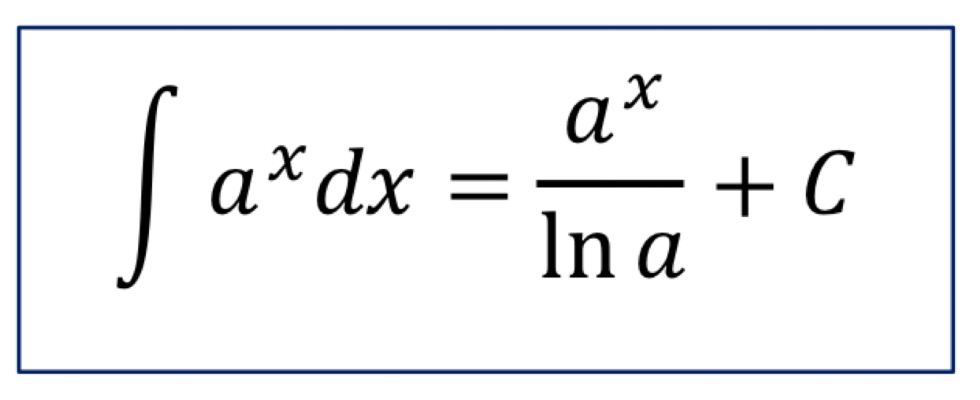AP Calc AB Anti-Derivative Rules
1/17
Earn XP
Description and Tags
All of the Anti-Derivative Rules you need to memorize!
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
Power Rule
The Power Rule states that the antiderivative of x^n is (x^(n+1))/(n+1) + C, where n is a real number and n ≠ -1.
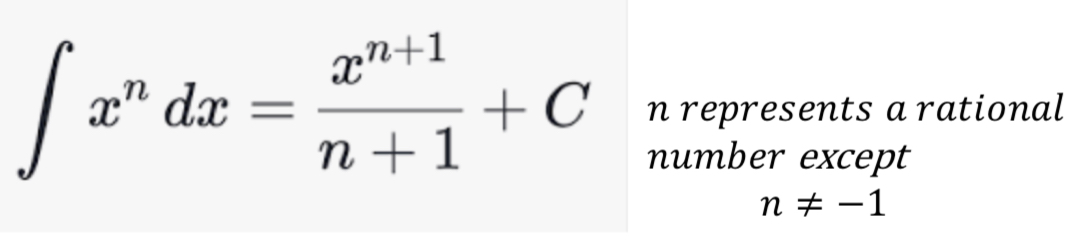
Constant Multiple Rule
The Constant Rule states that the antiderivative of a constant k is kx + C, where C is the constant of integration.
Constant Rule
Multiplier Rule
The Multiplier Rule states that the antiderivative of kf(x) is kF(x) + C, where F(x) is the antiderivative of f(x) and k is a constant.
Addition of Equations Rule
The Addition of Equations Rule states that the antiderivative of the sum of two functions f(x) and g(x) is the sum of their antiderivatives, expressed as F(x) + G(x) + C, where F(x) and G(x) are the antiderivatives of f(x) and g(x), respectively.
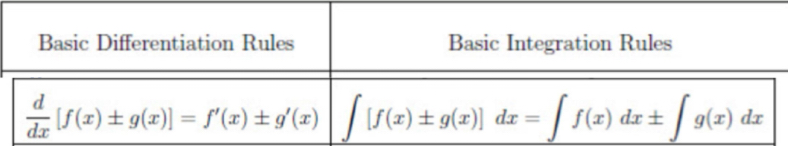
Integral of Sin
The antiderivative of sin(x) is -cos(x) + C.
Integral of Tan
The antiderivative of tan(x) is -ln|cos(x)| + C. Remember ABSOLUTE VALUE!
Integral of Secant
The antiderivative of sec(x) is ln|sec(x) + tan(x)| + C. Remember ABSOLUTE VALUE!
Integral of Cosine
The antiderivative of cos(x) is sin(x) + C.
Integral of Cotangent
The antiderivative of cot(x) is ln|sin(x)| + C. Remember ABSOLUTE VALUE!
Integral of Cosecant
The antiderivative of csc(x) is -ln|csc(x) + cot(x)| + C. Remember ABSOLUTE VALUE!
Integral of Secant Squared
The antiderivative of sec²(x) is tan(x) + C.
Integral of Cosecant Squared
The antiderivative of csc²(x) is -cot(x) + C.
Integral of Secant x Tangent
The antiderivative of sec(x)tan(x) is sec(x) + C.
Integral of Cosecant x Cotangent
The antiderivative of csc(x)cot(x) is -csc(x) + C.
Integral of e^x
The antiderivative of e^x is e^x + C.
Integral of 1/x
The antiderivative of 1/x is ln|x| + C. This is because the derivative of ln|x| is 1/x, confirming the relationship. You can’t use the power rule because x^-1 + 1 = 0, an exception from power rule. REMEMBER ABSOLUTE VALUE!
Integral of a^x
The antiderivative of a^x is {a^x}/{ln(a)} + C, where a > 0.