Phonetics year 2
4.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/121
Last updated 3:08 PM on 5/4/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
122 Terms
1
New cards
how is sound presented
variations in air pressure then vibrates in vocal cords
2
New cards
trough
area of low concentration of wave
3
New cards
loudness is affected by
amplitude , distance from source, density of item, presence of resonating body
4
New cards
larger the surface area \=
the larger the sound
5
New cards
denser the item\=
the more sound
6
New cards
frequency means the
number of waves
7
New cards
small area \=
small sound and amplitude
8
New cards
more wave cycles\=
higher the pitch
9
New cards
pitch remains the same regardless of
size
10
New cards
what is the only thing that changes depending on size
loudness
11
New cards
sinosoidal
any wave having the shape of a sine wave \= S
12
New cards
cps\=
cycles per second (same as HTZ)
13
New cards
Frequency equation \=
cycle % time taken
14
New cards
frequencies tell us \=
if wave is a vowel or consonant
15
New cards
vowel and consonant wave form together to make-
complex wave (played at same time)
16
New cards
complex wave\=
any wave that is not a sine wave
17
New cards
fundamental frequency\=
frequency of a complex wave
18
New cards
white noise
sound with equal amounts of power at every frequency within audible range
19
New cards
sound at audible level production\=
vibrations move back and forwards- causing waves- waves enter eardrum vibrating it and moving cochlear
20
New cards
crest
area of highest concentration of wave
21
New cards
frequency\=
number of cycles in a second
22
New cards
sinusoidal wave
Any Wave having shape of an S wave
23
New cards
shape of waves differing
can be differing for differing sound qualities
- differ if 2 different instruments
- differ if 2 different instruments
24
New cards
Descibles
how loud you can hear
25
New cards
how can loudness be represented-
the higher the crest the louder the sound
26
New cards
amplitude2\=
loudness
27
New cards
route mean square RMS
is the amplitude
28
New cards
dotted line on a graph\=
the average (mean) of the wave
- loudness of sound does not depend on its peak
- loudness of sound does not depend on its peak
29
New cards
frequency \=
wAVES
30
New cards
simple periodic sounds \=
sine wave
31
New cards
complex periodic sounds
2 or more sine waves - complex waveforms
32
New cards
aperiodic sounds
white noise
33
New cards
sunusoidal wave
an S sine wave
34
New cards
fundamental frequency\=
lowest frequency eg 100htz
35
New cards
first harmonic \=
the loudest sound wave (where the dotted line is or the crest)
36
New cards
Harmonics
How many times glottis opens and closes
Focuses on vocal cords before sound comes out mouth
Focuses on vocal cords before sound comes out mouth
37
New cards
Frequency
Resonance of the mouth
Is shaped and comes up to mouth for production
Is shaped and comes up to mouth for production
38
New cards
Spectrogram
Shows amounts of fundamental frequencies through differing dark area
- different levels of frequency within a word
- different levels of frequency within a word
39
New cards
Formants \=
Frequency from they vocal tract
Change due to shape of vocal tract
Change due to shape of vocal tract
40
New cards
Spectrum pitches
Higher the itch the more dense the spectrum
41
New cards
Spectrogram
Shows bursts of air in shaded areas
First shaded area is a formant
First shaded area is a formant
42
New cards
Spectogram formants
F1- low formant so low vowel
F2- low formant so back vowel
Highest formant- high vowel and front vowel
F2- low formant so back vowel
Highest formant- high vowel and front vowel
43
New cards
Nasalisation in vowels
Oral and nasal cavity are coupled together
Have low frequency resonance- formant
Antiresonace- no energy frequencies
Have low frequency resonance- formant
Antiresonace- no energy frequencies
44
New cards
Dipthongs
Affects duration, amplitude and formant frequencies
Second vowel s a target but not actually reached
Second vowel s a target but not actually reached
45
New cards
Vowel characteristics
Are voiced
Source- phonation
Periodic waveform
Source- phonation
Periodic waveform
46
New cards
Sonorant consonants
Voiced
Nasal stops, approximants, lateral approximants
Source0 phonation
Periodic waveform
Nasal stops, approximants, lateral approximants
Source0 phonation
Periodic waveform
47
New cards
Obstruent consonants characteristics
Fricatives plosives and affricates
Eg S
Is noise resulted from constricted airflow
Has a aperiodic waveform- no regular waves
Eg S
Is noise resulted from constricted airflow
Has a aperiodic waveform- no regular waves
48
New cards
Phases of plosive production
Plosive burst\= release of articulation - at end of consonant
Hold phase\= before plosive burst release - no sound occurs
- aspiration occurs after a plosive
Hold phase\= before plosive burst release - no sound occurs
- aspiration occurs after a plosive
49
New cards
Aperiodic english soundless
Voice3less fricatives - f the, s , sh, h
Voiceless plosives- p t k
Voiceless africate - ch
Voiceless plosives- p t k
Voiceless africate - ch
50
New cards
Aperiodic waveform
Waves have no regular cycles
51
New cards
Affricates sound process
Includes a plosive (stop) element then a fricative element
52
New cards
Homorganic
Occur at same place of articulation
53
New cards
\\\\ brackets
Phonemic transcriptions
* intonation
* intonation
54
New cards
\[\]
Phonetic transcriptions
* substitutions
* Allophonic detail
* Nasalisation
\
* substitutions
* Allophonic detail
* Nasalisation
\
55
New cards
Allophonic variation
Multiple pronunciation variants for the same phonological unit
Eg bottle and bo?le
Eg bottle and bo?le
56
New cards
Aspiration
Pt k are aspirated when in initial position and with a stressed syllable
But are not aspirated when in cluster eg spot
Are aspirated when on their own- pot, pan, pen
But are not aspirated when in cluster eg spot
Are aspirated when on their own- pot, pan, pen
57
New cards
Devoicing of liquids and glides
When unvoiced plosives are up before a stressed vowel they become devoiced- o below LRWJ
L R W J all are devoiced when applied after plosives PTK
L R W J all are devoiced when applied after plosives PTK
58
New cards
Dental realisations of alveolar sounds
Alveolar stops /t/, /d/ and /n/ and the alveolar lateral approximant /l/ are realised as dental articulations when they occur before a dental fricative - /θ/ and /ð/ )
The th when your Tongue touches between teeth
The th when your Tongue touches between teeth

59
New cards

Devoicing of plosives in word initial position
B d g - voiced plosives
When at start or end of word they become devoiced
When at start or end of word they become devoiced
60
New cards
Clear and dark L
plain \[l\] (‘clear l’) and velarised \[ɫ\] (‘dark l’)
\[l\] in the onset of a syllable, \[ɫ\] in the rhyme of a syllable:
Eg heal- darker and stronger
leaf \[liːf\] holiday \[hɒlɪdeɪ\] feel \[fiːɫ\] field \[fiːɫd\] battle \[b̥ ætlɫ̩\]
\[l\] in the onset of a syllable, \[ɫ\] in the rhyme of a syllable:
Eg heal- darker and stronger
leaf \[liːf\] holiday \[hɒlɪdeɪ\] feel \[fiːɫ\] field \[fiːɫd\] battle \[b̥ ætlɫ̩\]
61
New cards
Devoicing of obstruents in word final position
In word final position, voiced fricatives - b d ɡ v ð z ʒ dʒ become devoiced (voiceless)
62
New cards
Devoiced =
Voiceless
63
New cards
Intonation
Is context, Stress, Pitch
Fits into phonology
Is a suprasegmental system
Fits into phonology
Is a suprasegmental system
64
New cards
Suprasegmental system
Intonation
Prosody
Rhythm
Stress
Pitch
Amplitude
Voice
Prosody
Rhythm
Stress
Pitch
Amplitude
Voice
65
New cards
Segmental system
Is specific and wider contexts
Consonants and vowels
Consonants and vowels
66
New cards
Command/statement Function of intonation in English
Is falling intonation
Demonstrating final to a sentence
Demonstrating final to a sentence
67
New cards
Fallowing tone function of intonation in English
Demonstrates end of a sentence
68
New cards
Rising tone function of intonation in english
Demonstrates a sentence isn finished
Ill be late, as I don’t finish work until 6
Ill be late, as I don’t finish work until 6
69
New cards
Rise to fall function of intonation in english
Represents surprise or being impressed
70
New cards
Rising intonation function
Yes/no questions
71
New cards
Falling intonation function
Questions with detailed answers
72
New cards
Rising to falling intonation function
Show surprise or excitement
73
New cards
Falling to rising intonation function
Demonstrates uncertainty/doubt/hesitation
74
New cards
Nuclear tone
Centre tone
75
New cards
If word ends with a voiced plosives =
Plosive will become devoiced
76
New cards
If there’s ‘ng’ in middle of word =
‘Ng’symbol is always accompanied with g in WM
But never at WF
But never at WF
77
New cards
Where does nasalisation symbol appear
On the vowels in the word
Not the nasal
Not the nasal
78
New cards
Stress is often accompied (on plosives) by =
Aspiration

79
New cards
Devoiced will dominate ——— when next to each other =
Aspiration

80
New cards
N becomes dental when accompanied with =
T/d and th/thv

81
New cards
T becomes dental when accompanied with =
Th/thv

82
New cards
If there’s a silent space in a word
Eg house = ‘Ouse
This is always replaced with =
Eg house = ‘Ouse
This is always replaced with =
A space is always replaced with ? Glottal
Here is never a blank space in transcriptions
Here is never a blank space in transcriptions
83
New cards
Stress appears in which position on an C/V ?
BEFORE C/V
84
New cards
Can shwa be stressed?
No
85
New cards
How many voiceless plosive aspirations can there be in a sentence?
1
86
New cards
When are B d g devpoiced ?
wi and wf
87
New cards
When are V z 3 th devoiced?
WF
88
New cards
89
New cards
waveform types
aperiodic
periodic
sinusoidal
complex
periodic
sinusoidal
complex
90
New cards
how to measure waves
frequency = number of waves cycles in a second
more wave cycles= higher pitch
loudness changes the wave size
more wave cycles= higher pitch
loudness changes the wave size
91
New cards
higher the wave heigt=
larger the loudness
92
New cards
how is sound prodcuced ?
vibrations caused by an object that travel through air in waves
93
New cards
what is sound?
vibrations travelling though air pressure
94
New cards
how to measure sound
?
95
New cards
pitch
the more waves = higher the pitch
higher the pitch = denser the spectrum
* pitch remains the same regardless of size of objects
higher the pitch = denser the spectrum
* pitch remains the same regardless of size of objects
96
New cards
amplitude
the maximum extent of vibration
amplitude= loudness of sound
small area = small amplitude
RMS= route mean square
* doesn’t change depending on size
amplitude= loudness of sound
small area = small amplitude
RMS= route mean square
* doesn’t change depending on size
97
New cards
loudness
Changes dependent on size
higher the crest= louder the sound
loudness= amplitude
higher the crest= louder the sound
loudness= amplitude
98
New cards
loudness is impacted by
size
amplitude of sound waves
waves distance from sound source
quantity of energy that initiated the waves.
\
amplitude of sound waves
waves distance from sound source
quantity of energy that initiated the waves.
\
99
New cards
higher amplitude wave =
= more energy/intensity, thus they sound louder.
100
New cards
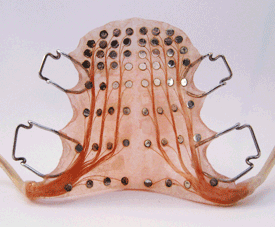
electropalatography (EPG) purpose
tracks articulation to see where errors are happening
measure tongue to palate contact during running speech
aka palatometry
measure tongue to palate contact during running speech
aka palatometry