Chapter 9 - Real Estate
1/93
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
94 Terms
The “bundle of rights” included in the legal ownership of land
Possession, Disposition, Enjoyment, Exclusion, Control
Actual Notice
Evidence of ownership provided by physical possession
Constructive Notice
Evidence of ownership provided by the recording of public documents; serves notice to the world as the true owner
30 years
Length of time in Florida that the root of title extends back from the recording of a claim
Chain of Title
A timeline of recorded documents linking past owners from the root of title to the present day
Title Plant
A compilation of public records containing copies of all real estate documents, arranged according to the date of recording in the public record
Title Search
A search of all documents that may affect title to property, where notations are made indicating such affect
Abstract
A date-order compilation with a caption page of all documents that may have an effect on the title to property being investigated
Opinion of Title
An attorney’s legal opinion as to the quality of title, based on a review of title history
Title Defects (Cloud on Title)
Claims or other factors that could cause a title to property to be declared invalid
Mortgagee’s (Lender’s) Title Insurance
Title insurance that protects the lender by paying the unpaid balance of the loan if the borrower should lose title to the property as a result of a defect
Mortgagor’s (owner’s) Title Insurance
Title insurance obtained by a property owner wishing to provide protections against issues in title
Lender’s Title Insurance (transferable to new lender) Note: Owner’s title insurance is NOT transferable
Title insurance that is transferable
Alienation of Title (can be voluntary or involuntary)
Transfer or conveying of ownership from one party to another
Voluntary transfer of title
Deed or Will (upon death of owner)
Testate
A person who died and left a will, voluntarily transferring title according to their wishes
Intestate
A person who dies without a will
Decendent
A person who died
Involuntary transfer of title
Descent and distribution, Escheat, Eminent domain, Adverse possession
Descent and Distribution
Title transfer determined by law to an individual’s heirs upon death when the individual died without a will
Escheat
Reversion of property to the state if someone dies without a will and has no known heirs
Eminent Domain
The government’s right to take private property for public benefit through a process called condemnation
Adverse Possession
Involuntary method by which an owner may lose title to another person who has taken control of the property
Conditions for adverse possession
Open, adverse, hostile, and exclusive possession of the property for a period of 7 continuous years and pay taxes for those 7 years.
“Slept on his rights”
An owner who failed to eject a trespasser, losing title to the hostile claimant by involuntary alienation
Deed
The document that is used to voluntarily convey ownership from one party to another
Requirements for a valid deed
In writing
Names of all parties
Legal description of the property
Legal rights being conveyed
Consideration (good or valuable)
Signed by a competent grantor and two witnesses
Granting clause
Delivery & acceptance
Grantor (signature required)
The party who voluntarily transfers (conveys) ownership
Grantee (signature not required)
The party who voluntarily receives ownership
The point at which title has been transferred
When the deed is voluntarily delivered to, and voluntarily accepted by, the grantee (does not have to be acknowledged or recorded)
Premises (granting) Clause
The only legally necessary clause in a deed
The items stated in a granting (premises) clause
Names of the parties
Words of conveyance
Consideration
Date of transfer
Legal description of the property
Habendum Clause (to-have-and-to-hold” clause)
The clause in a deed that specifies the bundle of legal ownership rights being conveyed
Reddendum Clause
The clause in a deed used in a remainder estate to reserve a right in the title, not the land
Warrants (or deed covenants)
The promises made by a grantor to the grantee giving assurances as to the quality of title
Warrant of Seisin
The promise by the grantor to the grantee that he or she owns and has the legal right to convey the property
Warrant of Quiet Enjoyment
The assurance given by the grantor to the grantee that no one will be able to make a claim against the ownership of the property
Warrant of Further Assurance
The promise given by the grantor to take whatever action is necessary to protect and defend the title forever
Warrant Against Encumbrances
The assurance given by the grantor that there are no encumbrances against the property other than those disclosed in the deed and that the grantor is responsible for liens or claims not listed in the deed
Covenant of Warranty Forever
The assurance given by the grantor that the grantee will be able to enjoy possession and uninterrupted use of the property
Quitclaim deed
The type of deed that contains no warrants (or covenants) of any kind, conveying any interest in the grantor may have in the property, if any
Bargain and Sale Deed
The type of deed that contains only one warrant, the warrant of seisin, stating that the grantor is the true owner of the property and has the legal right to convey it
General Warranty Deed
The type of deed that provides the best protection to the grantee that promises that the grantor is the true owner, has the right to sell, and will warrant and defend the title against any and all claims forever
Common uses for a quit claim deed
Cure defects or clouds on the title
Transfer of a spouse’s interest to the other spouse in a divorce action
General Warranty Deed
The type of deed given in a real estate sales contract if no deed type is specified
Quitclaim Deed
Deed that provides the least protection to the grantee and the fastest method of transfer
Personal Representative’s Deed
Deed used to convey the property of an individual who died intestate (without a will)
Guardian’s Deed
Deed used to convey the property of a minor by a grantor on the minor’s behalf
Committee’s Deed
Deed used to convey property owned by a mentally incompetent person
Master Deed
Deed used by a developer to convey land to a condominium association that can convey the individual units
Unit Deed
Deed that conveys individual condominium units from an association to the public
Cloud on Title
Term used to describe a property with a defective title
Suit to Quiet Title
Court action taken to resolve a dispute regarding a claim to title
30 years (as defined by MARTA to eliminate claims-in-antiquity)
The period by which outstanding claims to title must have been exercised to establish root of title in Florida
Police Power
The government’s right to restrict the use of land to protect the health, safety, or welfare of the citizens
Escheat
The right of the state to acquire ownership of property when an owner dies intestate (no will) and no lawful heirs can be located
Eminent Domain
The right of a local, state, or federal government to take private property for public use
Condemnation Proceeding
The negotiating process by which the local, state, federal government, railroads, and public utilities can take a private owner’s property for public use
Property Taxation
The power of local governments to levy taxes on private property, which if not paid, may result in an unpaid tax lien on the property that may be foreclosed in court
Police Power
The power of the government that is exercised by zoning, building codes, and health codes
The four types of governmental limitations on private property rights
Police power, Eminent domain, Taxation, and Escheat (“PETE”)
Deed Restrictions (usually recorded by the developer or builder on multiple properties at the same time)
The most common form of private limitations on property ownership
Easement
Limited right of access or use of someone else’s property for a specific purpose; an encumbrance that affects the owner’s rights and the property’s value
Easement in Gross
Easement most commonly illustrated by a utility company that gives one party the right of access to a property owner’s real estate; does not “run with the land”
Easement Appurtenant
Easement involving two or more parcels of property and “runs with the land” and will be binding on future owners
Easement by Necessity
Easement appurtenant where land is subdivided in a manner that creates a landlocked parcel, where the law assumes the owner has a legal right of access that will be imposed by the courts
20 or more years of continuous and uninterrupted use of a portion of another person’s property
Easement by prescription in Florida; once established by a court, creating public access
Encroachment
Unauthorized physical intrusion onto another’s property
Lessor
The owner (or landlord) of a leased property
Lessee
Renter of leased property
Items required for a valid lease agreement
Competent parties
Names and signatures of lessor and lessee
Consideration
Term of the tenancy
Legal description of the property
Net Lease (or triple net lease)
Lease in which the tenant pays a fixed rent plus all or a portion of the operating costs including insurance and maintenance; typically used for commercial and industrial leases
Gross Lease
Lease in which the tenant agrees to pay a fixed rental amount and the landlord pays all expenses related to the property including taxes, insurance, and maintenance; used for most residential leases.
Percentage Lease
Lease in which the tenant pays a monthly base rent plus a percentage of the annual or monthly gross sales of goods sold on the premises; commonly used in retail centers and malls
Lease-Option
Lease with an option to purchase within a specified time frame under specific conditions; typically a portion of the rent may be applied to the purchase
Graduated Payment or Step Up Lease
Lease containing specified rent adjustments (usually increased) at pre-determined times in the lease
Sale-Leaseback
Lease Where the owner sells the property to an investor with a condition that the new owner immediately leases it back to the seller, therefore freeing up the equity as cash
Assignment (the lessee becomes the assignor and the person receiving the rights becomes the assignee)
The transfer of leasehold rights of all of the leased space for the remaining period of time by the lessee, where the person receiving the rights pays rent directly to the landlord
Sublease or Sandwich Lease (the person subleasing becomes the sublessee and makes payments through the original lessee, the sublessor)
The transfer of less than 100% of the leased space or for a shorter period of time than the entire remaining lease period by the lessee where the lessee remains responsible for rent payments
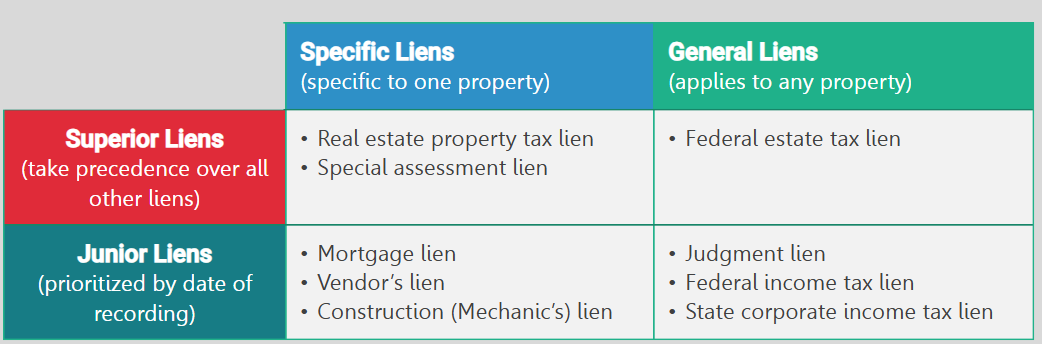
Lien (can be voluntary, such as a mortgage lien, or involuntary, such as a tax lien)
Financial claim against property by a creditor or unit of government that is used to secure the payment of a debt or obligation owed by the property owner
Superior Lien
Involuntary lien that takes precedence over other liens and are paid first in the event of a foreclosure; imposed by law without the owner’s consent
Junior Lien
Lien that is typically paid based on the date of recording, but always has lower priority than superior liens
Specific Lien
Classification of a lien that is specific to one property
General Lien
Classification of a lien that applies to any property the person may own
Real Estate Property Tax Lien
Type of superior lien owed by a property owner that is created January 1 of each year
Special Assessment Lien
Superior lien owed by a property owner that is assessed by local government for improvements such as road paving, sidewalks, and sewers
Mortgage Lien
Junior lien that is given by a borrower as a pledge of property as security for repayment of a loan
Judgment Lien (a type of general lien where the lawsuit may have had nothing to do with real property)
Junior lien imposed when a party is entitled to collect damages awarded by a court as the result of a lawsuit
Construction Lien (also referred to as a mechanic or materialmen’s lien)
Junior lien entitled to a builder or contractor who has not been paid money that is due for materials or labor used to build or improve a property
Federal Income Tax Lien
Junior lien placed against a property or individual for nonpayment of federal income taxes
Construction Lien (the lien dates back in priority to the date on which the first materials were delivered of labor was first performed on the property)
Junior lien where the lien date may be earlier than the date the lien was filed
Foreclosure
Method of enforcement for a lien
Lis Pendens
Notification of a pending lawsuit against a property owner
Summary of liens