Chem 108
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
Why should proteins be kept cold during purification?
To prevent thermal denaturation and microbial growth
What can cause protein denaturation?
Heat, pH shifts, detergents, organic solvents, heavy metals, oxidation, and foaming
What does A280 measure?
protein concentration through absorbance of aromatic amino acids
What absorbs at 280 nm?
aromatic amino acids in proteins (Trp,Tyr,Phe)
What absorbs at 340 nm?
NADH
What absorbs at 595 nm?
Coomassie dye in the Bradford assay
What is the structure of LDH?
Tetramer made of H and M subunits
What are LDH isozymes?
different combinations of M and H subunits
What are isozymes?
enzymes with the same function but different amino acid sequences and kinetics
What properties differ among isozymes?
Tissue expression, electrophoretic mobility, and KM/Vmax values
What is KM?
Substrate concentration at half Vmax, measure affinity
What is Vmax?
maximum reaction rate velocity, when all enzyme is bound to substrate
What is Kcat?
Turnover number, substrate molecules converted per enzyme per second
What changes in competitive inhibition?
Km increases, Vmax stays the same
What changes in noncompetitive inhibition?
Vmax decreases, KM unchanged
What changes in uncompetitive inhibition?
Vmax and Km decrease
How do you determine competitive inhibitor on a lineweaver-burk plot?
The lines intersect at the Y-axis
How do you determine noncompetitive inhibitor on a lineweaver-burk plot?
The lines intersect at the X-axis
How do you determine uncompetitive inhibitor on a lineweaver-burk plot?
They are parallel lines
What does the y-intercept represent on a lineweaver-burk plot?
1/Vmax
What does the x-intercept represent on a lineweaver-burk plot?
-1/KM
What is salting out?
Protein precipitation using ammonium sulfate?
How are proteins separated by ion exchange?
By charge, eluted using increasing salt (NaCl) concentration
What type of chromatography uses cibacron blue for LDH
Affinity chromatography
How does gel filtration work?
Separates by size, the larger proteins elute first
What is the principle of the Bradford assay?
Dye binds basic amino acids; absorbance shifts from 465 to 595
What is a drawback of Bradford assay?
It requires a standard curve, destroys the sample, not very fast
What are the advantages of A280
Fast, no standard curve, nondestructive
What are the disadvantages of A280?
many other materials absorb at A280, some proteins do not absorb significantly
What are the advantages of affinity chromatography?
very selective, fast, size/structure doesn’t need to be known
What are the disadvantages of affinity chromatography?
Need antibody, tag, or ligand attached to resin, expensive
How are bound proteins eluted in affinity chromatography?
Competition, by adding a solution that contains a species that binds tighter to the resin than the protein
What is the stationary phase for column chromatography?
The resin
What is the mobile phase for column chromatography?
Buffer solution
type of buffer is used to elute for ion exchange chromatography?
increasing concentration of salt buffers
How are proteins eluted for ion exchange chromatography?
ion exchange resins bind to the complimentary ions present in salts more tightly that the protein.
What does LDH do?
catalyzes the reduction of pyruvate to lactate through hydride anion transfer
Where is M form most prominent
anaerobic tissue
Where is H form most prominent
aerobic tissue
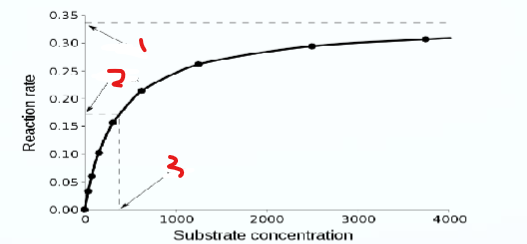
What does 1 represent
vmax
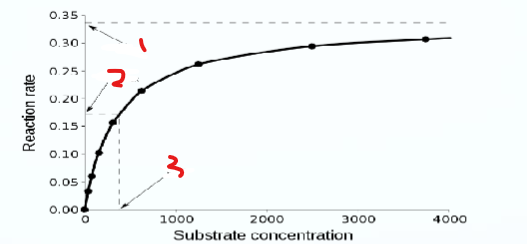
What does 2 represent
½ vmax
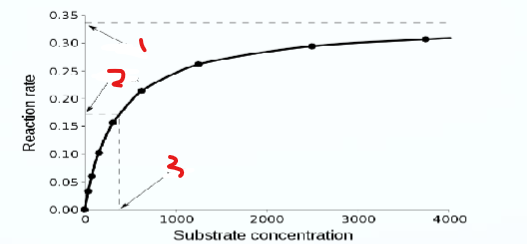
What does 3 represent
km
What is the michaelis-menten equation
v= vmax[S]o / Km+[S]o