UNIT 1 BIO 111 STUDY GUIDE (WIP)
4.5(2)
Card Sorting
1/85
Earn XP
Last updated 11:44 PM on 9/1/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
86 Terms
1
New cards
What are the **basic levels** of **Organization of Matter?**
Atoms, molecules, and macromolecules
2
New cards
Atoms
**smallest unit**; comprised of __nucleus__ (protons and neutrons in nucleus) and __electrons.__
3
New cards
Molecule
**Two or more atoms held together** by chemical bonds
4
New cards
Macromolecules
**Large molecules**; comprised of smaller units called **monomers**
5
New cards
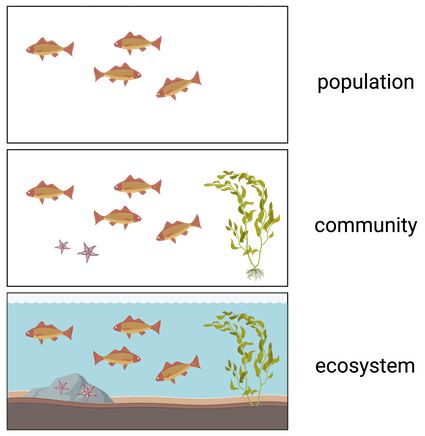
Population
**All individuals** of a **species** living within a specific area
6
New cards
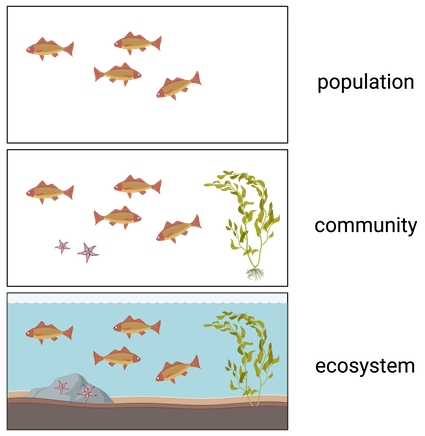
Community
**Sum of populations** inhabiting a particular site
7
New cards
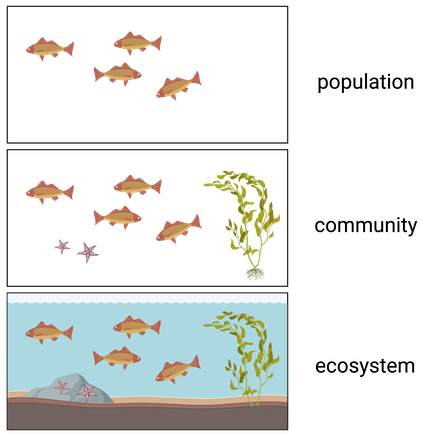
Ecosystem
Consists of all **living** things (**biotic**) AND **nonliving** things (**abiotic**)
8
New cards
Prokaryotic
Unicellular (**single celled**) organisms
9
New cards
Characteristics of prokaryotes
\-No nucleus; **contains nucleoid**
\-**Cell wall** (made of peptidoglycan)
\-contains flagellum or pili
\-**No membrane-bound organelles**
\-**Cell wall** (made of peptidoglycan)
\-contains flagellum or pili
\-**No membrane-bound organelles**
10
New cards
Eukaryotes
**multicellular** organisms
11
New cards
Characteristics of Eukaryotes
\-**True nucleus**, membrane surrounds DNA
**-Membrane bound organelles**
\-Cell membrane
**-Membrane bound organelles**
\-Cell membrane
12
New cards
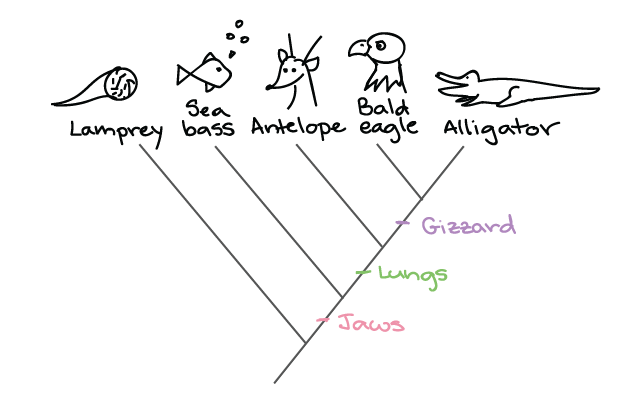
Phylogeny
reflects **evolutionary relationships** among organisms
13
New cards
A phylogenetic (or evolutionary) tree shows the relationship between what?
Shows the relationship of **bacteria, archaea, and eukaryota.**
14
New cards
What does a phylogenetic **rooted** tree show?
Shows various species diverged from a **common ancestor** (shown on example A)
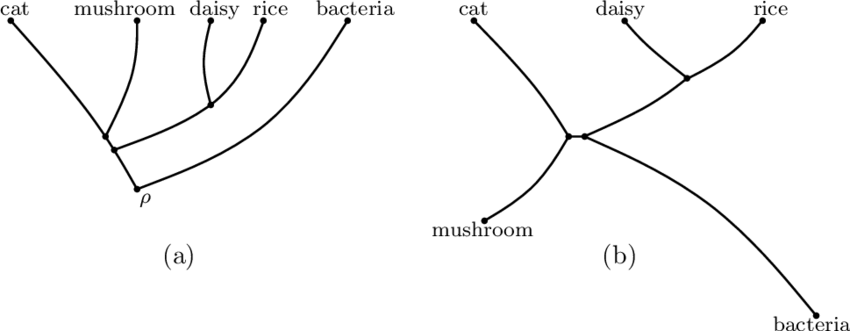
15
New cards
What does a phylogenetic **unrooted** tree show?
shows the **relationship amongst species** but does **NOT** share a common ancestor (shown on example B)
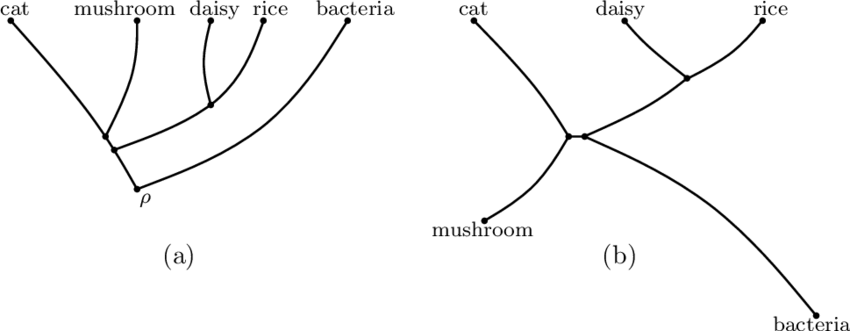
16
New cards
What is Taxonomy?
The science of classifying organisms.
17
New cards
Taxonomy scientists only refer to an organism only by its what? What is this called?
Genus and species, Binomial nomenclature.
18
New cards
Inductive Reasoning
**Analyzes trends or relationships in data** to arrive at a general conclusion. These data can be **qualitative (descriptive) or quantitative**.
19
New cards
Deductive Reasoning
**Begins from a general principle** or law and **applies it to a typical circumstance** to **predict** specific results.
20
New cards
Step 1 of Scientific Inquiry
**Observation**: aspect that is seen
21
New cards
Step 2 of Scientific Inquiry
Form a **hypothesis**: statement based on knowledge or experience from observation.
22
New cards
What MUST a hypothesis be for it to by a hypothesis?
**TESTABLE AND FALSIFIABLE**
23
New cards
Step 3 of Scientific Inquiry
**Experimental design** : situation to test hypothesis by collection of data
24
New cards
What do controls do in an experiment?
Controls provide a **basis of comparison**
25
New cards
Experimental variables
Factors that are altered in an experiment
26
New cards
What are the two types of experimental variables?
Independent variable and dependent variable.
27
New cards
Independent variable
**cause or reason** for an outcome; the variable that is **changed by the researcher**
28
New cards
Dependent Variable
what’s being measured in an experiment. It **changes based on the Independent Variable.**
29
New cards
Step 4 of Scientific Inquiry
Gathering data
30
New cards
Step 5 of Scientific Inquiry
**Interpreting results:** Assess whether the results are statistically significant
31
New cards
Step 6 of Scientific Inquiry
**Draw conclusion:** this is a THEORY, NOT PROOF. Many tests must be done to gather enough evidence to determine whether this data proves our hypothesis is true.
32
New cards
What is living matter composed primary of?
oxygen, carbon, hydrogen, and nitrogen
33
New cards
What are the three subatomic particles an atom is made of?
Protons (positively charged), Neutrons (neutral, uncharged), and electrons
34
New cards
The number of protons determines the ____________ and ________________
Atomic number, distinguishes an element from another
35
New cards
Electrons
**negatively charged** subatomic particles that are attracted to an orbit around the positively charged nucleus of an atom.
36
New cards
Where do electrons reside in an atom?
Shells; associated with the energy levels and are further organized into subshells and orbitals within each shell.
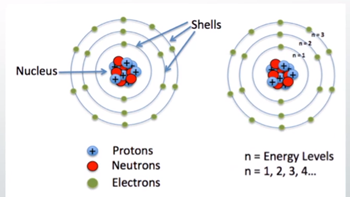
37
New cards
Isotopes
Atoms with the same number of protons but **different numbers of neutrons**
38
New cards
Ionic bond
The movement of electrons from one element to another; also referred to as electron transfer.
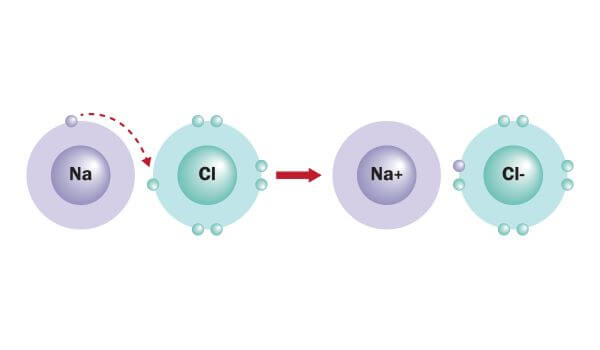
39
New cards
Cations
**POSITIVE** ions, LOSES ELECTRONS
40
New cards
Anions
NEGATIVE ions, GAIN electrons
41
New cards
Covalent bond
Electrons that are **shared**
42
New cards
Polar covalent bonds
Electrons that are **unequally** shared
43
New cards
Nonpolar covalent bonds
Electrons that are shared **equally**
44
New cards
Hydrogen Bonds
weaker bonds
45
New cards
van der Waals Interaction
weak attractions (also called intermolecular forces), arise from attractive or repulsive interactions between particles with permanent, partial, or temporary charges.
46
New cards
What makes carbon a flexible component of biological molecules?
Carbon is **tetravalent** (has four electrons)
47
New cards
What are functional groups?
atoms that confer specific properties to hydrocarbon chains or rings that define their overall chemical characteristics and function.
48
New cards
What is the structure, properties, and features of **hydroxyl**?
Structure: (shown in picture)
Properties: Polar (hydrophilic)
Features: presence of H and O
Properties: Polar (hydrophilic)
Features: presence of H and O
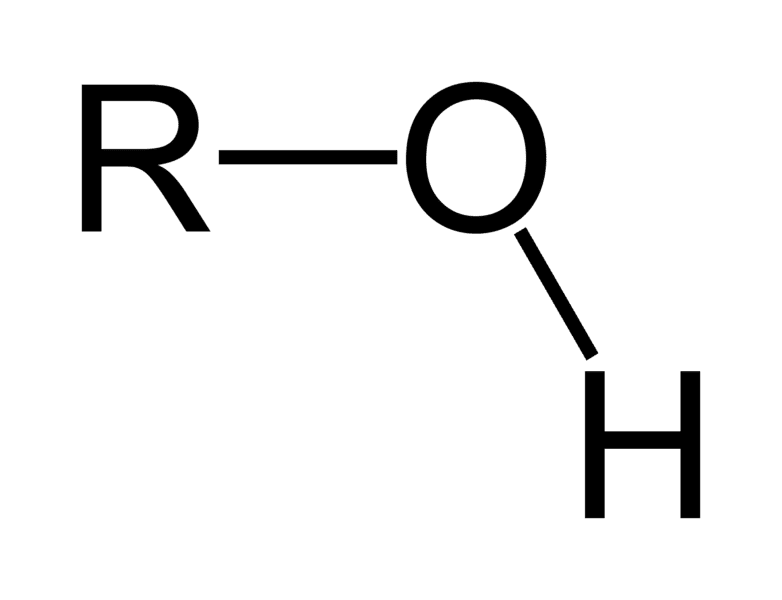
49
New cards
What is the structure, properties, and features of **sulfhydryl**?
Structure: (shown in picture)
Properties: Polar (hydrophilic)
Features: presence of S
Properties: Polar (hydrophilic)
Features: presence of S
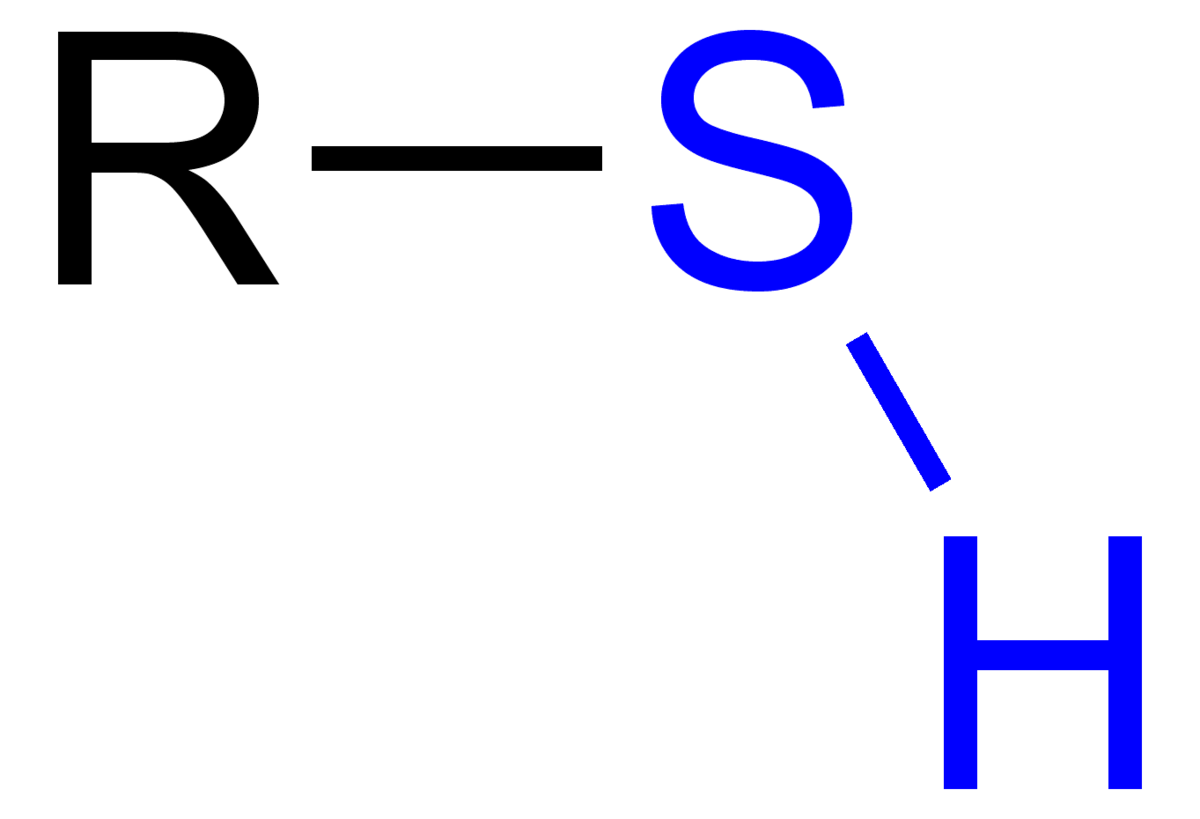
50
New cards
What is the structure, properties, and features of **methyl?**
Structure: (shown in picture)
Properties: Nonpolar (hydrophobic)
Features: presence of H and C
Properties: Nonpolar (hydrophobic)
Features: presence of H and C
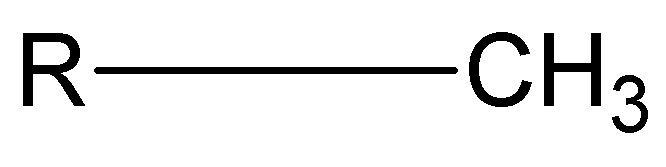
51
New cards
What is the structure, properties, and features of **carbonyl**?
Structure: (shown in picture)
Properties: Polar (hydrophilic)
Features: Central C and O
Properties: Polar (hydrophilic)
Features: Central C and O
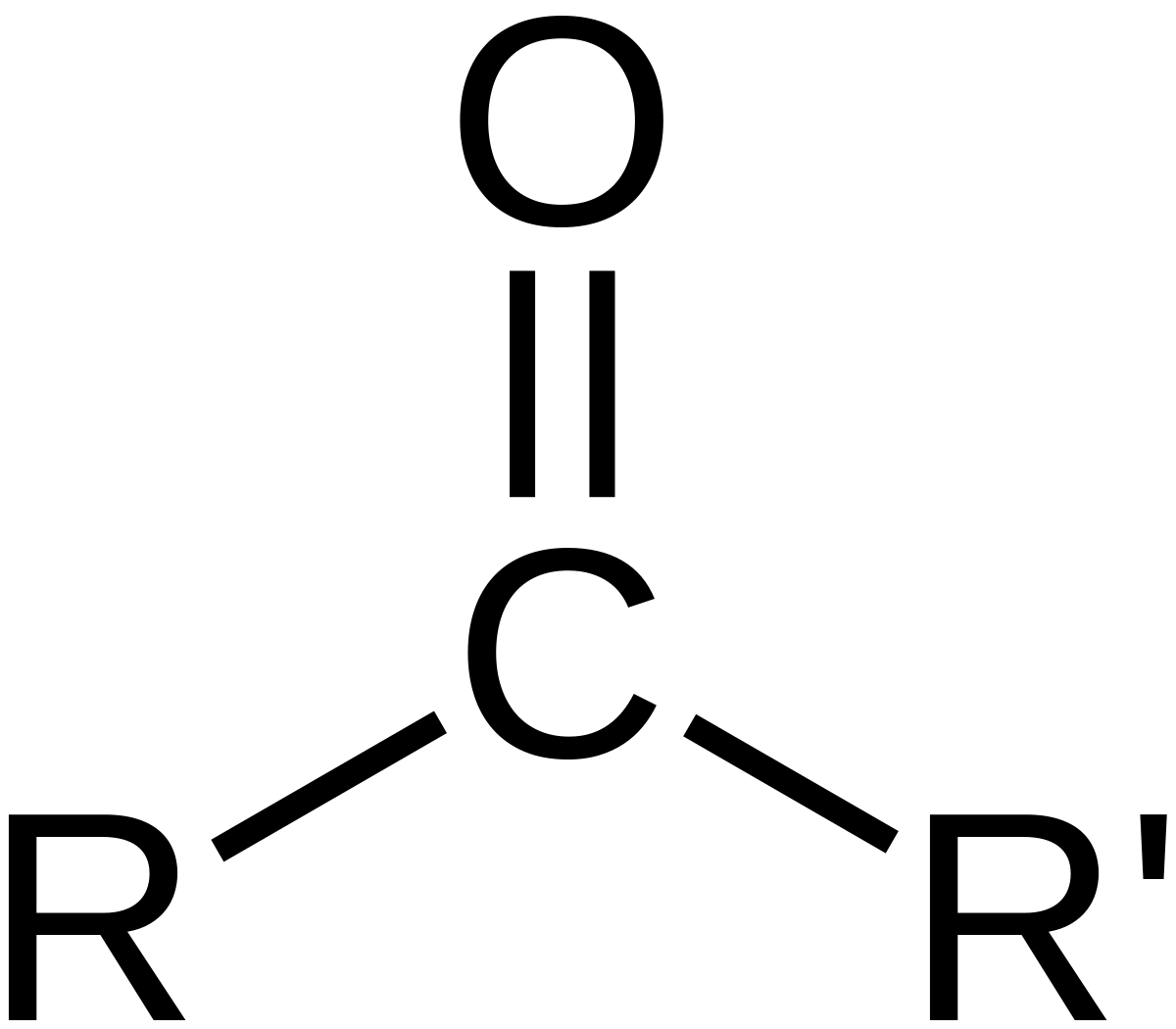
52
New cards
What is the structure, properties, and features of **carboxyl?**
Structure: (shown in picture)
Properties: Charged (acidic)
Features: Central C bond to O and OH
Properties: Charged (acidic)
Features: Central C bond to O and OH
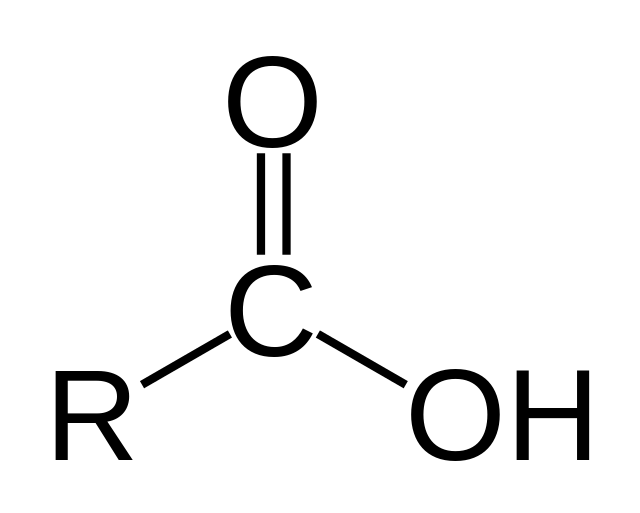
53
New cards
What is the structure, properties, and features of an **amino**?
Structure: (shown in picture)
Properties: Charged (basic)
Features: pressence of N
Properties: Charged (basic)
Features: pressence of N
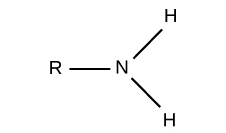
54
New cards
What is the structure, properties, and features of a **phosphate?**
Structure: (shown in picture)
Properties: Charged (acidic)
Features: presence of P
Properties: Charged (acidic)
Features: presence of P
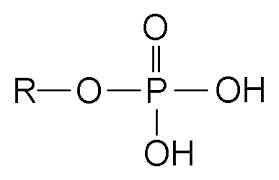
55
New cards
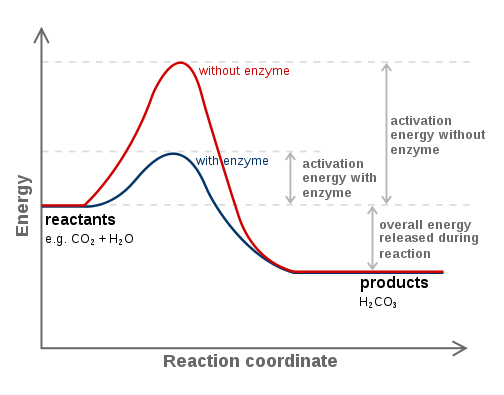
Enzymes
protiens that speed up reactions by reducing the activation energy
56
New cards
First Law of Thermodynamics
energy cana be coverted between forms; total energy is constant and transformed
57
New cards
Second Law of Thermodynamics
coversion of energy from one to another leads to loss of energy as heat; every energy transfer increases the entropy of the universe
58
New cards
Entropy
measure of randomness or disorder in a system
59
New cards
Organic molecule
any molecule containing (excludes CO2)
60
New cards
What are protiens composed of?
Amino acids
61
New cards
What are the key elements of an amino acid?
A central carbon atom, an amino group, a carboxyl group, a hydrogen atom, and an R group
62
New cards
What type of bond links amino acids of the protien’s primary structure?
A peptide bond; covalent bond
63
New cards
What kind of folds occur in the protien secondary structure?
Pleated sheet or alpha helix
64
New cards
What type of bonds maintain the protien teritary structure?
hydrophobic interactions, ionic bonding, hydrogen bonding, and disulfide linkages
65
New cards
What are the three factors that can cause denaturation of a protien?
Temperature, pH, and exposure to chemicals
66
New cards
What are the different types of lipids?
Fats, oils, waxes, phospholipids, and sterioids.
67
New cards
What are fats composed of?
fatty acids and glycerol
68
New cards
What are triglycerides consisting of?
1 glycerol and 3 fatty acids
69
New cards
How can we differentiate saturated, unsaturated cis, and trans fats?
Saturated - single bonds (-)
Unsaturated cis - double bond (=) cis is where H atoms adjacent to C=C
Trans fat - double bond, buy hydrogen is on two different planes
Unsaturated cis - double bond (=) cis is where H atoms adjacent to C=C
Trans fat - double bond, buy hydrogen is on two different planes
70
New cards
What part of the phospholipid is polar? Is it hydrophilic or hydrophobic?
The **head** (__phosphate and glycerol is located__) is polar, its **hydrophilic**
71
New cards
What part of the phospholipid is nonpolar? Is it hydrophilic or hydrophobic?
The **tail** (__saturated and unsaturated fatty acid__) is nopolar, its **hydrophobic**
72
New cards
What is the functions of waxes?
Waxes prevents water from sticking on the surface (fatty acid and alcohol chained together)
73
New cards
What is the defining feature of carbohydrates?
They’re always made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen
74
New cards
What are two examples of monosaccharides with five carbons?
pentose = 5 carbons; such as **deoxyribose and ribose**
75
New cards
What are three examples of monosaccharides with six carbons?
hexoses = 6 carbons, such as **glucose and fructose**
76
New cards
What are disaccharides? Provide three examples.
Two monomers that are connected; monosaccharides. Examples include **sucrose**
77
New cards
What form do animals store more energy in?
glycogen stores energy in animals; cellulose
78
New cards
What form do animals store energy in?
starch stores energy in plants; amylopectin
79
New cards
What type of bond links monosaccharides together?
A glycosidic bond
80
New cards
What type of sugar does DNA have?
Deoxyribose
81
New cards
Which type of sugar does RNA have?
Ribose
82
New cards
Which component is the same in all nucleic acids?
All have a nitrogenous base, a pentose sugar, and a phosphate group
83
New cards
Which nitrogen bases can have DNA?
C, T, A, and G
84
New cards
Which nitrogen bases can have RNA?
C, U, A, and G
85
New cards
Which type of reaction allows the formation of a new bond between and synthesis of macromolecules?
Dehydration synthesis; a condensation reaction
86
New cards
What type of reaction broke down a macromolecule into the monomers?
Hydrolysis