VCE Chemistry Unit 1 (copy)
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
83 Terms
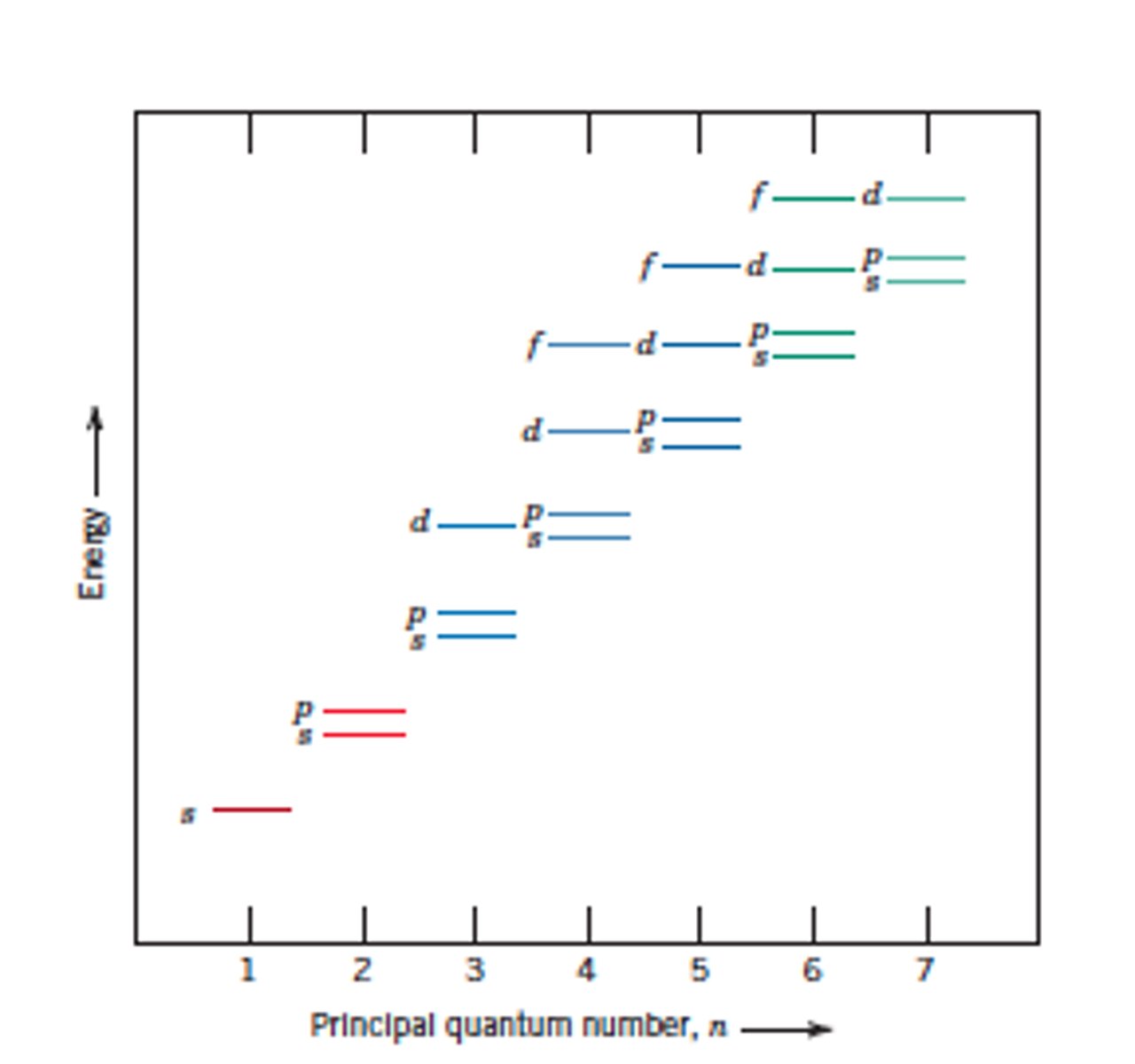
s sub-shell
1 orbital and max 2 electrons
p sub-shell
3 orbitals and max 6 electrons
d sub-shell
5 orbitals and max 10 electrons
f sub-shell
7 orbitals and max 14 electrons
copper and chromium exception
want either 5 or 10 electrons in 3d sub-shell so take one from 4s sub-shell
sub-shell arrangement
metallic bonding
bonding between two metals
properties of metallic bonding
- conduct electricity
- shiny (lustrous)
- high mp
- generally dense
- reflect light
- malleable and ductile
high boiling temperature (metallic)
due to strong electrostatic forces between cations and delocalised electrons holding lattice together
conduct electricity (metallic)
electrons move towards a positive electrode in a circuit
malleable and ductile (metallic)
when forces cause metal ions to move past each other and layers of ions are still held together by electrons
density (metallic)
because lattice of cations is so tightly packed together
reflect light (metallic)
light bounces off surface electrons to give a shiny appearance
metallic bonding limitations
- heavy metal mercury (liquid at room temp.)
- differences in electrical conductivity
- magnetic properties
lattice of cations
3D crystal lattice filled with protons and delocalised negative electrons that is held together by electrostatic forces
alloys
compounds of metals that are stronger, corrosion resistant and made of two or more metals with metals of similar sizes and lattice layers harder to move
metal reactivity
group 1 more reactive than group 2 and as elements go down groups reactivity increases because valence electrons are further away. Metals are more reactive than water
modifying metals
- work hardening
- annealing
- quenching
- tempering
- coating
work hardening
pushing metal crystals together as small crystals = less movement and harder material
annealing
heating metals and slowly cooling as it makes larger crystals as softer = more ductile
quenching
heating metals but rapidly cooling as it makes smaller crystals and harder but more brittle
tempering
heating to a lower temperature and slowly cooling to make medium crystals, so hard but less brittle
coating
coating metals to prevent corrosion
nanomaterials
- nanoparticles
- nanorods
- nanowires
nanomaterial applications
- wound dressings
- medicine
- sunscreen
- electronics
- superconductors
ionic bonding
bonding metal and non-metal together with high bp and mp, solid at room temp., hard and brittle, only conduct in liquid state, strong intramolecular forces
masses of particles
all masses are relative (in chemistry) with the standard reference point for all other atoms being carbon-12
isotope
same element but with a different mass (different nº of neutrons
relative isotopic mass
the mass of an atom of the isotope relative to carbon-12 mass (symbol = IR) with the value coming from a mass spectrometer
mass spectrometer
a machine that can measure the number of isotopes in a given sample and the abundance of them
relative isotopic abundance
the abundance of certain isotopes given in a percentage
relative atomic mass
the average mass of an element as most elements have many isotopes (symbol Ar)
Ar (relative atomic mass)
(relative isotopic mass x abundance%)+(..)+(..)÷100
relative molecular mass
mass of a molecule relative to carbon-12 but not referring to one element. Is equal to the sum of all Ar of every atom (symbol Mr)
relative formula mass
same as Mr except for the compounds that aren't non-metals (symbol Fr)
mol
a unit used by chemists to count atoms, ions/molecules (symbol N)
avogardos number
1 mol of any substance contains 6.02x10^23 particles (symbol Na)
n
mol (amount of substance)
Na
avogardos number
N
actual number of particles
molar mass
the mass in grams of one mole of a substance
compound
made up of 2 or more different atoms
percentage compound
tells you the percentage of different elements in a compound
empirical formula
the simplest whole number ratio of each atom in a molecule
molecular formula
gives the actual amount of atoms in a compound/molecule and can be the same or similar to empirical
non-metal properties
- low mp and bp
- often not solid
- soft when solid
- no electrical conductivity
intramolecular bond
bonding within a molecule which is strong
intermolecular bond
bonding between molecules which is weak
covalent bonding
sharing electrons and not transferring
lone pairs
the valence electrons not involved in bonding
molecular compound
molecular bond between different types of atoms
polyatomic molecule
more than two atoms in a molecule
shape of molecules
determine physical properties and is determined by VSEPR (valence shell electron pair repulsion)
VSEPR
the lone pairs repel each other and arrange themselves as far away from each other as possible which determines the shape and takes bonds and lone pairs into consideration
tetrahedral
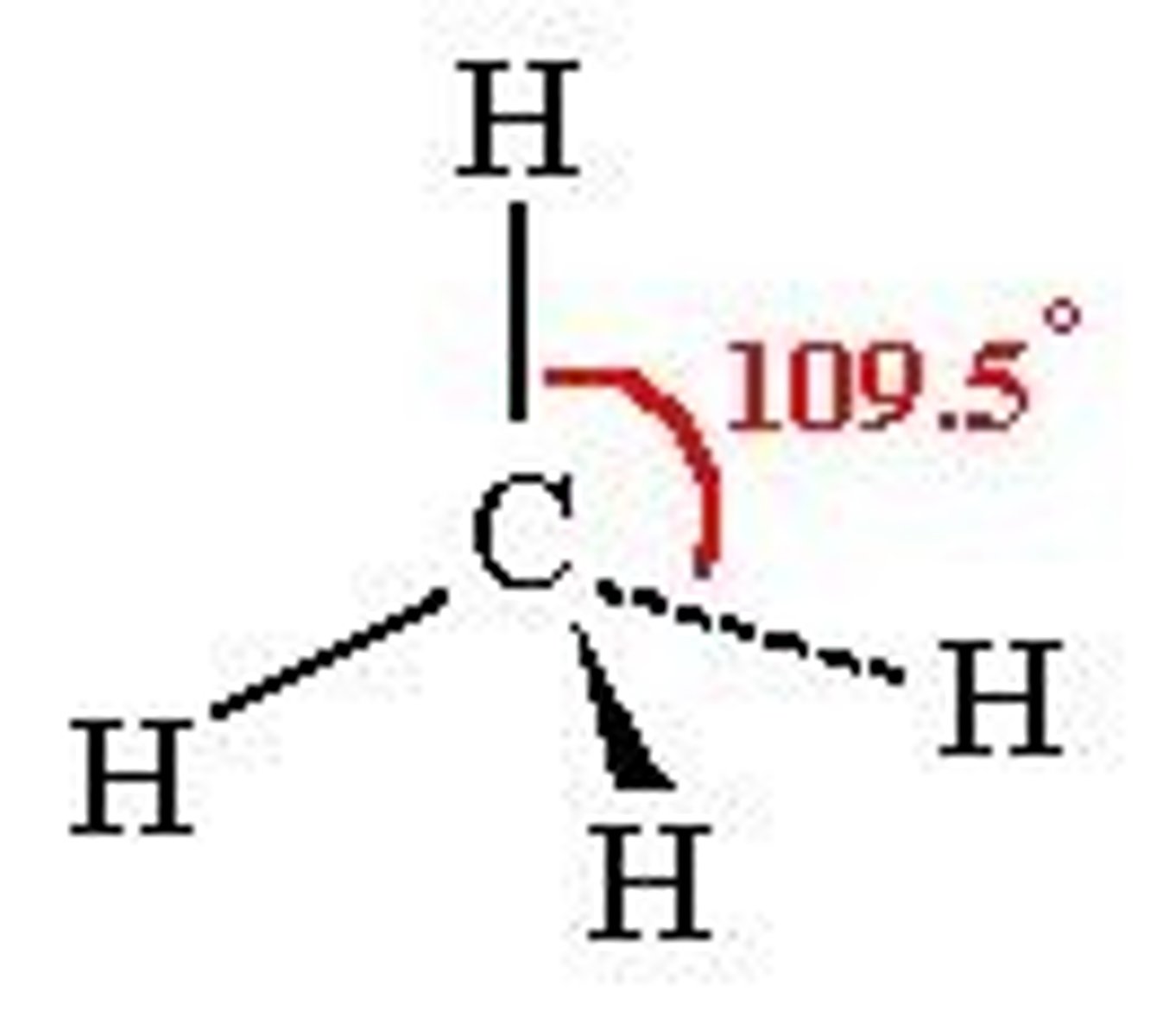
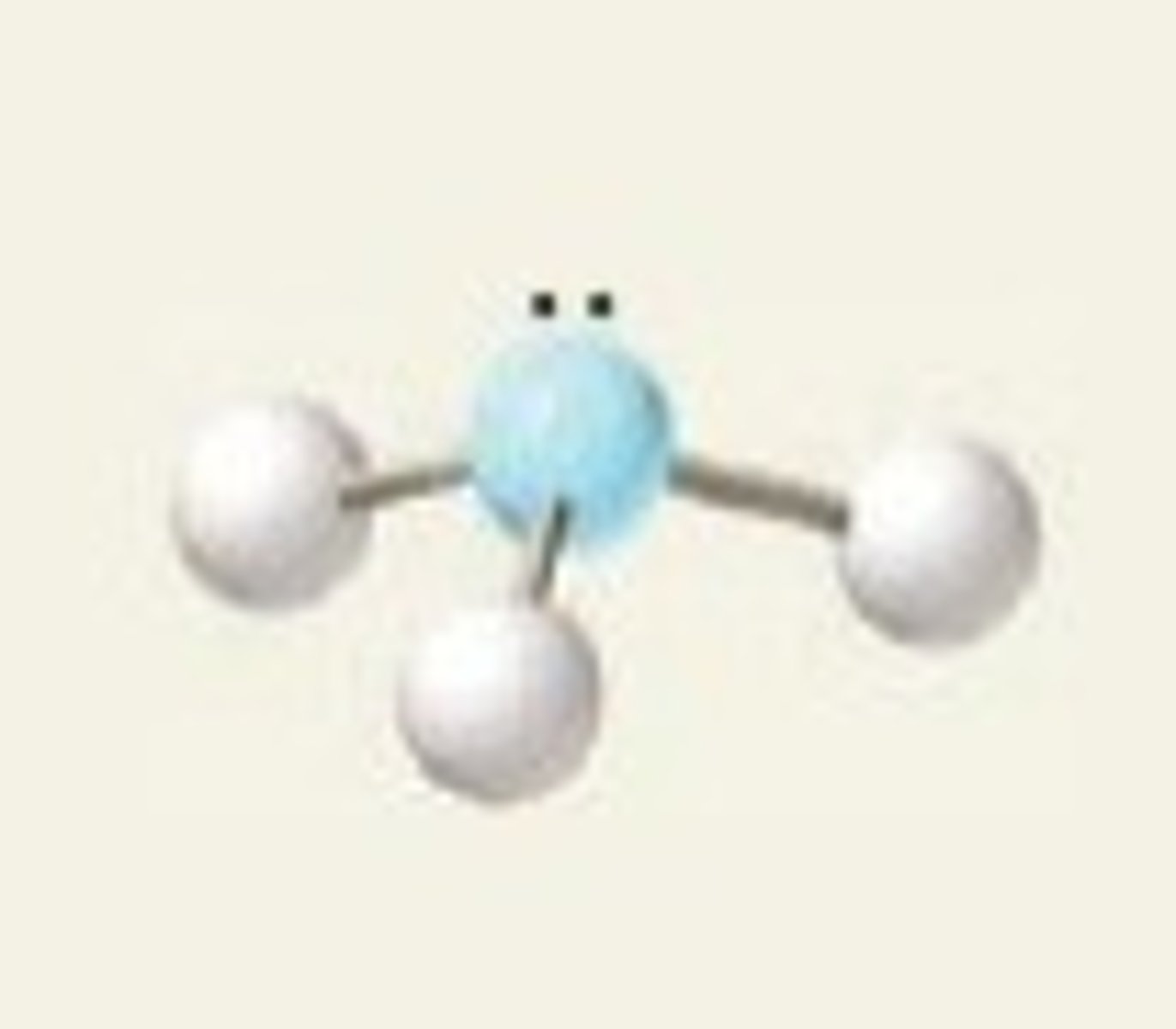
pyramidal

v-shaped or bent
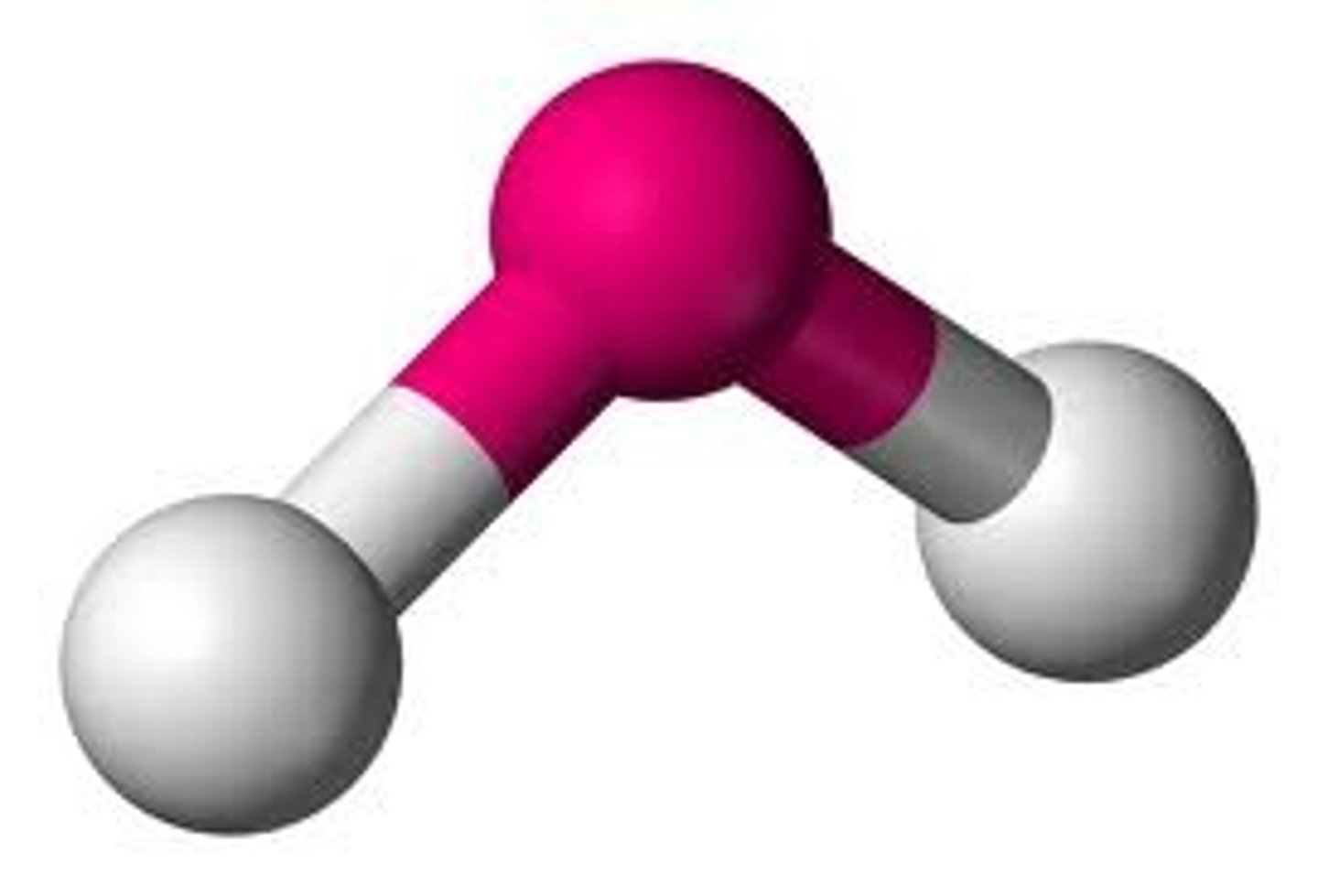
intermolecular forces
size, shape and polarity determine types of forces
- dipole-dipole
- hydrogen bonding
- dispersion forces
dipole-dipole forces
only in polar molecules and relatively weak since particle charges are small. More polar = stronger bonds due to the difference in E.N. and higher mp and bp
hydrogen bonding
type of dipole-dipole that occurs only between H and O, F or N. Is stronger than dipole-dipole but weaker than others with high mp + bp
dispersion forces
the only type of non-polar bondings but present in polar which is caused by temporary dipoles due to the random movement of electrons
organic chemistry
all non-metal chemistry
hydrocarbon
compound made of hydrogen and carbon
alkenes
has at least 1 double bond and doesn't dissolve in water, is non-polar and unsaturated. Stem name + 'ene'
addition reactions
part or all of the reactant becomes added to the alkene breaking the double bond and combusting
alkynes
has at least 1 triple bond and is unsaturated and structural isomers exist for 3C or above which increase/decrease mp + bp. Stem name + 'yne'
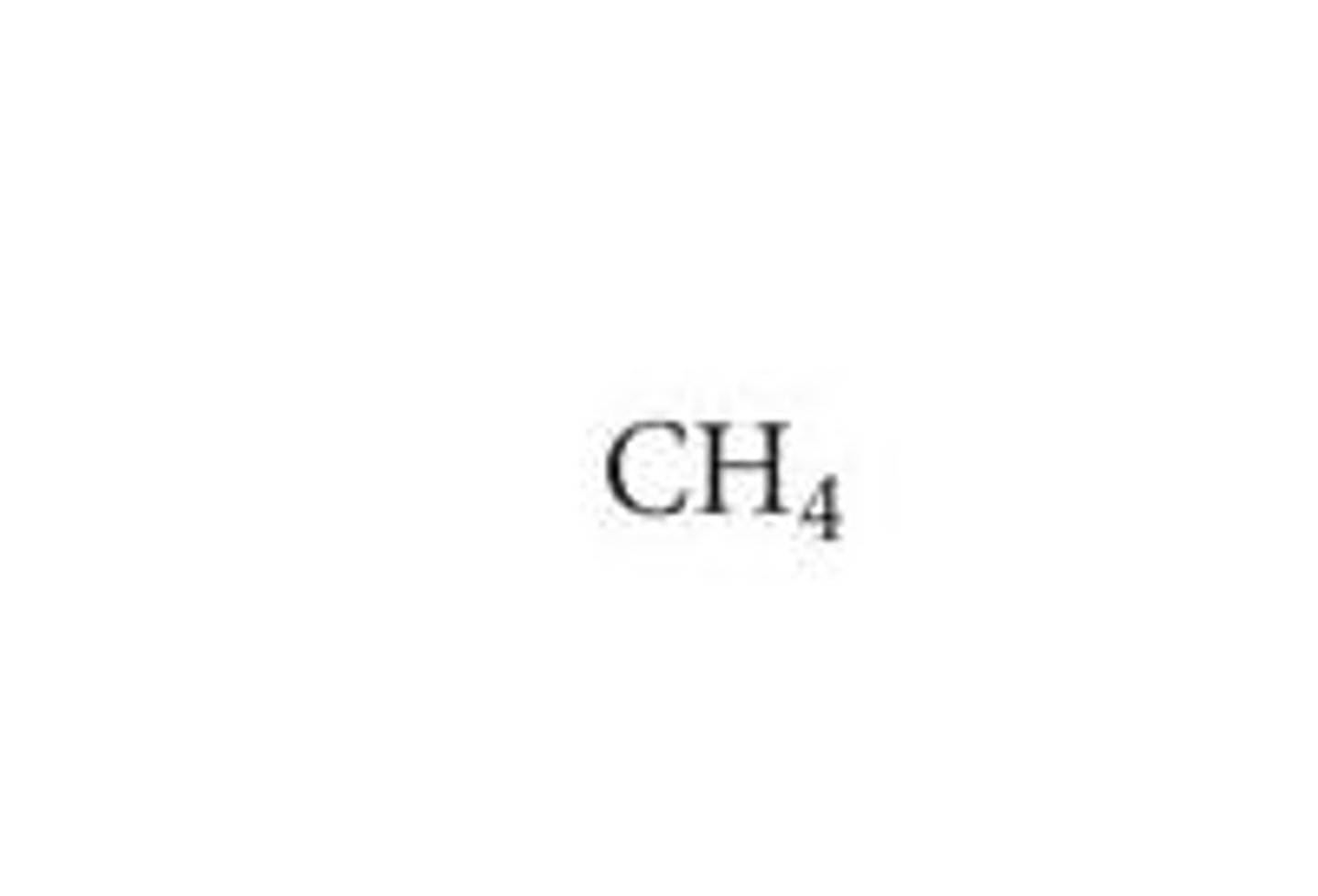
alkane
only single bonds which in non-polar, doesn't dissolve, relatively unreactive and has weak dispersion forces. Stem name + 'ane'
meth
1 carbon
eth
2 carbon
prop
3 carbon
but
4 carbon
pent
5 carbon
hex
6 carbon
hept
7 carbon
oct
8 carbon
non
9 carbon
dec
10 carbon
molecular formula
structural formula
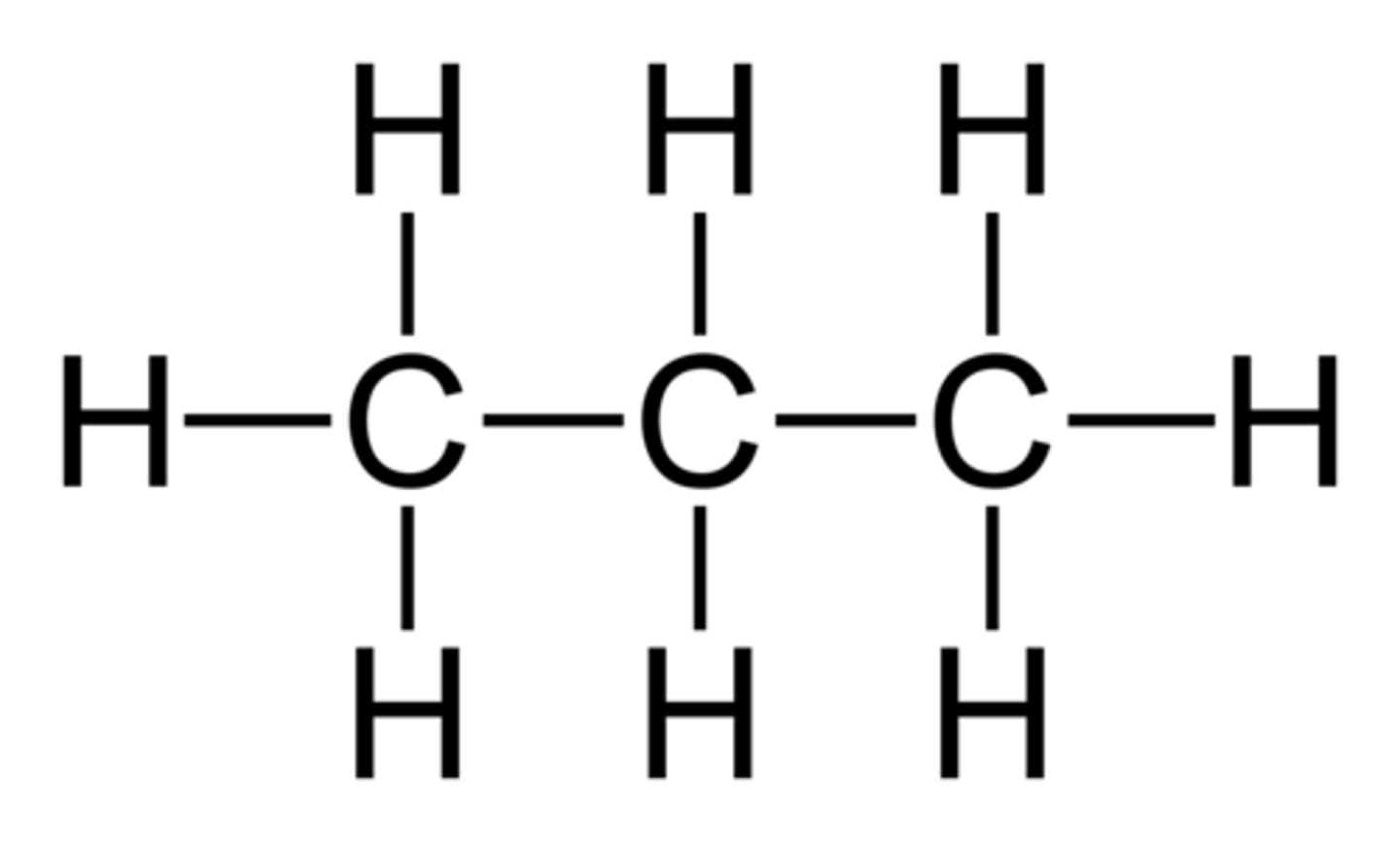
structural isomers
the same formula but a different structure
alcohols
when OH bonds to a carbon chain, hydrogen bonding can occur and mp + bp are higher. Stem name + 'ol'
carboxylic acids
carboxyl group with OOH added to a carbon chain which is more polar like an organic acid and can only be added at the end. Stem name + 'anonic acid'
esters
formed by a reaction between alcohol and carboxylic acid in the presence of sulfuric acid (catalyst) which forms artificial flavours and colours with condensation as a byproduct