Geology of Gemstones Final Exam
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
What is the chemical formula for quartz?
SiO2
What is the primary difference between macrocrystalline quartz (e.g., amethyst) and cryptocrystalline quartz (e.g., chalcedony)?
The size of the crystals
Silica Stability: What is the correct order of the varieties of silica from the least stable to the most stable?
Opal - Chalcedony - Chert
Geode and Agate Formation: A necessary first step for geodes and agates to form is what?
The creation of a void
What is the physical structure that causes the "play-of-color" in precious opal?
A microscopic grid of silica spheres that diffract light
Overburden
The waste rock or soil overlying the mineral/gem deposit that must be removed
Lode
Primary deposit; hard rock; substantial cost in personnel & equipment
Placer
Secondary deposit; lower cost; lower risk
Grade
The measure of concentration of a gemstone deposit, expressed as carats per ton
Mining and costs: lode
Substantial $ in personnel and equipment (open-pit operations to strip overburden and tunneling deep into the Earth); conventional hard rock mining methods can result in breakage or damage to gemstones; employ labor intensive hand-work or minimum-charge blasting to prevent fracturing
Mining and costs: placer
Lower-cost, lower-risk; simpler surface mining methods (digging shallow pits or shafts, recovering material directly from river sediments); action of moving water during transport smooths rough edges – makes faceting easier; transport results in cleaner stones
Property rights: ownership can be divided into surface rights and mineral rights
Surface rights = ownership and use of the land’s visible, usable surface; right to build, far, use land for residential, agricultural, or recreational purposes
Mineral rights (or subsurface rights) = ownership of the resources found below the surface (oil, gas, coal, metals, gemstones, and other valuable minerals)
Severed rights = one party owns the surface rights, and another party owns the mineral rights
Resources
Estimated amount of minerals/gems in a deposit based on the projections of geological evidence and knowledge at a given point in time
o Inferred = tonnage, grade, and mineral content can be estimated with a low level of confidence
o Indicated = tonnage, densities, shape, physical characteristics, grade, and mineral content can be estimated with a reasonable level of confidence
o Measured = tonnage, densities, shape, physical characteristics, grade, and mineral content can be estimated with a high level of confidence
Reserves
Subset of resources deemed economically viable for extraction
o Probable: economically mineable part of an indicated and, in some circumstances, measured mineral resource
o Proven: economically mineable part of a measured mineral resource
Physical properties of organic gemstones
Created by or derived from once-living organisms (coral, jet, amber, pearl, “fossil gemstones”), softer than many gemstones (Mohs 2-4, typically not faceted), not as valuable
Nacre (mother-of-pearl) is primarily composed of what?
The mineral and protein combination aragonite (calcium carbonate) and conchiolin
What is a cultured pearl?
A pearl that is farmed instead of naturally sourced
Amber is best described as what?
Fossilized tree resin
What is the age of amber deposits?
Millions of years old
What is jet and how does it form?
Burial of waterlogged, individual pieces of wood in organic-rich, anaerobic (oxygen-deficient) sediments; environment prevents normal decay and decay-causing bacteria, allowing wood to undergo a process of carbonization
“Hard Jet” = associated with marine environments (harder, more durable, and uniform material)
“Soft Jet” = forms in freshwater environments like swamps or lakes (softer, less dense, and more brittle)
What is fashioning?
The mechanical process involving the shaping, faceting, and polishing of a rough mineral crystal
What is cabochon?
This type of gemstone fashioning results in a smooth, rounded, often domed surface with a flat or slightly domed back
Brilliant cut
Rhomboid and triangular facets in a radial pattern
Step cut
Trapezoid or rectangular facets in concentric rows
Mixed cut
Combining brilliant and step cuts
Thermal treatment (Code H) - MOST COMMON ENHANCEMENT
Expose gemstone to high temps (200ºC - 2000ºC) for specific durations in specialized furnaces (annealing)
Induces changes that intensify or alter color, remove undesirable color zoning, improve clarity by dissolving or altering inclusions
Irradiation (Code R)
Subjecting gemstones to various forms of artificial radiation, such as electron beams or neutron beams
Change colors - often followed by heat treatment
Diffusion (Code U, BE)
Surface treatment with color-causing chemical elements during high temperature heating to penetrate the crystal structure
Surface Diffusion (Code U)
Technique creates a thin layer of color concentration near the surface of a light-colored or colorless sapphire
Beryllium Diffusion (Code BE)
Technique often applied to corundum to produce yellows, oranges, and pink-orange
Clarity Enhancement (Filling) Techniques
Use substances with refractive indices like the gem material
Visually minimize the appearance of surface-breaking fissures and improving the stone’s transparency
Oiling and Waxing (Code O/W)
Colorless, viscous oil, resin, or wax into the surface-reaching fractures
RI matching diminished the visibility of the internal fractures and inclusions
Resin and Glass Filling (Code F)
Use more durable substances such as colorless glass, plastic, or resins
Ruby fractures filled with glass, improving the gem’s transparency and color appearance
Advanced HPHT Processing (Code HP)
High-Pressure, High-Temp. treatment subjects diamonds and other gems to extreme conditions, closely replicating their formation environment
Treatment removes or lessens undesirable brownish coloration
Conditions for disclosure of enhancements/treatments
Mandatory if the treatment falls into one of 3 categories:
Non-Permanence: If the treatment is or may not be permanent (e.g., oiling or certain coatings)
Special Care Requirements: If the treatment requires specific care beyond routine handling (e.g., fracture-filled stones that are susceptible to chemical solvents or heat)
Significant Effect on Value: If the enhancement significantly alters the stone’s value (either increasing salability or decreasing rarity premium, such as HPHT treatment or glass filling), disclosure is required
Gemstones other than natural: synthetic
A manufactured gemstone that has the same chemical composition and atomic crystal structure as a natural stone
Gemstones other than natural: simulant
Imitation; Cubic zirconia is an example of a manufactured stone that is both a synthetic and a simulant
What are the 4Cs (diamond grading)?
Clarity, Color, Carat Weight (implied by "weight"), and Cut
What represents the highest clarity on the clarity scale?
“Flawless”
What does the term “total weight” (carat weight) in an advertisement for a piece of gemstone jewelry mean?
There are multiple stones and that is the total weight of all the stones
Purity and karat system: what is considered pure gold?
24K gold
Why are alloys made?
Precious metals are frequently combined with other metals to make jewelry because precious metals are generally too soft on their own
What is the alloy sterling silver’s composition?
92.5% silver and 7.5% copper
What is a troy ounce?
31.1 grams; 12 troy ounces in one pound
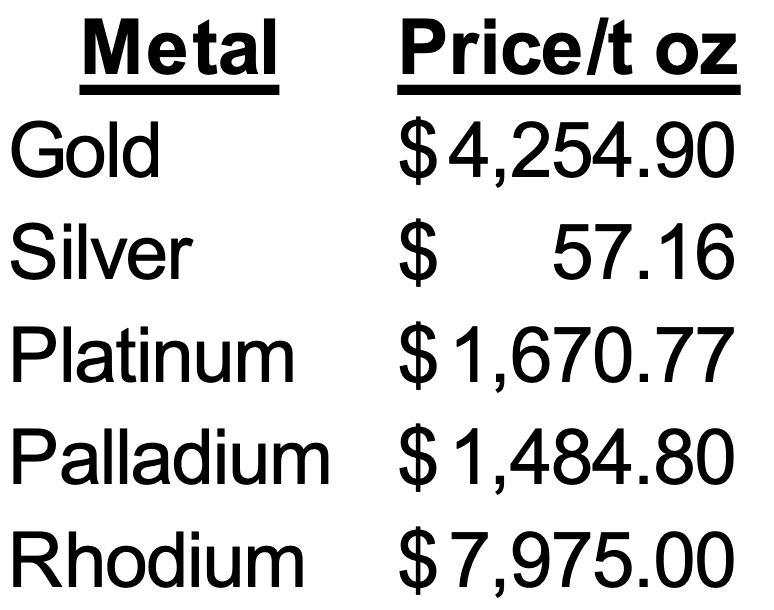
Value Comparison (per troy ounce) between precious metals
Rhodium > Gold > Platinum > Paladium > Silver