Ophthalmic Optics Exam II - MF Lenses
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
Segmented bifocal
a lens with a separate small plus lens used for near vision that is added to the main distance lens. Segment is usually visible and delineated by a line or change in curvature from the main lens. Can be used for presbyopic patients or patients having binocular/accommodative vision problems.
Add power
how much power the near segment adds to the distance lens power, resulting in a total power at near.
toric
The segment is always placed on the lens surface opposite to the ____ surface. (on the front, convex of the lens for a minus cylinder form lens)
Fused bifocal
bifocal having a glass distance portion with a higher index near segment that is fused to the glass portion. The front curvature is the same over the distance and near portions. Allows for a change in power via refractive index change without a change in curvature.
One piece bifocal
bifocal having a lens material that is all one index where the near portion is created by a change in curvature over the segment area. This results in a ledge at the transition to the segment.
glass
material used to make the carrier portion of all fused bifocals
Cemented
bifocal having a plus near segment that is glued to the main distance lens.
Flat top
the most popular bifocal segment type. Widths available are 22, 25, 28, 35, 40, and 45
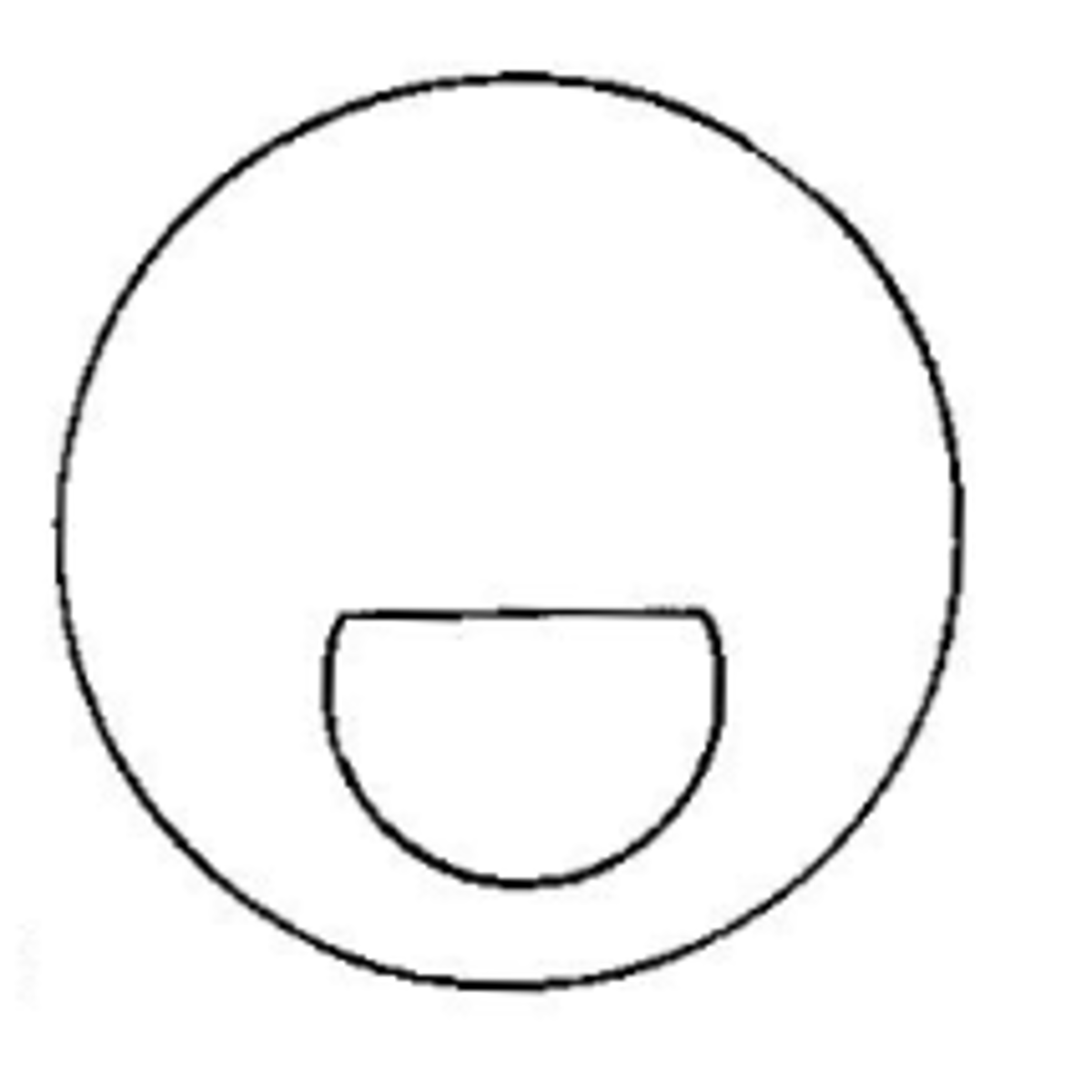
5 mm
for flat top bifocal widths 22-28, the OC is located how many mm below the top edge of the segment?
4.5 mm
for flat top bifocal widths 35, the OC is located how many mm below the top edge of the segment?
0 mm
for flat top bifocal widts 40 to 45, the OC is located how many mm below the top edge of the segment?
Curve top and Panoptik
variations of the flat top bifocal with some curvature at the top edge of the segment to make the edge less noticeable. Available 22 to 40 and 24 or 28 respectively.
4.5 mm
for curve top bifocals, the OC is located how many mm below the top edge of the segment?
Round
bifocal segment that is round and available in diameters 22 to 40 mm. OC is located at the center of the segment.
A style
style of round bifocal segment that are 38 mm wide and semicircular with a maximum height of 19 mm
Ultex
round segs that are almost a full circle 38 to 40 mm wide offering a high segment height.
Ribbon
bifocal segments which are round segments that have had the top and bottom cut off so that they have straight edges at the top and bottom.
B seg
ribbon segment that is 9 mm high and 22 or 25 mm wide. OC is half the height
R seg
ribbon segment that is 14 mm high and 22 or 25 mm wide. OC is half the height
Executive/Franklin
bifocal segment where the near portion goes across the entire lens width. This gives a wide field of view for near work but creates a noticeable ledge because the segment is so wide. OC is located at the top edge of the segment at the line.
Trifocals
multifocal lens having three segments, a distance, intermediate, and near. Power of the intermediate portion is half of the add power. Add power must be greater than +1.50 D. The height of the intermediate portion is typically 7 mm. Widths are 25, 28, and 35.
ED trifocal
trifocal that has an executive intermediate portion and a smaller near segment. Only comes with a 28 mm wide near segment.
Occupational segmented multifocal
multifocal that have two segments stacked one on top of the other with a distance portion dividing them. For a double D lens these are two near segments. For a quadrifocal these are a near segment and a trifocal segment.
Near visual point
the position of the eyes when reading with a bifocal. Usually about 10 mm down from the distance MRP. Never coincides with the distance OC, and doesn't always coincide with the near OC.
distance
Horizontal prismatic effect in the near segment is usually due to the ____ lens power
Seg height
distance from the top edge of the segment to the bottom of the frame box
Pupil height
distance from the pupil to the bottom of the frame box.
Seg drop
the distance from the pupil center to the top edge of the segment. Normally the pupil is at the datum line, but this is not always true.
Image jump
the prismatic effect due to the near segment alone creates an illusion where the image moves upwards as the eyes move from the distance portion into the near segment.
less
Lens styles where the OC is closer to the segment edge will produce (more or less) of a prismatic effect. Ie) executive will have less of an image jump than a FT BF.
down
Prismatic effect of image jump is always base _____ because the segment if plus power.
Vertical image displacement
prismatic effect due to both the carrier lens and near segment. Occurs because the reading level is displaced from the distance OC and usually the segment OC as well.
Slab off prism
used to compensate for the vertical prism imbalance where there is a relative BD prism in near vision. In glass lenses, this is placed ALWAYS as a base up prism on the most minus lens. Or in plastic, it could be base down prism on the most plus lens as well.
horizontal
Segments can be decentered from the near PD to induce _____ prism at near only.