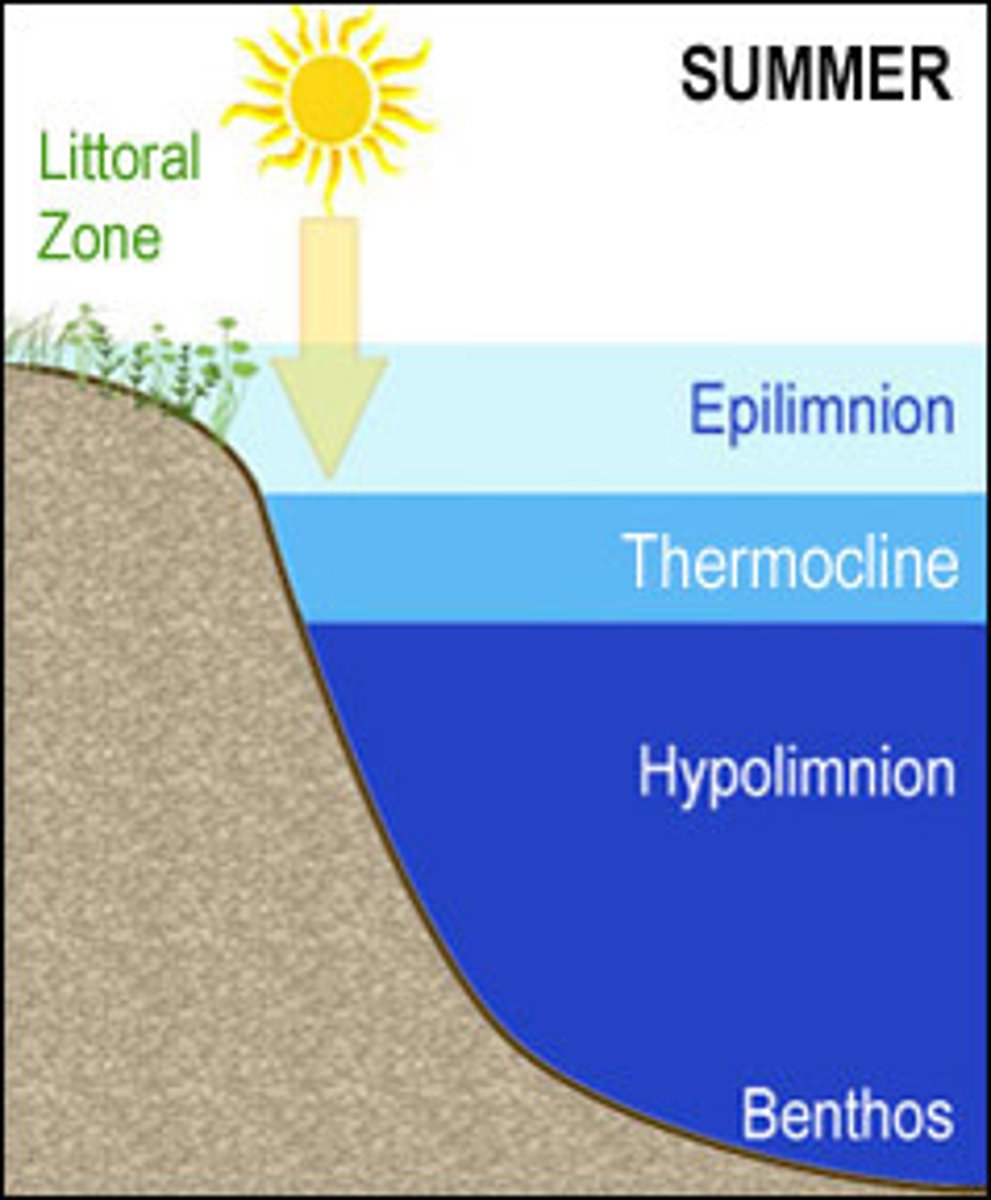
How does oxygen concentration change in lakes?
oxygen concentration decreases with depth
Where is the highest concentration of nutrients in lakes?
at the bottom layer
What process involves cooling, sinking water pushing up a nutrient-rich lower layer in lakes?
turnover