unit 2 review
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
define centrifugation. what is its importance in separating particles based on their density?
separating liquids/liquid suspensions based on density with centrifugal force; samples will create layers based on density after centrifugation
what is a benchtop centrifuge? what is its size, speed (RPM), and angle of force?
compact centrifuge typically used in laboratory settings for small-scale sample processing and separation; can hold 5-50 mL tubes; up to 3000 RPM; can have fixed-angle (25-45 degrees) or swing-out rotors
what is a microcentrifuge? what is its size, speed (RPM), and angle of force?
powerful compact tabletop centrifuge; 1.5-2.0 mL; up to 12,000 RPM; usually have fixed-angle heads (25-45 degrees)
what is an ultracentrifuge? what is its size, speed (RPM), and angle of force?
high-speed centrifuge; may be floor-standing instruments due to their size and weight; over 50,000 RPM; can have fixed-angle (25-45 degrees) or swinging bucket rotors
what are the 6 rules for handling a centrifuge?
never spin tubes w/o cap
always use tubes that fit your respective centrifuge
never use centrifuge on uneven surface
never use centrifuge w/ open lid
do not open if it is still moving
never put your hands/fingers in centrifuge until it is fully stopped
why is it important to select appropriate tubes for sample preparation before centrifugation?
different centrifuges has different capacities; tubes should be chemically inert and suitable for the sample to prevent contamination; select tube size to fit the sample volume
what is the importance of accurately labeling samples prior to centrifugation?
to avoid confusion and cross-contamination after centrifuging
how does ensuring uniformity of sample density contribute to the effectiveness of centrifugation?
helps w/ balanced separation, prevents mixing, and ensures reproducible results during centrifugation
what role does proper sample preparation play in the accuracy and reliability of centrifugation results?
proper sample preparation ensures good centrifugation and reproducible outcomes
what is the correct procedure for loading samples into centrifuge tubes? include proper positioning to maintain balance and prevent leakage.
select suitable tubes and ensure caps are securely tightened; load tubes evenly on opposite sides of the rotor for balance (make dummy tube w/ same amount of water on opposite side)
what are the 3 different micropipettes? what are their ranges?
P-20: 2-20 microliters
P-200: 20-200 microliters
P-1000: 100-1000 microliters
how do micropipettes use piston-driven mechanisms?
piston moves within a cylinder, creating vacuum for aspiration and expelling liquid for dispensing
what role does air displacement play in the operation of micropipettes?
piston movement creates partial vacuum, displacing air from the pipette tip and allowing liquid uptake; volume of liquid aspirated is determined by volume of air displaced
what does the plunger of a micropipette do?
allows adjustment of liquid volume, creates vacuum for aspiration, and expels liquid during dispensing in a micropipette
what does the tip ejector button of a micropipette do?
used to release disposable tips from the micropipette after use
what does the volume adjustment knob of a micropipette do?
enables precise setting of liquid volume to be aspirated or dispensed by adjusting the position of the piston within the micropipette barrel
what does the tip cone of a micropipette do?
holds the disposable pipette tip securely in place during aspiration and dispensing, ensuring a tight seal to prevent leakage and ensure accurate liquid transfer
how do you properly handle a micropipette to prevent damage or contamination?
don’t invert micropipette w/ substance in tip; replace tip between samples, do not touch tip cone or sample to avoid contamination; do not take in more liquid than cone can hold to prevent substance from going into pipette
how do you properly handle a micropipette to ensure accurate measurements?
to take up liquid: go to 1st stop
to expel liquid: go to 2nd stop
how should you read a volume beaker? which part of the meniscus do you use?
meniscus (curved surface of the liquid) should be read at the bottom
what kind of image does a compound light microscope generate?
2D image w/ color (from staining samples)
what kind of image does a dissecting microscope (stereoscope) generate?
3D color image w/ low magnification
what kind of image does a confocal microscope generate?
3D & colorful image (from image stacking & laser beams)
what kind of image does a scanning electron microscope (SEM) generate?
3D & black/white
what kind of image does a transmission electron microscope (TEM) generate?
2D image w/ scattering of electrons
list microscopes in order of increasing magnification.
stereo (dissecting), light compound, confocal, scanning electron, transmission electron
what is the difference between magnification and resolution in microscopy?
magnification: increase in size of an object when viewed through a microscope compared to when viewed with the naked eye
resolution: determining the level of detail visible in the image
which microscopes require non-living samples? which can have living ones?
non-living: SEM, TEM, dissecting
living: light compound, confocal
how do you calculate the total magnification of a compound light microscope?
total magnification = magnification of objective lens x magnification of eyepiece
why do specimens need to be stained to be properly viewed using a compound light microscope and/or a confocal microscope?
to enhance contrast of thin samples, highlight specific features, and improve visibility when viewed under a microscope w/ light directly pointed at it
which microscopes make images with light? which ones make images with electron beams?
light: dissecting, light compound, confocal (laser beams)
electrons: SEM; TEM
why do confocal microscopes can generate three-dimensional images of fluorescently labeled specimens?
they have optical sectioning, which means 3D images can be made from high-resolution stacks of images
what is chromatography? how does it separate mixtures based on physical and chemical properties?
technique used to separate and analyze mixtures into their individual components; compounds w/ different physical & chemical properties interact differently with the stationary phase, causing them to move at different rates
what is the stationary phase?
immobile material in chromatography that interacts w/ the sample compounds; may be a solid or a liquid supported on a solid.
what is the mobile phase?
solvent or gas that carries the sample through the stationary phase in chromatography
what is polarity? how is it used in chromatography?
distribution of electric charge within a molecule, resulting in regions of partial positive and negative charge; used to separate compounds based on their differing polarities
what is binding affinity? how is it used in chromatography?
strength of interaction between substance and stationary phase; higher affinity to the stationary phase = longer retention time
what is paper chromatography?
sample dotted on paper, and paper is dipped in water (solvent), allowing components to move up by capillary action and separate based on affinity to paper and solvent
what is thin-layer chromatography (TLC)?
sample applied as a spot on a thin layer of stationary phase (usually silica gel/alumina) on a plate; plate developed in a solvent, allowing compounds to move at different rates based on their affinity to the stationary phase
what is gas chromatography (GC)?
sample is vaporized and carried by inert gas through a stationary phase, separating components based on their affinity to the stationary phase; components detected as they elute from the column
what is liquid column chromatography (LC)?
uses vertical glass jar (column) with a highly absorbent solid (usually silica); substances are dissolved in mobile phase (eluant) and forced to flow through a column (stationary phase)
what is high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC)?
aka high-pressure chromatography; mixture is forced through a column at high pressure (approx. 400x atmospheric pressure); faster, more precise, and more sensitive than regular LC
what is retention factor (Rf)? which types of chromatography use it?
distance traveled by the compound divided by the distance traveled by the solvent front ; used in thin-layer chromatography (TLC) & paper chromatography
what is retention time (Rt)? which types of chromatography use it?
duration a compound spends traveling through a chromatography column; used in gas chromatography (GC) & liquid chromatography (LC)
how do you interpret chromatograms to identify substances present in a mixture?
by analyzing peaks; each peak represents a substance
how do you tell if a sample is a pure substance or a mixture on a chromatogram?
pure substances do not separate (one dot/peak); mixtures separate into 2 or more dots/peaks
how do you tell how many components there are in a mixture on a chromatogram?
by counting the number of peaks on graph or counting number of dots on paper
what is mass spectrometry? what is its purpose in analyzing the molecular composition of substances?
technique for identifying molecular composition; used to determine substance identity, structure, and quantity in various fields
how does mass spectrometry work?
ionizes a sample, separates ions by mass-to-charge ratio, and detects ion abundance to determine molecular composition
what are the 4 steps of mass spectrometry?
ionization: sample bombarded with electrons to create positively charged ions
acceleration: ions are accelerated using an electric field to give them kinetic energy.
deflection: ions are deflected by a magnetic field according to their mass-to-charge ratio (m/z), causing them to separate based on mass
detection: the separated ions are detected by measuring their abundance or their arrival time at a detector, allowing for the determination of the sample's composition
why is the data from a mass spectrometry procedure graphed using intensity and mass-to-charge ratio of ions? what does a peak mean?
to visualize ion abundance and mass relative to charge; a peak on mass spec. data shows an ion (height of the peak shows abundance of that ion in the sample)
how many grams are there in 2.00 liters of a 0.456 M HCl solution? (molar mass of HCl = 36.46 g/mol)
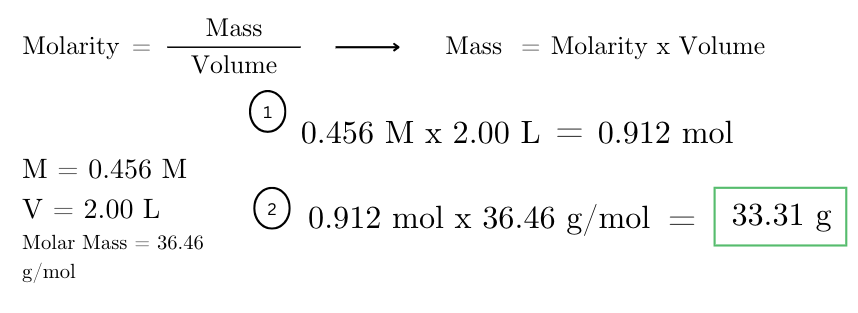
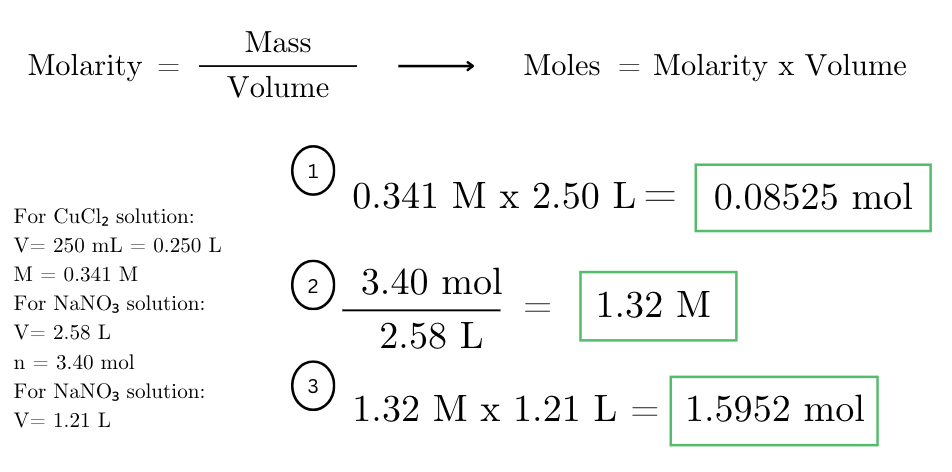
how many moles of CuCl2 are there in 250. mL of 0.341 M solution? if 3.40 moles of NaNO3 was dissolved into 2.58 L, what is the molarity? if you measured 1.21 liters of the solution, how many moles would you have?
what mass of NaCl was dissolved to form 2.37 liters of a 2.49 M solution? (molar mass of NaCl = 58.44 g/mol).
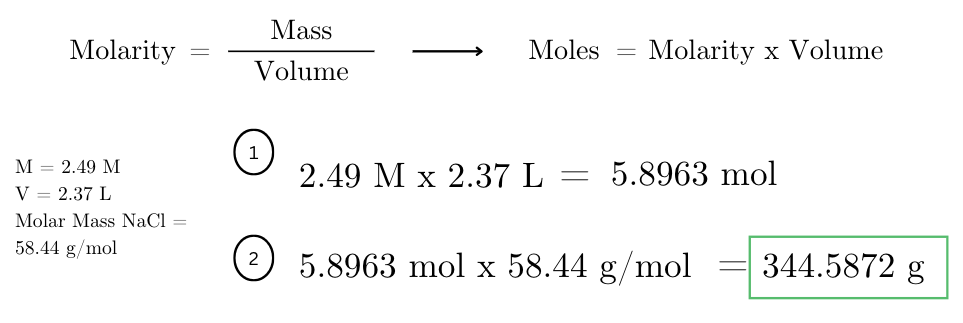
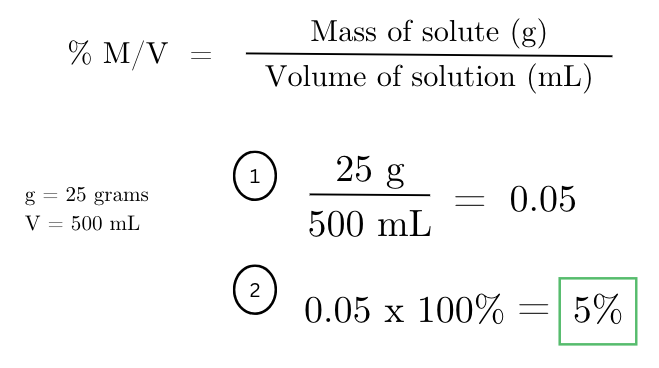
calculate the % mass/volume (w/v) of a solution if 25 grams of solute are dissolved in 500 mL of solvent.
a solution contains 75 mL of ethanol dissolved in 250 mL of water. what is the % volume/volume (v/v) concentration of ethanol in the solution?

determine the molarity of a solution containing 0.5 moles of solute dissolved in 2 liters of solvent.
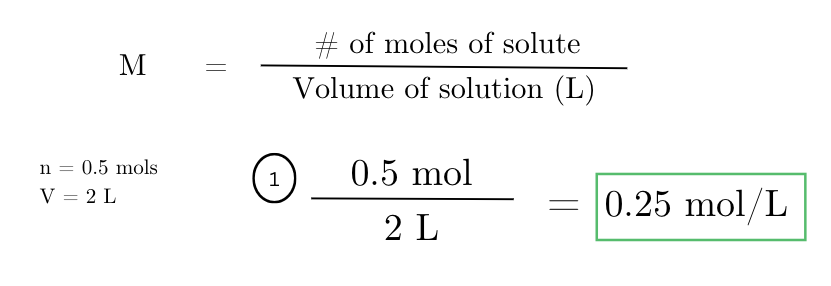
calculate the parts per million (ppm) concentration of a pollutant in a lake if 5 grams of the pollutant are dissolved in 1000 liters of water.
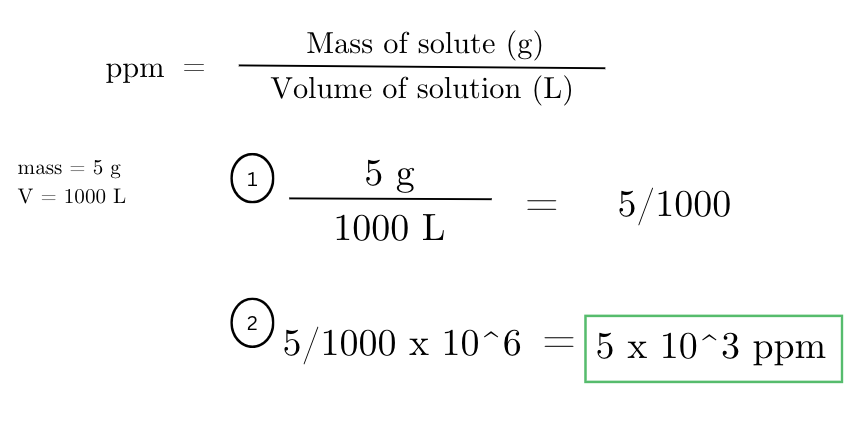
a solution contains 2 micrograms of a particular toxin in 1 liter of water. what is the concentration of the toxin in parts per billion (ppb)?
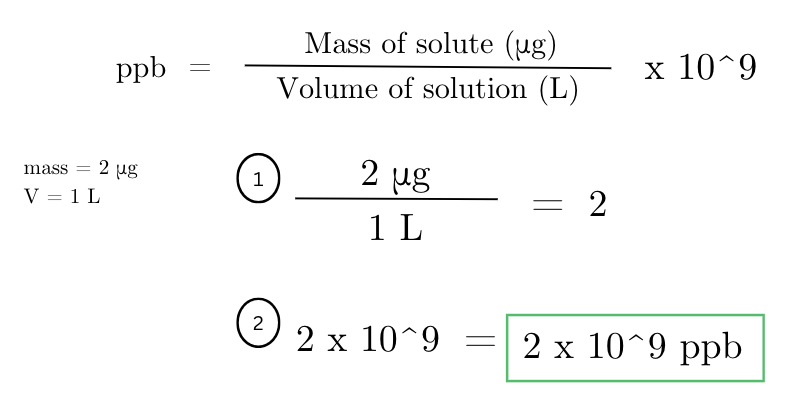
how many grams of glucose (C6H12O6) are needed to prepare 500 mL of a 10% w/v glucose solution?
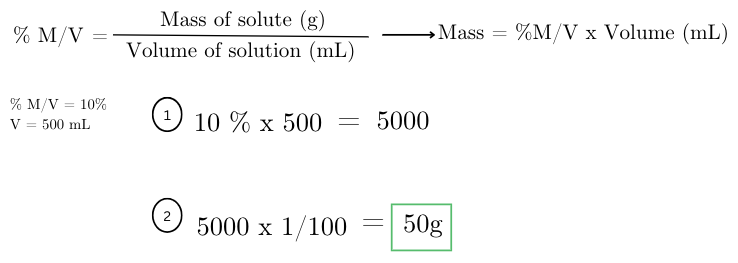
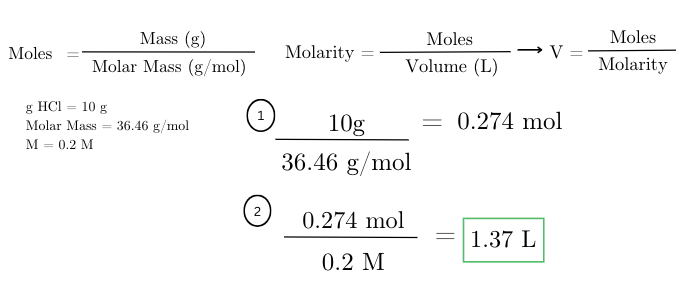
what volume of 0.2 M hydrochloric acid (HCl) solution can be made using 10 grams of HCl?
calculate the mass of potassium nitrate (KNO3) needed to prepare 250 mL of a 0.5 M KNO3 solution.
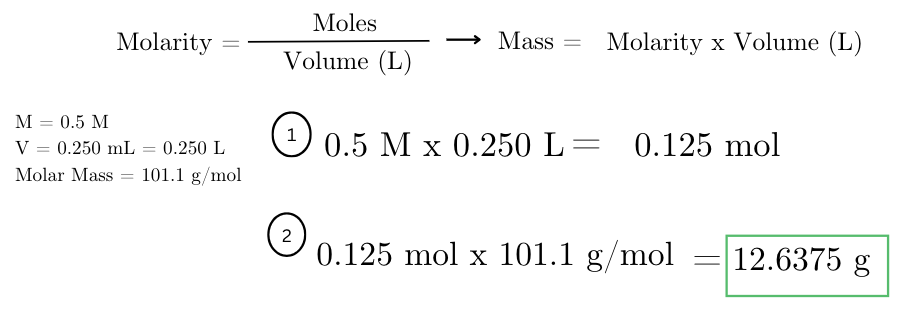
determine the amount of sodium chloride (NaCl) needed to prepare 1 liter of a 5% w/v NaCl solution.

how many micrograms of a pesticide are needed to make a 1 ppb solution in 1 liter of water?
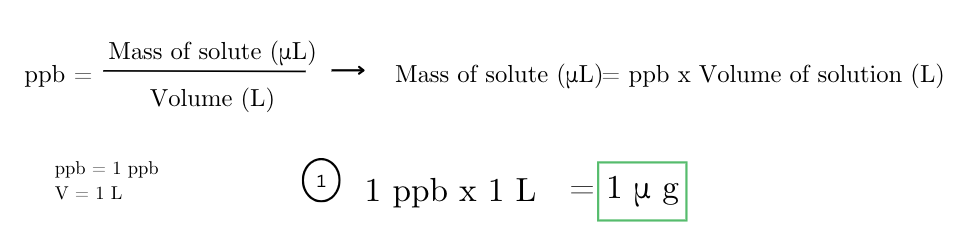
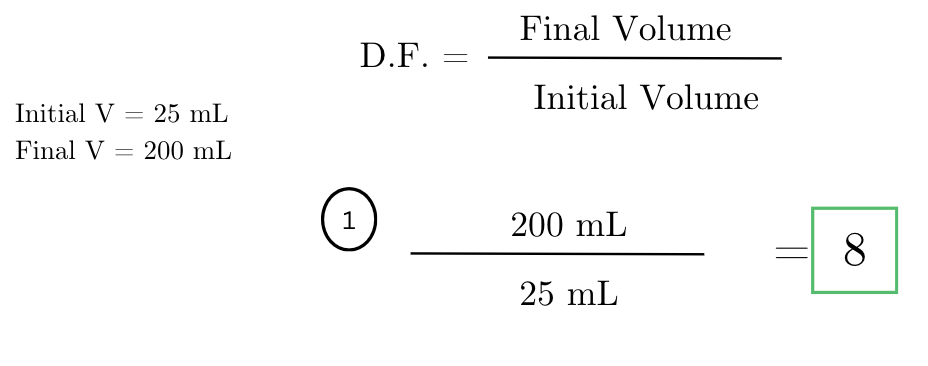
you have a stock solution with a concentration of 0.2 M. if you dilute 10 mL of this stock solution to a final volume of 100 mL, what is the dilution factor?
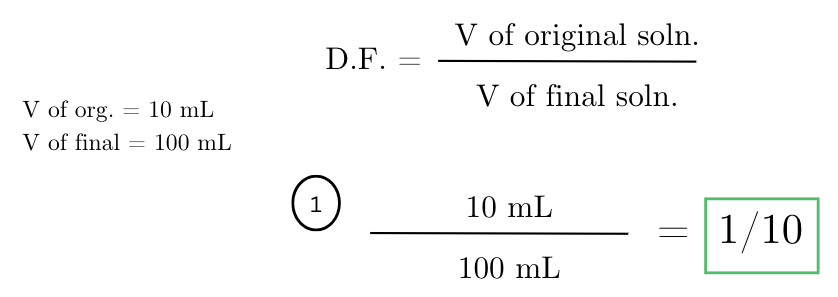
a sample is diluted by adding 1 mL of the sample to 9 mL of water. what is the dilution factor for this dilution?
1/10
a solution is diluted by adding 1 part of the solution to 4 parts of solvent. what is the dilution factor for this dilution?
1/5
you dilute a solution by adding 25 mL of the solution to a final volume of 200 mL. what is the dilution factor?