Fiscal Policy
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
What is Fiscal Policy?
Changes to government spending or taxation
What are the 2 types of government spending?
Current Spending
Capital Spending
What is current spending?
Spending on public services, e.g. road maintenance or NHS wages
What is capital spending?
Spending on infrastructure, e.g. new bridges, or opening new schools
What are direct taxes?
Taxes paid directly from the individual to the government
income tax
corporation tax
stamp duty
What are indirect taxes?
Tax that is levied on goods and services, passed onto consumers through price increases
VAT
Excise duty
2 types of Indirect Tax: Ad Valorem and Specific
What is Ad Valorem Tax?
Tax set as a percentage of the price of the good
e.g. VAT at 20%
What is Specific Tax?
A fixed amount of tax on a good
e.g. £1 for every litre of petrol
What are progressive taxes?
Taxes that increase in value with income
e.g. income tax brackets
What are Proportional taxes?
Taxes that take the same proportion from all taxpayers incomes
e.g. National Insurance contributions
What are Regressive Taxes?
Taxes that take a larger proportion of income from taxpayers as their income falls
e.g. excise duty
What is a government budget deficit?
When government expenditure exceeds tax revenue
What is a government budget surplus?
When government tax revenue exceeds government expenditure
What is a government balanced budget?
When government spending = tax revenue
What is a cyclical budget deficit?
A temporary budget deficit depending on the economic cycle
During a recession it is high
Caused by automatic stabilisers
Why is the cyclical budget deficit high in a recession?
As government spending increases, in order to boost AD and cover JSA
Government reduces income tax to stimulate spending
What is a structural budget deficit?
Doesn’t depend on the economic cycle
Difference between tax revenue and government spending
What is national debt?
Total amount of money which the government borrowed, and what they owe to 3rd parties
How can a budget deficit lead to demand-pull inflation?
Government spending increases
AD increases
Economy is near or at full capacity, so demand exceeds supply
Firms increase their prices
What are 2 causes of a budget deficit?
Automatic Stabilisers
Discretionary Policy
What are automatic stabilisers?
Automatic response by the government or economy to a change in economic conditions
Incomes fall —> so government receives less income tax revenue
More unemployed —> more spending on welfare benefits (JSA)
However the JSA benefits stabilise the economy, as peoples incomes don’t fall to zero when unemployed
What is Discretionary Policy and how does it cause a Budget Deficit?
A deliberate change in policy from the government
Budget deficit can occur as
Gov may reduce tax brackets, so they receive less income tax
Gov may make it easier to get JSA or increase the value JSA
Gov may increase spending on building schools, hospitals etc
What is expansionary fiscal policy?
Reduced taxation and increased government spending
Used to boost AD and economic activity during a recession
Creates a budget deficit
What is a diagram for expansionary fiscal policy?
Shows a shift right of AD, and an extension in the SRAS curve
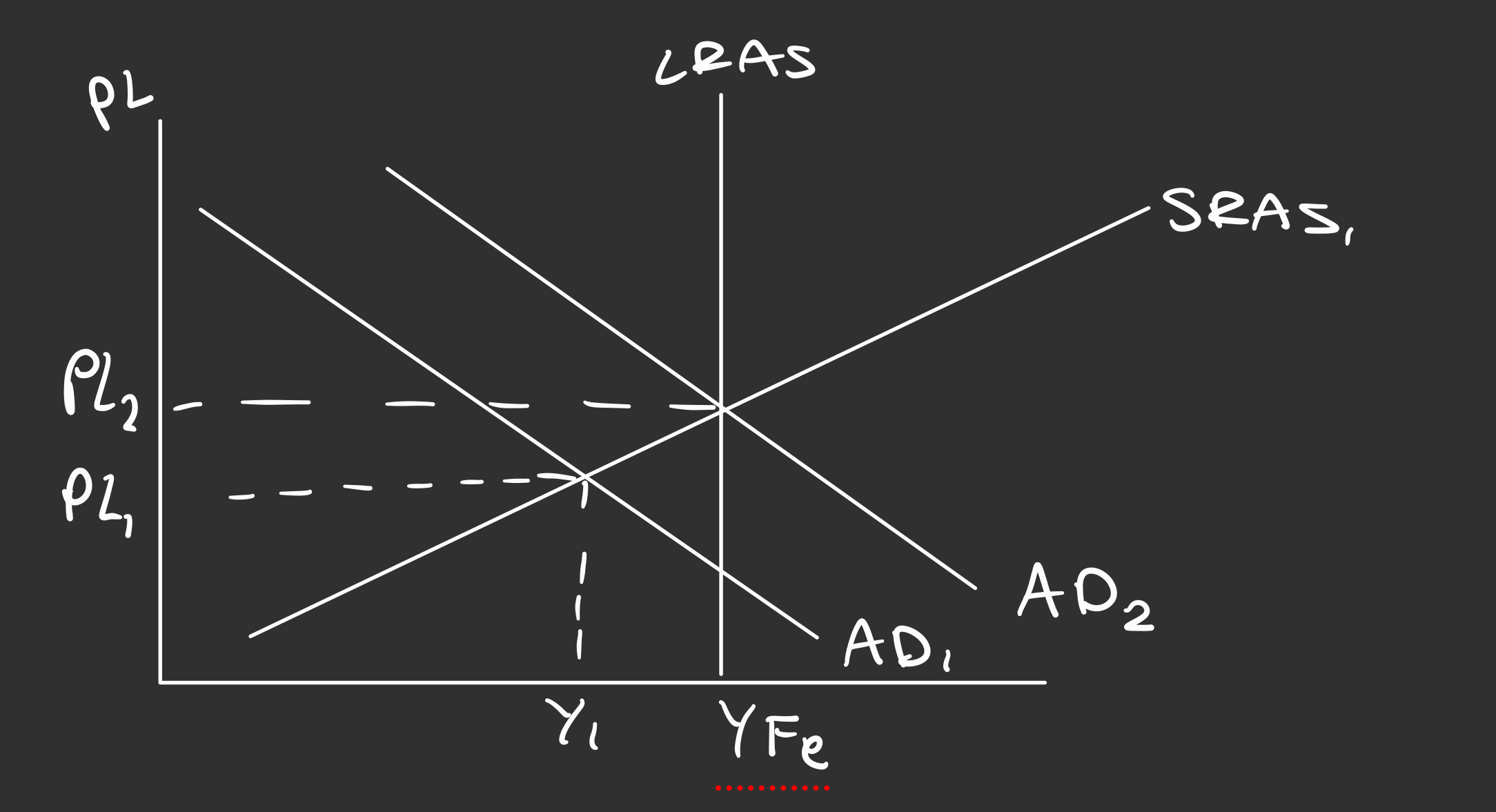
What are benefits of expansionary fiscal policy?
Economic growth
Reduced unemployment as demand for labour increases
‘Crowding In’
What is ‘Crowding In’?
Higher government spending = Increased investment in private sectors
Firms expect the economy to grow due to injections from the government
Therefore they invest in machinery, technology etc
What are drawbacks of expansionary fiscal policy?
Overstimulation
‘Crowding Out’
What is overstimulation?
When aggregate demand increases rapidly that the supply can’t increase quickly enough to match the increased demand
This creates demand-pull inflation
Business costs rise as workers being made to work harder so want pay rises
What is ‘Crowding Out’?
Private sector firms buy government bonds, so the government has money to spend
So instead of saving their money with the bank, the private sector firms use it to buy government bonds
This reduces the supply of money in the ‘loanable funds market’ meaning that less money is available to lend out.
This increases interest rates
What is contractionary fiscal policy?
The increase in tax levels and reduced government spending
Reduces the Budget Deficit
AD falls and economic activity contracts
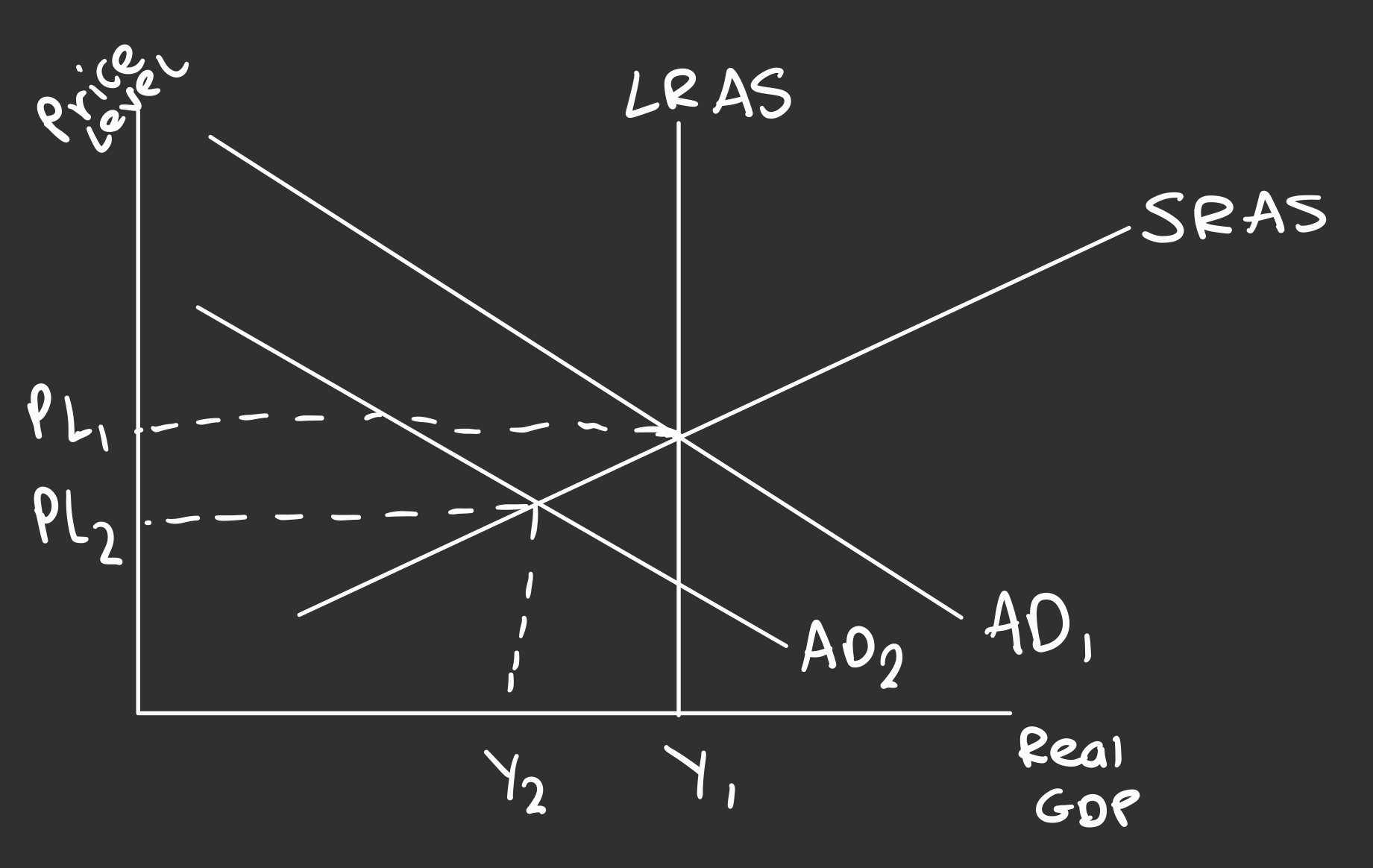
What is the diagram for contractionary fiscal policy?
AD shifts left, SRAS contracts and Price Level falls
What is the Laffer Curve?
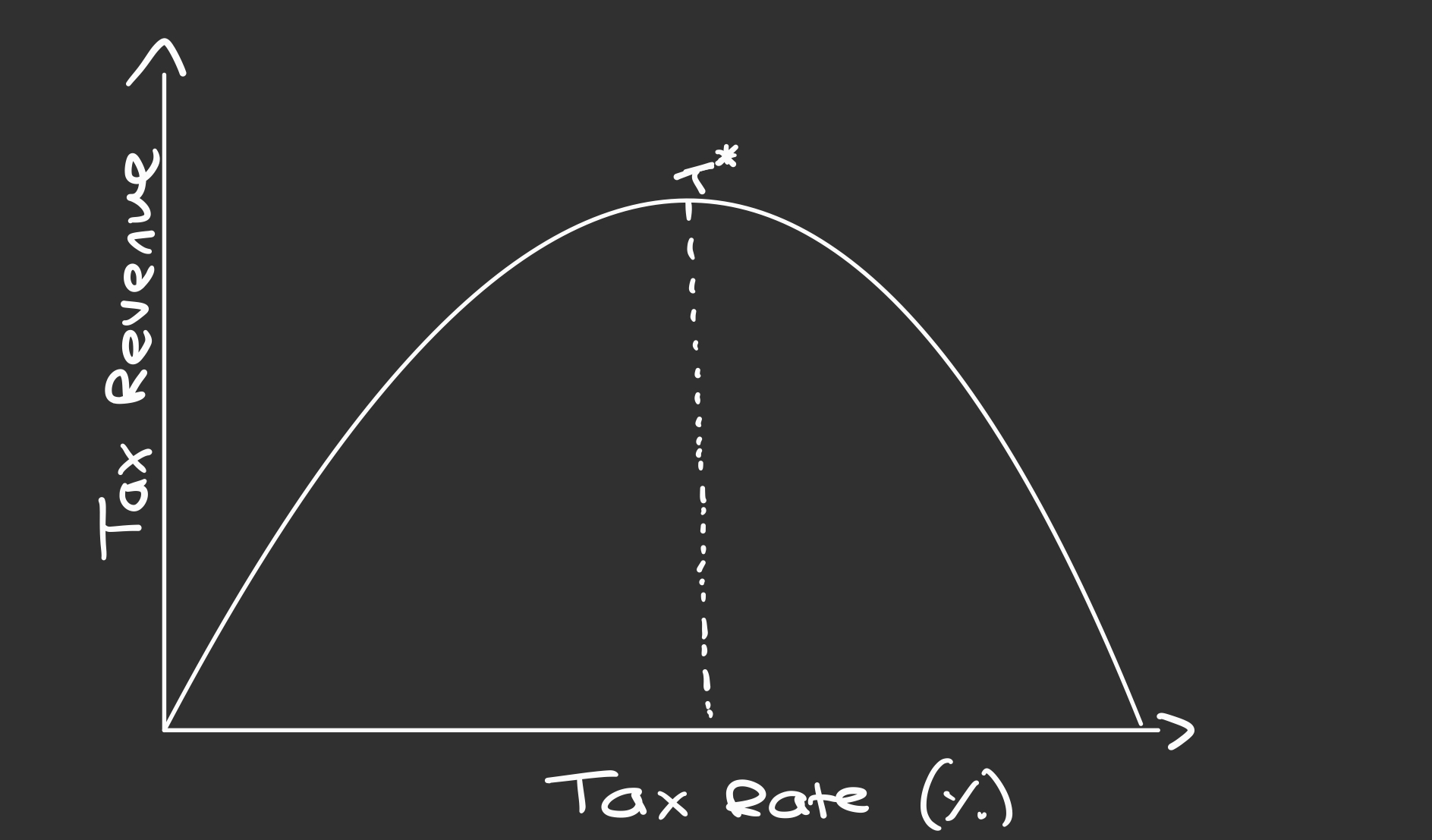
What does the Laffer Curve show?
When tax rates are very low, tax revenue is also very low
However, when tax rates are very high, tax revenue is very low
In between, is the maximum tax rate that maximises revenue
Why is tax revenue low when tax rates are high?
Increased tax avoidance or evasion
Individuals may leave to other countries
High tax rates for low income workers may disincentivise working (voluntary unemployment)
Evaluate use of decreasing on macroeconomic objectives