W7 starred: prenatal adaptations & maternal changes in pregnancy
1/40
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Adaptations During Pregnancy & Preventative Care
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
When is the embryonic period?
beginning of 3rd week to end of 8th week after conception
What are the 3 layers developed in the embryonic disc?
ectoderm
mesoderm
endoderm
What happens at the end of the embryonic period?
All major organ systems are in place
What are teratogens? What happens when they’re exposed in the embryonic period?
substances or agents that can cause birth defects (major structural and functional damage to the developing organs)
What are some physical examples of teratogens?
ionizing radiation (ie; x-rays)
hyperthermia (ie; hot tubs, sauna, high fever)
What are some chemical teratogens?
prescription meds (chemo, thalidomide (sedative), isotretinoin (acne med), valproate (anticonvulsant- seizures, bipolar))
recreational drugs / cigs / alcohol
environmental chemicals (ie; lead, mercury, pesticides)
What are some infectious agents teratogens?
rubella virus
herpes simplex virus
syphilis
What are some metabolic conditions teratogens?
malnutrition
diabetes
thyroid disorders
Gestational age (GA) is what?
how you date a pregnancy
describes how far along it is from LMP (last menstrual period)
What is quickening?
can feel fetal movement
What is brown fat?
type of adipose tissue that helps maintain body temp (when you get too cold)
prominent in late fetal & newborn stages
What is lanugo?
fine, soft hair typically seen covering body and limbs of late fetus / newborn
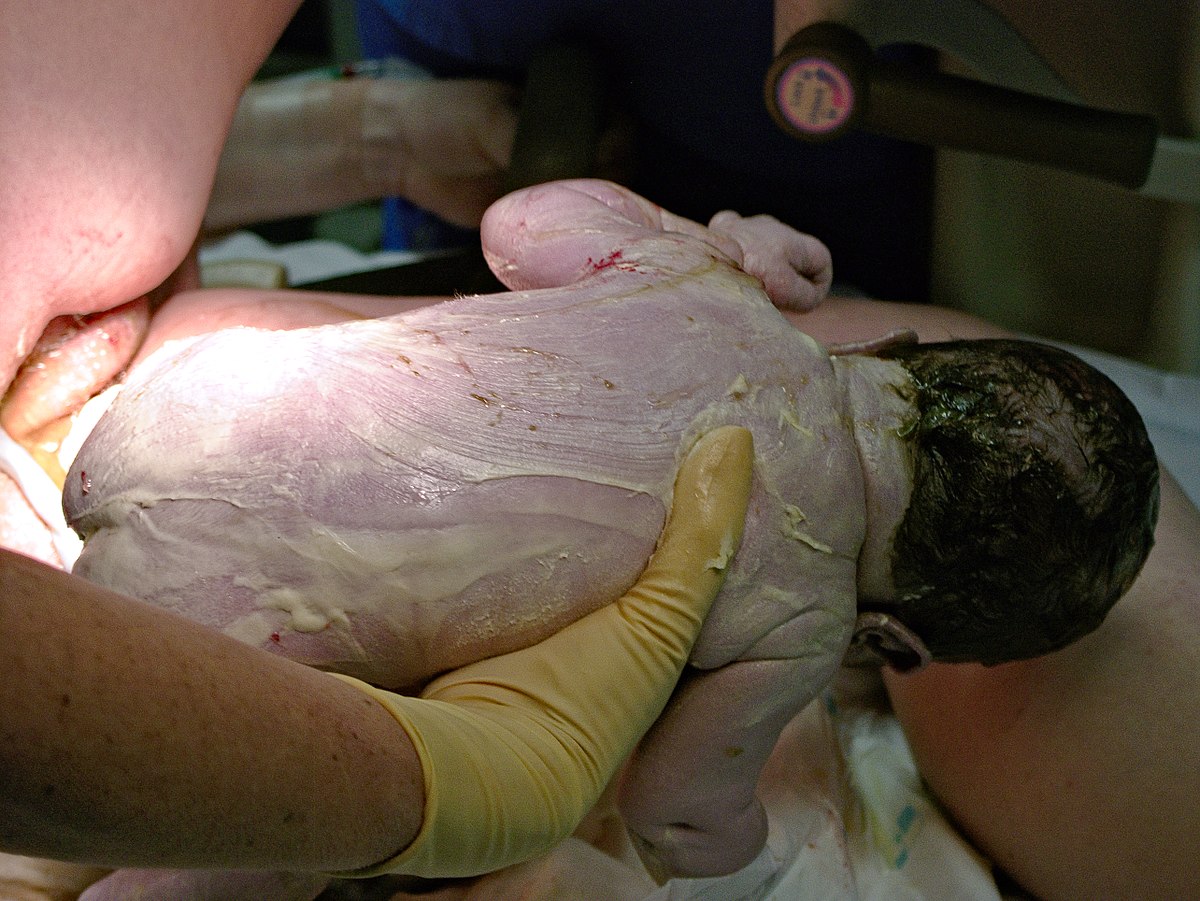
What is vernix caseosa?
white, creamy substance that develops on the skin of the fetus in the 3rd trimester
protects newborn
facilitates extra uterine adaptation of skin the first postnatal week if not washed away after birth
What is pulmonary surfactant?
lipoprotein complex that lines the alveoli of the lungs
decreases surface tension to promote lung expansion after birth and prevents lung atelectasis (collapse)
Major functions of the placenta
produces hormones critical for maintaining pregnancy (estrogen, progesterone, hCG)
transports substances between maternal & fetal circulation
a. acts as respiratory organ for gas exchange
metabolizes & synthesizes agents necessary for transferring gas & nutrients & removing waste products
provides an immunological barrier between maternal & fetal systems
How much does the placenta weight at birth?
1/6 weight of fetus at nirth
Is there mixing of maternal & fetal blood?
No; maternal and fetal blood do not mix
The placenta is in contact with what of the pregnant person
uterine wall
What is the placenta composed of?
chorion
amnion
umbilical cord
Where does the exchange of the maternal & fetal substance happen?
in the intervillous space
What are the 3 placental hormones?
hCG
Estrogen
Progesterone
What does hCG do?
rapidly increases
stimulates corpus luteum to produce estrogen & progesterone
this is what causes you to have positive pregnancy
Which hormone is responsible for causing a positive pregnancy tst?
HCG
What does estrogen do?
stimulates uterine growth
increases blood supply to uterine vessels
helps in developing ductal system in breasts for lactation
associated with; hyperpigmentation, vascular changes in skin, increased activity of salivary glands, hyperemia (++ blood flow) of gums and mucus membranes
What does progesterone do?
maintain endometrial layer for implantation of fertilized egg
stimulates lobes of breasts for lactation
relaxes smooth muscle of uterus (for growth and quiescence?)
produced by corpus luteum, then by placenta
The umbilical cord has how many arteries and veins?
2 arteries, 1 vein (AVA)
In the fetus, the artery(s)/vein(s) carries deoxygenated blood away from the fetal heart to the placenta
arteries (2 arteries)
In the fetus, the artery(s)/vein(s) carries oxygenated blood & nutrients from the placenta to the fetal heart
1 vein
The umbilical arteries carry _____________
a. oxygenated blood to the placenta
b. deoxygenated blood to the placenta
c. maternal immunity to the placenta
d. nutrient rich blood to the placenta
b. deoxygenated blood to the placenta
The umbilical vein carries _____________
a. oxygenated blood to the fetal heart
b. deoxygenated blood to the placenta
a. oxygenated blood to the placenta
d. nutrient rich blood to the placenta
a. oxygenated blood to the fetal heart
A new parent is distressed by the “thick white substance” covering their newborn because it “looks gross”. What action by the nurse is most appropriate?
a. Scrub it all off and bathe the baby right away.
b. Reassure them that it will go away
c. Report the findings to the provider
d. Explain that vernix cassenas protects the fetal skin from amniotic fluid in the uterus
d. Explain that vernix cassenas protects the fetal skin from amniotic fluid in the uterus
What are maternal cardiovascular system changes during pregnancy?
decreased systemic vascular resistance (progesterone relaxes smooth muscle) (blood vessel are wider - vasodilation)
lower BP
blood volume increases ~45%
increase cardiac output (heart pumping more blood) ~50%
heart rate increases 15-20 bpm
heart is deviated up and left (pushed by expanding uterus
hypercoagulable (more likely to clot)
What are maternal respiratory system changes during pregnancy?
increase in oxygen use
pressure on diaphragm (from growing uterus)
this limits lung expansion/capacity
slight hyperventilation
RR is unchanged, breath is deeper
What role do estrogen and progesterone play in the respiratory system of a pregnant person?
Estrogen: increases vascularity of mucous membranes
Progesterone:
decreases airway resistance (relaxes smooth muscle)
raises sensitivity of CO2 in the respiratory center
increases awareness of need to breathe
What are the endocrine system changes in the pregnant person?
Estrogen:
increases vascularity
relaxes pelvic ligaments
decreases maternal insulin sensitivity (more insulin resistance)
Progesterone
relaxes smooth muscle
suppresses FSH/LH (to prevent ovulation)
decreases uterine contractility
decreases maternal insulin sensitivity (more insulin resistance)
hCG
maintains corpus luteum production of estrogen & progesterone until placenta takes over their production
hPL (human placental lactogen)
decreases maternal metabolism of glucose (so higher blood sugar)
growth hormone
What are GI changes in a pregnant person? not starred
slowed emptying of stomach
decrease of GI tone & motility (constipation)
heartburn (pyrosis)
hyperemia in mouth (due to increased estrogen)
ptyalism (more saliva)
increased absorption in large & small intestine
What are maternal urinary system changes in pregnancy? not starred
increases urinary frequency
increase GFR (kidneys filtering more blood)
hypertrophy (larger) bladder walls
increase risk of UTI (cause of less effective urine emptying?)
ureters are longer
What are maternal integumentary (skin) changes in pregnancy? not starred
hyperpigmentation (cause of ++estrogen & progesterone)
hair growth rapid, hair loss slower
increased circulation (++sweat & sebaceous glands) —> acne
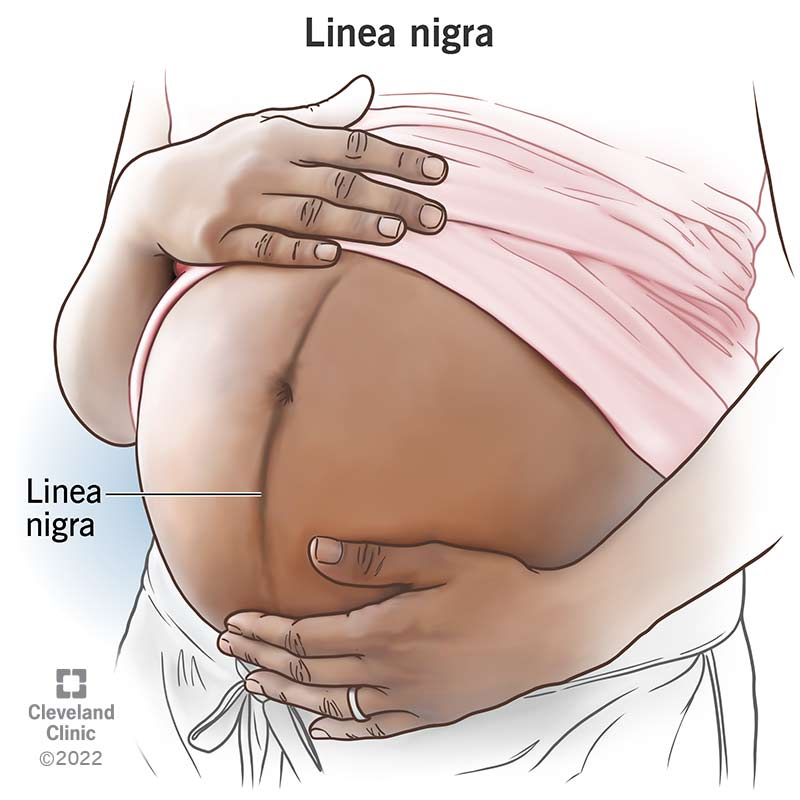
Linea nigra (not starred)
dark vertical line that appears on stomach during pregnancy
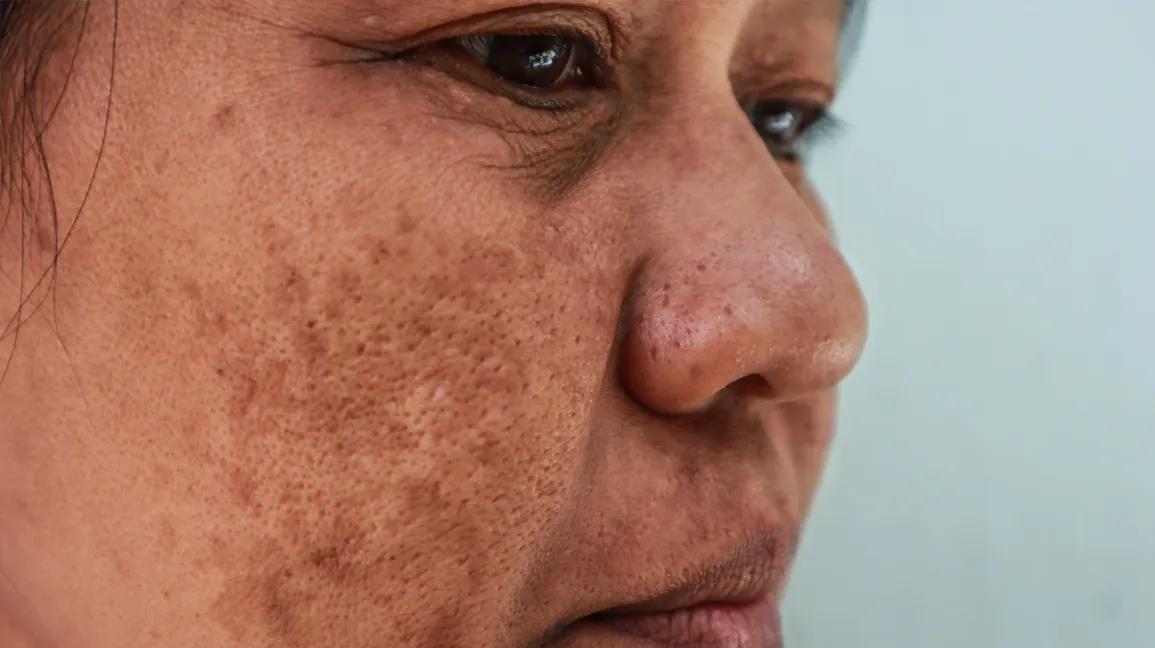
Chloasma or melasma (not starred)
darker skin patches
Striae gravidarum
stretch marks