Practicum 3
1/125
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
126 Terms
occipital bone
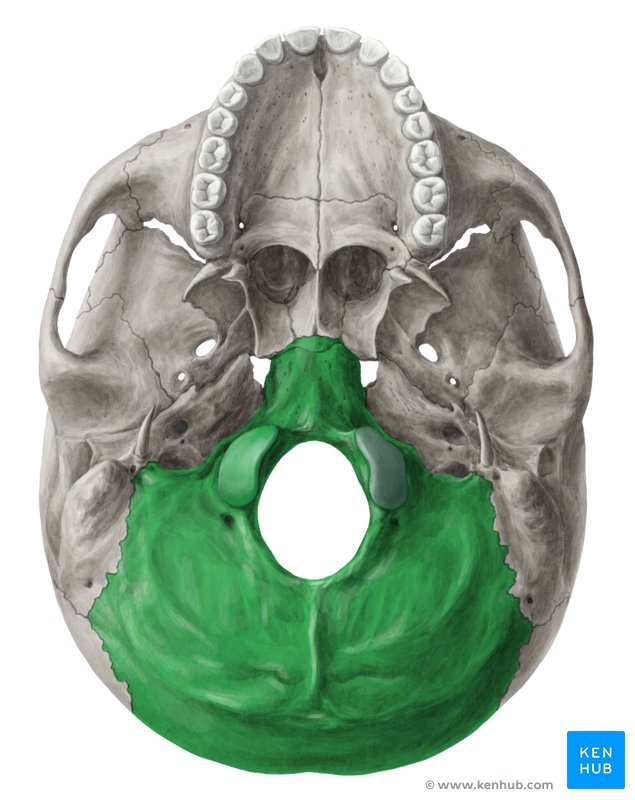
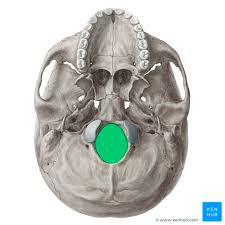
foramen magnum
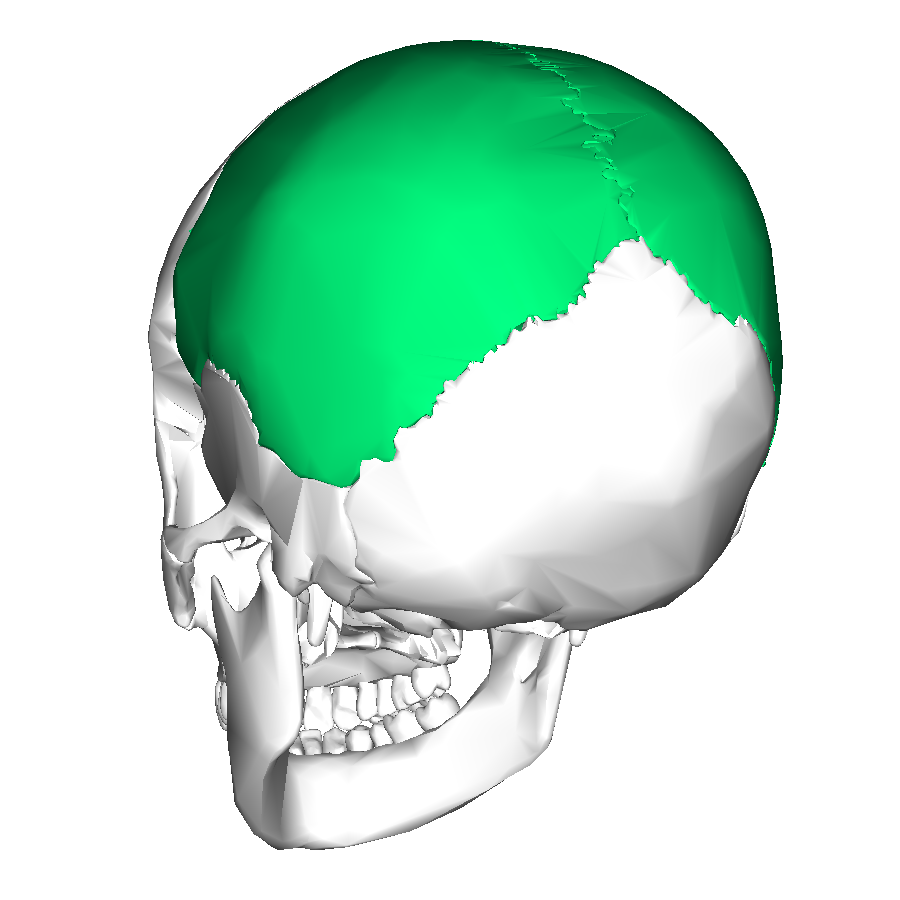
parietal bones (L/R)
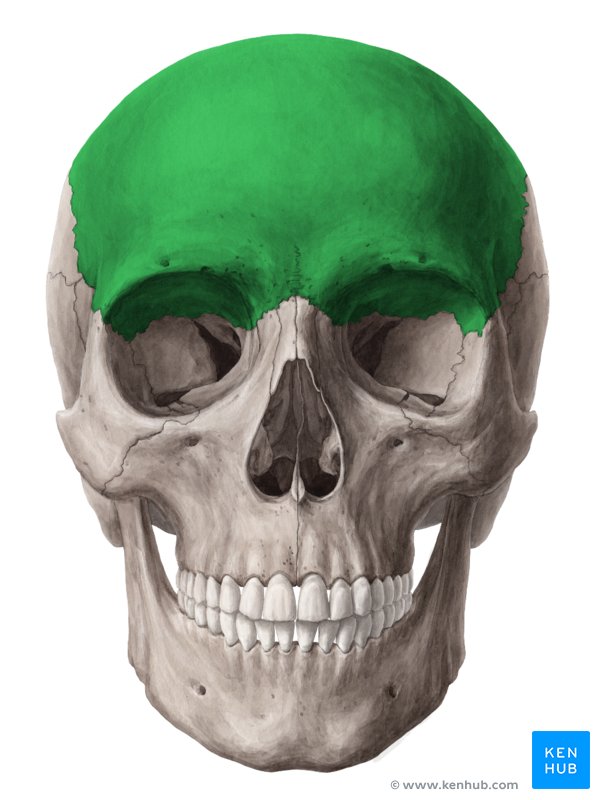
frontal bones
temporal bones (L/R)
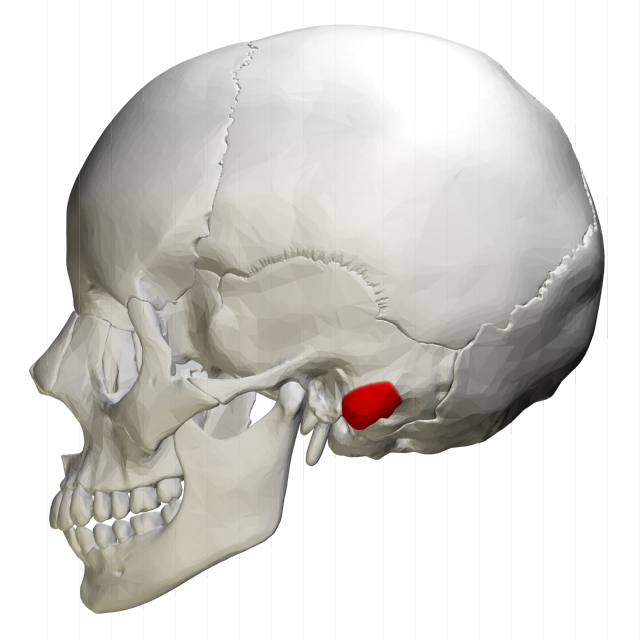
mastoid process
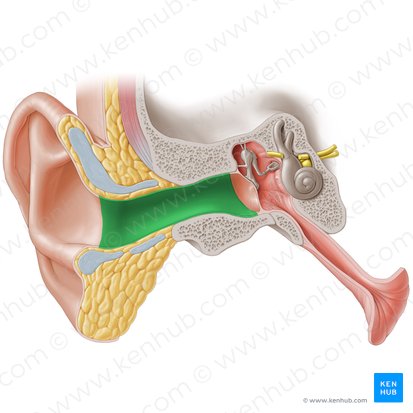
external acoustic meatus
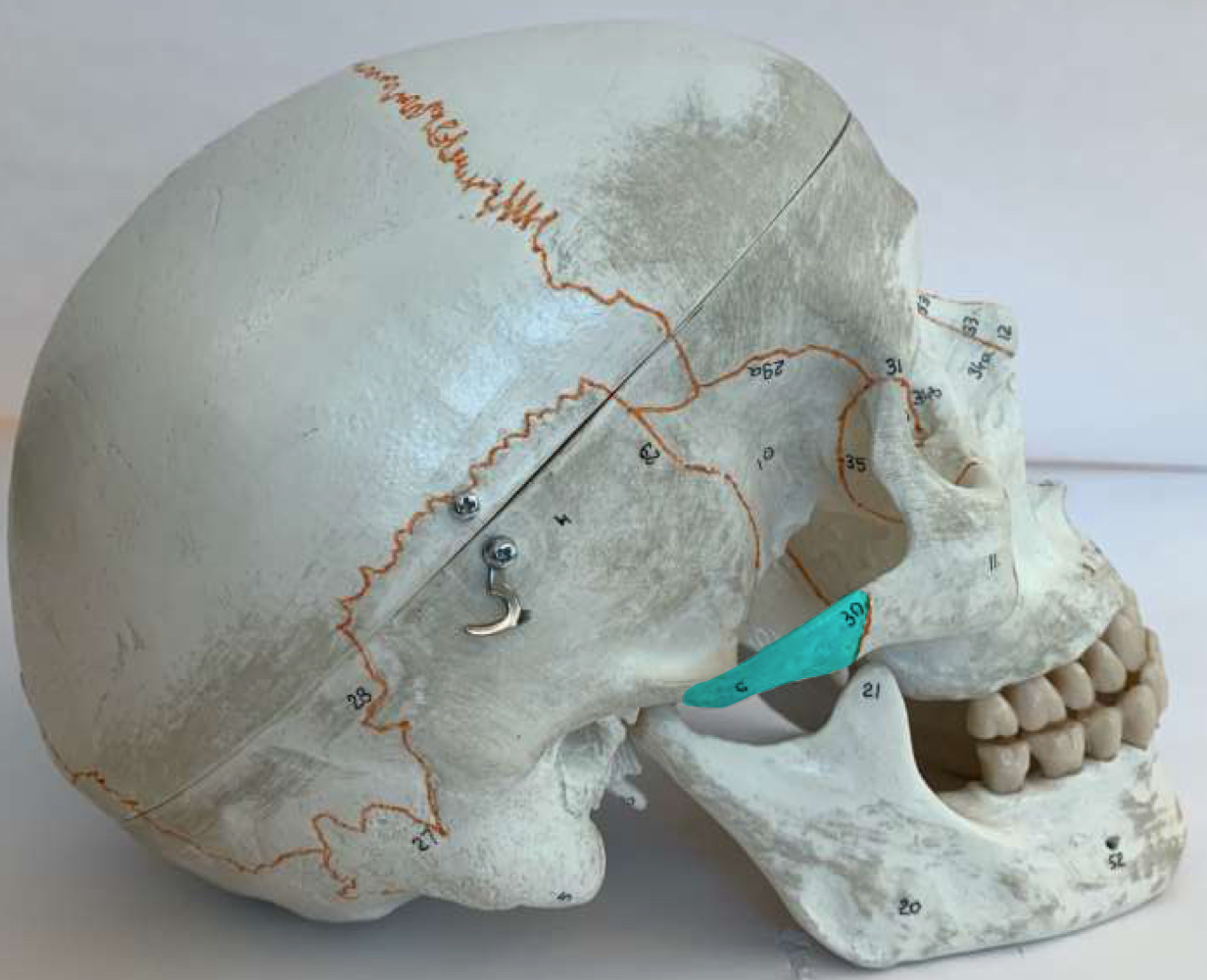
zygomatic process
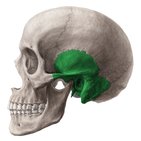
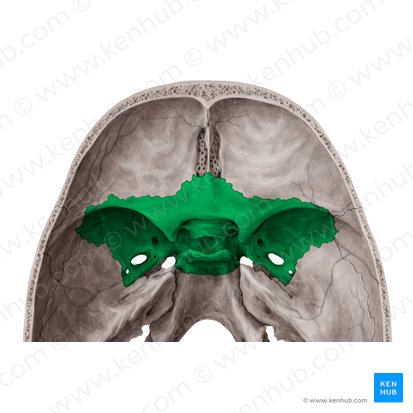
sphenoid bone
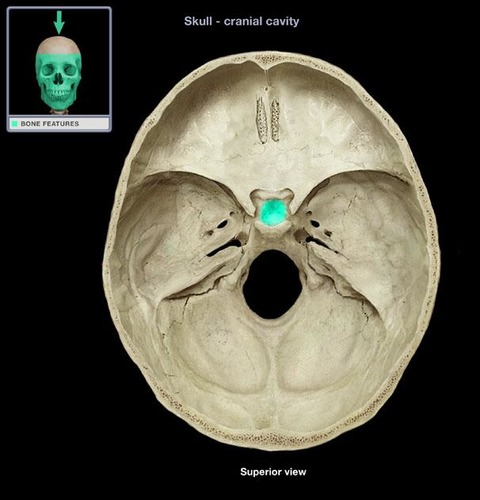
sella turcica
ethmoid bone
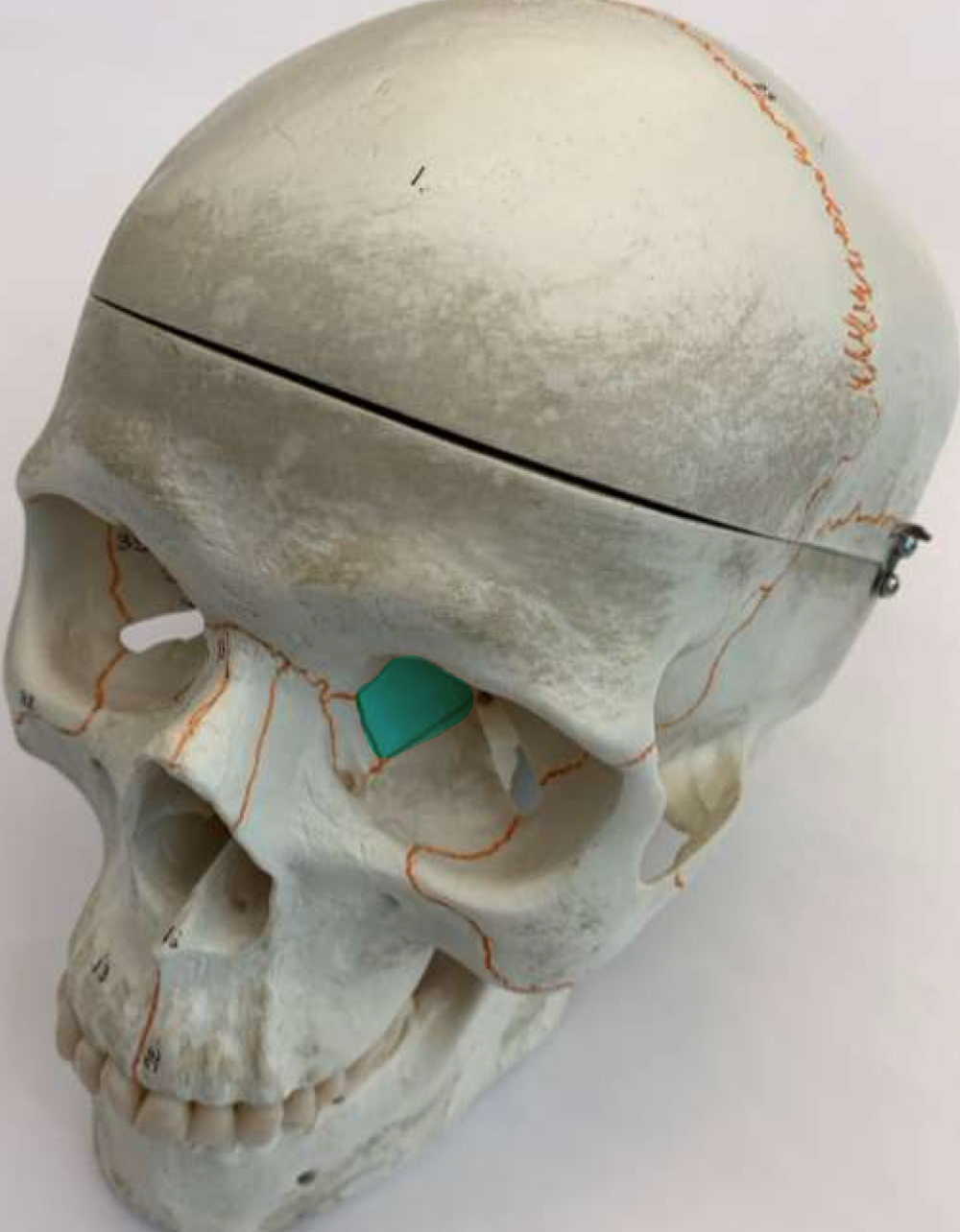
crista galli
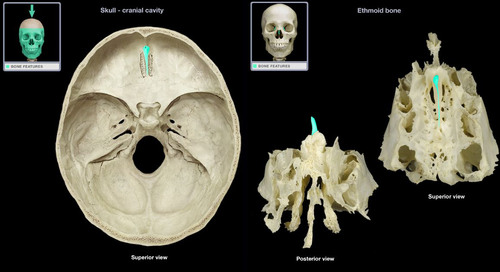
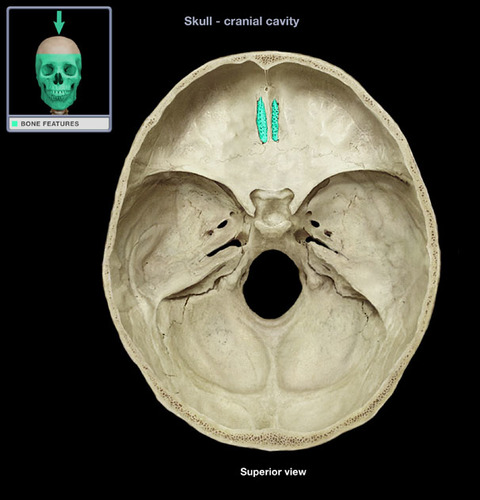
cribriform plate
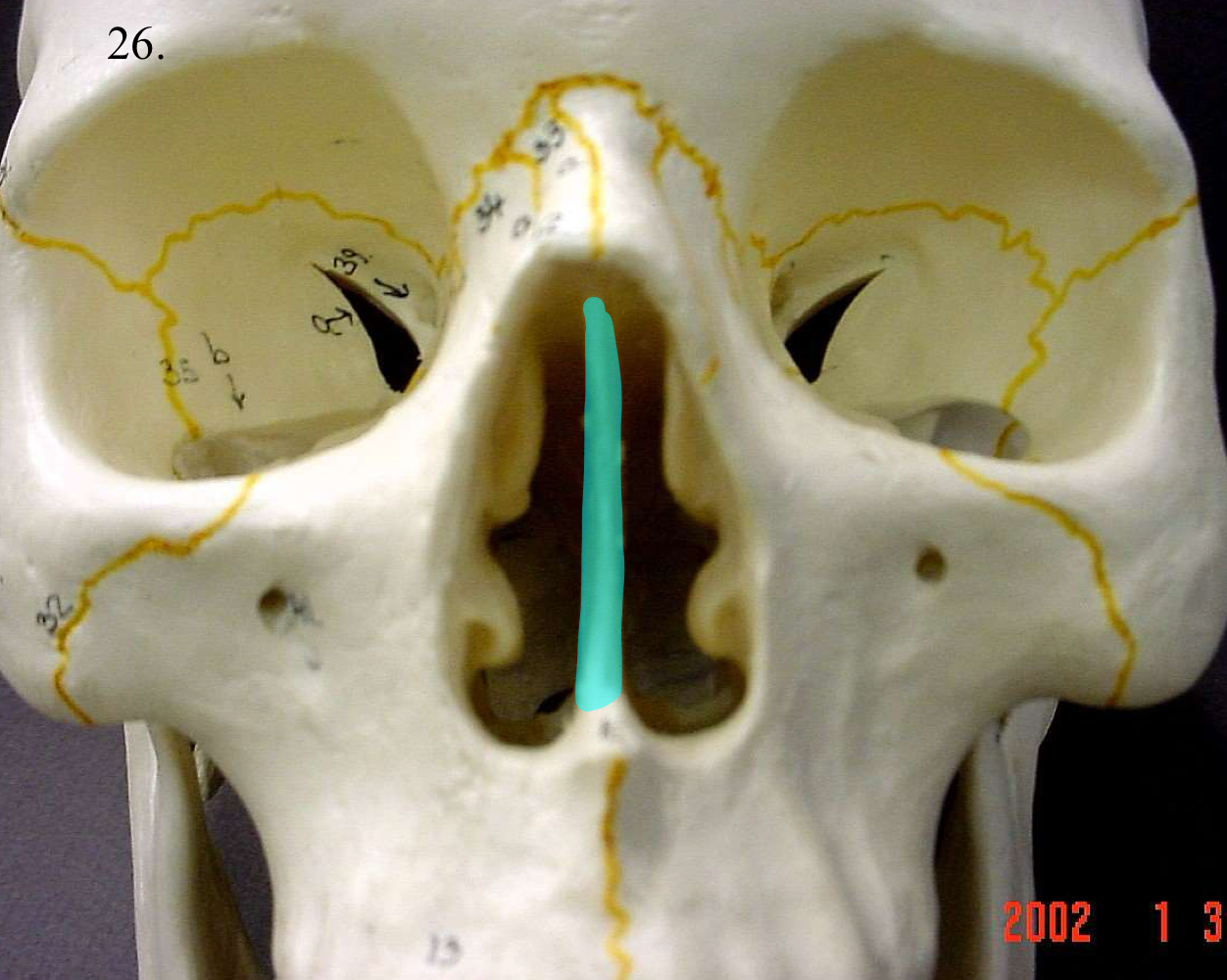
perpendicular plate
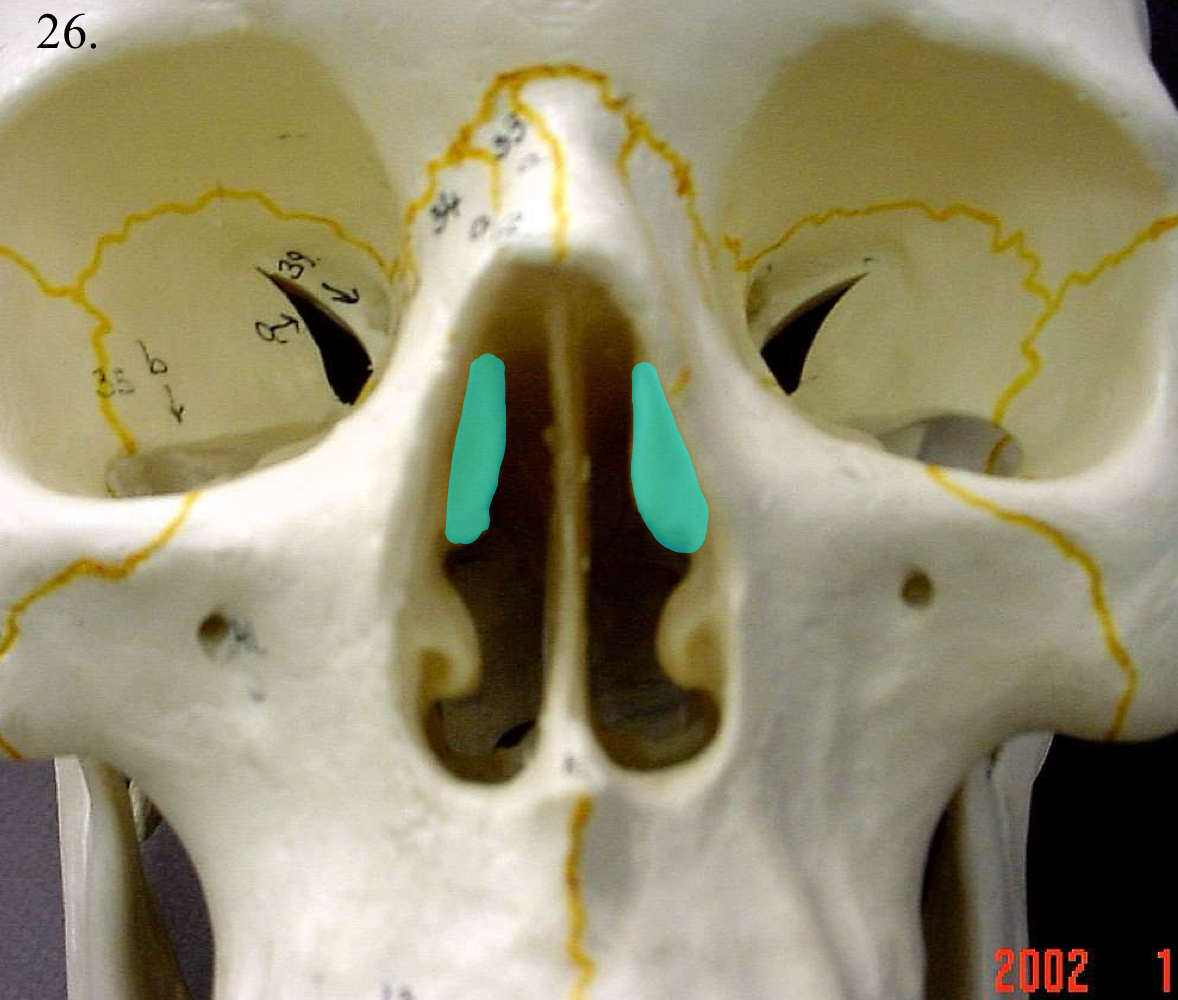
nasal conchae middle
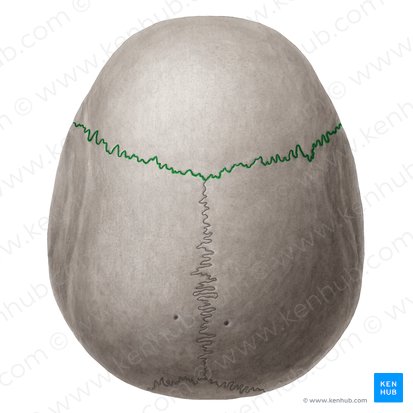
coronal suture
lambdoidal suture
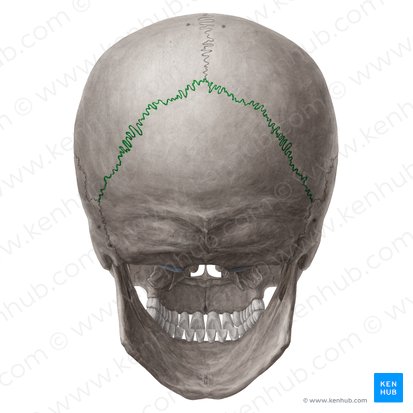
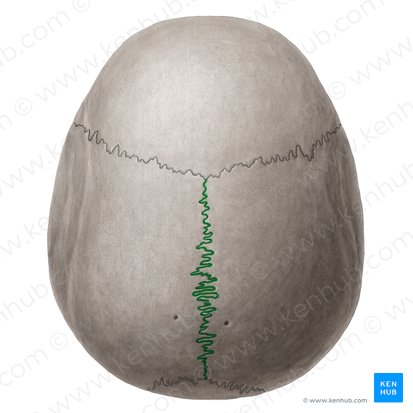
sagittal suture
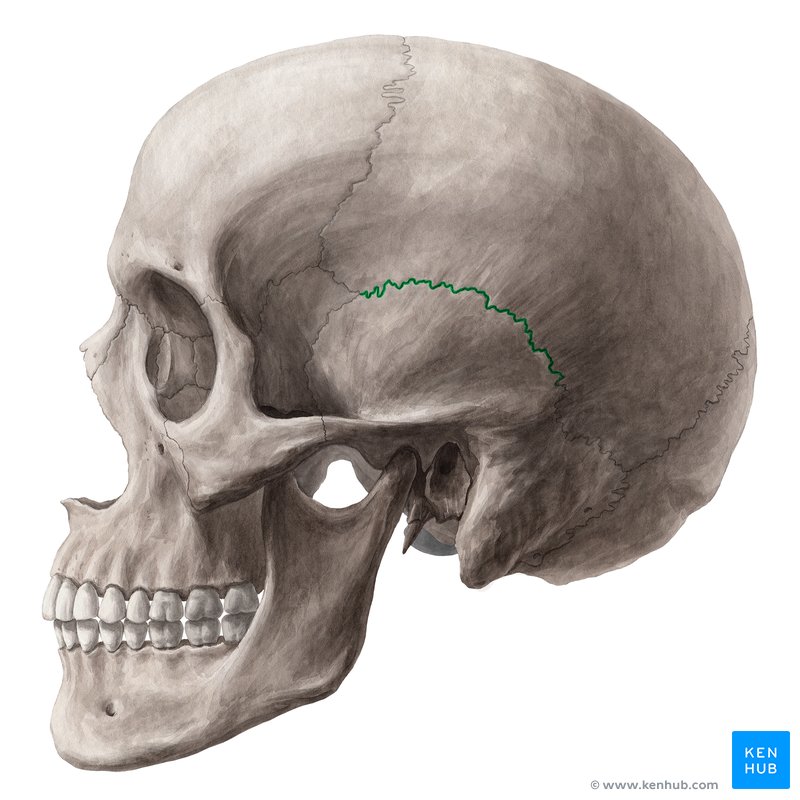
squamous suture
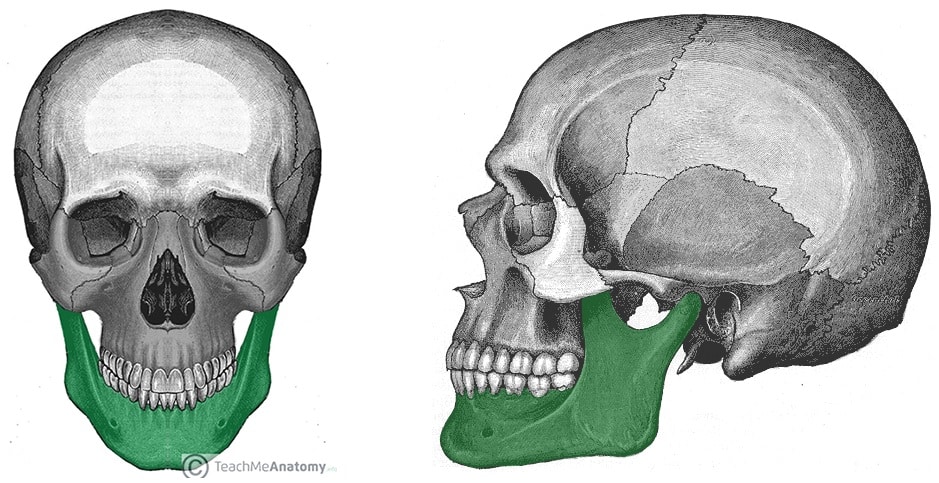
mandible (jaw)
condylar process
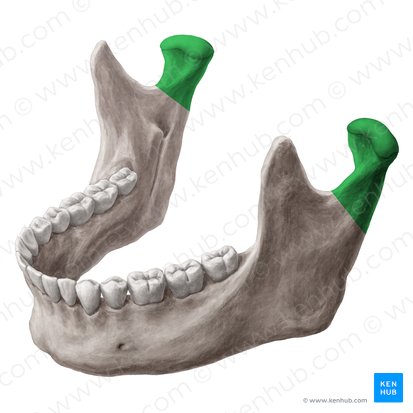
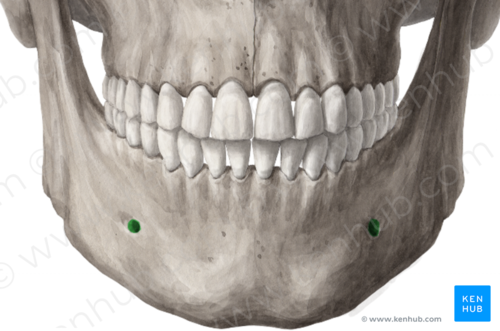
mental foramen
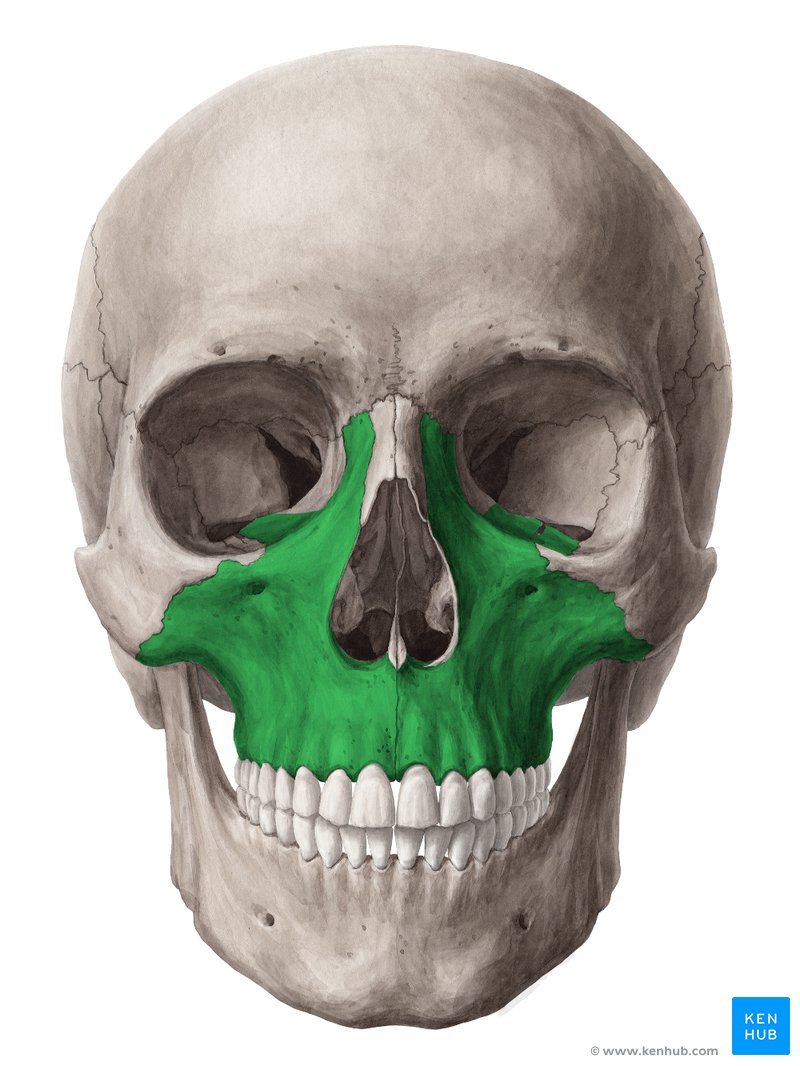
maxillae (L/R)
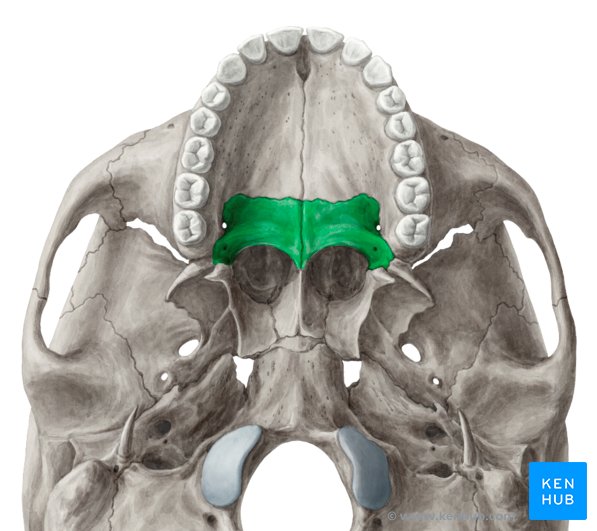
palatine bones (L/R)
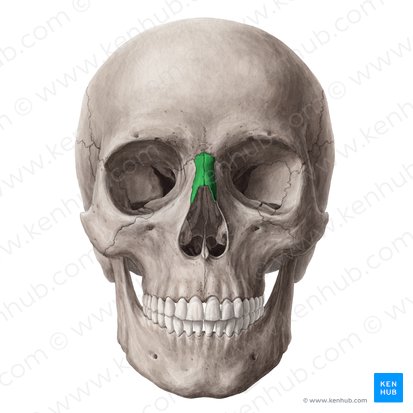
nasal bones (L/R)
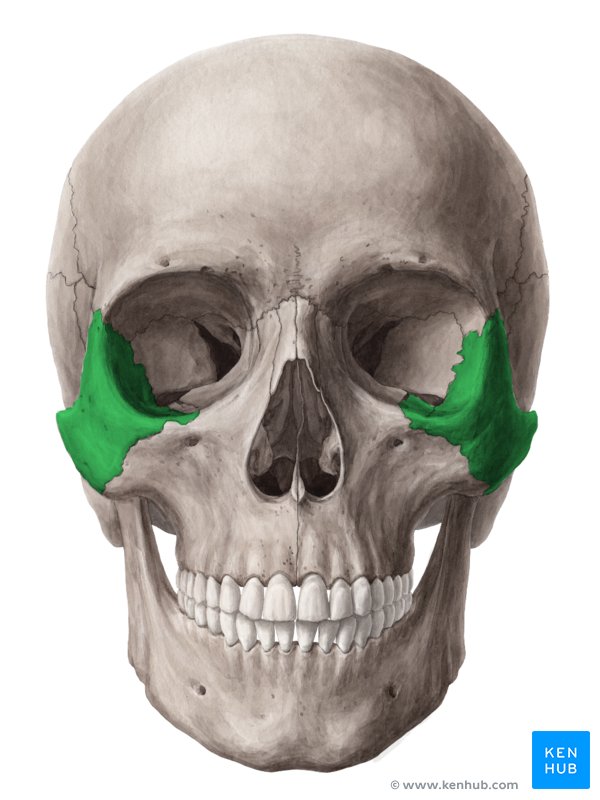
zygomatic bones (L/R)
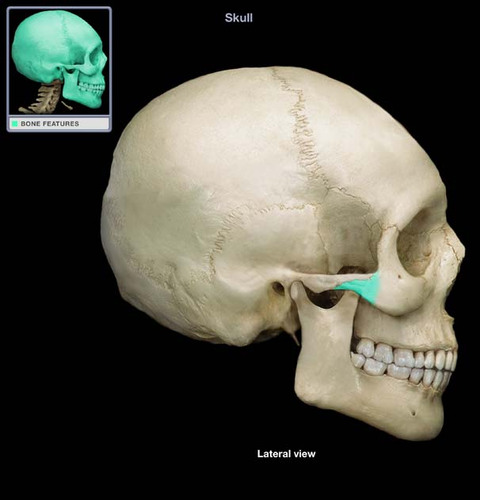
temporal process
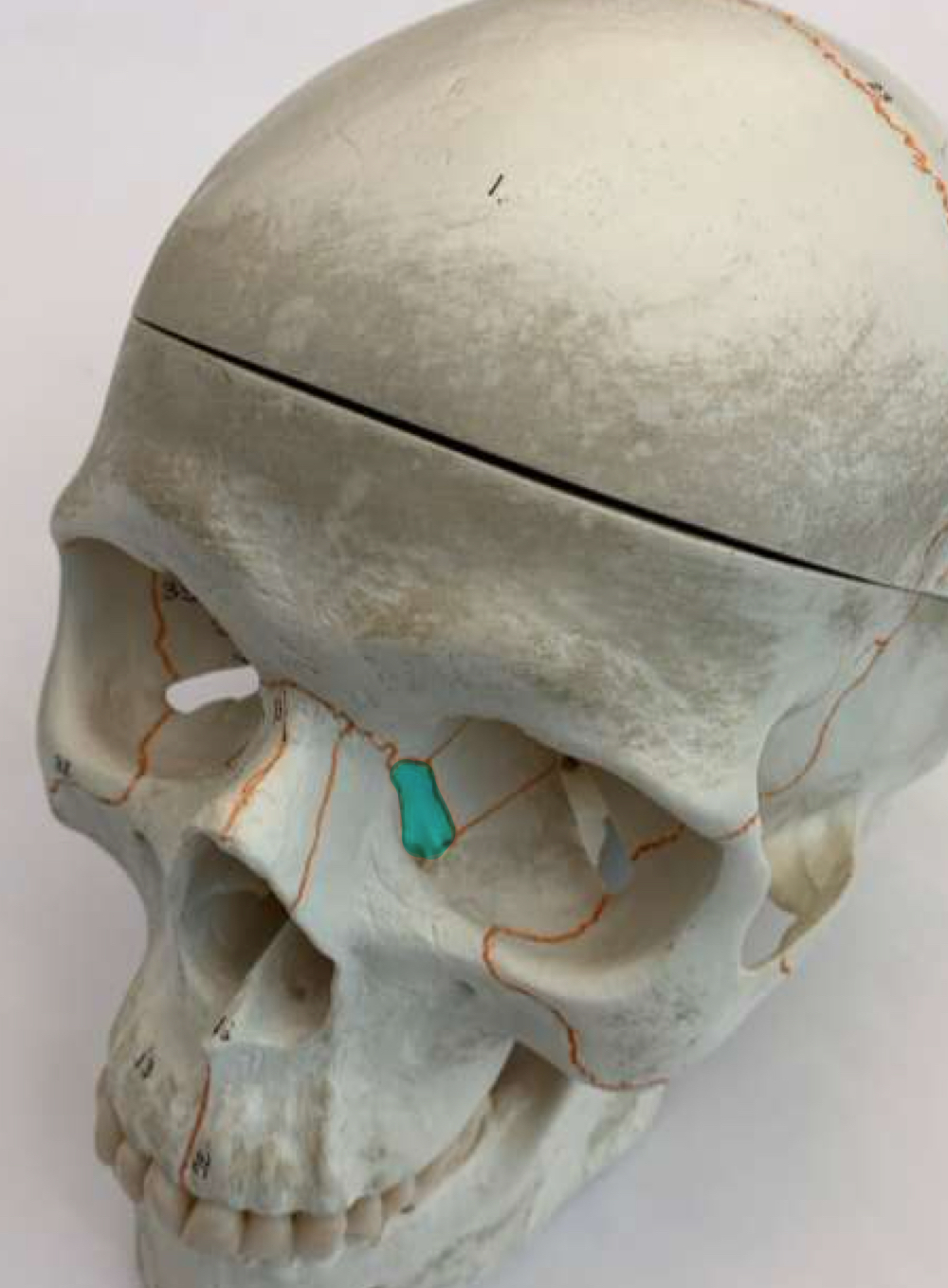
lacrimal bones (L/R)
vomer
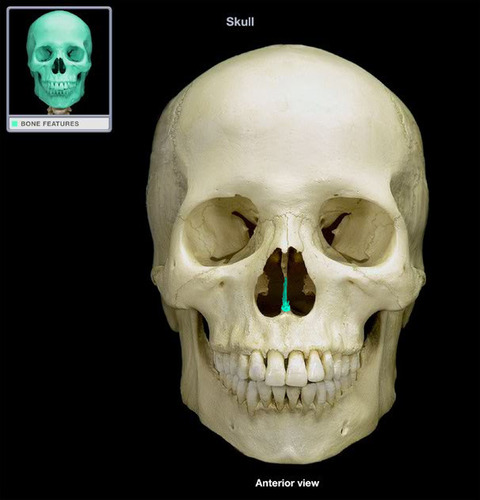
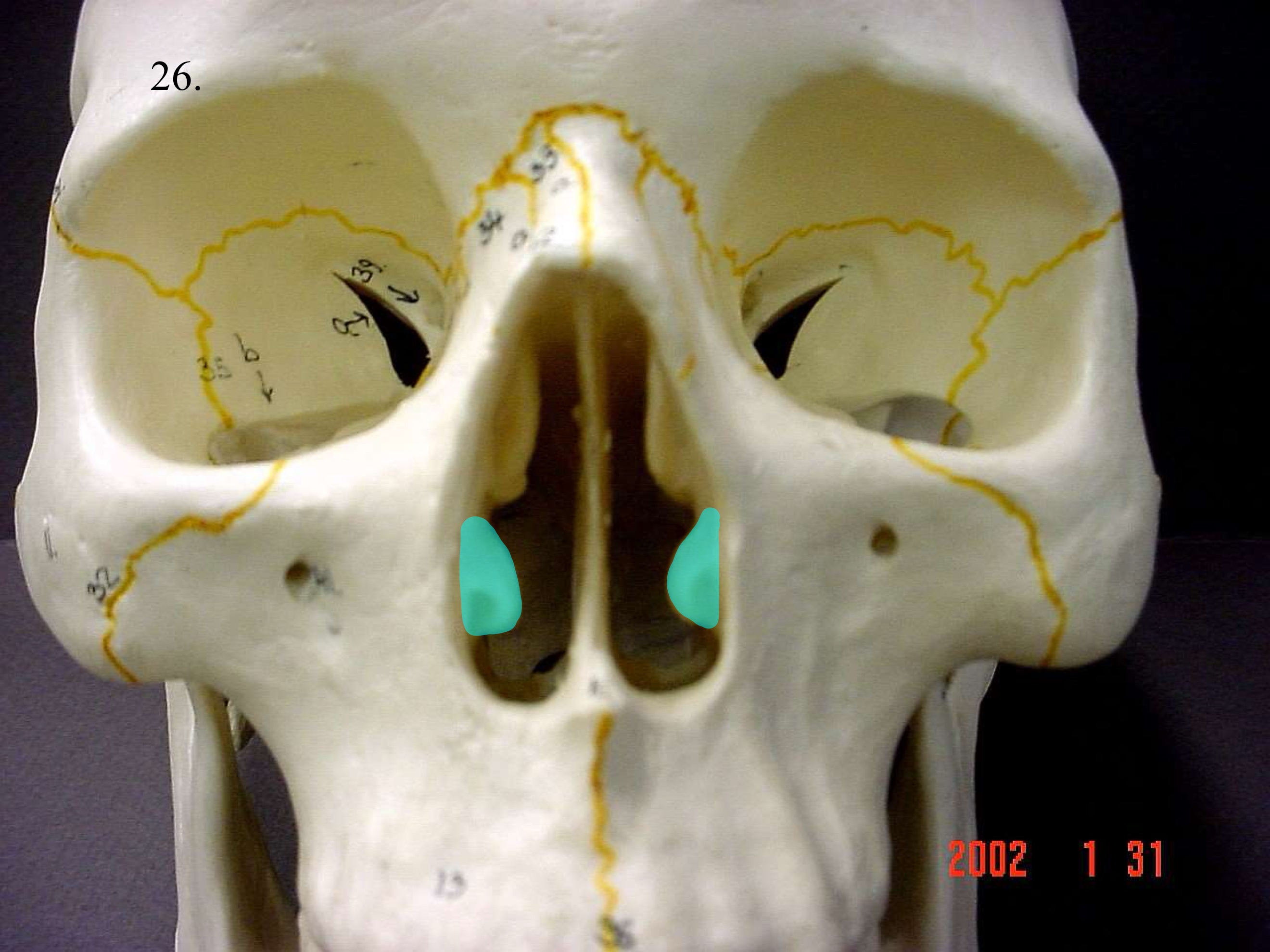
inferior nasal conchae
hyoid
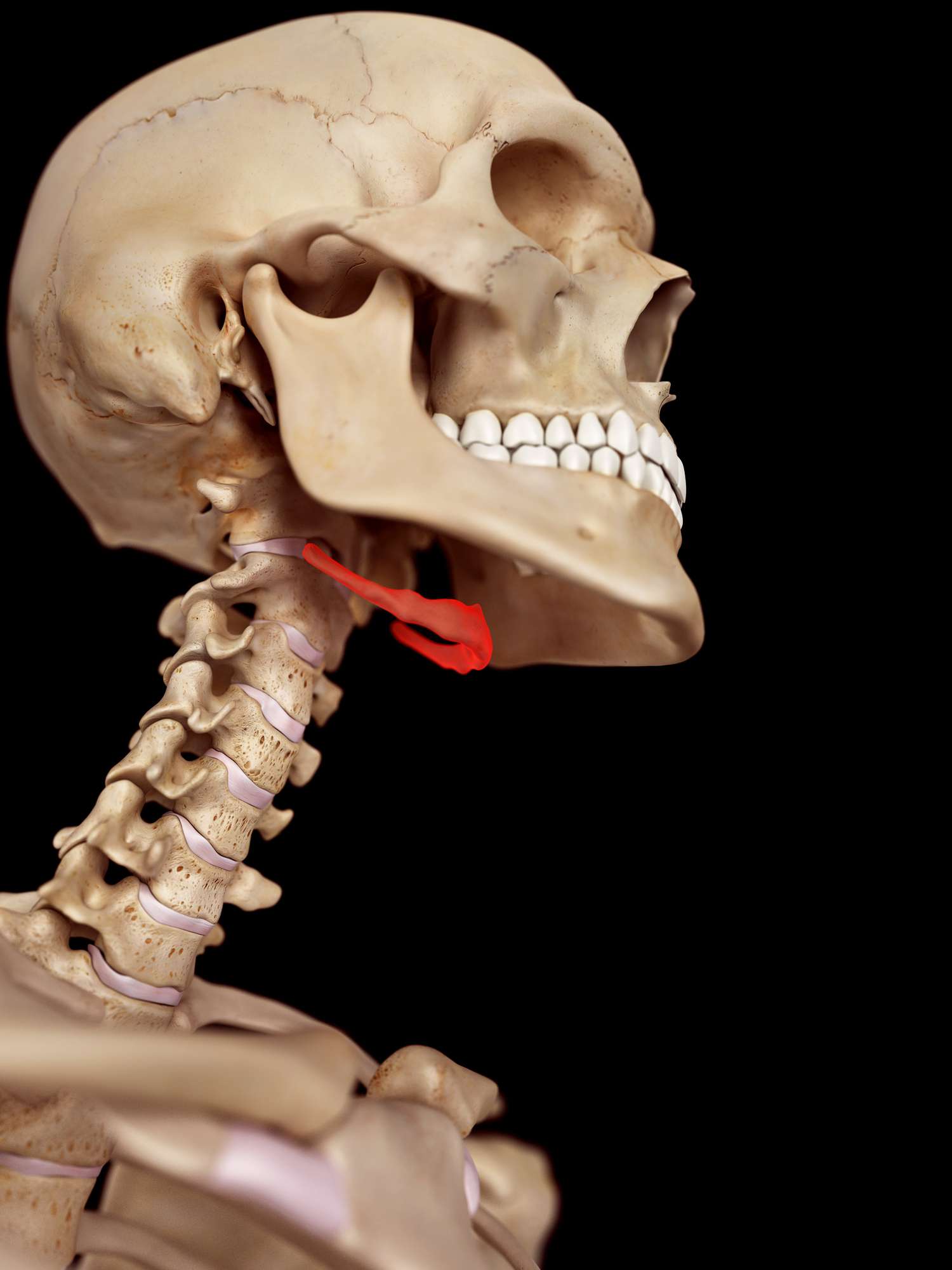
temporomandibular joint
temporal bone and mandible joint
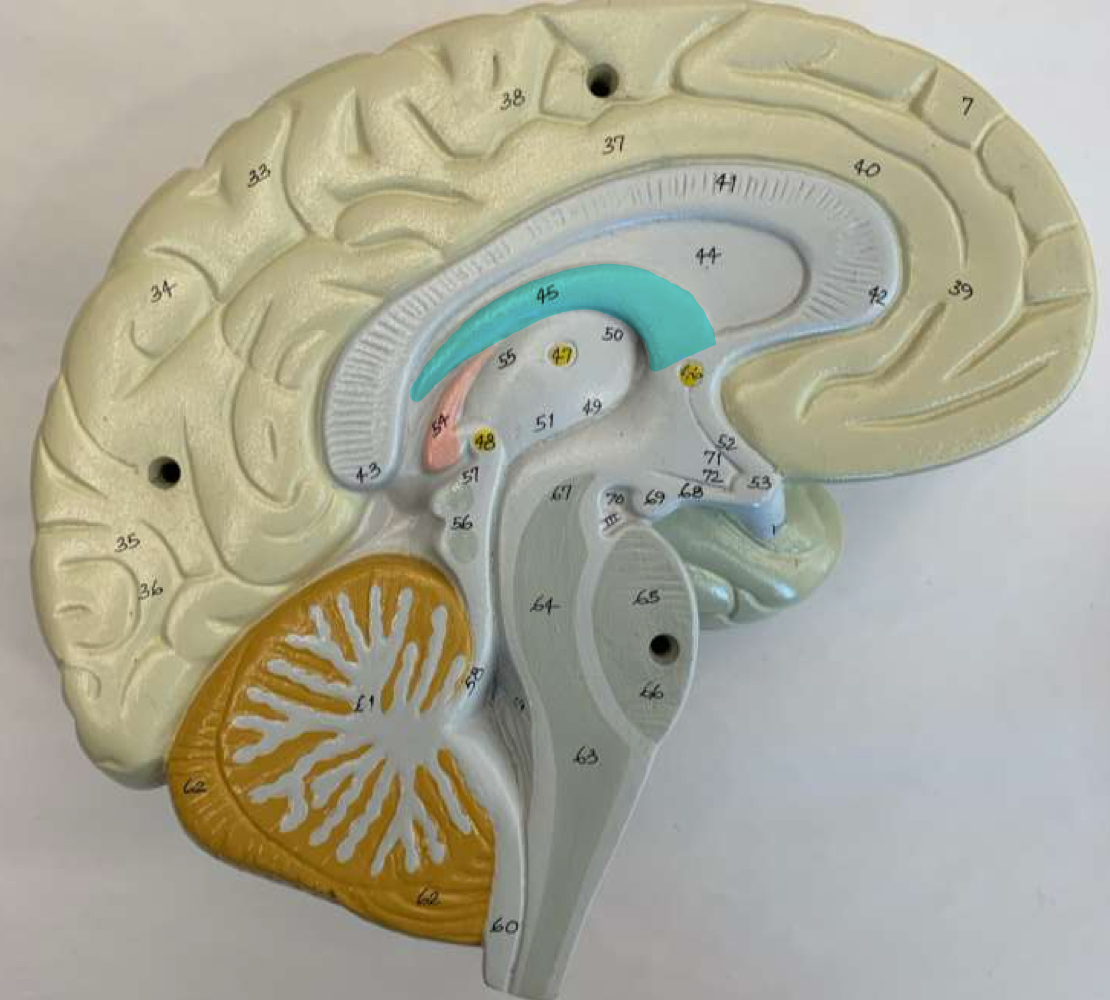
cerebrum
gyri, sulci, cortex, white matter tracts, corpus callosum, and fornix
cerebrum
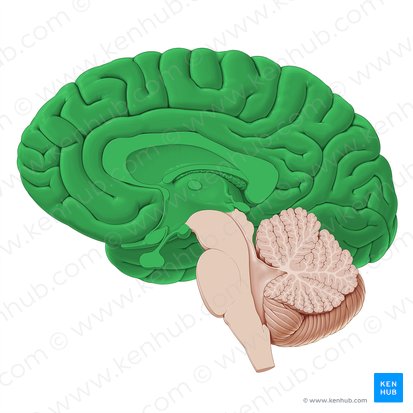
gyri
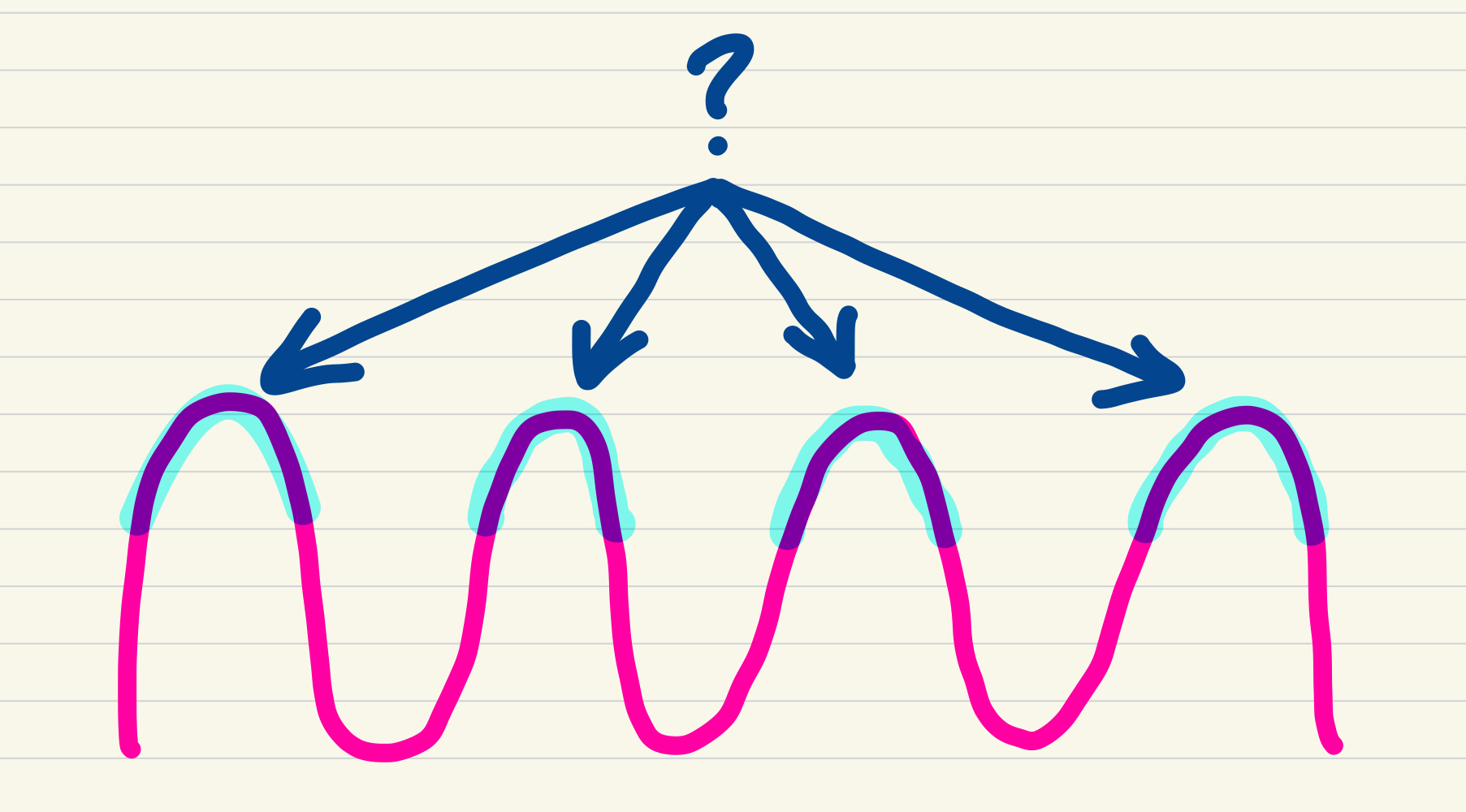
sulci
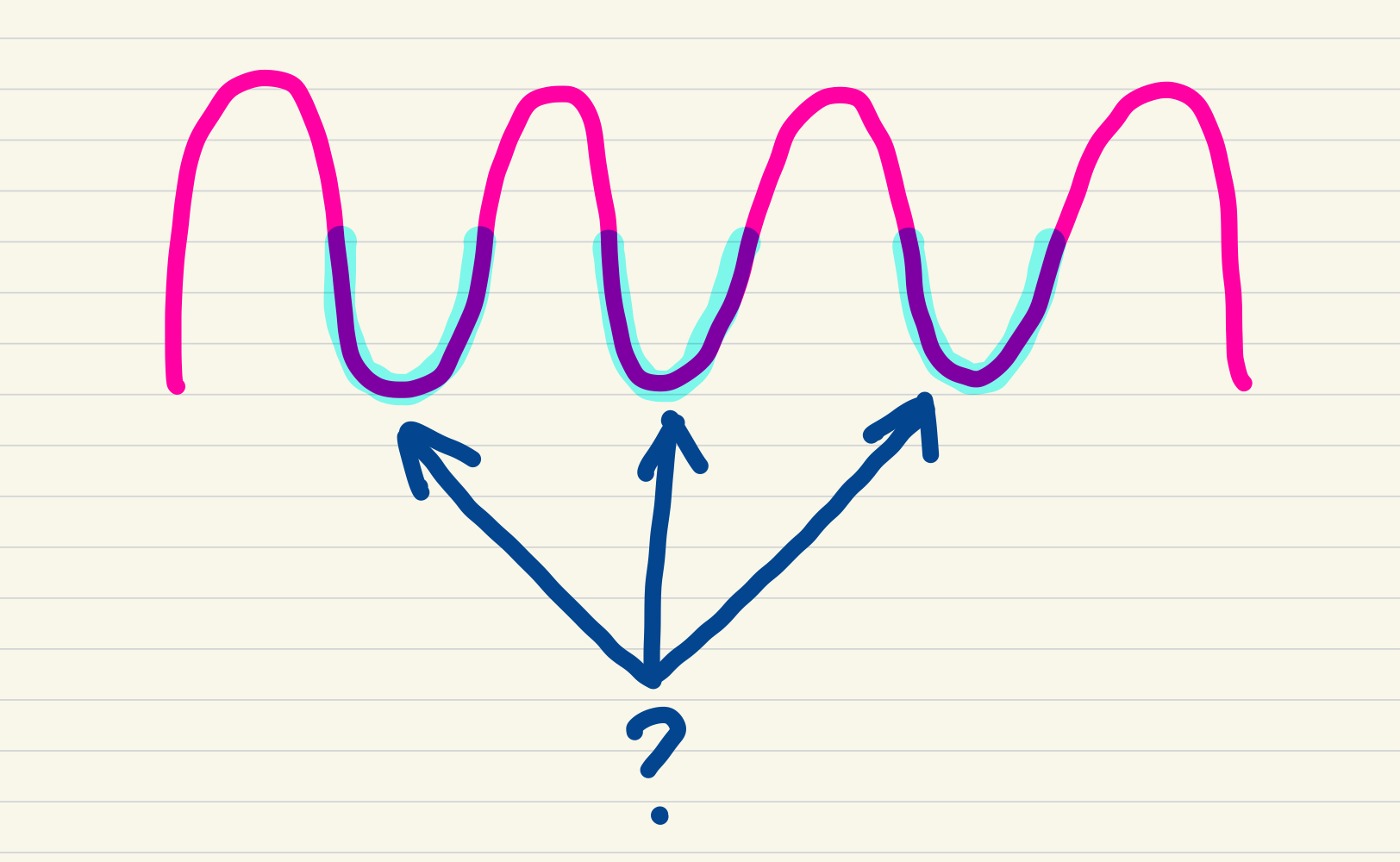
cortex function
superficial gray matter
white matter tracts
corpus callosum and fornix
corpus callosum
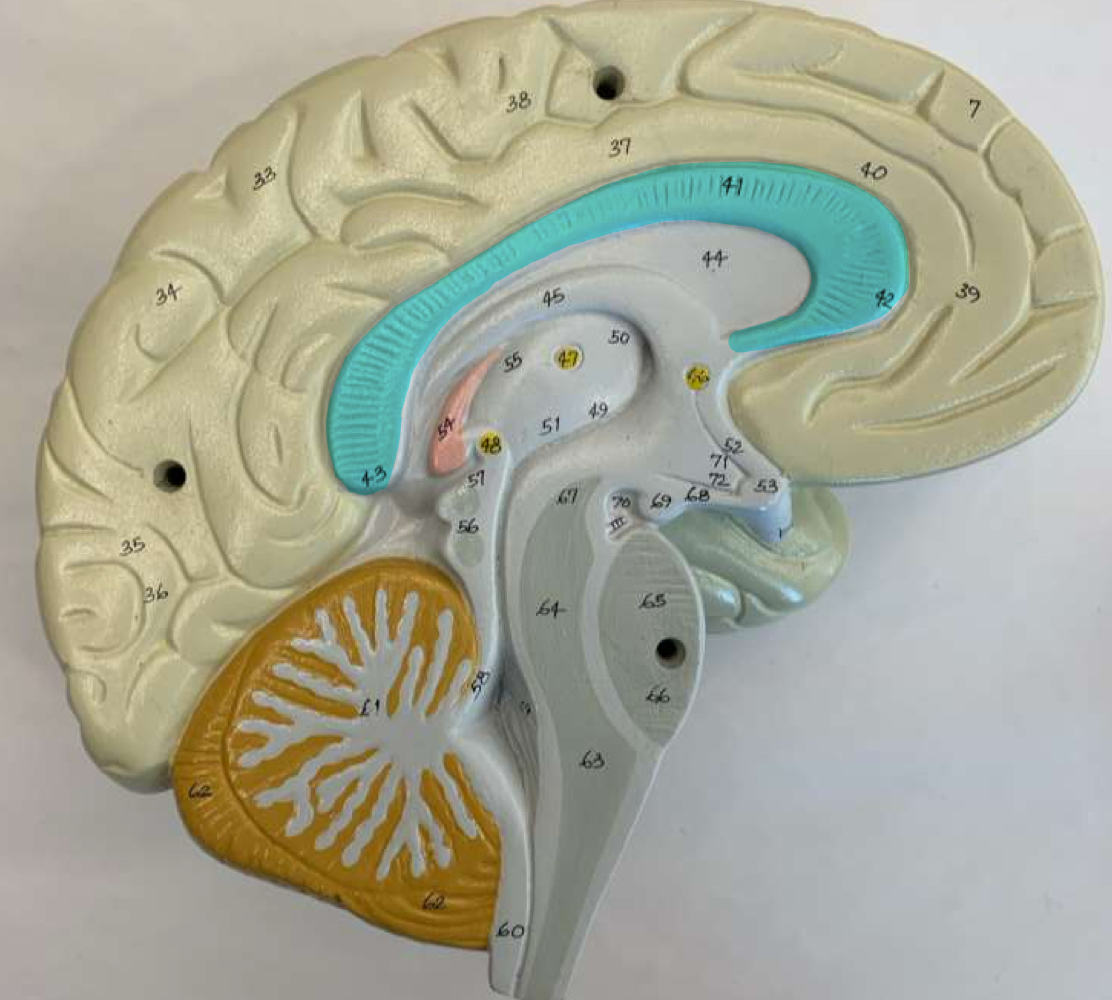
fornix
gyri function
ridge of the cortex
sulci function
depression of the cortex
corpus callosum function
connects right and left hemispheres
fornix function
white matter tract from the hippocampus, which is important in memory formation
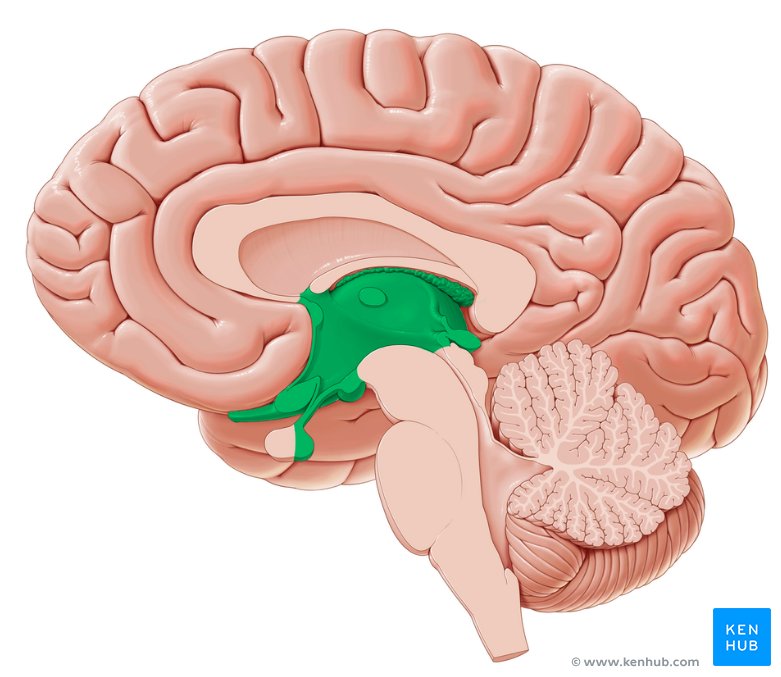
thalamus, hypothalamus, and epithalamus
diencephalon region parts
diencephalon
thalamus function
processes incoming sensory information and directs it to the appropriate area of the cerebrum
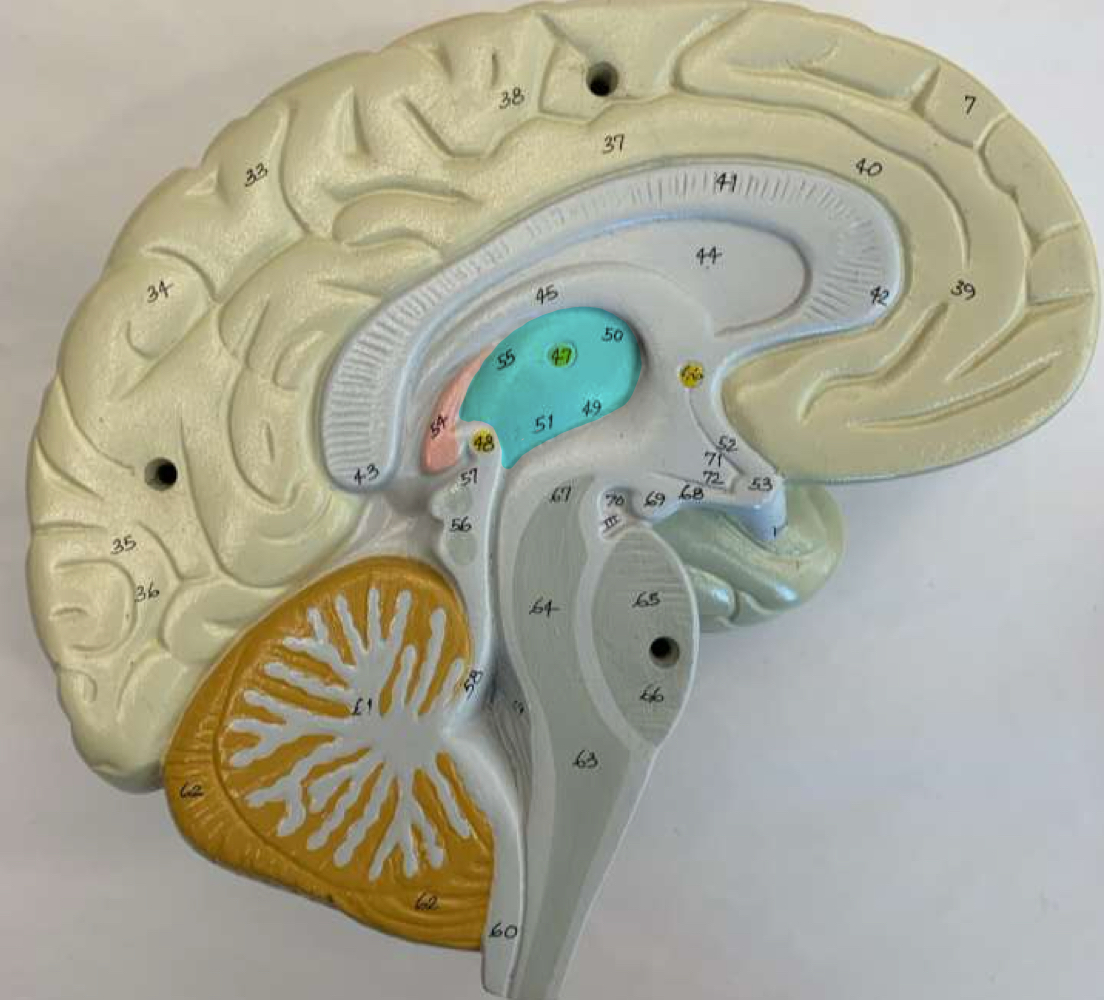
hypothalamus function
hormone and autonomic control center of the brain
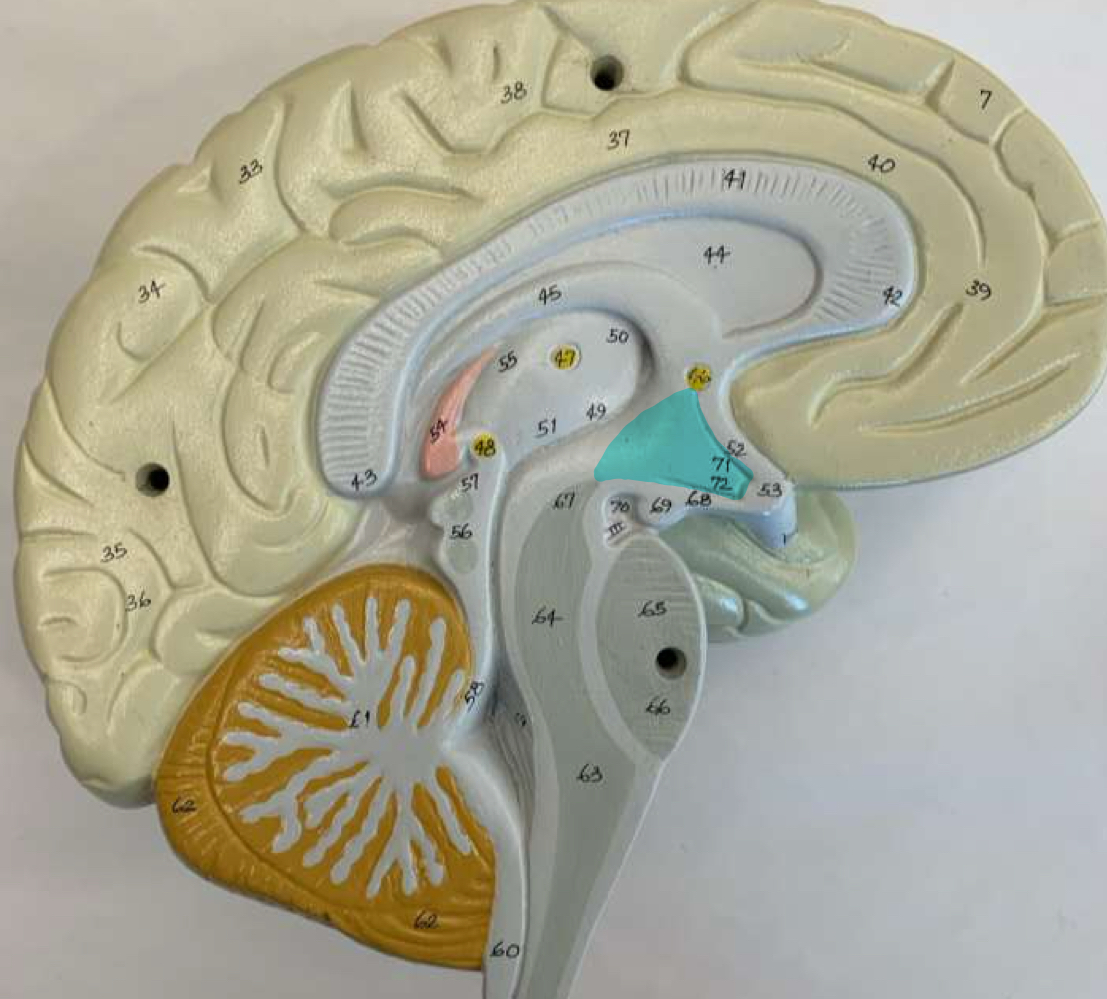
epithalamus function
contains the pineal gland
thalamus
hypothalamus
epithalamus
corpora quadrigemina
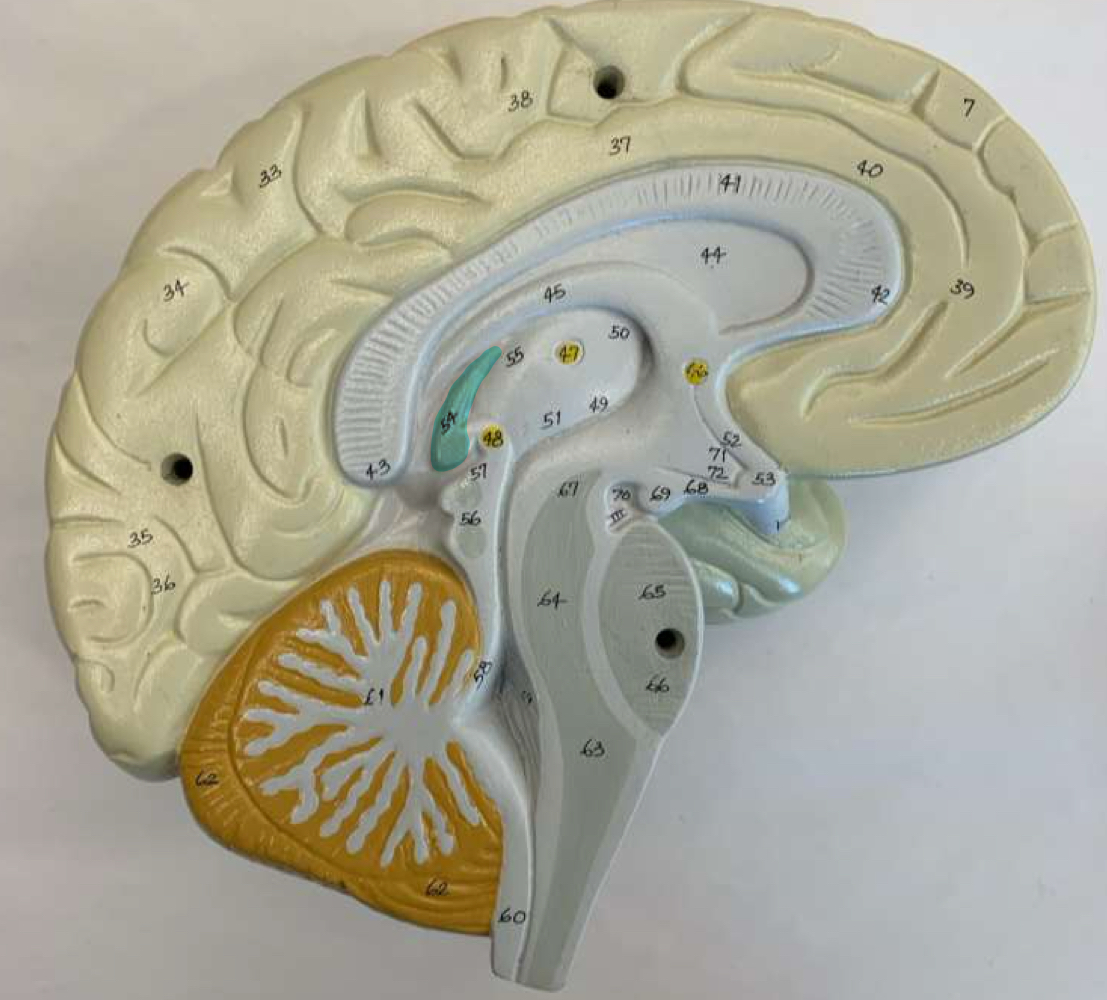
midbrain region
superior colliculus and inferior colliculus
corpora quadrigemina
corpora quadrigemina
latin for “quadruplet bodies”
superior colliculus function
processes visual reflexes
inferior colliculus function
auditory reflexes
superior colliculus
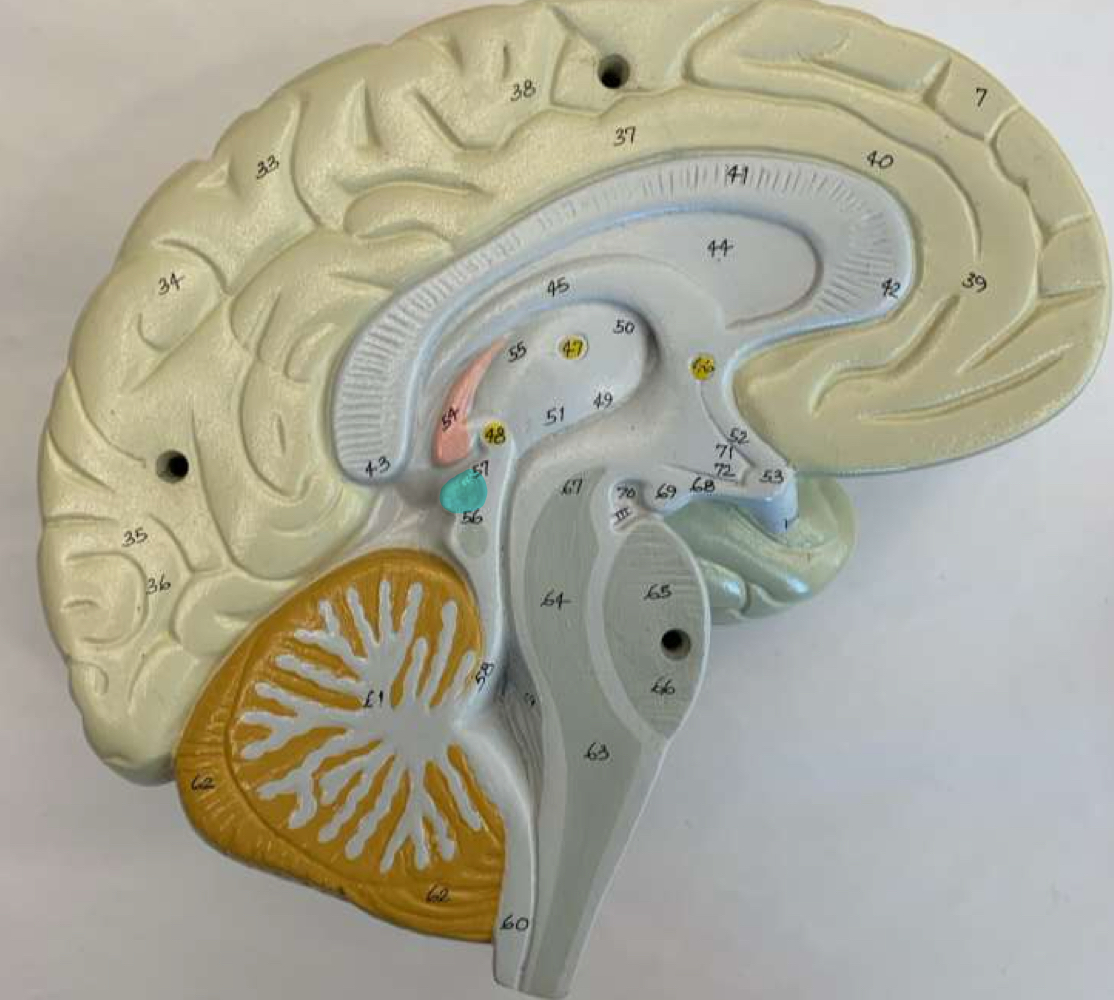
inferior colliculus
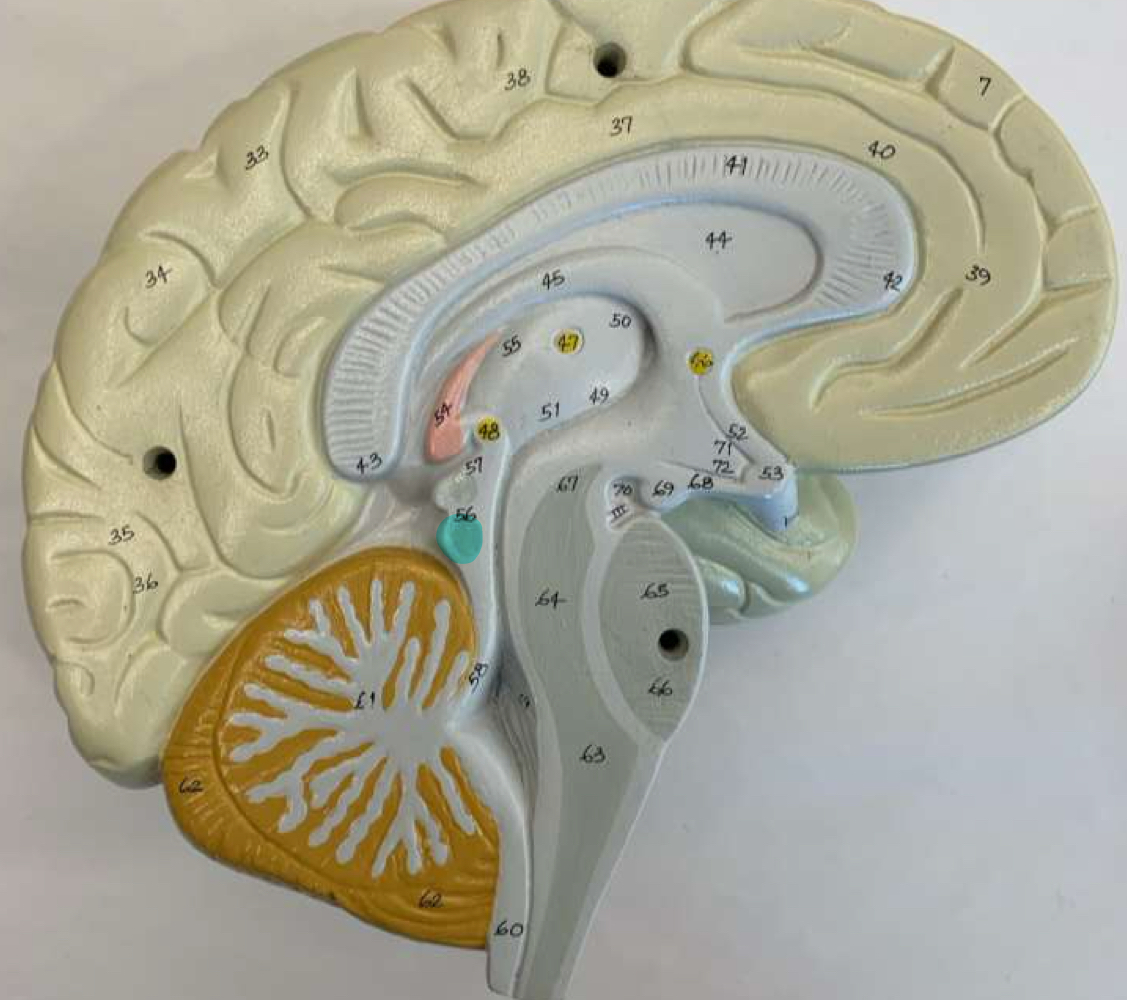
pons function
relay center between the forebrain and cerebellum; also helps regulate sleep
pons
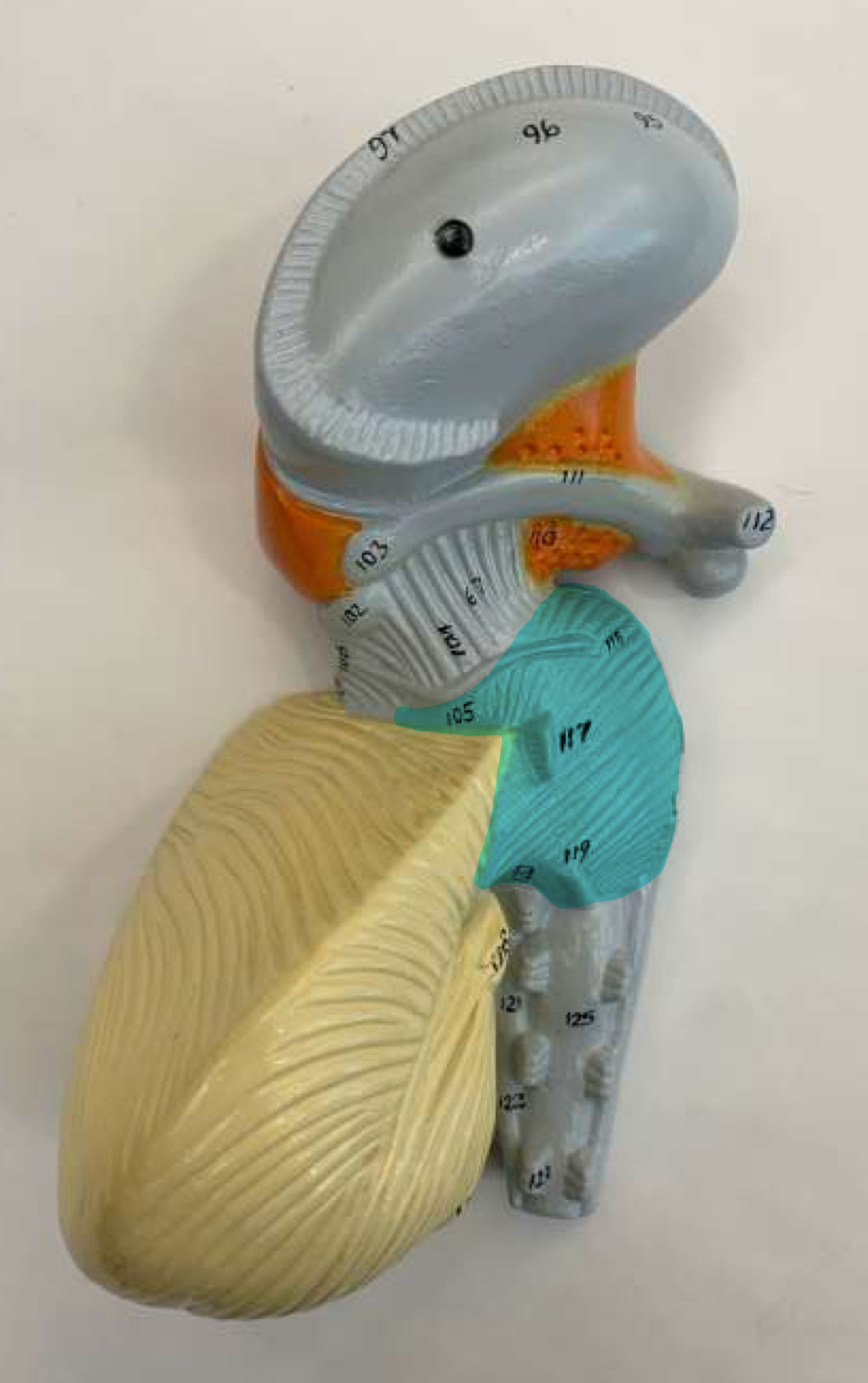

cerebellum function
motor learning, balance, equilibrium
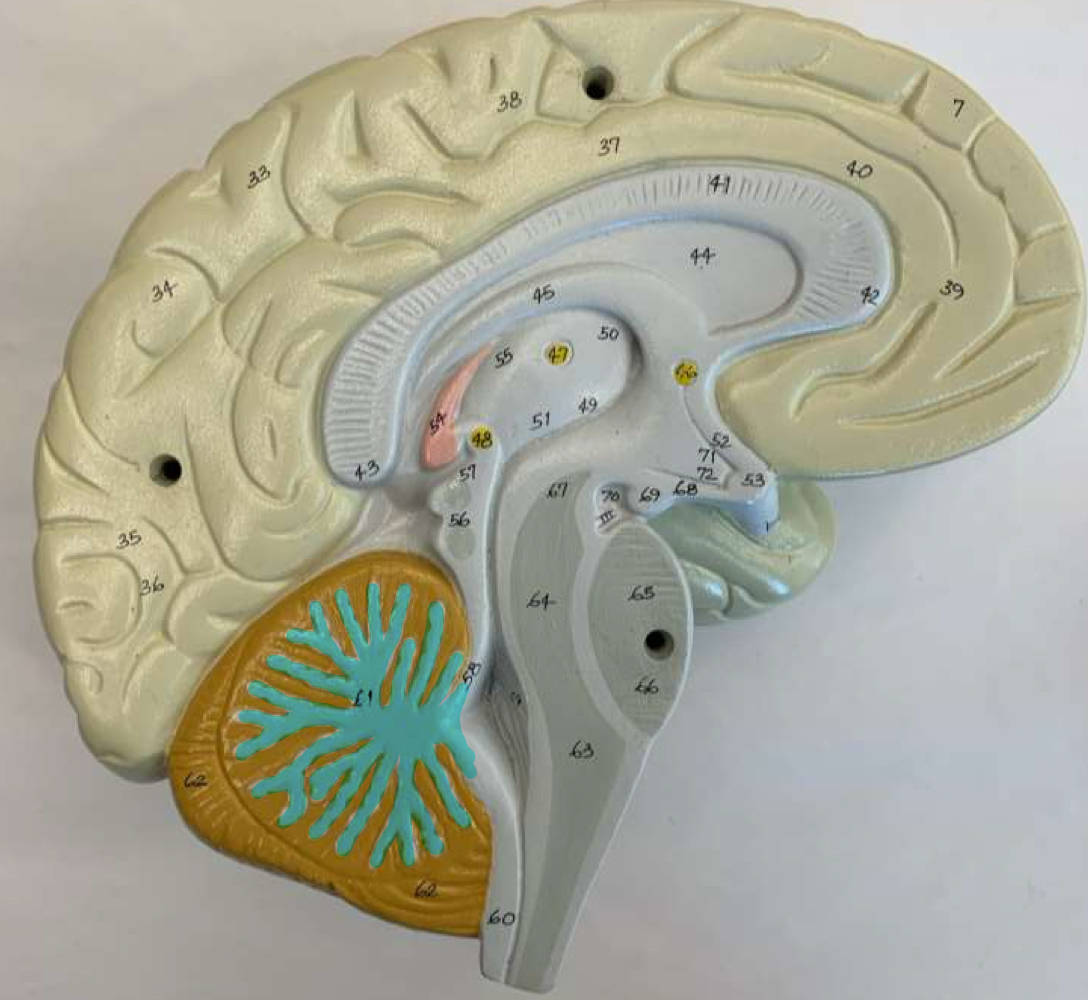
arbor vitae
cerebellum region
arbor vitae function
visual description of how the white and gray matter are arranged in the cerebellum (tree of life)
cerebellum
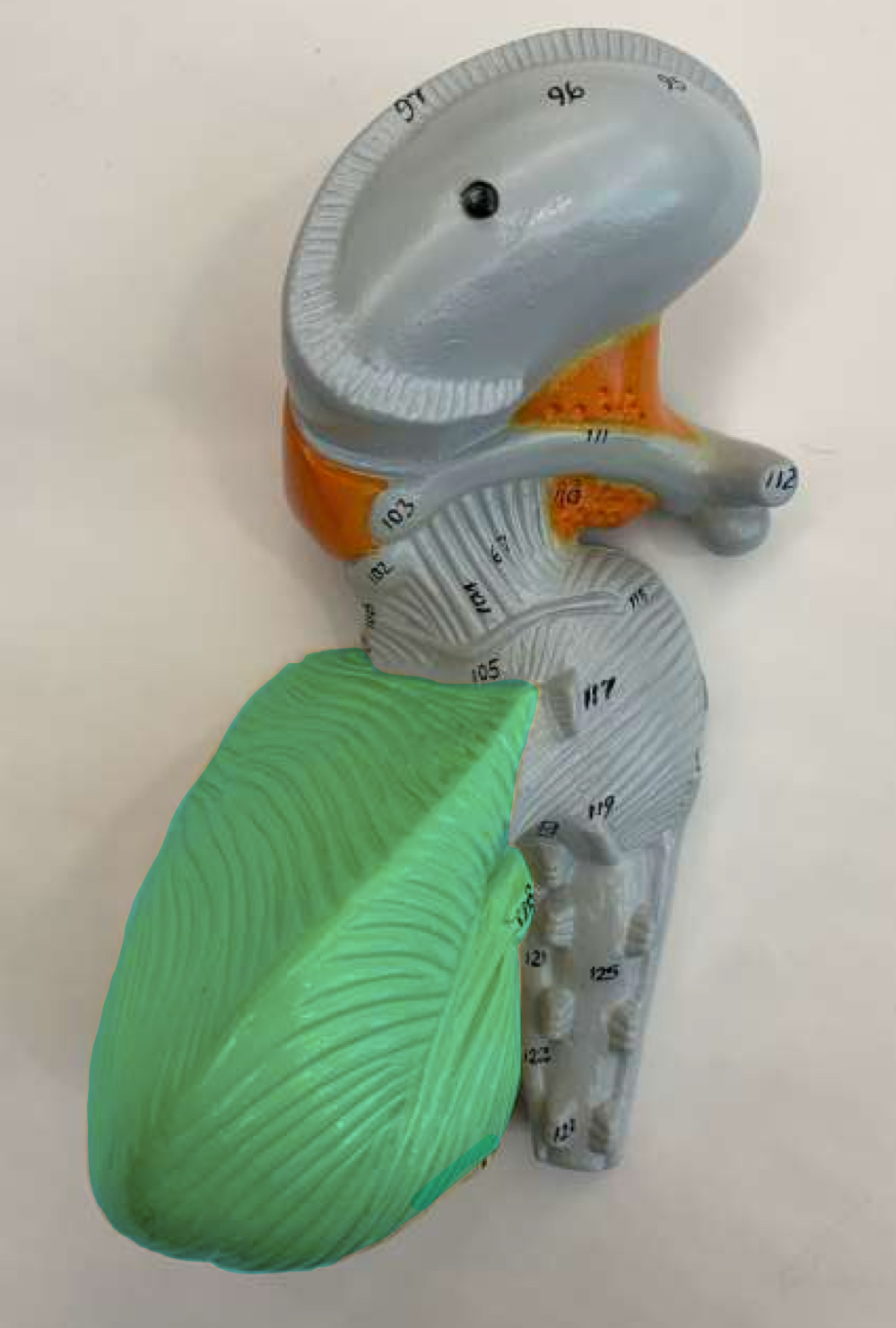

arbor vitae
medulla oblongata function
regulates several ANS functions: respiration, cardiac function, vasodilation, and reflexes like vomiting and swallowing
medulla oblongata
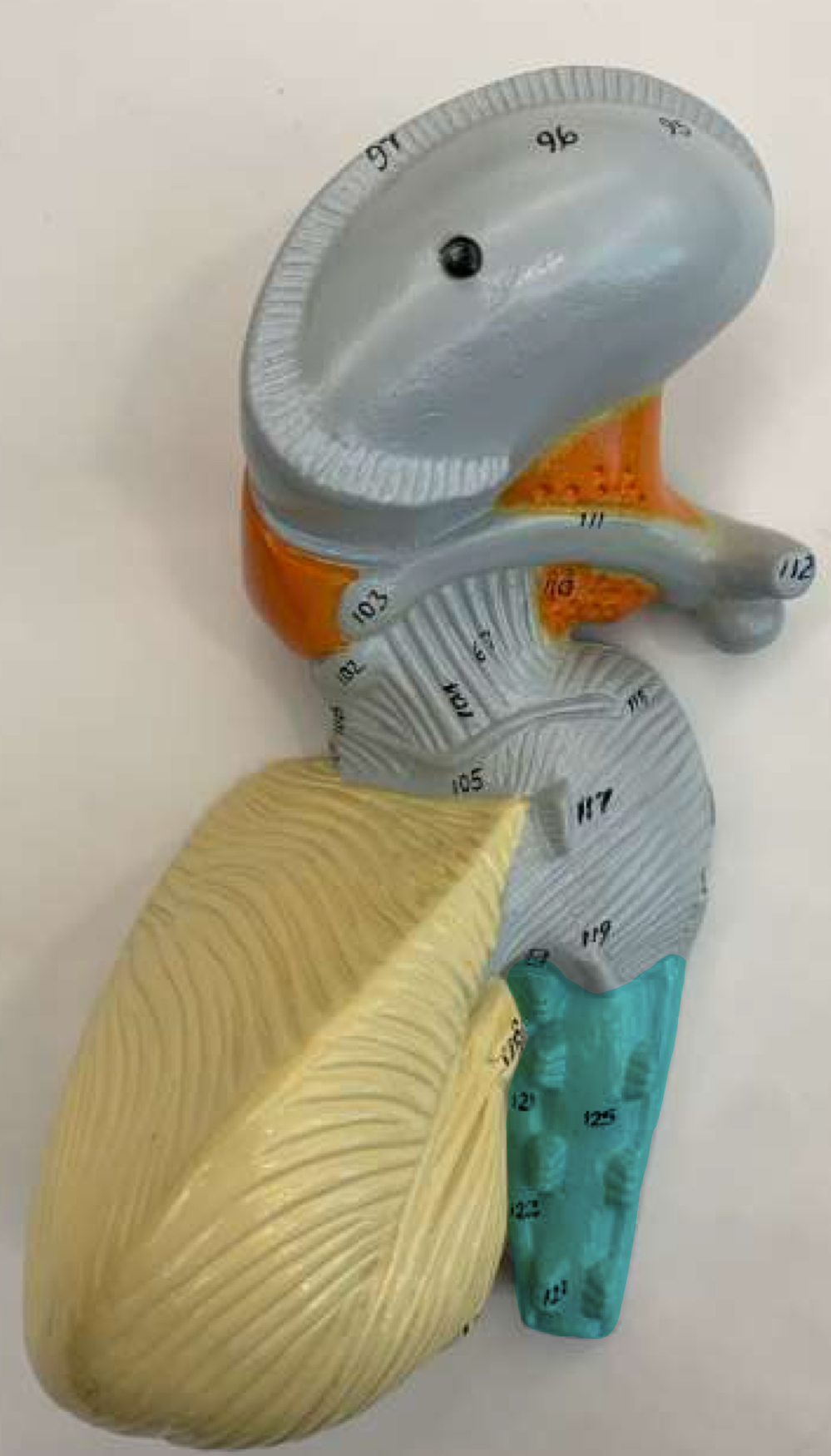

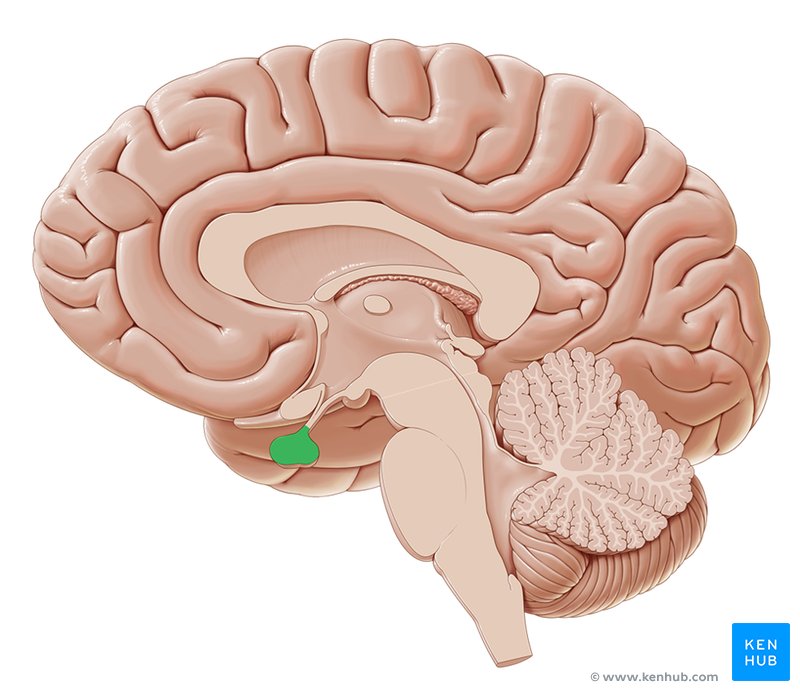
pituitary gland function
secretes hormones that affect the entire body
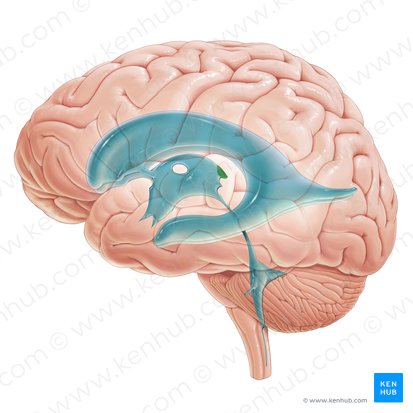
ventricles functions
spaces within brain that contain CSF
pituitary gland
ventricles
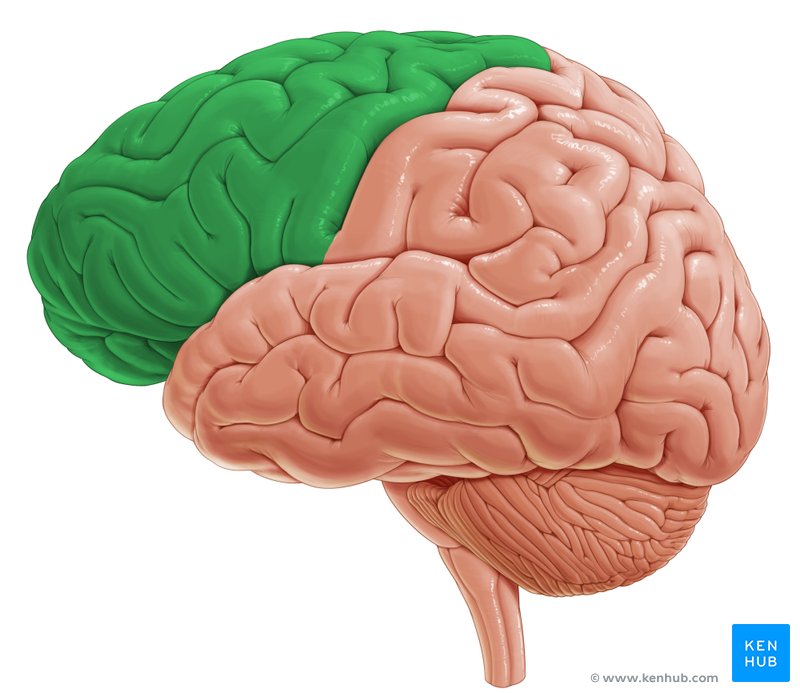
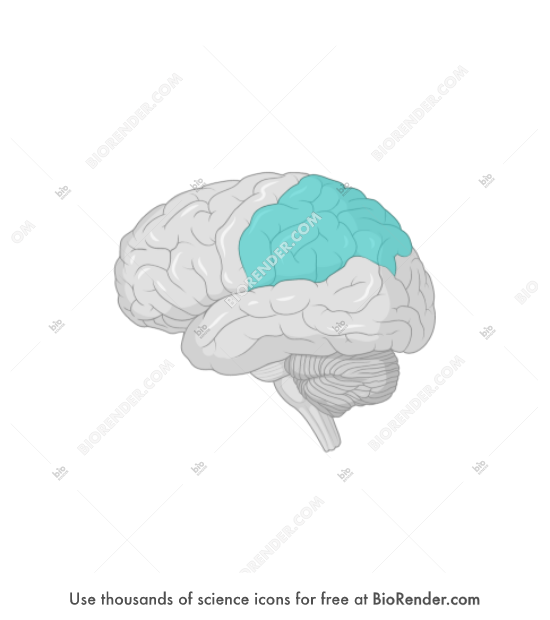
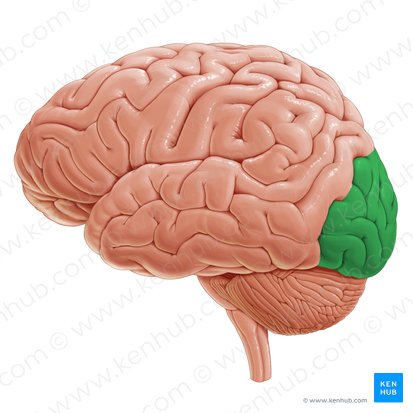
frontal lobes, parietal lobes, occipital lobes, temporal lobes
cerebrum lobes
prefrontal cortex
frontal lobe feature
frontal lobes function
executive function, attention, primary motor cortex, language
pre-frontal cortex function
in frontal lobe, executive function
parietal lobe function
integrating sensory information of touch, pressure, taste, pain
occipital lobe function
contains the primary visual cortex that processes visual information
temporal lobe function
processes sensory information for hearing, memory formation
frontal lobe
parietal lobe
occipital lobe
temporal lobe
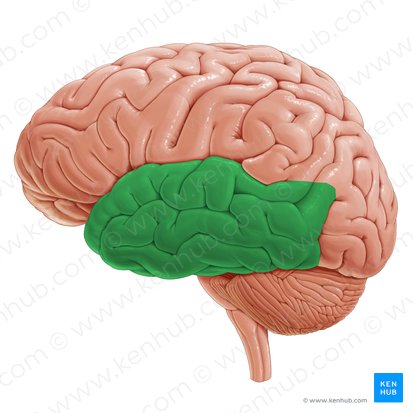
pre-frontal cortex
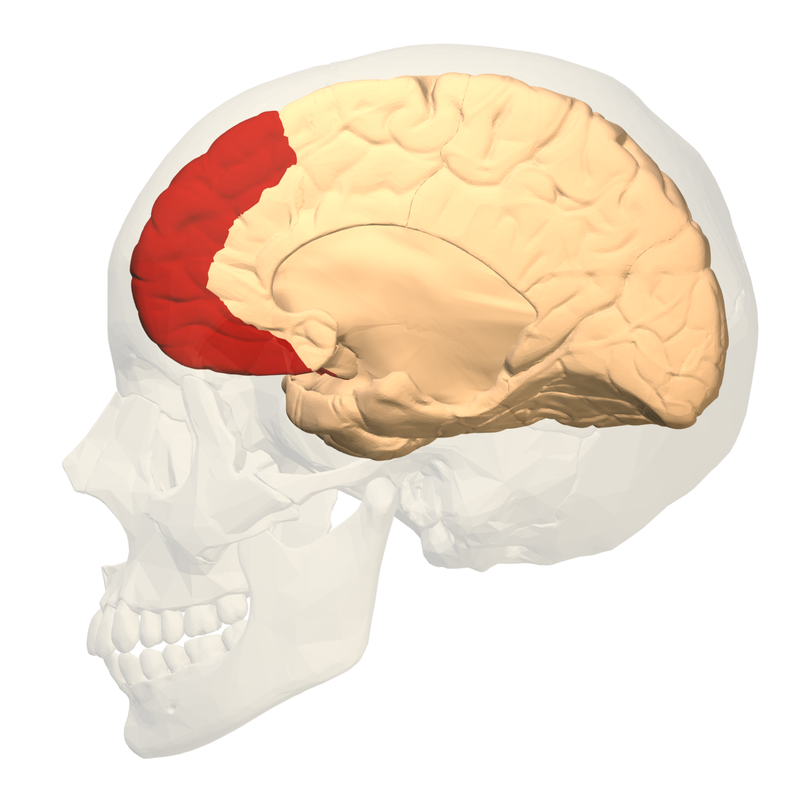
pre-central gyrus and post-central gyrus
gyri features
gyri function
ridge of the cortex
primary motor cortex
pre-central gyrus location
primary somatosensory cortex
post-central gyrus location
longitudinal fissure, central sulcus, lateral sulcus, parieto-occipital sulcus, and transverse fissure
sulci features
sulci function
depression of the cortex
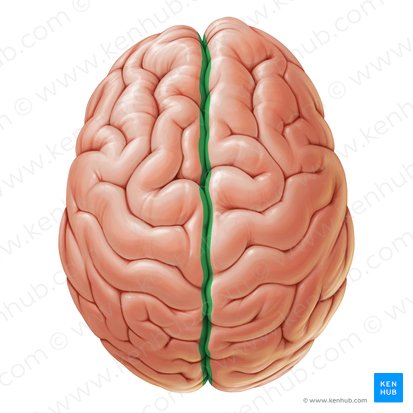
longitudinal fissure function
separates the right and left hemispheres
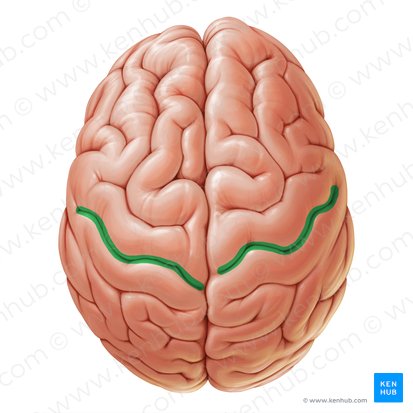
central sulcus function
separates the frontal lobes from the parietal lobes
lateral sulcus function
separates the temporal, frontal, and parietal lobes
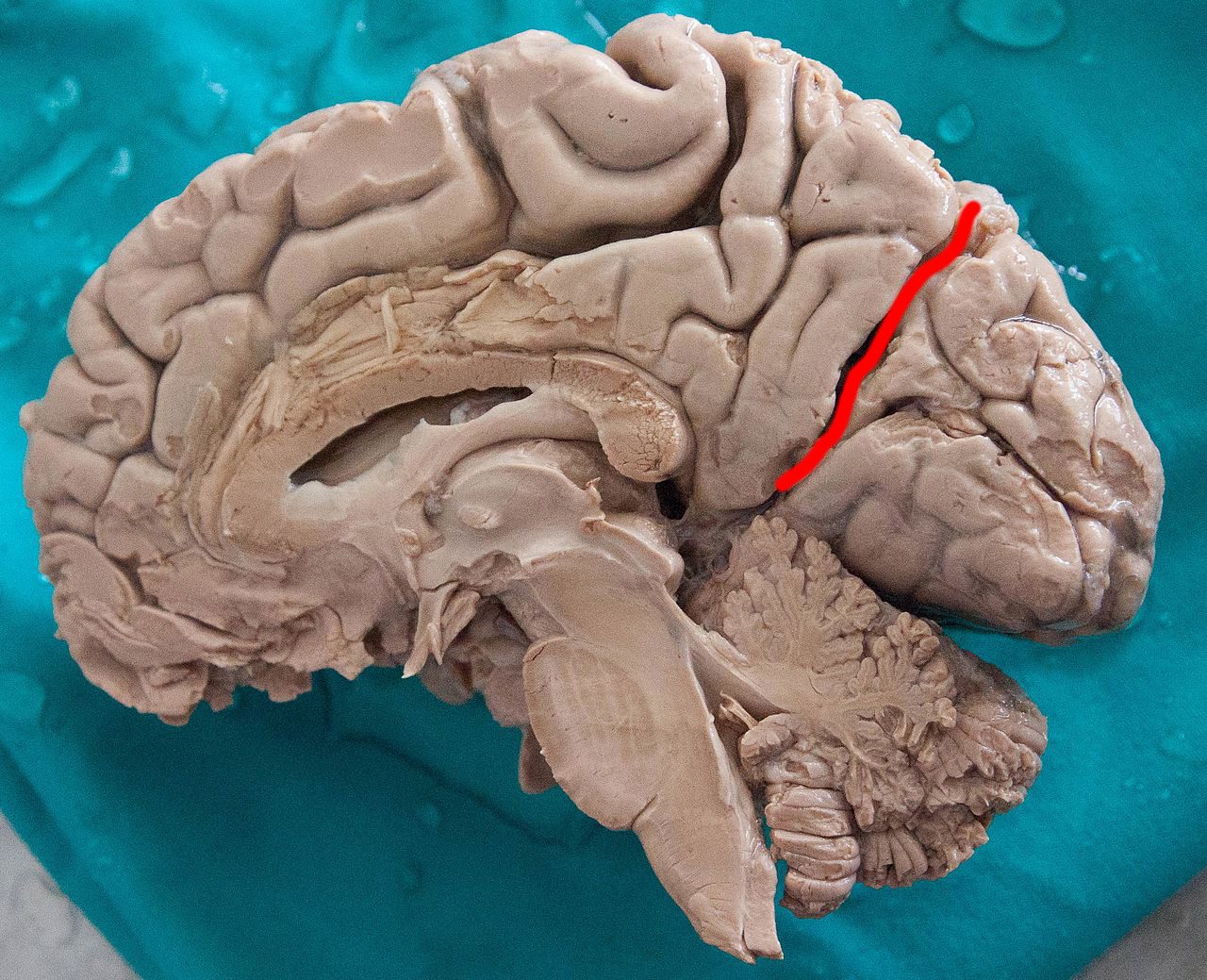
parieto-occipital sulcus function
separates the parietal lobes from the occipital lobes
transverse fissure function
separates the cerebrum and cerebellum
longitudinal fissure
central sulcus
parieto-occipital sulcus
cervical enlargement function
for motor/sensory neural connections to/from the upper extremity
lumbar enlargement
for motor/sensory neural connections to/from the lower extremity