Lab 2 (Proton NMR)
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
What is the advantage of using a delta scale for the chemical shift as opposed to hertz?
When using the delta scale the chemical shift it standardizes for all spectrometers since it is independent of magnetic field/
What is a multiplet?
A signal on an NMR spectra that splits into multiple smaller peaks due to neighboring protons
What does upfield mean?
When a signal appears more to the right on the NMR (lower chemical shift)
What is TMS in proton NMR?
The reference compound that is used to standardize the NMR (has a signal of 0 ppm)
What does FID mean?
Free Induction decay
What does it mean when a proton is deshielded?
It means it has less electron density (near electronegative atoms or double bonds), generally are at higher chemical shifts than other protons
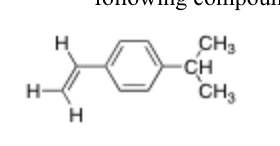
What is the chemical shift and multiplicity for each group of protons in this compound?
7 Unique Protons
3 different vinylic protons ~4.5-6.5
All triplets
2 aryl Protons next to pi bond substituent ~6.5-8
All Doublets
2 Aryl protons protons next to isopropyl group ~6.5-8
All doublets
2 methyl protons on isopropyl ~.9
Doublet
1 Methine proton on isopropyl group ~1.7
Septet
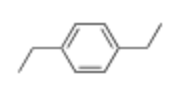
How many signals would you see in this structure?
3 Unique signals due to symmetry
Methyl group at end (Triplet)
Methylene group (quadruplet)
Neighboring aryl protons (Doublets)
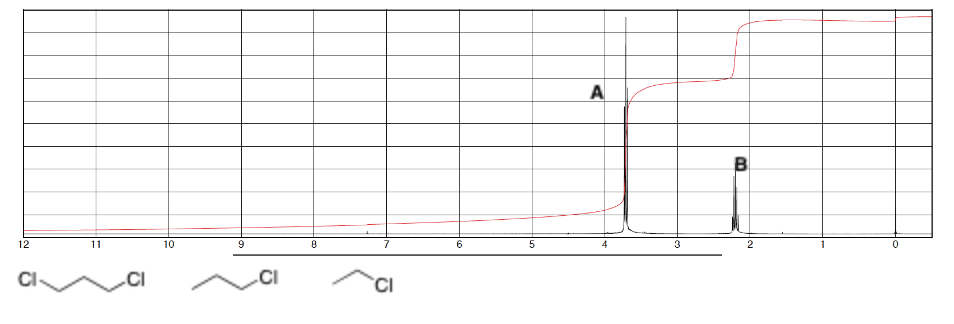
Determine the relative integrations of signal A and B in the spectra and identify which compound it most likely is for, explain.
Integrations appear to be 2 and 1
Most likely 1st compound because higher integration proton is the one with larger integration (more deshielded, aka closer to Cl)
Also there are only 2 unique signals so can’t be 2nd compound
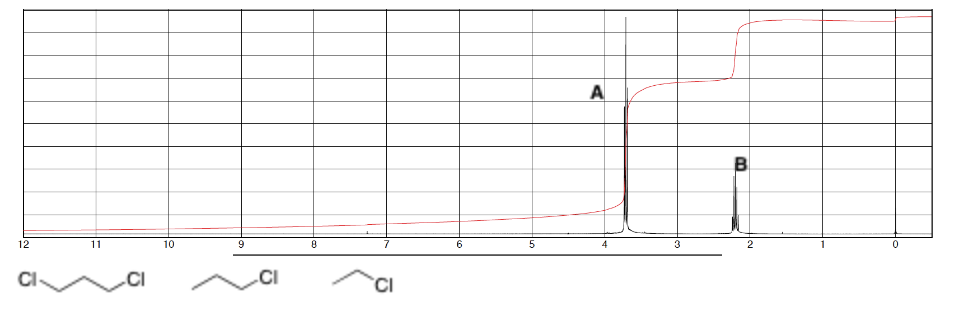
For the spectrum which group of protons is more deshielded, A or B?
A since it has a higher chemical shift
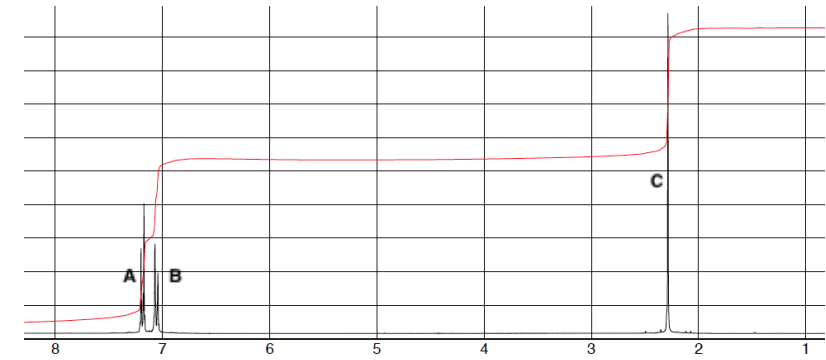
For this spectrum which signal is more downfield
A since it is the highest chemical shift
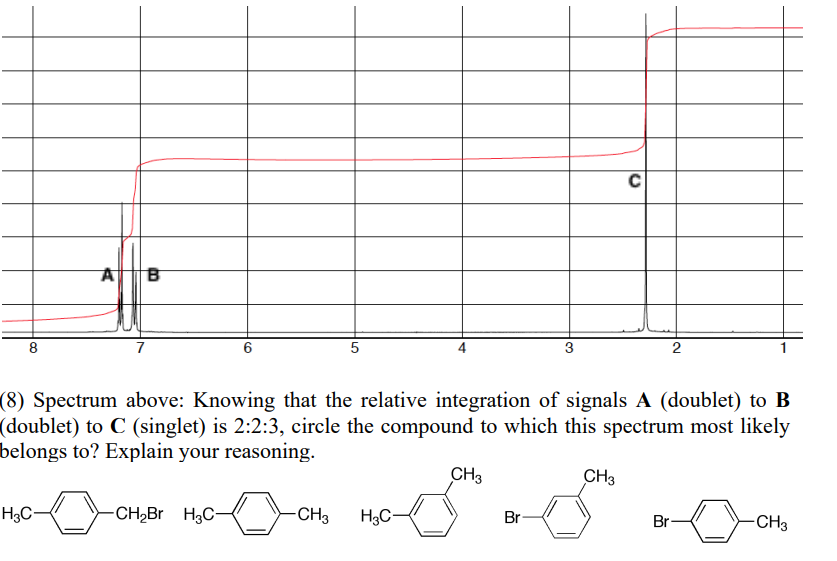
If the integration of A (doublet) B (doublet) and C (singlet) is 2:2:3 which compound would the spectrum be for and explain reasoning
3 unique signals
Isolated methyl group from 3 integration singlet
Both 2 integration doublets are most likely aryl protons
Both pairs have 2 integration because they are symmetrical
Only structure that matches this is the last one
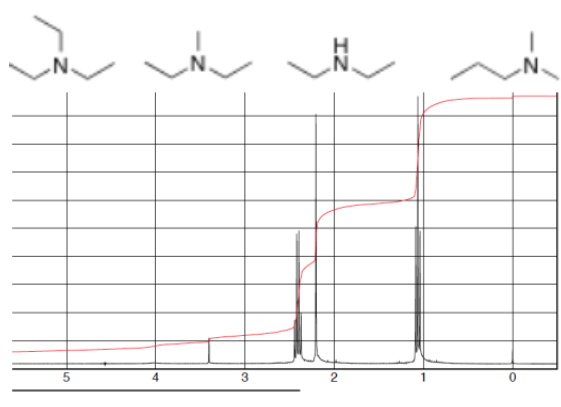
If the integration of signals A (quartet) B (singlet) C (triplet) are 4:3:6 which compound would this spectrum belong to?
3 Unique signals
Signal B is most likely from a methyl group directly attached to Nitrogen
Signal A is most likely from 2 symmetrical methine groups
Signal C is most likely from 2 symmetrical methyl groups
This matches with Structure 2
Parameter in 1H NMR spectroscopy which tells us about a number of protons in close neighborhood of a given proton is:
(1) Integration
(2) Chemical shift
(3) Multiplicity
(4) TMS neighborhood of a given proton is:
Multiplicity
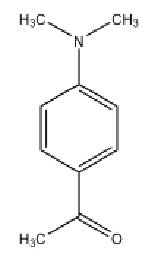
How many signals (multiplets) should you observe for the following compound?
4 Unique Signals
1 From 2 methyl groups attached to amine
1 from equivalent aryl protons next to amine
1 from equivalent aryl protons next to ketone
1 from methyl group on ketone
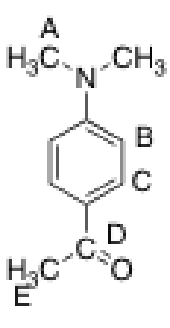
Which of the protons in the following compound should appear at the highest chemical shift in 1H NMR?
B or C since aromatic protons typically have the highest chemical shifts (second to aldehyde and carboxylic acids)
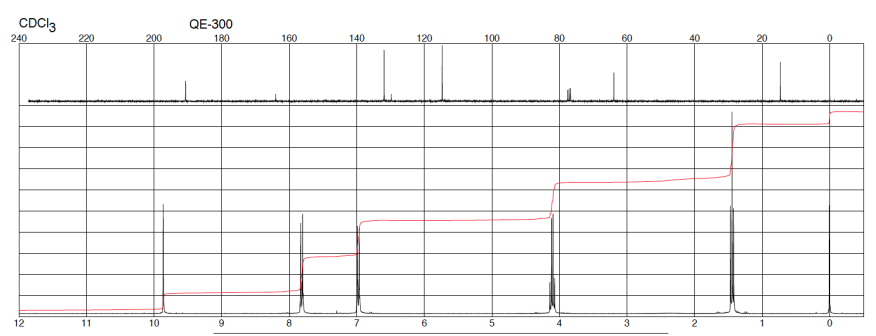
Which statement about compound which 1H NMR spectrum is shown above is incorrect?
1. Compound has an aldehyde group.
2. Compound has aromatic ring
3. Compound is a monosubstituted derivative of benzene
4. Compound has an ethyl group
3, this is because of the 2 different signals in the 6.5-8 ppm range