Engng Math 145 Matrices
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
Coefficient and Augmented Matrix
Augmented is like coefficient but with coefficients to right of equal sign too.
Row echelon form
All zero rows are at bottom
In each non-zero row, each leading entry is in a column to the left of any leading entries below it.
Reducing to REF is called Guassian elimination.
Elementary row operations
Only do one ERO at a time.
Multiply rows by constant
Swapping rows
Adding or subtracting rows from each other
Parameter variables
Used when REF matrix has a row with >1 non-zero elements OR zero row equal to zero, so infinitely many solutions.
Process: All non-pivot variables must be set to a parameter variable (s, t, u, v), and pivot variables must be solved for in terms of the parameter variables.
eg. 2x + 3y = 4 → x = 2 - (3s) / 2, where y = s
No real solutions & infinitely many solutions
Has zero row equal to non-zero. eg. 0 = 5
Has zero row equal to zero. eg. 0 = 0. This is because some rows are scalar multiples of each other.
Reduced row echelon form
Is in REF
Every non-zero row’s leading entry is a 1 and there are no other non-zero entries in the leading entry’s column.
Reducing to RREF is called Gauss-Jordan elimination.
Diagonal & scalar matrix
Diagonal matrix is square matrix in which all non-diagonal entries are 0.
Scalar matrix is diagonal matrix where all diagonal entries are equal to each other, but not 0.
Upper and lower triangular matrix
Square matrix where all entries below/above diagonal are zero (opposite to it’s name).
n x n Identity matrix
Square matrix with dimension n.
All non-diagonal entries are zero and diagonal entries are 1.
Mathematically equal to 1.
Equal matrices and zero matrices
Same size and all entries equal.
Zero matrix has only zero entries.
Matrix addition/subtraction and scalar multiplication
Can add matrices if same size arithmetically.
For subtraction use A - B = A + (-1)B
Multiply each entry by scalar.
Matrix multiplication
Dot multiply rows of first matrix with columns of second matrix.
Order matters.
Transpose matrix and symmetry
AT : Rotate A clockwise 90o, then mirror horizontally.
Symmetric when A = AT
Transpose rules
(A + B)T = AT + BT
(AT)T = A
(AB)T = BTAT
(kA)T = kAT
(Ar)T = (AT)r
For every square matrix A, A + AT is symmetric.
For any matrix A, AAT and ATA are symmetric.
Pivot variables
Pivot variables are the variables with leading elements attached to them when matrix is in REF. eg:
2x + 3y + z = 5
0x + y + 2z = 1 (this matrix has infinitely many solutions)
0x + 0y + 0z = 0
y & x are pivot variables.
Determinants
Defined for square matrices
Denoted as det(A) or |A|
Det of 1×1
= a
Det of 2×2
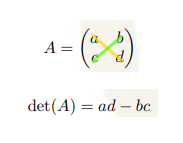
Det of 3×3
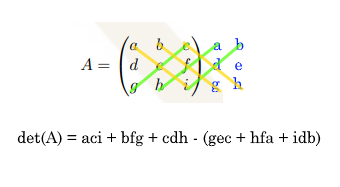
Minor determinant
Mij of A is det(A), but with ith row & jth column removed
Co-factors of a matrix
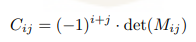
Determinants using cofactors
A = [aij], where n > 2:
det(A) = ai1Ci1 + … + ainCin (calculate by rows)
det(A) = a1jC1j + … + anjCnj (calculate by columns)
if first row has more zeros than first col, choose row formula. vice versa.
a is term of matrix, C is cofactor
Determinant properties
Where A, B = nxn matrices & k is constant
det(AT) = det(A)
det(A-1) = 1 / det(A)
det(kA) = kn det(A)
det(AB) = det(A) det(B)
If A has zero row/column; det(A) = 0
If A has 2 identical rows/cols; det(A) = 0
Note: det(A+B) is NOT equal to det(A) + det(B)
EROs:
Swapping 2 rows/cols of A; det(A) = -det(new)
Multiplying row/col of A by k; det(A) = 1/k det(new)
Adding a multiple of a row/col of A to another row/col; det(A) = det(new)
Determinant of triangular matrix
det(Atri) = product of the entries on its main diagonal
used for “solve via properties”
Inverse of a matrix
AA-1 = A-1A = I, where I is nxn identity matrix
If A-1 exists → A is called invertible/non-singular.
Properties of inverse matrix
Where A & B are invertible, c is constant, n is positive integer, r & s are integers.
If A = invertible matrix, then A-1 only has one solution
(A-1)-1 = A
(cA)-1 = (1/c) A-1
(AT)-1 = (A-1)T
(AB)-1 = B-1A-1
A-n = (A-1)n = (An)-1
ArAs = Ar+s
(Ar)s = Ars
Requirement for matrix to be invertible
nxn matrix A is invertible if and only if det(A) ≠ 0.
Inverse of 2×2 matrix
ad - bc is det(A)
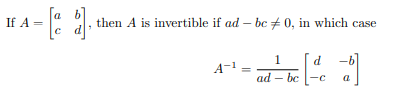
Inverse of nxn matrix
For an invertible matrix A,
A-1 = 1/det(A) * adj(A)
picture of adjugate of A →
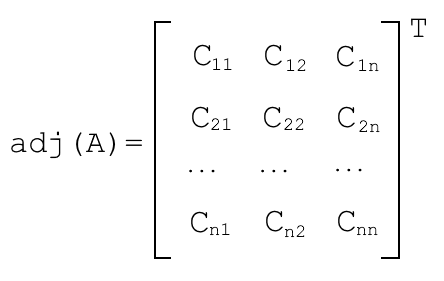
Determining inverse with EROs (Gauss-Jordan Method)
Let A be nxn matrix. If sequence of EROs transforms A to I, then same sequence of EROs transforms I to A-1.
Solving Ax = b
Ax = b → A-1Ax = A-1b → Ix = A-1b → x = A-1b
where A is nxn coefficient matrix, x ∈ {x1, …, xn}, b is constant terms of system.
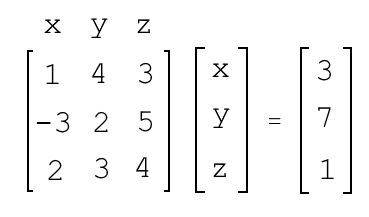
Fundamental theorem of invertible matrices
Let A=nxn matrix. The following statements are equivalent:
A is invertible (det(A)≠0)
Ax = b has unique solution for every b in ℝn
Ax = 0 has only the trivial solution
Reduced row echelon form of A is In
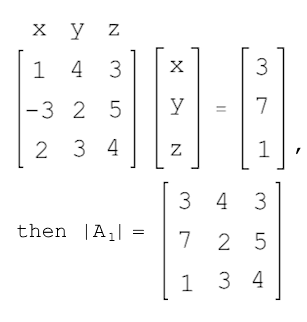
Cramer’s Rule
For Ax = b, then
xk = |Ak| / |A|, for k ∈ {1,2,…,n},
where Ak is A but kth col is replaced by b.
Picking method for question
Determinants:
Formula: 1×1, 2×2 or 3×3 matrices
Co-factors: matrix has row/col with many zeros
Properties: “default” method for > 3×3 matrices
Inverses:
Formula: 2×2 matrix
Adjoint/co-factors: only when specified in question
Gauss-Jordan: “default” method for > 2×2 matrices
Solving linear systems:
Gauss/Gauss-Jordan: “default” method
x = A-1b: if inverse is known
Cramer’s rule: if determinants are known