Chapter 6 - Pedigree Analysis
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
Human Genetics Study Challenges
Controlled Matings Unethical
Long generation time
Small family size
Pedigree
Family tree that outlines the inheritance of one or more characteristics.
Pedigree Symbols
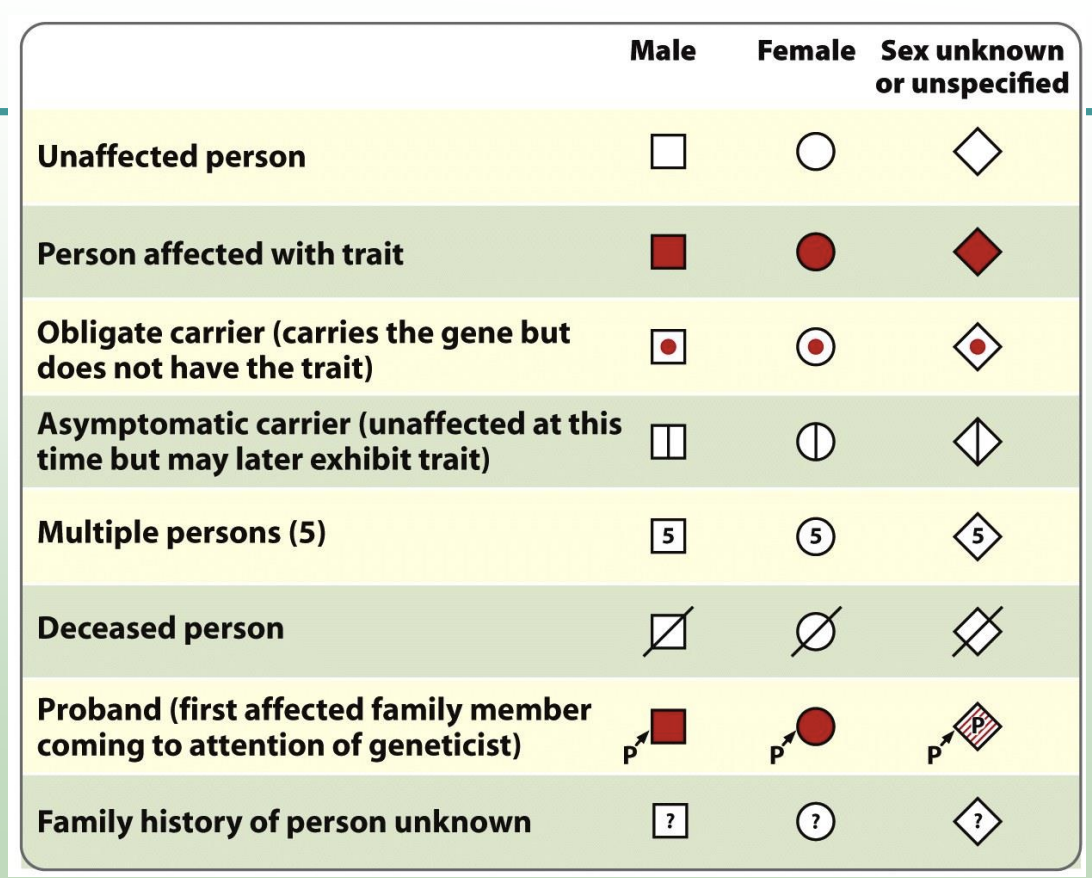
Proband
First affected family member coming to attention of geneticist (initiates pedigree)
Types of Inheritance Patterns
Autosomal Recessive
Autosomal Dominant
Sex-linked recessive
Sex-linked dominant
Y-linked inheritance
Autosomal Recessive Trait
Equal number of affected males and females
Affected individuals often born to unaffected parents
Skipped generations
For rare recessive alleles, new carriers marrying into family is unlikely
Higher possibility of trait appearing in consanguinity/inbreeding happens
Autosomal Dominant
Equal number of affected males and females, both sexes transmit trait
Affected individual has at least one affected parent
Trait appears in every generation
Unaffected parents do not transmit trait
X-linked recessive trait
Suspect if more males affected
Affected sons usually born to unaffected mothers, so can skip a generation.
Never passed from father to son.
X-linked Dominant Trait
Appears in both males and females; often more female
Doesn’t skip generations
Suspect if only daughters of an affected father are affected
Y-linked Trait
All male offspring of an affected male are affected
The trait is passed directly from father to son, showing no skipping of generations.
Dominant mutations
lethal or severely detrimental when homozygous
In the case of a rare mutation
Assume that an unrelated individual marrying into the family is homozygous for the wild-type