Light Microscopy Techniques for Cell Visualization
1/473
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
474 Terms
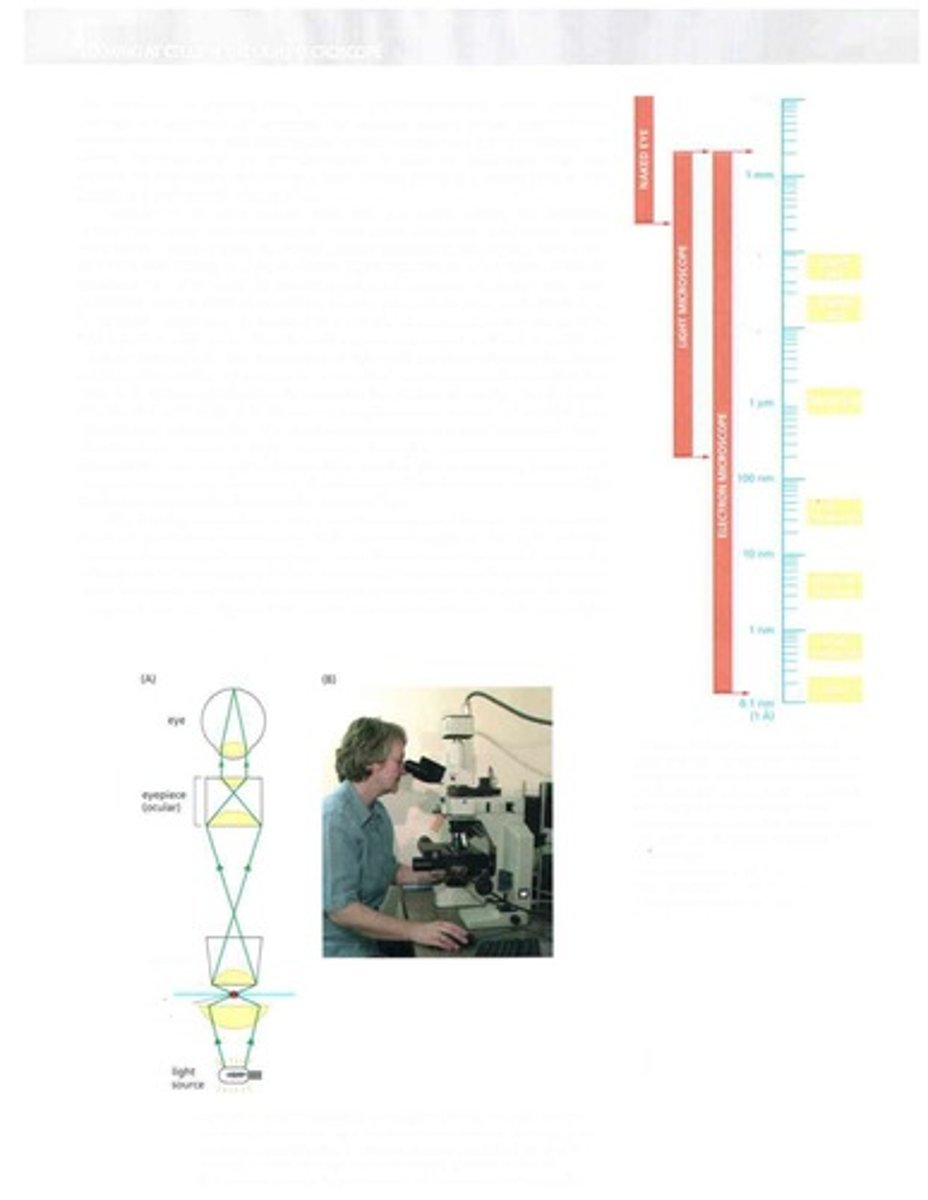
Light Microscope
Instrument for viewing small objects using light.
Plant Cell
Cell type with rigid cell wall and chloroplasts.
Animal Cell
Cell type lacking cell wall, more flexible structure.
Bacterium
Single-celled organism, prokaryotic structure.
Virus
Infectious agent, requires host to replicate.
Ribosome
Cellular structure for protein synthesis.
Globular Protein
Protein with a compact, spherical shape.
Cell Wall
Rigid outer layer of plant cells.
Chloroplast
Organelle for photosynthesis in plant cells.
Prokaryotic Cell
Cell without a nucleus, simpler structure.
Eukaryotic Cell
Cell with a defined nucleus and organelles.
Microscopy
Technique for magnifying small objects.
Resolution
Ability to distinguish two close objects clearly.
Magnification
Increase in apparent size of an object.
Staining
Technique to enhance visibility of cell structures.

Cytoplasm
Gel-like substance within a cell.
Nucleus
Control center of eukaryotic cells.
Cell Membrane
Barrier that controls entry and exit of substances.
Organelles
Specialized structures within a cell.
Cell Theory
Fundamental concept that all living things are composed of cells.
Cell Division
Process by which a cell splits into two.
Tissue
Group of similar cells performing a specific function.
Organ
Structure composed of different tissues working together.
Bacteria
Smallest discernible objects in light microscopy.
Mitochondria
Cellular organelles about 500 nm wide.
Wave Nature of Light
Light behaves as waves, affecting image clarity.
Optical Diffraction
Bending of light waves around edges of objects.
Interference Effects
Light waves combine, altering brightness and clarity.
In Phase Waves
Waves reinforcing each other, increasing brightness.
Out of Phase Waves
Waves canceling each other, reducing brightness.
Limit of Resolution
Smallest distance at which two objects appear distinct.
Wavelength of Light
Distance between successive peaks of light waves.
Numerical Aperture
Measure of lens system's light-gathering ability.
Entry Pupil Width
Diameter of lens opening in a microscope.
Violet Light
Light with a wavelength of approximately 400 nm.
Micrometer (µm)
Unit of length equal to 10^-6 meters.
Nanometer (nm)
Unit of length equal to 10^-9 meters.
Angstrom Unit (Å)
Unit of length equal to 10^-10 meters.
Condenser Lens
Focuses light onto the specimen in microscopy.
Objective Lens
Lens that magnifies the specimen image.
Eyepiece Lens
Lens through which the viewer observes the image.
Fringes
Patterns created by interference of light waves.
Circular Pattern
Diffraction pattern from a point light source.
Dark Ring
Area in diffraction pattern indicating resolution limit.
High Magnification
Increased enlargement of an object for detailed viewing.
Detection
Ability to observe objects below resolution limit.
Fluorescently labeled microtubule
Thin structures visible despite resolution limitations.
Diffraction effects
Causes blurring in observed microscopic images.
Angular resolution
Minimum angle between two distinguishable points.
Cone of illumination
Shape of light rays collected by lenses.
Numerical aperture (NA)
Lens's light-collecting ability, affects resolution.
Refractive index (n)
Measure of light bending in different media.
Wavelength of light (λ)
Distance between successive peaks of light waves.
Working distance
Distance between lens and specimen for focusing.
Depth of field
Thickness of specimen plane in focus.
Phase-contrast microscope
Enhances contrast in transparent specimens using phase shifts.
Differential-interference-contrast microscope
Uses interference to visualize living cell structures.
Dark-field microscope
Illuminates specimen from the side, enhancing visibility.
Brightness in microscopy
Importance of light intensity for clear imaging.
Living cell observation
Studying cells without fixation or freezing.
Fluorescence microscopy
Uses emitted light from fluorescent labels for imaging.
Specimen preparation
Process that may distort or lose cell components.
Light scattering
Process used to visualize features of living cells.
Image blurring
Result of diffraction and resolution limits.
Dark-field microscopy
Illuminates cells from the side, creating bright objects.
Bright-field microscopy
Forms images by direct light passing through cells.
Phase-contrast microscopy
Enhances phase differences to visualize transparent cells.
Differential-interference-contrast microscopy
Uses interference effects to visualize cell structures.
Time-lapse movies
Records frames over time to speed up events.
Digital imaging systems
Use electronic techniques for enhanced microscopy.
Charge-coupled device (CCD)
Sensitive camera technology for low-light imaging.
Image processing
Enhances and analyzes images for better clarity.
Optical faults
Imperfections in microscopes affecting image quality.
Low-light conditions
Environments where light levels are insufficient for visibility.
Fluorescent molecules
Substances that emit light when excited by radiation.
Image digitization
Converts images into electronic format for processing.
Contrast enhancement
Improves visibility of small differences in images.
Random background irregularities
Unwanted variations affecting image clarity.
Digital subtraction
Removes background defects from images.
Microtubules
Cytoskeletal structures with a diameter of 0.025 µm.
Cell migration
Movement of cells from one location to another.
Mitosis
Process of cell division resulting in two daughter cells.
Optical components
Parts of a microscope that manipulate light.
Image noise
Unwanted random variations in image data.
High contrast
Significant difference in light intensity for visibility.
Stained cells
Cells treated with dyes to enhance visibility.
Living cells
Cells that are actively functioning and not fixed.
Fixation
Process to preserve and immobilize tissue samples.
Common Fixatives
Substances like formaldehyde used for tissue preservation.
Cross-linking
Formation of covalent bonds to stabilize proteins.
Embedding Media
Waxes or resins used to support tissue during sectioning.
Microtome
Device for cutting thin sections of tissue.
Section Thickness
Typical thickness of sections is 1-10 micrometers.
Hematoxylin
Dye that stains DNA and acidic proteins blue.
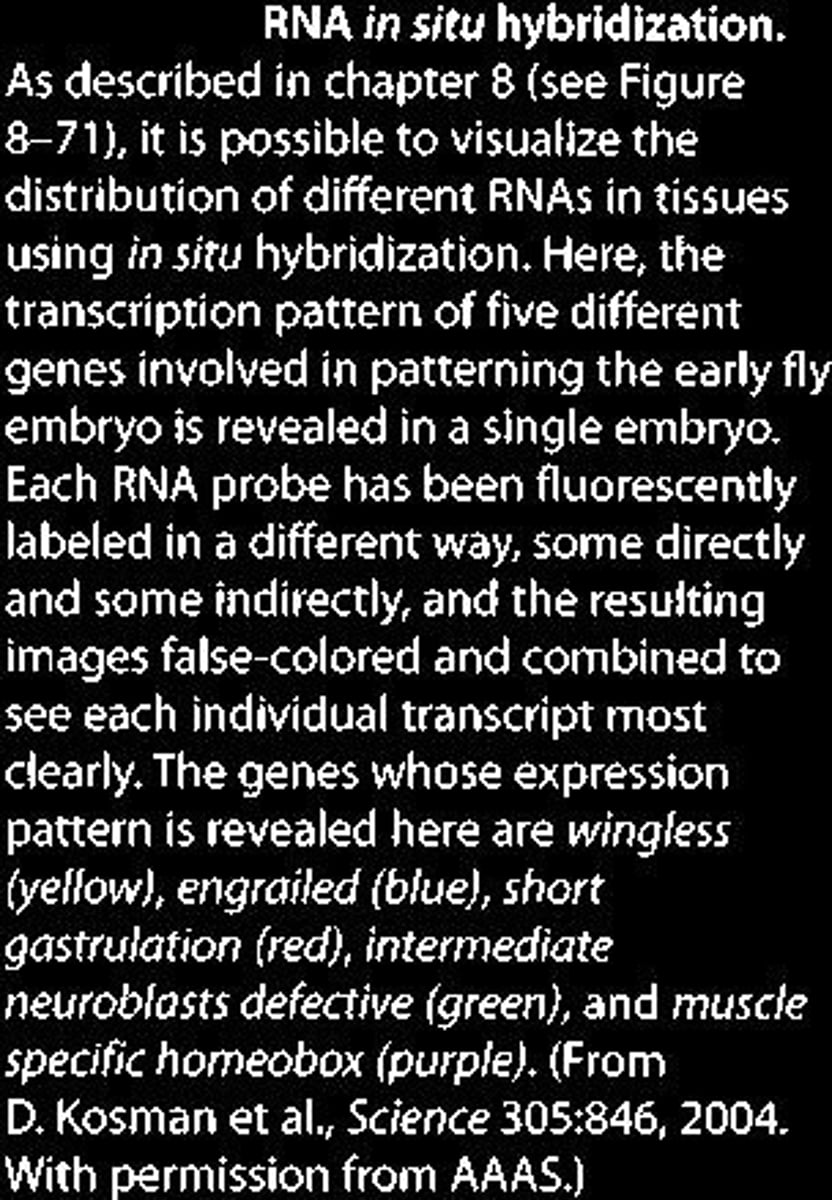
In Situ Hybridization
Technique to visualize RNA distribution in tissues.
Fluorescent Probes
Markers used to localize specific proteins in cells.
Histology
Study of microscopic structure of tissues.
Eosin
Dye that stains cytoplasm and extracellular matrix pink.
Safranin
Dye that stains lignified cell walls red.
Fast Green
Dye that stains cellulosic cell walls green.