anatomy 403: neuro 3
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
direct motor pathways
somatic = voluntary = skeletal muscle
motor cortex: contains upper motor neurons
the primary motor area of the cerebral cortex is responsible for initiation of voluntary movements (_____, _____)
spinal cord: contains lower motor neurons (alpha motor neurons)
these neurons connect to skeletal muscle
area 4, prefrontal cortex
direct motor pathways
name the pathway
motor cortex → subcortical white matter → internal capsule → crus cerebri → basal pons → pyramids → corticospinal tracts → spinal cord ventral horn → central roots → peripheral nerves → skeletal muscle
direct motor pathways
the _____ is responsible for thinking about moving
premotor cortex
direct motor pathways
the _____ is responsible for initating movement (upper motor neurons)
primary motor cortex (precentral gyrus)
direct motor pathways
internal capsule
_______: carries motor axons to trunk and extremities
continues as the crus cerebri
_____: carries fibers that go to brainstem
______ tracts: motor cortex to skeletal muscles of head and neck to coordinate precise, voluntary movements, travel in this area
posterior limb, genu, corticonuclear
direct motor pathways
_____: motor cortex to skeletal muscles of head and beck to coordinate precise, voluntary movement, travel in genu of internal capsule
corticonuclear tracts (corticobulbar)
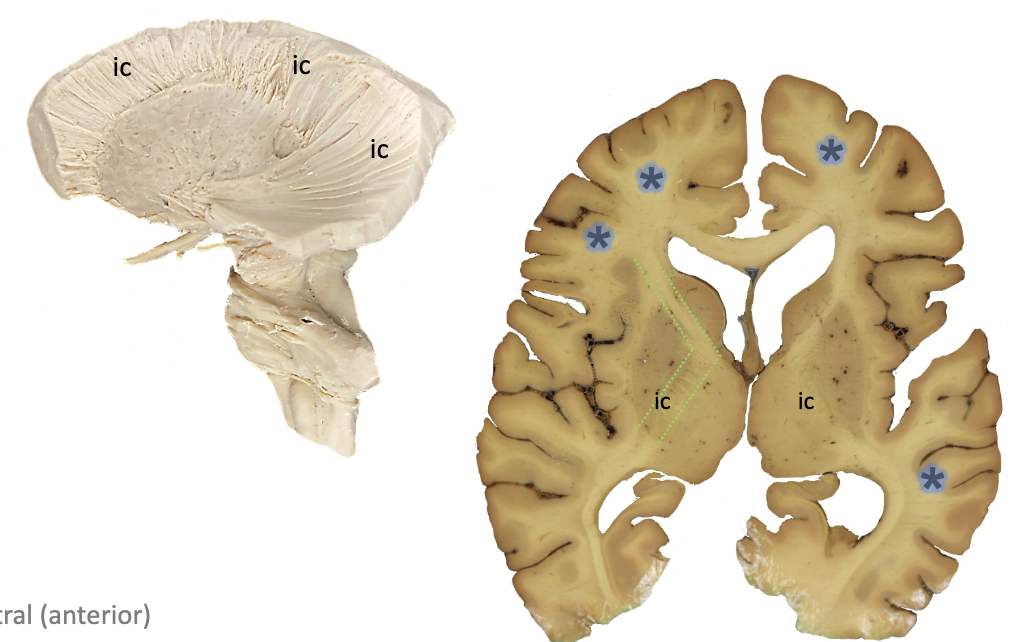
ic?
subcortical white matter
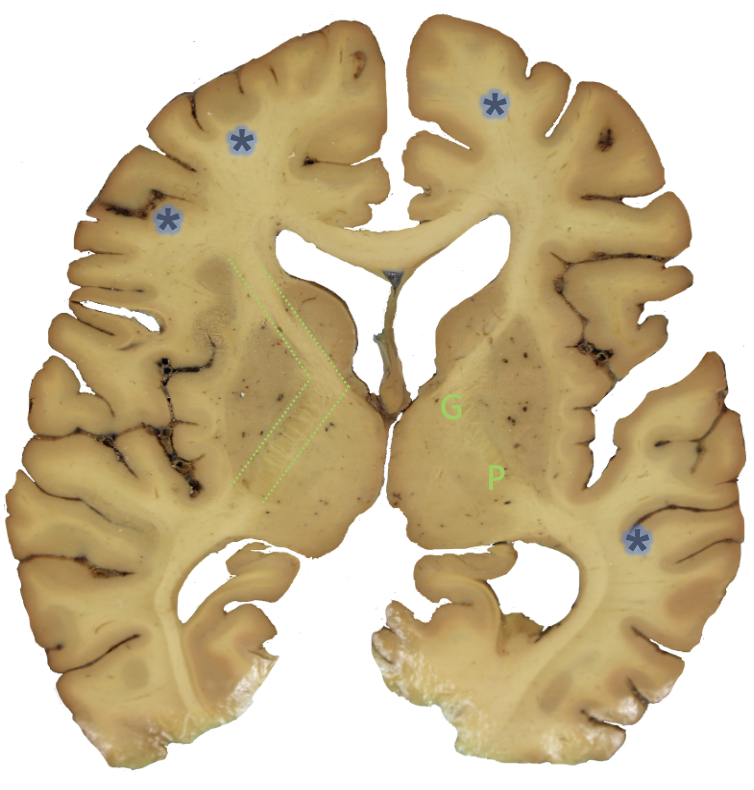
g?
genu
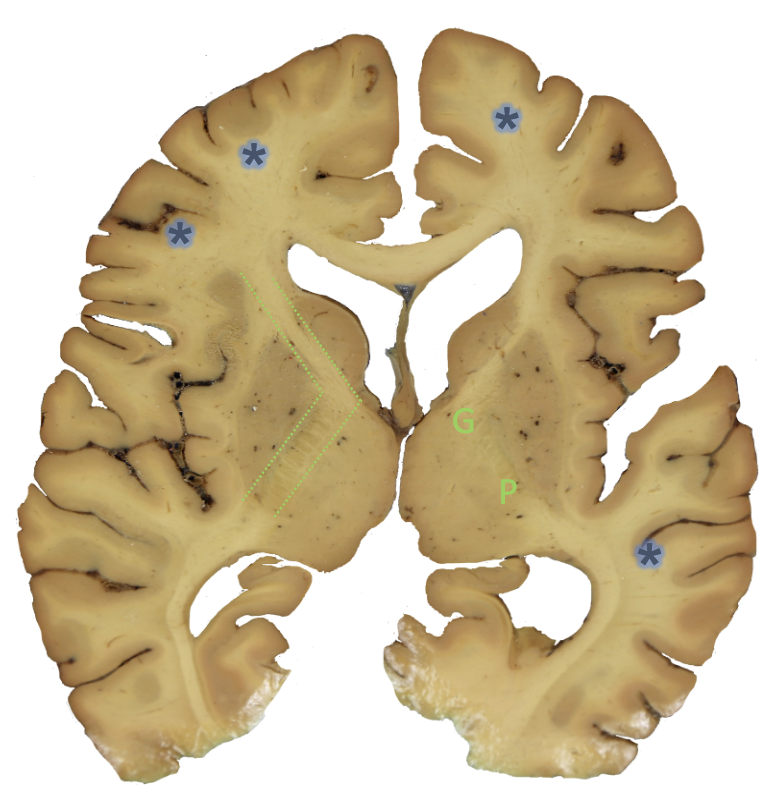
p?
posterior limb
direct motor pathways
lower motor neurons = motor nuclei of cranial nerves ___, ____, ____, and ___
V, VII, IX, XIII
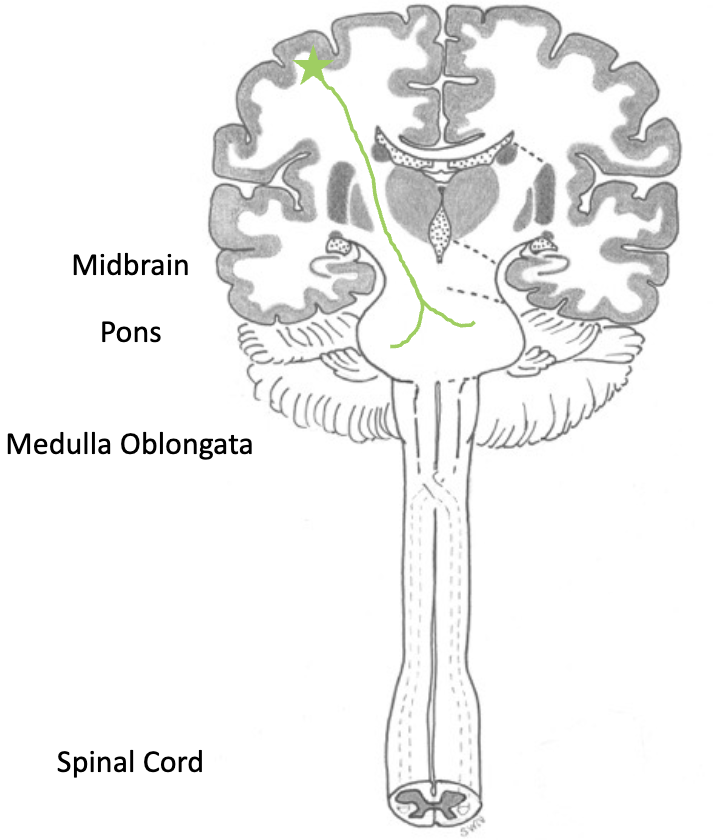
direct motor pathways
discrete voluntary (somatic) movement of muscles of neck, larynx, tongue, head, and face
axons travel through the _______, genu of the internal capsule and crus cerebri
axons cross ______ at the level of the motor nucleus they innervate (lower motor neurons, no discrete decussations)
innervate head and neck muscles via the cranial nerves
unlike spinal cord, innervation is often ______
corona radiata, midline, bilateral
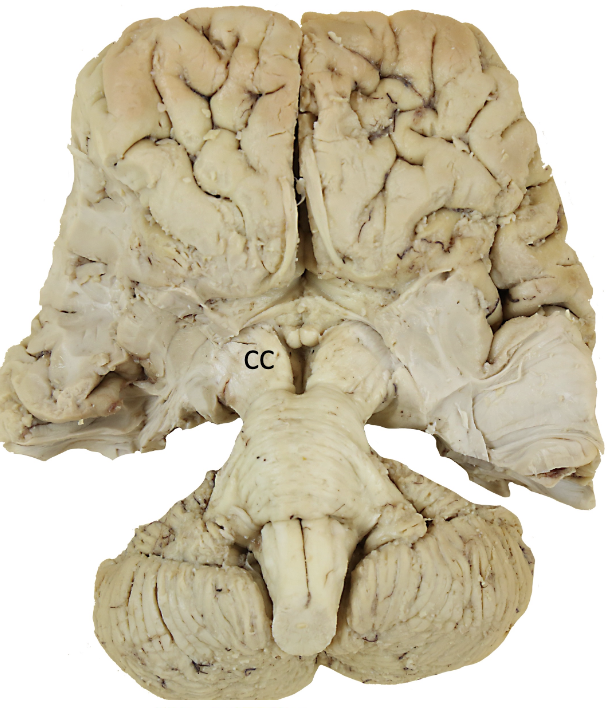
direct motor pathways
the crus cerebri is the continuation of the posterior limb of the ______
the base of the midbrain
internal capsule
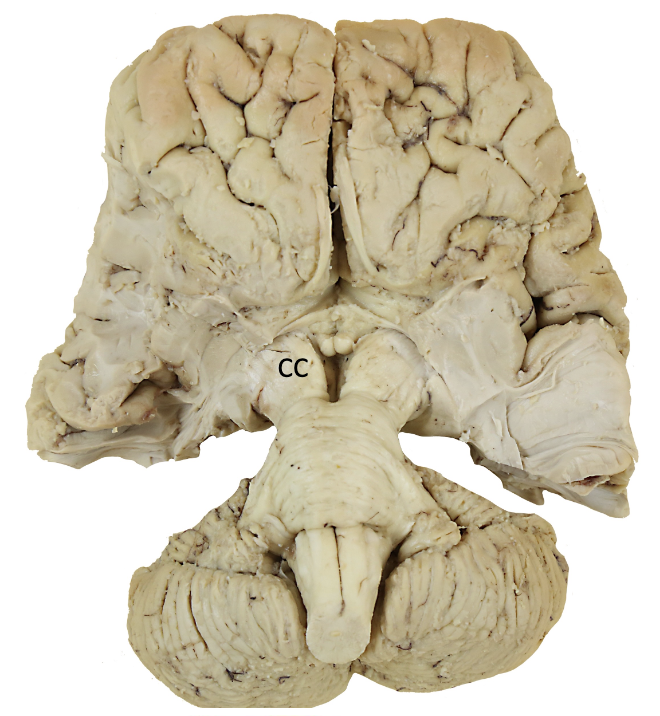
cc?
crus cerebri
direct motor pathways
______: defines the border between the spinal cord and medulla oblongata
pyramidal decussation
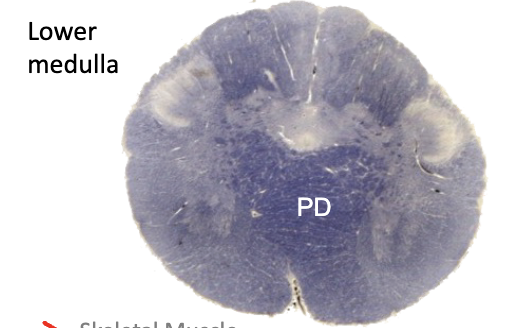
pd?
pyramidal decussation (diagram)
direct motor pathways
corticospinal tracts:
_____ corticospinal tract: all fibers have crossed here
_____ corticospinal tract: cross in the spinal cord
lateral, ventral
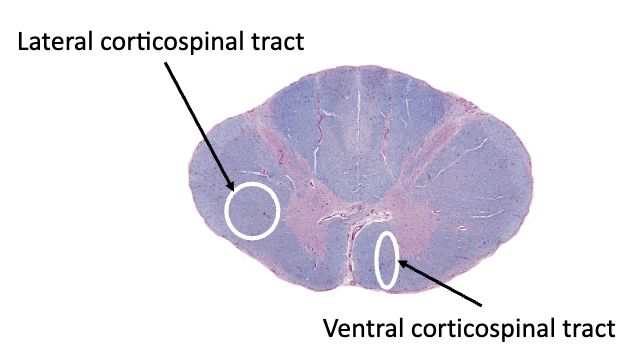
direct motor pathways
lateral corticospinal tract:
motor cortex control skeletal muscles on the _____ side of the body
precise, voluntary movements of the arms and legs
fibers cross at the ________
opposite, pyramidal decussation
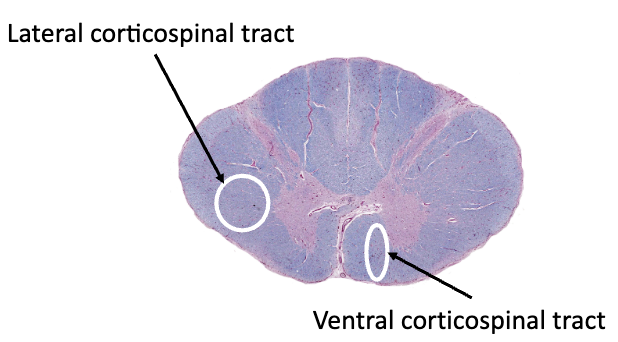
direct motor pathways
ventral (anterior) corticospinal tract
motor cortex control of skeletal muscles on _____ sides of the body
trunk movements (trunk moves as a unit)
most of the fibers cross in the spinal cord and some don’t
both
direct motor pathways
spinal cord ventral horn
corticospinal tracts synapse in the _____
alpha motor neurons project their axons via the _____
ventral horn, ventral roots
indirect motor pathways
NOT part of the pyramidal process
3 descending pathways: _____, _____, _____
vestibulospinal tract, reticulospinal tracts, tectospinal tract
indirect motor pathways
what organs make up the vestibulospinal tract?
vestibular nuclei, pons, and medulla
indirect motor pathways
what organs make up the reticulospinal tract?
reticular formation found throughout the brainstem
indirect motor pathways
what organs make up the tectospinal tract?
superior colliculi and midbrain
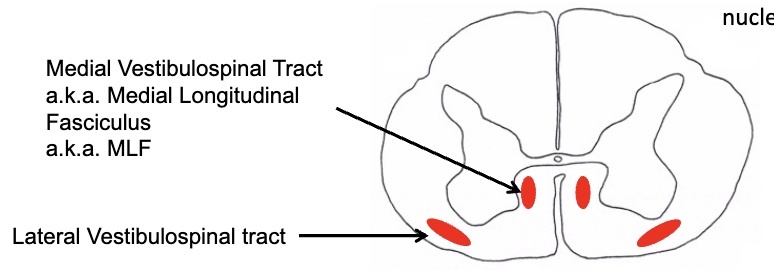
indirect motor pathways
vestibulospinal tracts
reflexive regulation of balance and posture
medial vestibulospinal tracts descend _______ through cervical segments of spinal cord and influences neck musculature
lateral vestibulospinal tracts descends to _______ segments of spinal cord, antigravity muscles
bilaterally, lumbar-sacral
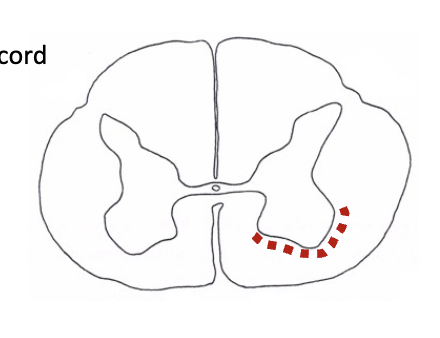
indirect motor pathways
reticulospinal tracts (reticular formation found throughout brainstem)
functions to set ________ (adjust posture) in anticipation of a movement
origin = reticular formation in pons and medulla
found at all levels of the spinal cord
muscle tone
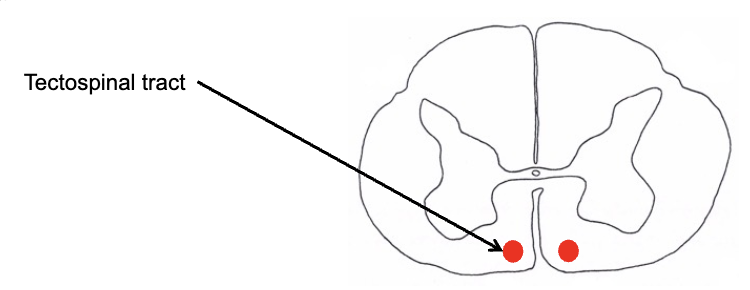
indirect motor pathways
tectospinal tract
mediates reflexive movement of head and neck in response to _____ stimuli (predominantly vision and hearing)
originates from the _______ (SC, midbrain) and descends through cervical levels of the spinal cord
sensory, superior colliculus
basal nuclei aka basal ganglia
the basal nuclei are a collection of interconnected subcortical nuclei that function as a central link in the part of the motor system that translates the ______ to move into action
“______”
“select” desired behaviors and “inhibit” unwanted behaviors
while these are called the basal ganglia, we all know that ganglia are by definition OUTSIDE of the CNS
desire, organ of habit
basal nuclei
do not make direct or indirect ______ connections with the motor neurons in the spinal cord or brain stem
consist of parallel, anatomical loops that originate in the cortex, pass through the basal nuclei, project to ________ then back to the cortex
synaptic, dorsal thalamus
basal nuclei
what makes up the striatum?
caudate nucelus and putamen
basal nuclei
what is located in the pallidum?
globus pallidus
basal nuclei
what part of the basal nuclei is in the brain stem?
substantia nigra
basal nuclei
what part of the basal nuclei is in the diencephalon?
subthalamic nucleus
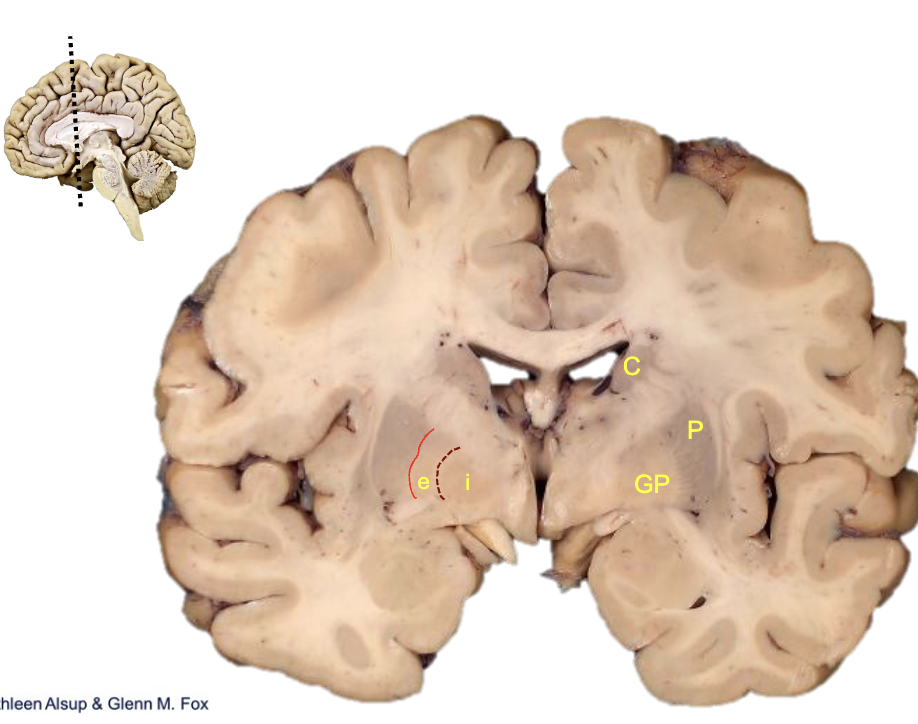
what is c?
caudate
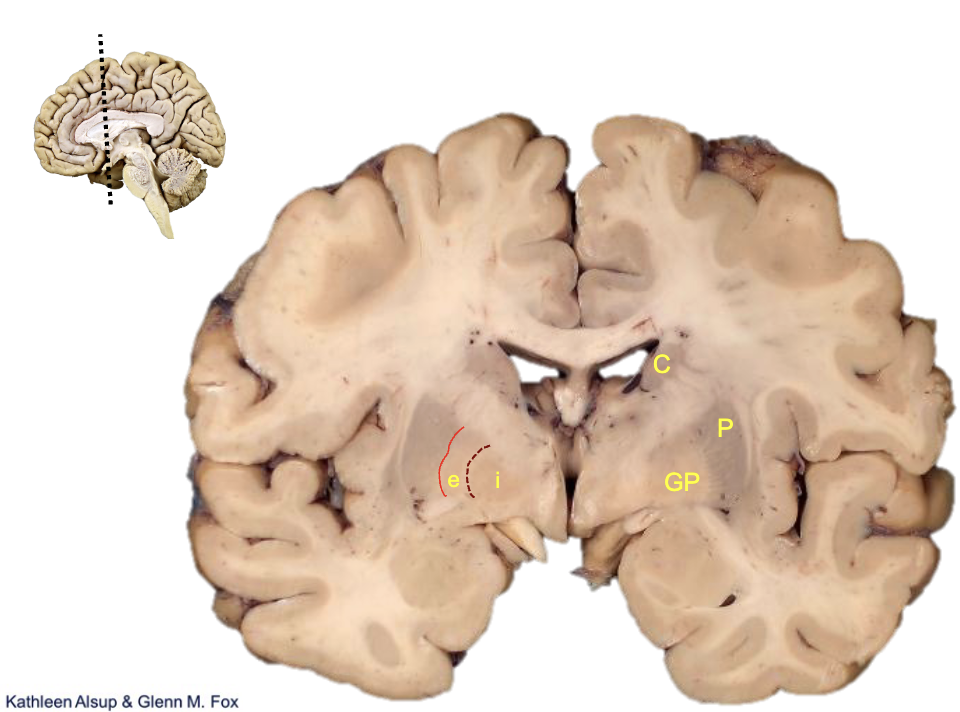
what is p?
putamen
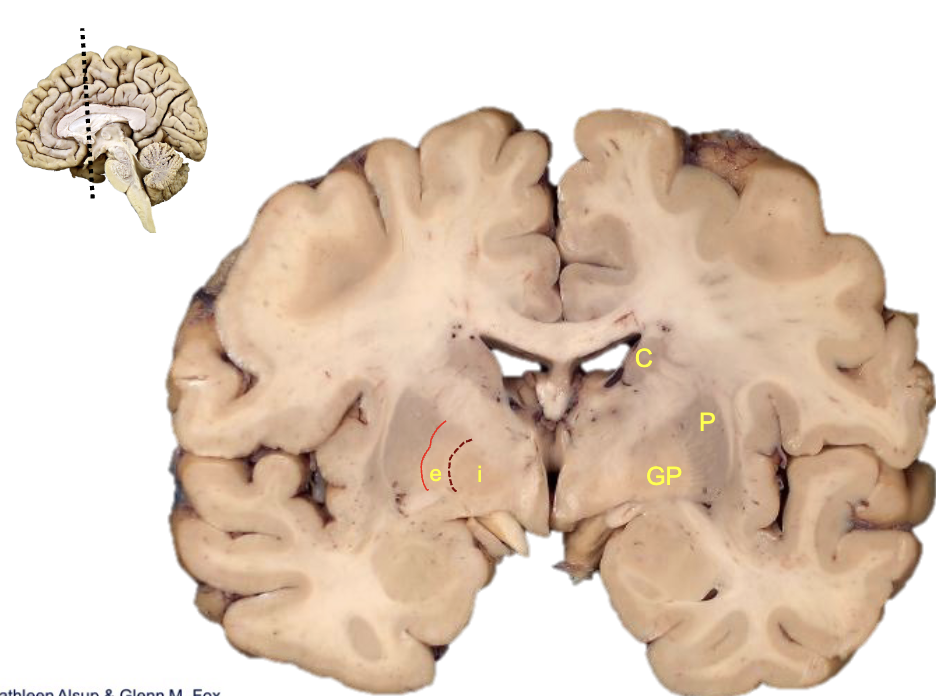
what is gp?
globus pallidus
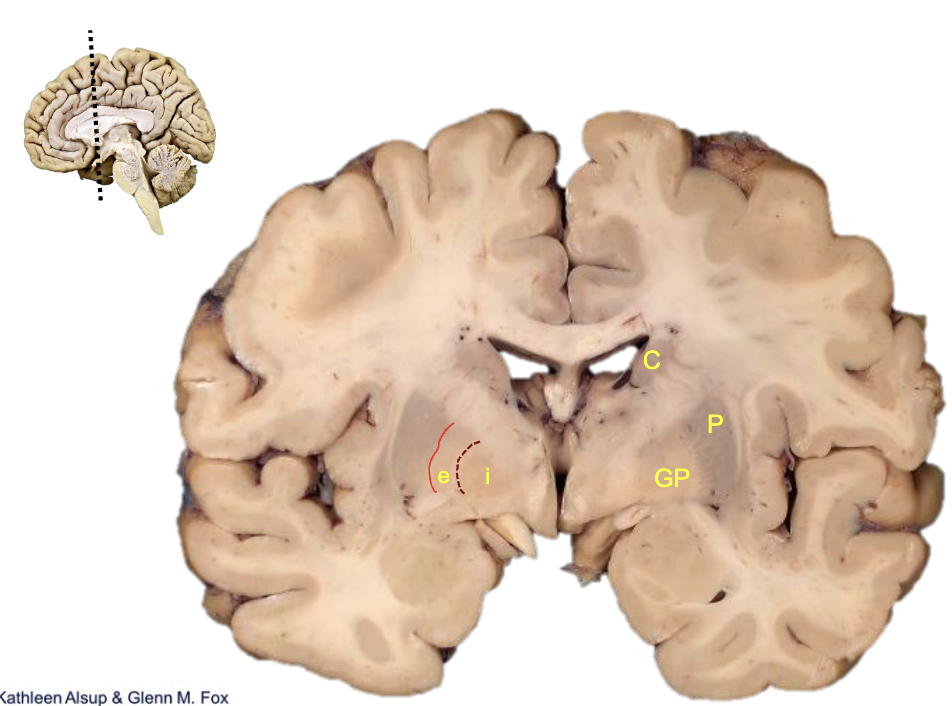
what is i?
internal segment
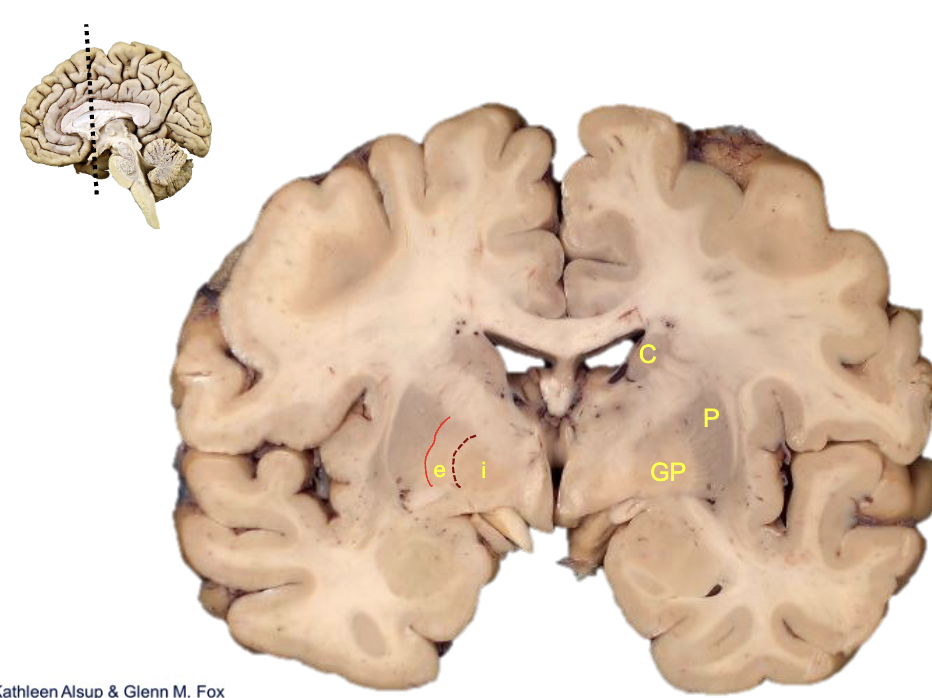
what is e?
external segment
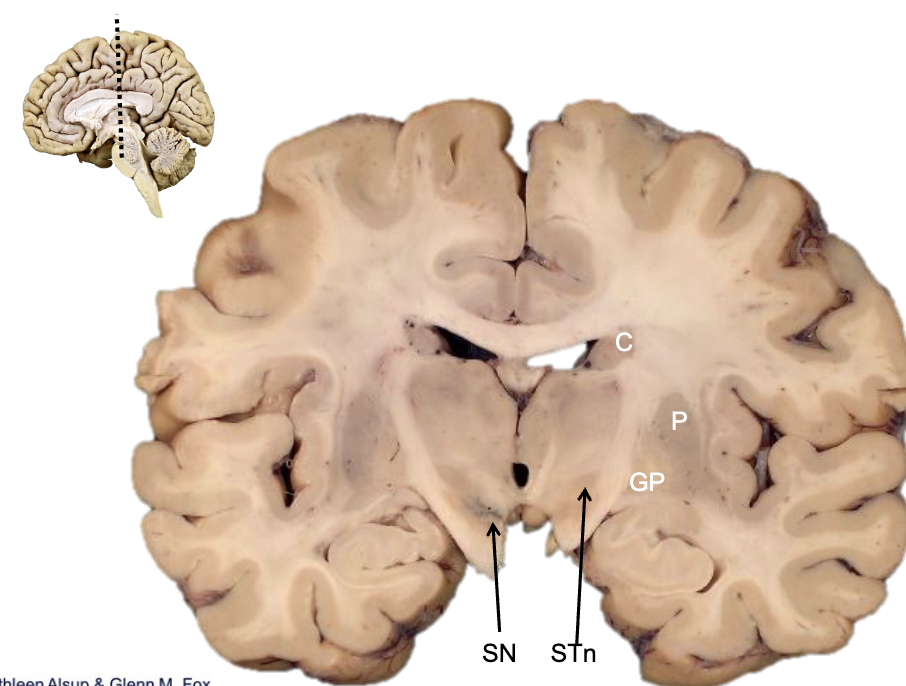
what is STn?
subthalamic nucleus
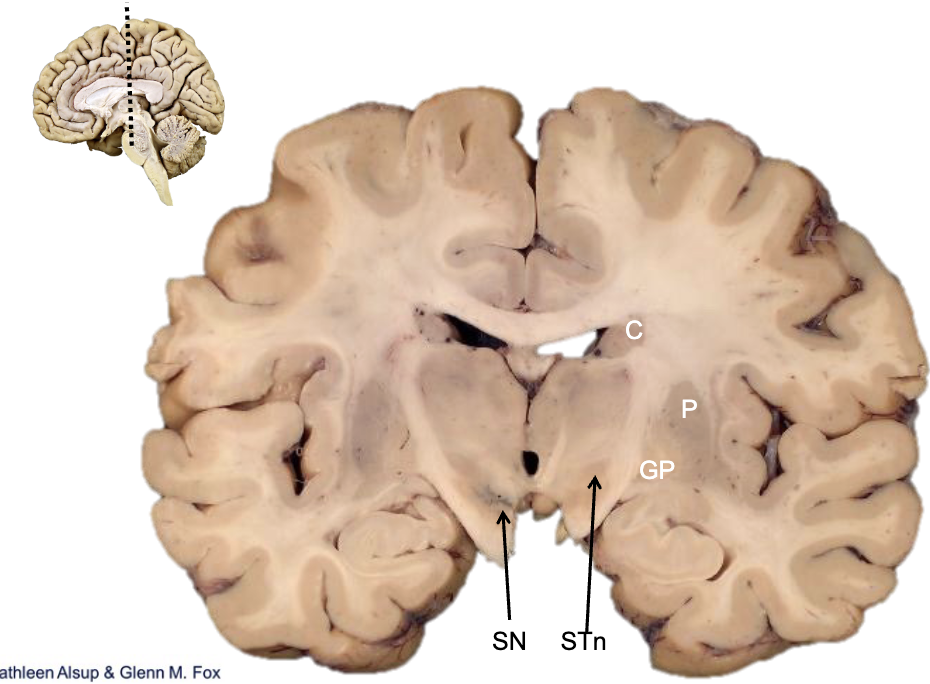
what is SN?
substantia nigra
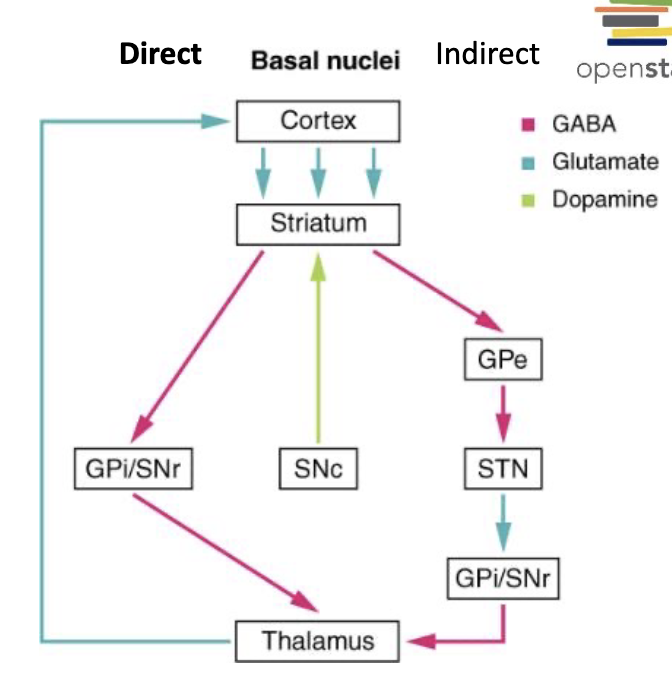
basal ganglia
______ facilitates appropriate motor programs
______ inhibits competing motor programs
direct pathway, indirect pathway