Acids and Alkalis (KS3)
1/37
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
Define ‘acid’
A substance with a pH of <7 which releases positive hydrogen ions when dissolved (H+). Physical properties include a sour taste.
Define ‘alkali’
A substance with a pH of >7 that releases negatively charged hydroxide ions (OH-); a base that dissolves in water. Physical properties include a soapy/slippery feeling. They can also be referred to as a base or basic substance.
Define ‘base’
A substance that neutralises an acid.
What is the pH range for weak acids?
6-4
What is the pH range for strong acids?
3-0
What is the pH range for weak alkalis?
8-10
What is the pH range for strong alkalis?
11-14
What does pH stand for?
Potential of hydrogen
What is a salt?
A substance that is formed by the neutralisation of an acid using an alkali; it is soluble and often has a crystalline appearance when dried.
What is the word equation for neutralisation?
Acid + Alkali → Salt + Water
What is the neutral pH?
7
What is an example of an indicator?
Litmus/Litmus paper
Define ‘indicator’
A substance which changes colour when exposed to an acid/base, revealing whether it is one of the two.
Define ‘universal indicator’
A substance which changes colour when exposed to an acid/base, revealing the exact pH based off of a chart.
What is saponification?
A fat or oil turned into a soap via alkaline reaction.
What is hydrolysis?
A chemical compound breaking down from a reaction with water or hydrogen-related compounds.
On the pH scale, metal oxides are…
Basic/Alkaline
On the pH scale, non-metal oxides are…
Acidic
What happens when there is too much of either an acid or a base?
The salt formed becomes either slightly acid or alkaline
Why is water produced alongside a salt?
Due to the positive hydrogen ions from the acid and and the negative hydrogen ions from the alkali forming bonds.
Is salt normally neutral?
Yuh huh bro, pH of 7
What are real-life examples of alkalis?
Cleaning products such as soap and drain cleaner. Baking soda can also be used to treat bee venom and they can be found in certain medications to alleviate stomach acid issues.
What are real life examples of acids?
Lemon juice (pH of 2), vinegar; sulphuric acid in labs.
How are salts named?
By combining the first name of the acid and the metal of the alkali
Hydrochloric acid + Sodium hydroxide → Sodium chloride + Water
What is crystallisation? (Salts)
When the liquid is evaporated from the neutralised solution, crystals form as the salt created begins to dry and the water is evaporated away.
What is flavin?
A pigment that can act as a universal indicator.
Where can flavin commonly be found?
Apple skin, red cabbage, poppies, cornflowers, plums, grapes, etc.
What is flavin’s natural colour?
Purple
What is chemical weathering?
The process of chemicals, primarily acidic, causing erosion often by wet deposition.
Why are cleaning products alkaline?
Because the higher pH helps to break down acidic substances/oils/fats/bacteria. When paired with a disinfecting agent, alkalis make excellent and versatile cleaning products.
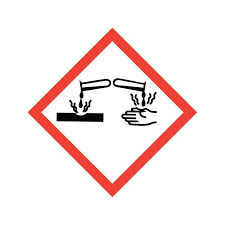
What does this symbol mean?
The substance is corrosive.

What does this symbol mean?
The substance is a minor hazard (irritant, slight toxicity)
What is litmus made from?
Types of lichen (dye).
How does corrosion work?
By oxidising the surface of an object (MAINLY METALS). Susceptibility to corrosion varies depending on how ionised (able to bond with oppositely charged ions) a substance is. For example, gold is resistant to corrosion due to its stable electron configuration.
Which pollutants are most responsible for acidic rain?
Carbon dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and sulphur dioxide.
What happens when pollutants infect water supplies?
The rain becomes acidic.
Which element is toxic to fish gills and other underwater creatures on occasion?
Aluminium
What crucial nutrients are released from the soil when the pH lowers, making the soil infertile?
Aluminium, calcium, magnesium