Chem Unit 0
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/105
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
106 Terms
1
New cards
H3P
Hydrogen phosphide
2
New cards
What is the percent nitrogen (by mass) in ammonium carbonate, (NH4)2CO3?
29\.16%
3
New cards
Which one of the following elements forms ions with two different valences?
iron(+3, +2)
4
New cards
Calculate Avg. Atomic Mass
1. Take its percent abundance and turn it into a decimal
2. Then take the percent that is now a decimal and multiple it with its mass in amu
3. Repeat the same steps (1 and 2) for the other isotope
4. Then add both isotopes together
Ex: .40 x 24.02 amu= 9.608
.60 x 26.10 amu= 15.66
15\.66 amu + 9.608 amu= 25.268 amu
5
New cards
What is the formula of the ionic compound formed between Mg and Br?
MgBr2
6
New cards
Matter
anything that takes up space and has mass
7
New cards
Matter is classified as
solid, liquid, gas
8
New cards
Matter Composition
elements, componds, mixtures
9
New cards
Pure Substance
made up of only one component
10
New cards
Examples of elements
Carbon (C), Helium (He), Oxygen (O), Nickel(Ni)
11
New cards
Examples of compounds
sodium chloride, glucose, calcium carbonate, water
12
New cards
Mixture
Made up of two or more components
13
New cards
Hetergeneous
Can see the parts, dissimlar (oil and water); its compostion can be either different or similar to each other
14
New cards
Homogeneous
All portion are uniform, similar in nature; same composition and properties( salt water)
15
New cards
Decanting
Pouring off liquid from a precipitate- shows insolubility
16
New cards
Distillation
Seperates homogeneous mixtures of a liquid and solid- are poured through filter paper and funnel
17
New cards
Gravity Filtration
A hetergeneous mixture of a liquid and solid are poured through filter paper and funnel
18
New cards
Vacuum filtration
A vacuum is set up with a sink appratus to aid the filtration process
19
New cards
Physical property(only state and apperance change)
Only apperance and state change, still the same compostion and substance. Ex: Boiling and cutting, color of a substance, melting and density, alcohol evaporating
20
New cards
Chemical property(alters the composition of matter)
Alters the composition of the matter. Ex: New substance, rusting nails, burning magnesium, bubbles forming on metal when dropped in acid, when white phosporous is exposed to air it will burn spontaneously
21
New cards
Energy
The capacity to do work(applying a force over a given difference)
22
New cards
Kinetic energy
The motion of an object
23
New cards
Potential energy
The position of an object, energy stored by an object
24
New cards
Thermal\=kinetic
The temperature of an object
25
New cards
Law of Conservation of Energy
Energy cannot be created or destroyed
26
New cards
Temp conversion
C\= (F-32)/1.8, K\=C + 273.15
27
New cards
Sig figs rules
1\. Non-zero digits are always significant. 2. Any zeros between two significant digits are significant. 3. A final zero or trailing zeros in the decimal portion ONLY are significant. 73.00( 4 sig figs, everything after a decimal with a digits in front are significant) 7300(2 sig figs), no decimal , so the trailing zeros don't count
28
New cards
Sig Figs Rules for Multiplication and Division
Answer should have fewest sig figs: 2.389 x 2.5= 5.1
The 2.5 has 2 sig figs, so should the answer
The 2.5 has 2 sig figs, so should the answer
29
New cards
Sig Figs Rules for Addition and Subtraction
Round to the number with the least sig figs but round based on its last placement. 2.54, you would round the number to the hundrendth place. Ex: 2.456 x 2.54= 6.39(since 2.54 ends at a hundredth, so will the 6.39)
30
New cards
Precision(refers to reproductivity of a laboratory measurment)
A measure of how close a series of measurements are to one another
31
New cards
Accuracy
How close the measure is to the actual value
Ex: The bulls eyes on the practice test was neither accurate nor precise becasue the measurements were not close to each other and the points were not close to the bulls eye
Ex: The bulls eyes on the practice test was neither accurate nor precise becasue the measurements were not close to each other and the points were not close to the bulls eye
32
New cards
Wafting
smelling a chemical substance
33
New cards
When a pure solid substance was heated, a student obtained another solid and a gas, each of which was a pure substance. From this information which of the following statements is ALWAYS a correct conclusion?
The orginal solid is not an element, otherwise only one physical change would have occured
34
New cards
The prefix mili stands for(0.001)
10^-3
35
New cards
Chromatography
Seperates the components in a mixture
36
New cards
Percent Error Formula
Estimated number- Actual number/Actual number x 100
37
New cards
Law of Conservation of mass
Matter cannot be created nor destroyed
38
New cards
Law of definite Proportions
All samples of a compound have the same proportions of the component elements
39
New cards
Law of Multiple Proportions
When two elements form two different coumpounds, the ratio of their masses can be express as small whole numbers
40
New cards
Dalton Atomic theory
**1.** Each element is composed of tiny, indestructible particles called atoms.
**2.** All atoms of a given element have the same mass and other properties that distinguish them from the atoms of other elements.
**3.** Atoms combine in simple, whole-number ratios to form compounds.
**4.** Atoms of one element cannot change into atoms of another element. In a chemical reaction, atoms only change the way that they are bound together with other atoms.
**2.** All atoms of a given element have the same mass and other properties that distinguish them from the atoms of other elements.
**3.** Atoms combine in simple, whole-number ratios to form compounds.
**4.** Atoms of one element cannot change into atoms of another element. In a chemical reaction, atoms only change the way that they are bound together with other atoms.
41
New cards
Structure of Atom
Protons and neutrons are inside the nucleus, electrons are outside the nucleus in electron clouds, relative mass of protons and neutrons is , relative mass of electron is 0
42
New cards
Isotopes
atoms with the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons
43
New cards
Natural Abundance
the relative amount of each isotope in a given sample of an element
44
New cards
Average atomic mass
a weighted average of an elements mass based on the masses and abundance of each isotope
45
New cards
Mass Spectroscopy
an analytical technique that measures the natural abundance of isotopes
46
New cards
Cations and Anions
Cations lose electrons(positive charge), Anions gain electrons(negative charge)
47
New cards
Which of the following is a metalloid( the stair case on the periodic table)
As, Si, B, Te, At
48
New cards
Which of the following is a transition metal
Ni, Co, Cu, Zn, Zr
49
New cards
Which of the following is an alkali metal( the first column on the periodic table, except H)
K, Na, Li, Rb, Cs
50
New cards
Which of the following is an lanthanide( the 6th row)
Eu, Au, Hg, Ta, La
51
New cards
Ionic Bonds
Transfer metals
52
New cards
Covalent Bonds
Share metals
53
New cards
Diatomic Molecules(I Have No Bright Or Clever Friends)
\
H2, N2, O2, F2, Cl2, Br2, and I2.
BrINClHOF
HONClBrIF
I Have No Bright Or Clever Friends
H2, N2, O2, F2, Cl2, Br2, and I2.
BrINClHOF
HONClBrIF
I Have No Bright Or Clever Friends
54
New cards
Ate vs Ite( ate is bigger, it is smaller)
If there are two ions in the series,
the one with more oxygen atoms has the ending *-ate*, and
the one with fewer has the ending *-ite*.
the one with more oxygen atoms has the ending *-ate*, and
the one with fewer has the ending *-ite*.
55
New cards
Oxyanions(per means more than, hypo means less than)
If there are more than two ions in the series then the prefixes *hypo-*, meaning *less than*, and *per-*, meaning *more than*, are used.
56
New cards
Organic compounds
Contain, hydrogen, carbon and sometimes oxygen or nitrogen
57
New cards
Burning organic compounds
For mass analysis, can be used to determine the original emperical formula
58
New cards
Naming compounds
Ionic Compounds: just give the names of the two ions involved
* Transition Metals use Roman Numerals to show the charge
* -ide ending just means the element
* Molecular (Covalent): use the number prefixes
* Acids: H and an anion
* Anion ending determines acid name
* Hydrates: Ionic compound name followed by prefix showing how many water molecules
* Transition Metals use Roman Numerals to show the charge
* -ide ending just means the element
* Molecular (Covalent): use the number prefixes
* Acids: H and an anion
* Anion ending determines acid name
* Hydrates: Ionic compound name followed by prefix showing how many water molecules
59
New cards
Certain properties are characterstic of meals. Which property means that you can pound the substance into a foil
Malleability
60
New cards
Which element has the highest melting point
W
61
New cards
Cathode rays start at the
negative electrode
62
New cards
cathonde rays are
positive ions
63
New cards
Which wil be delfected the least in a mass spectrometer
\+1, 4 amu( large mass small charge)
64
New cards
In milikian oil drop tpe experiment, the charge on four oil drops was found to be(divide by smallest factor)
1- 3.33 coulombs
2\.67- 8.88
2- 6.66
3\.33- 11.10
2\.67- 8.88
2- 6.66
3\.33- 11.10
65
New cards
What is the charge on the elctron according to this experiment
1\.11 coulomb
3\.33 divided by 3= 1.11
3\.33 divided by 3= 1.11
66
New cards
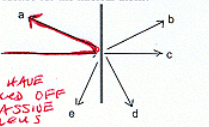
What scattered particle the best evidence for nuclear attom(balance)
a
67
New cards
Which of the following is an isotope of the element with 20 protons and 22 neutrons-42
Calcium 40 because 42-20= 22, and 18 neutrons
68
New cards

Match the answers to the key
Gamma is a high energy form of light
Beta is a high speed electron, associated with neutron changing into proton
alpha used by ernest rutherford as “probe”
Gamma is the most penetratng of the “bequerel rays”
Beta is a high speed electron, associated with neutron changing into proton
alpha used by ernest rutherford as “probe”
Gamma is the most penetratng of the “bequerel rays”

69
New cards

Use the following key to math individuals
John Dalton’s atom has been called “billiard ball” model
J.J Thomas has studied matter in cathode ray tubes, and has added to the atomic theory the idea that atomas had positive and negative parts
Democritus has a philosophical idea included the term “atomos”
J.J Thomas has studied matter in cathode ray tubes, and has added to the atomic theory the idea that atomas had positive and negative parts
Democritus has a philosophical idea included the term “atomos”

70
New cards
Which elements did mendeleev leave spaces for
Ga, Ge, Sc
71
New cards
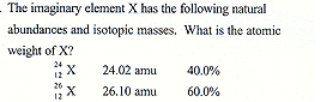
The imaginary elemnent X has the following natural abundances and isotopic masses. What is the atomic weight of X
25\.3 amu
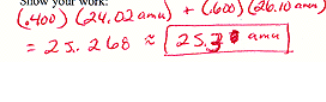
72
New cards

Calculate the % abundances of two isotopes of cooper
62\.9298x + 64.9278(1-x)= 64.546amu
0\.3818 = 1.998x
19\.11% cu-63
80\.89% cu-65
0\.3818 = 1.998x
19\.11% cu-63
80\.89% cu-65

73
New cards
What is the formula of the ionic compound formed between Ca and P?
Ca3P2
74
New cards
What is the name of the SO32– ion?
sulfite
75
New cards
What is the correct formula and charge for the chromate ion?
CrO42
76
New cards
The correct name for CCl4 is
carbon tetrachloride
77
New cards
The correct formula for hydrogen telluride is
H2Te
78
New cards
The correct name for S2Cl2 is
disulfur dichloride
79
New cards
The correct name for NO2 is
nitrogen dioxide
80
New cards
The molar mass of (NH4)2S is closest to
68 g/mol
81
New cards
How many atoms are in 12 molecules of glucose, C6H12O6?
288
82
New cards
Calculate the number of atoms in 4.0 x 10-5 g of aluminum.
8\.9 x 10^17
83
New cards
What is the mass of **one molecule** of octane, C8H18?
1\.89 x 10-22 g
84
New cards
A compound consists of the following elements by weight percent:
carbon - 40.0%
oxygen - 53.3%
hydrogen - 6.7%
The ratio of carbon : oxygen : hydrogen in the empirical formula is
carbon - 40.0%
oxygen - 53.3%
hydrogen - 6.7%
The ratio of carbon : oxygen : hydrogen in the empirical formula is
1:1:2
85
New cards
An organic compound which has the empirical formula CHO has a molar mass of 232. Its molecular formula is:
C8H8O8
86
New cards
Of the following, the only empirical formula is
HNF2
87
New cards
When CaSO4·y H2O is heated, all of the water is driven off. If 34.0 g of CaSO4 \[molar mass = 136\] is formed from 43.0 g of CaSO4·y H2O, what is the value of y?
2
88
New cards
A metal sample weighing 30.9232 grams was added to a graduated cylinder containing 23.26mL of water. The volume of water plus the sample was 24.85mL. Which setup will result in the densit of this metal.
30\.9232/24.85-23.26
89
New cards
Mercury has a density of 13.58g/mol. What is the volume of mercury when its poured out to obtain 0.5000 g of mercury
0\.03682
90
New cards
Kelvin to celsius to fahrenheit
K= C +273.15
F= (c-32)/1.8
F= (c-32)/1.8
91
New cards
Chromate
CrO4^2-
92
New cards
Chromite
FeCr2O4
93
New cards
Sulfate
SO4^2-
94
New cards
Sulfite
SO3^2-
95
New cards
Nitrite
NO2⁻
96
New cards
Nitrate
No3^-
97
New cards
What is the atomic number of potassium
19
98
New cards
how many electrongs are in the potasium nucleus
0
99
New cards
Signs of Chemical Change
1. Permanent color change
2. Gas release(bubbles/odo)
3. Precipitate produced
4. Light given off
5. Heat absorbed or released
100
New cards
Pb3N2
Lead(II) nitride