AQA GCSE Geography - Paper 2
1/67
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Paper 2 of AQA Geog - resources, economic world, urban issues. (ADD FLASHCARDS FOR NIGERIA CASS STUDY - SECTION B)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
What is a resource?
A stock or supply of something that has a value or purpose.
Define the term malnutrition
A state of poor nutrition due to lacking minerals & vitamins.
What are the three most important resources?
food, water, energy
What is water scarcity?
When a region lacks sufficient water resources to meet its demand
Describe the two main types of water scarcity
Physical water scarcity = Lack of water due to climate, landscape & environment
Economic water scarcity = When a region cannot afford to extract water (it may be deep underground or expensive)
What are food miles?
the distance food travels from where its produced to where its consumed
What is a carbon footprint?
Amount of CO2 and other greenhouse gases emitted over the full life cycle of a product, service or event.
List some positive & negative impacts of importing food in the UK
PROS:
Wider selection of foods- don’t need to eat seasonally)
Cheaper costs → lower labour & raw materials
More land available → build housing & other facilities
CONS:
Increased carbon footprint (links to global warming)
Uncertain food quality due to differing food safety regulations
Local farmers may lose their jobs having to compete with an international market
List some positive & negative impacts of exporting food for LICs
PROS:
Money generated goes to economic increasing development
High demands keep people in employment
Creates good political relations between countries
CONS:
Can lead to overcultivation of land, reducing the soil’s fertility
Corrupt governments may misuse money made from exporting
Increasing the country's carbon footprint
Describe & explain 3 ways the UK can reduce food imports
Agribusiness = Large scale, capital-intensive commercial farming. It reduces food miles & ensures fresher, higher quality food
Organic farming = Small scale, holistic farming. It reduces food waste & encourages people to source their food sustainably
Buying locally = food miles under 30 miles. It helps local business flourish, reduces carbon footprint & is more affordable
Why is demand for water increasing in the UK?
Population is increasing
More houses being built
An increase in the use of water-intensive domestic appliances
Define water surplus
When available water supply exceeds demand
Define water deficit
When water supply is not sufficient to meet its demand
Define energy mix
the composition of different energy sources used to supply demand
Why is energy an important resource?
Energy powers computers, transportation, communications, cutting edge medical equipment and much more
Why is the UK energy mix changing? (give at least 3 reasons)
More renewables are being used to reduce CO2 emissions (linked to EU regulations)
Decline in fossil fuel reserves
Many coal mines have closed down
Less fossil fuels are being used to stop being dependent on imported fossil fuels
How can the UK increase renewable energy?
Increase prices of fossil fuels
Impose legislation on companies to use more renewable energy
Install more wind farms (the UK is a windy island)
Reduce price of solar panels to encourage UK buyers
Use excess food waste for biofuel
List some positive & negative impacts of using fossil fuels (give at least 2 of each)
PROS:
Can generate a high amount of electricity in a single location
Allows smaller mining towns to make money
Powered the industrial revolution, pulling millions out of poverty
CONS:
Greenhouse gases emitted contribute to climate change (eg can cause acid rain)
Expensive to mine since it's deep underground
Risk of oil leaks & oil rig explosions
Finite resource - meaning it will run out
List some positive & negative impacts of using renewable energy sources
PROS:
Low carbon emissions
Generates jobs in technology
Low maintenance
CONS:
High set up costs
Affects bird migration
Noise / visual pollution
Define water quality
Refers to the suitability of water for drinking, recreational uses, and as habitat for aquatic life
Define food security and food insecurity.
Food security = reliable access to a sufficient quantity of affordable, nutritious food
Food insecurity = Lack of reliable access to a sufficient quantity of affordable, nutritious food
Define food surplus and food deficit
Food surplus = When supply of food exceeds its demand
Food deficit = When supply of food is insufficient to meet its demand
List some causes of food insecurity
Rapidly growing population, narrowing the gap between available supply & demand
Famine caused by climate (eg droughts or floods)
Political unrest
Lack of suitable land
List some causes of water scarcity
Droughts & climate change
Contaminated/polluted water supplies
Lack of infrastructure to properly invest in their water resources
War & conflict
Impacts of food insecurity
Famine & malnutrition
Conflict & political unrest (can lead to local & international dispute)
Increase in food prices (example: poor harvest -> rise in food price -> famine)
Over-cultivation of land leading to desertification (when land become desert & soil becomes infertile
What are the top (6) strategies to increase food supply?
Irrigation = supplying extra water to farming areas when the water supply is unreliable / low. It can increase crop yields but can cause salininisation of soil
Aeroponics = using air rather than soil to grow plants. Plants are easily maintained BUT specialist knowledge is necessary
Hydroponics = growing plants directly in water rather than soil. Plants are easily maintained BUT specialist knowledge is necessary
Green revolution = during the 1960s, when scientists developed new strains of seeds which produced higher yields of crop.
Biotechnology = when plants, animals and fish are genetically modified. Makes plants resistant to pests, diseases or herbicides BUT has unclear impacts on health & environment
Appropriate technology = small-scale, low tech projects made to suit needs of local people.
Define sustainability
meeting the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs
Give an example of a case study that demonstrates large scale food production (what they do + impacts)
𝐀𝐥𝐦𝐞𝐫𝐢𝐚 - 𝐢𝐧 𝐒𝐨𝐮𝐭𝐡-𝐞𝐚𝐬𝐭 𝐒𝐩𝐚𝐢𝐧
Built industrial-sized greenhouses using hydroponics for plants + sourced the water using irrigation
PRO = Less resources needed to produce crops on a larger scale
CON = Inhumane work conditions
Give an example of a case study that demonstrates the increase of sustainable food supply (what they do + positive impacts)
𝐌𝐚𝐤𝐮𝐞𝐧𝐢 - 𝐢𝐧 𝐊𝐞𝐧𝐲𝐚
Improving access to food & clean water supply by building sand dams to provide a reliable water supply to villages & running a training programme for farmers
PROS: Crop yields increased, labour times decreased, spread of water-borne diseases decreased
What are some examples of the regional and global significance of Nigeria?
Regional:
Economic powerhouse (Giant of Africa - oil, agriculture)
Cultural influence (afrobeats, nollywood)
Global:
Top oil producers in the world
Very large diaspora (impacts labor markets across world)
What is the informal agreement for alternating political leaders in Nigeria?
Aka. Zoning principle: alternates between leaders from north & south every 2 years
Promotes ethnic representation + political stability (everyone feels included by leadership roles)
What is development?
= Improvement in living standards through better access & use of resources (economic, social, environmental)
What are some economic indicators of development?
GDP per capita
GNI per capita
Employment type (proportion of people in each industry sector)
What is GDP per capita?
= Total of goods/services in country per person per year
(Gross Domestic Product)
What is GNI
= Sum of money earned by people/businesses in a country
(Gross National Income)
What are some social indicators of development?
Infant mortality (kids who die before 1 - per 1000 babies born)
Literacy Rate (% of people over 15 who can read & write)
Life Expectancy (average lifespan of person in country)
What is the HDI?
= A mixed indicator of development (from 0 to 1) that composes of:
life expectancy
Education level
Income per capita
Why is HDI a more reliable of development?
It takes both economic & social factors into account
What is the Demographic Transition Model?
= shows population change over time, studying birth & death rate in 5 stages
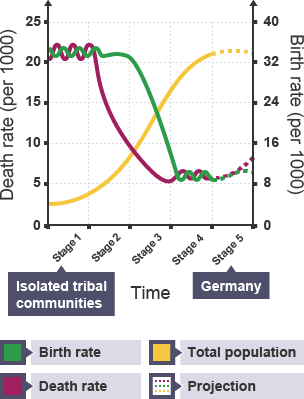
Describe the 5 stages of the Demographic Transition Model (+ give examples of countries in each) :
1 → High BR & DR, balanced population - eg. Amazonian tribes
2 → High BR, rapidly declining DR, very high PG (children = economic assets, medicine improvement) - eg. Kenya
3 → Rapidly declining BR, slowly declining DR, high PG (family planning, equality bringing more women to work) - eg. India
4 - Low BR + DR, high & balanced population (contraception, desire for smaller families) - eg. UK
5 - Low BR, higher DR, population decline (ageing population no longer replacing itself) - eg. Japan
BR = birth rate, DR = death rate, PG = population growth
What are some physical factors affecting uneven development? (+ how?)
Access to natural resources - water, oil, timber etc
Natural hazards - frequent hazards limits development
Climate - limits industry, attracts tourists, rainfall helps farmers
Location - landlocked affects trade, scenery attracts tourists
What are some human factors affecting uneven development? (+ how?)
Aid - projects to improve infrastructure/services, corrupt governments misuse it
Education - highly skilled workers makes more money for country & pay more tax
Politics - corruption & instability affects trade and investments into country
History - colonialism stunts development greatly
What is the development gap?
= difference in levels of development between the richest and poorest countries
What are some consequences of uneven development?
Wealth - developed countries = richer, less developed = poorer
Health - developed countries = better healthcare & longer lifespan, less developed = opposite
Migration - Skilled workers move to more developed countries for better standard of living → “brain drain”
Explain some ways to reduce the Global Development Gap? (+ name 3 with pros & cons)
✧Aid - can be invested well into services & infrastructure, corrupt governments misuse it
✧Debt Relief - (debt is forgiven/interest reduced) - more money spent on development, local might not get say
Foreign Direct Investment (a country buying property/infrastructure in another) - better access to finance/technology, country may need to comply to conditions set by investing country
Fair Trade - (farmers get fair price for goods produced) - better pay improves development of economy, barely any money reaches farmers
✧Microfinance Loans (small loans to people in LICs) - people can make startups, no proof that it reduces poverty on large scale
How has tourism helped reduce development gap? (The Gambia)
Multiplier effect - tourism jobs →investment in recreational services → money made to country’s infrastructure → industry improves
Poverty rates 📉 - 58% (2003) to 48.4% (2010)
Investment into healthcare - 📉 maternal mortality & AIDS
What attracts tourists to The Gambia?
Located in West Africa → variety of coastal/marine habitats + hot climate + close to Europe
Kunta Kinteh Island - a UNESCO heritage site
What are some potential setbacks of tourism in The Gambia?
Risky to be reliant on tourism:
Ebola crisis repelled tourists → 60% drop in tourism ( Ebola didn’t actually reach Gambia!)
Tourism = generally seasonal → many people jobless in monsoon season
Tourism companies (eg Thomas Cook + TUI) keep large profits from locals → economic “leakage”
What is urbanisation & where is it occuring?
= increase in the proportion of people living in urban areas (towns & cities)
Rapidly in LICs/NEEs
What is causing urbanisation? (3 causes)
Natural increase, rural-to-urban migration, advancements in technology, healthcare, education etc
What is a megacity & where are they growing?
= cities with population > 10 mil
Slowly in HICs, rapidly in LICs/NEEs -> due to urbanisation
Give 3 reasons why Rio is an important city
Christ the Redeemer statue, 2016 Olympics, Rio carnivals
Why has Rio’s population grown? (3 reasons)
migration, pull factors [education, job opportunities, industry] and natural increase
What are some social and economic opportunities created by urban growth in Rio?
Social: healthcare for citizens, education (rio = 97% literacy vs 80% rural literacy)
Economic: growth of tertiary sector, investment from manufacturing companies
What are some challenges created by urban growth in Rio’s favelas?
Spread of disease due to densely populated (infant 💀 = 50 per 1000 kids)
High crime rates - drugs & gangs (PPU set up in 2008 to combat this)
Poor infrastructure (risk of landslides)
Name an example of how urban planning is improving the quality of life for the urban poor:
CASE STUDY: The Favela Bairro Project in Rio
What was the Favela Bairro Project?
= project to develop existing favelas to improve quality of life for the urban poor.
How did the Favela Bairro Project help to improve life for the urban poor in Rio? (3 ways)
Provided essential services (electricity, water, sanitation),
relocated people on steep hills to brick houses,
street lighting for safety
Was the Favela Bairro Project successful?
Partially successful but unsustainable:
❌ Expensive to develop all growing favelas + residents didn’t have skills to maintain infrastructure
Why is London an important city?
capital city, GDP of £526 billion, one of largest financial markets in world
Why has London grown?
1. Industrial revolution attracted migrants from other parts of the UK (economic migrants),
2. Young students from abroad to attend prestige unis
What opportunities have been created by urban change in London? (refer to relevant case studies)
SHOREDITCH:
Social: Ethnic diversity, vibrant arts scene (eg jazz events)
Economic: Pop-up mall, Silicon Roundabout brings TNC investment
TFL:
Social: integrated travel -> convenient to travel all over London for cheaper
Economic: Crossrail tube line -> increases property value in surrounding areas + shortens commute times
What challenges have been created by urban change in London?
Social: Inequality -> eg. Kensington & Chelsea: Notting Hill vs Elgin Crescent (place of Grenfell)
Economic: Gentrification -> eg. Shoreditch: original citizens can’t afford housing
Name a way London is being made a more sustainable urban area (+ definition):
Urban Greening =increasing proportion of green spaces in city - eg. rooftop gardens
Social: Encourages outdoor physical activity
Environmental: Purifies air -> reduces effect of CO2 emissions
Define what ‘greenfield’ and ‘brownfield’ sites are:
Greenfield site = area of land that has not been developed previously
Brownfield site = an old industrial site that has been previously developed on
Name an example of urban regeneration project in London:
CASE STUDY: Lower Lea Valley in Stratford
Why did the Lower Lea Valley need regeneration?
Held one of biggest ports in world → closed down → people unemployed & became deprived area → left a lot of brownfield sites
What are some of the main features of the regeneration project?
Turned brownfield site → Queen Elizabeth Olympic Park for 2012 Olympic games
Atheltes’ Village (formely for olympic athletes) → East Village (residentil housing)