Aviation Weather Test 3 (Lessons 10,11,12)
1/130
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
131 Terms
Air mass
Large body of air with uniform temperature and humidity.
How are air masses classified?
According to their temperature and mositure properties
3 types of temperature
Artic (A), Polar(P), Tropical (T)
A
Artic
P
Polar
T
Tropical
Types of moisture
Continental (c ) Maritime (m)
c
Continental(over land)
m
Maritime (over water)
What classification is Florida (over land)
cT
High pressure classifications(letters)
cP (continental polar), cA(continental artic)
Low pressure classifications(letters)
cT(continental tropical), mT(maritime tropical), mP(maritime polar)
How is high pressure characterized?
Cooler, denser air causing air to sink(cold=high pressure).
How is low pressure characterized?
Rising warm air which creates low-pressure area(warm/ moist=low pressure).
Front
A boundary between two air masses.

What front is this?
Cold

What front is this?
Warm

What front is this?
Stationary

What front is this?
Occluded

What is this?
Dry line
Warm front
Occurs when a warm mass of air replaces a body of colder air (move slowly).
Cold front
Cold dense and stable air replaces warm air(faster).

Squall line
Narrow band of thunderstorms/showers right along or ahead of a cold front.
Stationary front
A front that stalls or moves very slowly over an area (ex. 2 weeks of straight rain in Florida).
Occluded front
Occurs when both fronts merge/collide (cold and warm).
Cold front occlusion
The cold front overtakes the warm front and the air behind the cold front is colder than the air ahead of the warm front.
Warm front occlusion
Opposite of cold front occlusion, air behind the cold front is warmer than the air ahead of the warm front.
Wave cyclone
A low pressure circulation that forms and moves along a front.
How do all wave cyclones start out as?
A stationary front
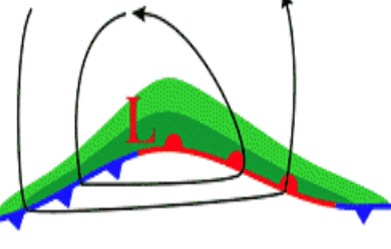
What is this “hump” called?
A kink
Dry line
Boundary hundreds of miles long seperating a moist air mass and a dry air mass (most common in Texas).
Dry line weather
B/c drier air is more dense than moist air, the dryline forces moist air up into the atmosphere as it moves east.
How do clouds form?
Condensation of water vapor in rising currents of air.
What is the dry adiabatic lapse rate?
3 degrees C per 1,000 feet
What is the saturated adiabatic lapse rate (low altitude)?
1.5 degrees C per 1,000 feet.
What is the saturated adiabatic lapse rate (high altitude)?
3 degrees C per 1,000 feet.
What is an unsaturated air parcel?
Air with relative humidity less than 100%.
What does the amount of water vapor air can hold depend on?
Air temperature(warm=lower relative humidity, cooler=higher RH).
Does dewpoint decrease as we go up into the atmosphere?
Yes
Dew Lapse Rate
0.5 degrees C per 1,000 feet.
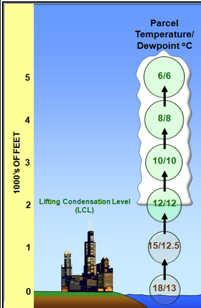
Lifted Condensation Level (LCL)
Level where an air parcel becomes saturated (RH=100%).
What happens to temp and dew point with a decrease in altitude?
Both increase
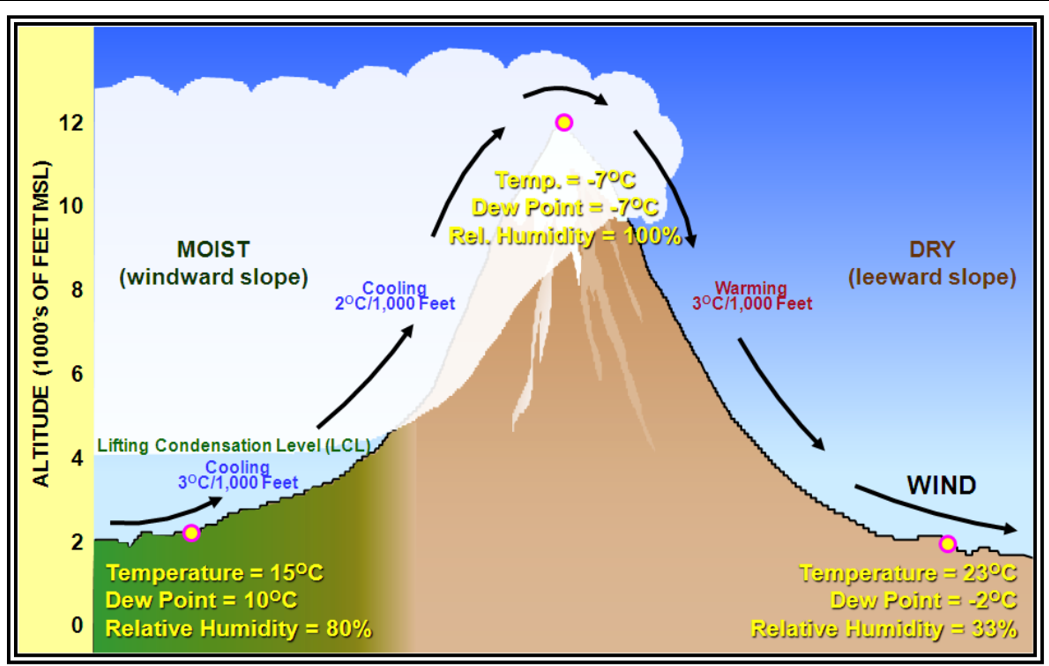
Orographic lifting
Occurs when air is forced to rise over a mountain. (one side is dry the other side is moist).
Windward slope
Moist side
Leeward slope
Dry side
Frictional effects
high pressure moves clockwise and outward while low moves counterclockwise and inward.
How does high pressure= clear skies
High pressure air is sinking, compressing, and warming.
How do winds act with high pressure?
Move away
How does low pressure favor precipitation?
Low pressure causes air to rise, expand, and cool.
How do winds act with low pressure?
Move into
Fontal lift
Occurs when the cold denser air moves under warm, less dense air.(when fronts meet)
Overrunning
Warm air rises over the cooler air
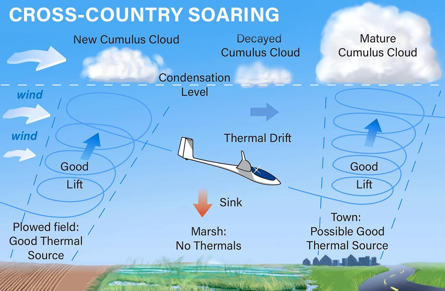
Buoyancy
Air near the ground warms differently based on the albedo effect. (ex. town warms faster which equals good lift).
Rain making clouds
Cumulonimbus and nimbostratus.
What do middle clouds start with?
Alto
What do high clouds start with?
Cirr
How to identify a low cloud?
Not with alto/cirr.
What are high clouds made out of?
Ice crystals

What cloud is this?
Cirrus

What cloud is this?
Cirrocumulus

What cloud is this?
Cirrostratus
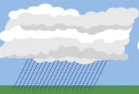
What cloud is this?
Nimbostratus(one of the rain clouds and can cause turbulence).

What cloud is this?
Cumulus (fluffy and low)
Layer/blanket clouds
Anything that ends with stratus (nimbostratus,altostratus, cirrostratus).

What cloud is this?
Stratus

What cloud is this?
Altostratus

What cloud is this?
Cirrostratus
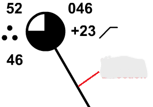
Long line of wind barb
Wind direction
Short line of wind barb
Wind speed

Clear

Few

Scattered (25%)

Partly cloudy (50%)

Mostly cloudy (75%)

Overcast

Sky obscured (ex. smoke)

How many knots?
50 knots

How many knots(shorter line)?
5 knots

How many knots (longer line)?
10 knots

How many knots?
75 knots (50+10+10+5)
What do you round to if wind is 3-7 knots?
5 knots
What do you round to if wind is 8-12 knots?
10 knots
Precipitation
Any form of water particle that falls from the atmosphere and reaches the ground (ex.snow, rail,hail,etc)
Necessary ingredients for precipitation?
Water vapor
Sufficient lift (adiabatic lapse rate)
Growth
What happens when water droplets become too heavy to be suspended in the air?
They fall to the surface.
What happens to evaporation the smaller the water droplet is?
Evaporation is faster
What are the two growth processes that helps water fall to the surface?
Collision-coalescene
Ice crystal process
Convection
Warm air rising
What are the common sources of vertical motion?
orographic effects, frictional effects, frontal lift, and buoyancy
What happens if both growth processes fail?
Water droplets will evaporate or sublimate before they reach the ground.
Collision-coalescence
Collisions occur between cloud droplets (rain) of different sizes. They stick together to form larger droplets which causes them to fall as rain if they are too large to be suspended in the air.
What is suspected to be the main growth process in warm, tropical air masses?
Collision-coalescence
Ice crystal process
Occurs in colder clouds where super cooled water droplets and ice crystals are present.
Where are ice crystals the main growth process?
Mid-latitude and high latitudes.
Precipitation types
Snow
Ice pellets(sleet)
Freezing rain
Rain
Hail
What determines the type of precipitation that occurs at the surface?
Vertical distribution of temperatures
When does snow occur?
When temperatures remain below freezing throughout the entire depth of the atmosphere (below 0 degrees C/ 32 F).
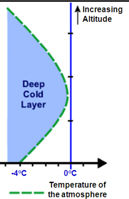
What precipitation is this?
Snow
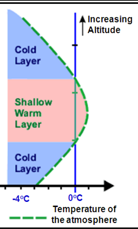
What precipitation is this?
Ice pellets/sleet
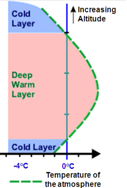
What precipitation is this?
Freezing rain