Chapter 4 Micro
1/108
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
109 Terms
Imagine you are a microbiologist trying to isolate new species of prokaryotes. You collect numerous samples and return to your lab, where you proceed to encourage any prokaryotes present to grow. Disappointingly, you are not successful. Which is the LEAST likely explanation for this outcome?
Compounds or conditions that you provided inhibited their growth.
The prokaryotes depended on a close association with others in order to grow.
You did not manage to provide them with all the major elements, trace elements, and growth factors necessary to support their growth.
Your atmospheric conditions did not sufficiently match those found in their environment.
There were no prokaryotes present where you sampled.
There were no prokaryotes present where you sampled.
Bacteria and archaea typically divide by a process known as .___________ ________
binary fission
Bacteria growing in a natural environment experience ______.
Multiple choice question.
dynamic and complex conditions
conditions similar to that of the laboratory
dynamic and complex conditions
What term is used to describe a group of microbes co-existing in polymer-encased communities?
Multiple choice question.
Biolayer
Biofilm
Slime layer
Slime film
Biofilm
Which of the following does not describe interactions of mixed microbial communities?
Multiple choice question.
Conditions in mixed microbial associations are readily reproduced in the laboratory.
Microbial cells can consume O2, creating microenvironments in which anaerobes can thrive.
Microbes can compete for nutrients.
Some microbes can synthesize toxic compounds to inhibit competitors.
Microbes can interact cooperatively and even foster the growth of species that otherwise could not survive.
Conditions in mixed microbial associations are readily reproduced in the laboratory.
Some species of microorganisms can be found in environments where no unprotected human could survive.
True false question.
True
False
True
Multiple Choice Question
Which of the following is most likely to be a pure culture?
Multiple choice question.
A bacterial lawn of growth covering an agar plate.
A Petri dish covered with bacteria following inoculation from a single patient.
A broth culture growing in a flask.
A single colony growing on a streak plate.
A single colony growing on a streak plate.
This figure shows a bacterium dividing. The mechanism is called
binary fission
A colony is a distinct mass of microorganisms which develop from a single cell growing on a solid medium.
True false question.
True
False
True
Which environment is more dynamic and complex?
Multiple choice question.
A laboratory environment
Soil and its surroundings
Soil and its surroundings
Culture media are usually solidified by the addition of a polysaccharide extracted from seaweed. This polysaccharide is known as
agar
Many bacterial communities secrete polysaccharides and other hydrophilic polymers. This mesh-like accumulation can help protect the bacteria growing within from antibiotics or disinfectants. These communities are called
biofilms
When bacteria or archaea are grown on agar plates or in tubes or flasks of broth, these closed systems are a _______culture. By contrast, cells can also be grown in an open system, or a continuous culture.
batch
Consider interactions of mixed microbial communities. Match the descriptions in the left column with those that best correlate with them in the right column.
Instructions
Difficult to reproduce in the laboratory
Simpler to reproduce in the laboratory
Inhibit competitors
Nutrients for another microbe
Creation of low O2 microenvironment
Production of metabolic wastes by one microbe
Conditions in close microbial associations
Consumption of O2 by aerobic growth
Synthesis of toxic compounds
Pure cultures
Difficult to reproduce in the laboratory & Conditions in close microbial associations
Simpler to reproduce in the laboratory & Pure cultures
Inhibit competitors & Synthesis of toxic compounds
Nutrients for another microbe & Production of metabolic wastes by one microbe
Creation of low O2 microenvironment& Consumption of O2 by aerobic growth
A(n)______ culture contains only ONE species of microorganisms descended from a single cell.
pure
A graphical representation of a changing population size over time is called which of the following?
Multiple choice question.
growth curve
histogram
generation time
growth curve
An isolated ______ is a distinct mass of microorganisms appearing on a solid medium, arising from the multiplication of a single cell.
colony
______ phase describes the initial phase after bacterial cells are placed into a new environment and are gearing up for cell division, but their numbers have not yet increased.
lag
The polysaccharide found in marine algae that is commonly used to solidify culture media is called ______.
agar
peptone
starch
gelatin
agar
In which phase of the growth curve is the generation time measured?
Multiple choice question.
Death
Lag
Log
Stationary
Log
A batch culture has which of the following characteristics?
Multiple select question.
It is a closed system.
It is an open system.
Nutrients are not renewed.
It typically involves growth of bacteria or archaea either on agar plates or in tubes or flasks of broths.
Wastes are not removed.
Cells are maintained in a state of continuous growth.
It is a closed system.
Nutrients are not renewed.
It typically involves growth of bacteria or archaea either on agar plates or in tubes or flasks of broths.
Wastes are not removed.
During which phase of growth does the number of new cells balance the number of declining cells?
Multiple choice question.
Stationary phase
Log phase
Death phase
Lag phase
Stationary phase
Which of the following does not describe interactions of mixed microbial communities?
Multiple choice question.
Conditions in mixed microbial associations are readily reproduced in the laboratory.
Microbes can interact cooperatively and even foster the growth of species that otherwise could not survive.
Microbes can compete for nutrients.
Some microbes can synthesize toxic compounds to inhibit competitors.
Microbial cells can consume O2, creating microenvironments in which anaerobes can thrive.
Conditions in mixed microbial associations are readily reproduced in the laboratory.
In a growth curve, cell numbers increase exponentially during the log phase and decrease exponentially during the death phase.
True false question.
True
False
True
The characteristic pattern that shows the changes in size of a bacterial population over time in a broth culture is called a bacterial . _________ __________
growth curve
In what ways is microbial growth in a colony the same as growth in a liquid?
Multiple select question.
Cells in either situation are all in the same phase of growth at the same time.
Cells in both situations experience the same levels of nutrients.
In both cases, cells compete with one another for available nutrients.
Both involve a lag phase followed by exponential growth.
In both cases, cells compete with one another for available nutrients.
Both involve a lag phase followed by exponential growth.
Which of the following characterizes the lag phase of a normal bacterial growth curve?
Multiple choice question.
Cells are undergoing logarithmic cell division.
Depletion of nutrients and buildup of waste. While some cells multiply, others die, and the overall population remains relatively constant.
Cells are declining exponentially.
Cells are synthesizing enzymes needed for growth but not increasing in number.
Cells are synthesizing enzymes needed for growth but not increasing in number.
Which device is used to keep cells in a state of constant growth?
Multiple choice question.
Chemostat
Flow cytometer
Spectrophotometer
Thermocycler
NMR
Chemostat
The log (logarithmic) phase of a normal growth curve is also referred to as the______ phase.
exponential
Some microorganisms live in harsh environments that kill most other organisms. The term used to describe an organism with this characteristic is .______
extremophiles
The ______phase of the bacterial growth curve is when there are an equal number of cells dividing as there are dying.
stationary
Which of the following describes the optimum temperature of a psychrophile relative to a thermophile?
Multiple choice question.
It is lower than a thermophile.
It is higher than a thermophile.
It is the same as a thermophile.
It is lower than a thermophile.
In which phase of the growth curve is the number of viable cells decreasing?
Multiple choice question.
log
lag
stationary
death
death
Match the term on the left with the description of the optimum temperature environment.
Instructions
psychrophile
cold Arctic regions
Match the term on the left with the description of the optimum temperature environment
.
Match the term on the left with the description of the optimum temperature environment.
psychrotroph
refrigeration
Match the term on the left with the description of the optimum temperature environment.
mesophile
human body
Match the term on the left with the description of the optimum temperature environment.
thermophile
compost heap
Why are cells growing in a colony on solid media likely to be in many more different phases of growth than cells growing in liquid culture?
Multiple select question.
Cells grow much more quickly in liquid culture, so they are more likely to stay in the same phase.
Growth on solid media provides a greater abundance of nutrients, so cells are able to rapidly separate out into different phases of growth.
Unlike cells on the edge of a colony, those in the center of a colony face depleted levels of nutrients and O2, yielding different phases of growth.
Cells in liquid culture experience a relatively uniform environment, so they are much more likely to be in the same phase of growth.
Unlike cells on the edge of a colony, those in the center of a colony face depleted levels of nutrients and O2, yielding different phases of growth.
Cells in liquid culture experience a relatively uniform environment, so they are much more likely to be in the same phase of growth
A continuous culture system that adds nutrients and removes waste in order to maintain a constant growth rate and cell density is called a _____
chemostat/ bioreactor
Which term describes a microorganism that has an optimum temperature between -50C and 150C?
Multiple choice question.
Psychrophile
Mesophile
Thermophile
Psychrotroph
Psychrophile
Consider the following environmental factors. Which have the most impact on microbial growth?
Multiple select question.
wind speed
pH
atmosphere
water availability
odor
temperature
pH
atmosphere
water availability
temperature
A species grows most rapidly at its____ growth temperature.
optimum
Which term describes a microorganism that has an optimal temperature between 15∘C and 30∘C, but grows well on refrigerated foods?
Multiple choice question.
Mesophile
Thermophile
Psychrotroph
Psychrotroph
he five groups used to categorize microorganisms with respect to growth temperature (psychrophile, psychrotroph, mesophile, thermophile, and hyperthermophile) ______.
Multiple choice question.
represent the entire range at which the organisms in the groups can grow.
are based on optimum growth temperatures.
are precise with respect to the dividing lines between each group.
are based on optimum growth temperatures.
Human pathogens, adapted to growth in the human body, are ______.
Multiple choice question.
psychrophiles
hyperthermophiles
mesophiles
psychrotrophs
thermophiles
mesophiles
In what ways is microbial growth in a colony the same as growth in a liquid?
Multiple select question.
In both cases, cells compete with one another for available nutrients.
Cells in both situations experience the same levels of nutrients.
Both involve a lag phase followed by exponential growth.
Cells in either situation are all in the same phase of growth at the same time.
In both cases, cells compete with one another for available nutrients.
Both involve a lag phase followed by exponential growth.
An environment with little or no O2 present is called a(n)________ environment
anaerobic
If you wanted to study psychrophilic microorganisms, you would most likely find them ______.
Multiple choice question.
in water from a hot tub
growing on your skin
in lakes fed by glaciers
in lakes fed by glaciers
Which of the following describes a microbe that must have O2 to survive?
Multiple choice question.
Semi aerobe
Facultative aerobe
Passive aerobe
Obligate aerobe
Obligate aerobe
Some microorganisms live in harsh environments that kill most other organisms. The term used to describe an organism with this characteristic is .________
extremophile
From which body site could a facultative anaerobe be isolated?
Multiple choice question.
Surface of skin
Any of these locations
Intestine
Deep wound
Any of these locations
Multiple Choice Question
A ______ is most likely to be implicated in spoilage of refrigerated foods.
Multiple choice question.
mesophile
thermophile
psychrotroph
hyperthermophile
psychrotroph
Bacteria that cannot multiply if O2 is present, and are often killed by even brief exposure to air, are termed _______ ________
obligate anaerobes
E. coli and most other common bacteria are ______.
Multiple choice question.
mesophiles
thermophiles
psychrotrophs
hyperthermophiles
psychrophiles
mesophiles
A(n________) is an aerobe that requires O2 at a concentration less than that in the atmosphere.
microaerophile
If O2 is present in an environment, it is said to be _______.
Multiple choice question.
aerobic
aerotactic
aerophilic
aerobic
Which of the following organisms does not use O2 at all for growth?
Multiple choice question.
Aerotolerant anaerobe
Facultative anaerobe
Microaerophile
Aerotolerant anaerobe
A(n)______ aerobe, or strictly aerobic organism, requires O2 for survival.
obligate
Regardless of the pH of the external environment, microbial cells maintain a constant internal pH, typically near neutral. For example, prokaryotes that grow in alkaline conditions bring ______ into the cell.
protons
Which of the following correctly describe facultative anaerobes?
Multiple select question.
Their growth is faster when O2 is available.
They can only grow in the absence of O2.
They can grow without O2.
They can grow in the presence of O2 but do not use it to harvest en
Their growth is faster when O2 is available.
They can grow without O2.
If you inoculated a test tube of cooled liquid agar with an obligate anaerobe and incubated it, where would you expect to find growth?
Multiple choice question.
Only at the bottom of the tube.
Throughout the tube.
Only at the top of the tube.
Only at the bottom of the tube.
Which answer best explains the events in the figure leading to plasmolysis?
Multiple choice question.
There is a greater concentration of water outside the cell, so water flows from inside to outside the cell.
The solute concentration inside the cell is greater than outside the cell, causing water to diffuse out of the cell via osmosis.
The solute concentration of the medium is greater than that in the cell, causing water to diffuse out of the cell due to osmosis.
There is more solvent outside the cell than inside, so water exits the cell.
The solute concentration of the medium is greater than that in the cell, causing water to diffuse out of the cell due to osmosis.
A microbe that requires small amounts of O2 (2-10%) for aerobic respiration but is inhibited by higher concentrations is called a(n) ______.
Multiple choice question.
microaerophile
aerotolerant anaerobe
obligate aerobe
facultative anaerobe
microaerophile
Carbon, oxygen, hydrogen, nitrogen, sulfur, and phosphorus, are examples of chemical substances called ________ ________, which are the essential components of the cell's macromolecules.
major elements
A microbe that doesn't use O2 but can grow in environments containing O2 is described as a(n) _______anaerobe.
aerotolerant
Microbial cells must maintain a near-neutral internal pH. Because of this, bacteria that grow in acidic environments have mechanisms to ______.
Multiple choice question.
pump out OH- that enter the cell
bring OH- into the cell
bring H+ into the cell
pump out H+ that enter the cell
pump out H+ that enter the cell
An organism that must consume organic matter is called a(n) .______
heterotroph
What term is used to describe organisms that use CO2 as a carbon source?
Multiple choice question.
Heterotrophs
Saprotrophs
Autotrophs
Autotrophs
If the solute concentration is higher outside the cell than inside the cell, water will diffuse out due to osmosis. This will result in
plasmolysis
What term is used to describe chemical substances such as carbon or phosphorous, which are found in large quantities in cells?
Multiple choice question.
Macroelement
Megamolecule
Macromolecule
Macrocompound
Major element
Major element
Animals could not survive without autotrophs because without them the world would run out of ______.
Multiple choice question.
organic nitrogen
organic carbon
inorganic nitrogen
inorganic carbon
organic carbon
Which of the following organisms does not use O2 at all for growth?
Multiple choice question.
Microaerophile
Facultative anaerobe
Aerotolerant anaerobe
Aerotolerant anaerobe
Which of the following contain nitrogen?
Multiple select question.
Carbohydrates
Proteins
RNA
DNA
Fats
Proteins
RNA
DNA
Which type of organism requires organic compounds for its carbon and energy needs?
Multiple choice question.
Autotroph
Heterotroph
Phototroph
Heterotroph
Nitrogen fixation is the process by which some prokaryotes convert atmospheric nitrogen into _______and then incorporating that into cellular material.
ammonia or NH3
A(n)_______ requires only carbon dioxide as a sole carbon source.
autotroph
What term is used to describe essential organic compounds, such as a vitamin or amino acid, that must be provided in the diet?
Multiple choice question.
Inhibitory regulators
Trace element
Virulence factors
Growth factors
Growth factors
Autotrophs play a crucial role in the cycling of carbon in the environment by converting inorganic carbon to an organic form. This process is called carbon .______
fixation
Unlike sugar, proteins provide which of the following elements?
Multiple choice question.
Hydrogen
Nitrogen
Oxygen
Carbon
Nitrogen
Which term is used to describe organisms that can obtain energy directly from sunlight?
Multiple choice question.
Chemotrophs
Phototrophs
Saprotrophs
Phototrophs
Some microorganisms can convert nitrogen gas (N2) to ammonia in a process called _______.
Multiple choice question.
denitrification
nitrogen fixation
nitrogen assimilation
nitrification
nitrogen fixation
An autotrophic organism that uses light for energy and carbon dioxide as a carbon source is termed a _______
photoautotroph
A______ factor is an organic compound, such as a vitamin or an amino acid, that a given microorganism cannot synthesize and therefore must be provided in the growth medium.
growth
Which is the best general description of a medium used to support bacterial growth in a Petri dish?
Multiple choice question.
It contains only agar because contact with the air will provide the rest of the nutrients.
It may have very few nutrients, or it may have many different nutrients to support widely varying growth requirements.
It must contain all possible nutrients, so that all microbes can grow.
It contains only agar, which serves as a rich source of nutrients to support a diversity of microbial growth.
It must have minimal nutrient content, so that microbes are forced to manufacture their required nutrients.
It may have very few nutrients, or it may have many different nutrients to support widely varying growth requirements.
A medium that contains an ingredient that inhibits the growth of some bacteria, while allowing others to grow, is called a(n) ______ medium
selective
Selective media are used for which of the following?
Multiple choice question.
Isolating a specific microbe from a mixed population
Growing fastidious microbes only
Differentiating a specific microbe from a mixed population
Growing a broad spectrum of microbe
Isolating a specific microbe from a mixed population
An organism that gets its energy directly from sunlight is called a(n) ______
phototroph
A photoautotroph obtains energy from ______ and carbon from ______ in order to make organic compounds.
Multiple choice question.
organic compounds; organic compounds
sunlight; organic compounds
inorganic chemicals; CO2
sunlight; CO2
sunlight; CO2
Which of the following best describes how the atmospheric needs of aerobic microbes can be met?
Multiple choice question.
In a sealed container flushed with a gas like CO2 to remove all the O2.
In a special aerobic chamber.
By growing them in the air.
By growing them in the air.
Which describes the various laboratory media used to cultivate bacteria?
Multiple choice question.
They are diverse in nutrient content and consistency.
There are few different types.
They are all similar with respect to their nutrient content.
They are diverse in nutrient content and consistency.
You are setting up an enrichment culture to look for bacteria that can use phenol as a carbon source. In your medium, you provide a variety of major elements and trace elements, plus phenol. Other than that contained in the phenol, what must you avoid adding if you hope to enrich for phenol-degraders?
Multiple choice question.
Phosphorus
Potassium
Iron
Nitrogen
Carbon
Carbon
hich of the following describe selective media?
Multiple select question.
Allow the growth of desired organisms
Display visible differences among microorganisms
Select for growth of a broad spectrum of organisms
Inhibit the growth of certain species
Allow the growth of desired organisms
Inhibit the growth of certain species
Media used to isolate specific types of microorganisms from saliva, feces, or any other sample that contains many microbial species are called ._______
selective
direct cell count typically determines only the number of live cells in a sample.
True false question.
True
False
False
Viable cell counts determine the number of ______.
Multiple choice question.
live cells
cells capable of multiplying
total cells (live and dead)
cells capable of multiplying
How are liquid batch cultures most often aerated to support the growth of aerobic microbes?
Multiple choice question.
They are grown in tubes or flasks that are shaken continuously.
Air is pumped into the tubes or flasks to supply sufficient O2.
Pure O2 flows under pressure from a gas cylinder into the tubes or flasks to supply maximum O2.
They are grown in tubes or flasks that are shaken continuously.
How many colony-forming units (CFUs) are presumed to result in a single colony using the viable plate method?
Multiple choice question.
2
10
Several (unknown)
1
1
How might an enrichment culture be used to isolate organisms capable of nitrogen fixation?
Multiple choice question.
Exposing the culture to atmospheric nitrogen gas
Exposing the culture to sunlight to encourage photosynthetic growth
Using a media that does not contain any form of nitrogen, and exposing it to the atmosphere
Provide media that are rich in nitrogen in an inorganic form
Using a media that does not contain any form of nitrogen, and exposing it to the atmosphere
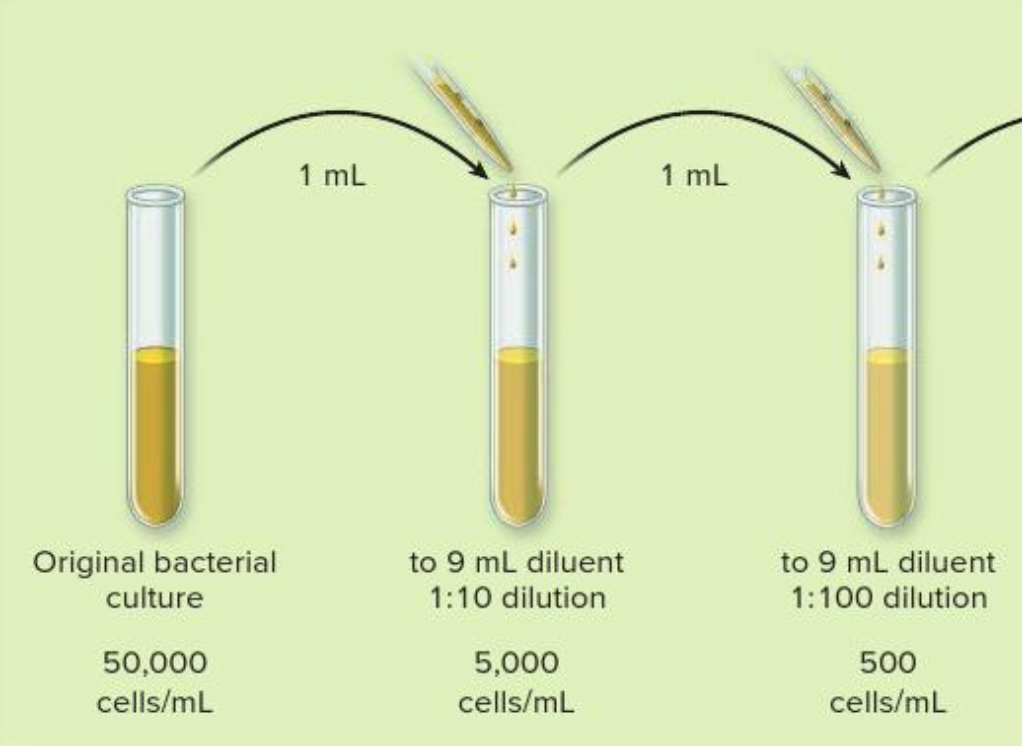
The steps shown in this figure are part of a technique called
serial dilution